Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
2006 Exam Paper
Încărcat de
nicholasiDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
2006 Exam Paper
Încărcat de
nicholasiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
M ONASH U NIVERSITY D EPARTMENT OF E LECTRICAL & C OMPUTER S YSTEMS E NGINEERING ECE4414/ECE5414 Performance of Telecommunication Networks Final Examination, 2nd
Semester, 2006
(Please give your answers briey, and in point or tabular form wherever possible. None of your answers to any of the questions should exceed one page.) 1. (10 marks) Answer the following questions on cell switches. (a) Consider an N N cell switch that operates in a time-slotted manner. Assume that in a slot all the N inputs get a cell. Also assume that a cell has output j as 1 its destination, with probability N for j = 1, . . . , N and that the destination of a cell is independent of the other cells. What is the probability that there will be no destination conict that is, that each cell will choose a different destination? Explain. (b) Consider the same case as above except that a cell arrives at an input with probability . Among the cells that arrived in the same time-slot, what is the probability that there is no destination conict? Explain. 2. (10 marks) Draw a timeline diagram for the sliding window algorithm with send window size (SWS) = receive window size (RWS) = 4 frames for the following two situations. Assume the receiver sends a duplicate acknowledgment if it does not receive the expected frame. For example, it sends DUPACK(2) when it expects to see FRAME(2) (the frame with sequence number 2) but receives FRAME(3) instead. Also, the receiver sends a cumulative acknowledgment after it receives all the outstanding frames. For example, its sends ACK(5) when it receives the lost frame FRAME(2) after it already received FRAME(3), FRAME(4), and FRAME(5). Use a timeout interval of about 2 RTT (round trip time). (a) Frame 2 is lost. Retransmission takes place upon timeout (as usual). (b) Frame 2 is lost. Retransmission takes place either upon receipt of the rst DUPACK or upon timeout. Does this scheme reduce the transaction time? 3. (20 marks) For an M/M/1 queue, arrival rate is items per unit time and service rate is items per unit time. Let n be the number of items in the system, and pn be the steady-state probability of nding n items in the system (waiting and being served). (a) Draw the state diagram for this system and obtain the balance equation. (b) Show that p0 = 1 (where = / ), and obtain a general expression for pn . (c) Show that the average number of items in the system is /(1 ). 1
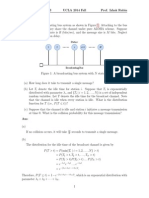
(d) State Littles formula, and use it to obtain an expression for the average residence time. 4. (10 marks) Consider the following network topology:
In the diagram above, vertices represent routers and edges (arcs) represent links between routers. The numerical annotation on the links represents link costs (higher costs indicate worse links). Answer the following questions: (a) Use Dijkstras link-state algorithm to nd the set of shortest paths from router D to other routers in the network. You need to show the step-by-step progression of the link-state routing algorithm at router D and explain the activity in each step. (b) Give the nal routing table at router D. 5. (10 marks) Compare and contrast the link-state and distance-vector algorithms. Give your answer in tabular format. 6. (10 marks) Answer the following questions on routing in the global Internet and autonomous systems. (a) What is an autonomous system? (b) What is an interior routing protocol? What is an exterior routing protocol? (c) What do BGP-4, OSPF and RIP stand for? (d) Compare BGP-4, OSPF and RIP by using a table similar to the following: P ROTOCOL BGP-4 OSPF RIP I NTRA -AS
OR I NTER -AS?
T RANSPORT P ROTOCOL U SED
(End of paper, total 70 marks)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Exam #1 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1Document5 paginiExam #1 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #187bbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam #2 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1Document4 paginiExam #2 For Computer Networks (CIS 6930) SOLUTIONS : Problem #1svahidsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2005 SP CN Midterm1Document8 pagini2005 SP CN Midterm1rameshnuvkekaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNDC Assignment 02Document3 paginiCCNDC Assignment 02joe nindaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Packet Delay in Models of Data NetworksDocument18 paginiPacket Delay in Models of Data NetworkssplouvrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datalink AnswersDocument3 paginiDatalink AnswersNguyễn Văn HiếnÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW 05 SolutionsDocument5 paginiHW 05 Solutionsgmu.rajendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN Final AnswerDocument9 paginiCN Final AnswerMicle JackÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENSC427 Final 1231Document4 paginiENSC427 Final 1231477889997mÎncă nu există evaluări
- MST Latest 2025Document8 paginiMST Latest 2025bndianonymousÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 1Document6 paginiProblem Set 1AnushaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6th Sem Cse 2010 Scheme - Cn2 (Back Paper) December 2013Document2 pagini6th Sem Cse 2010 Scheme - Cn2 (Back Paper) December 2013Pawan BhaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faculty of Engineering, Sciences & Technology: Assignment # 03 - Spring Semester 2020Document8 paginiFaculty of Engineering, Sciences & Technology: Assignment # 03 - Spring Semester 2020Muhammad Usman AfaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions MidtermDocument10 paginiSolutions MidtermVineet RawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Study Resource Was: Multiple Choice Questions ( × . )Document3 paginiThis Study Resource Was: Multiple Choice Questions ( × . )Đình NghĩaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21fa MidtermDocument15 pagini21fa MidtermmisschuachinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce252a 2014 Fall HW 2 SolutionsDocument8 paginiCe252a 2014 Fall HW 2 SolutionsPloy PraeployÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Computer Networking (SSC 4) Exercise SeriesDocument27 paginiIntroduction To Computer Networking (SSC 4) Exercise SeriesMahmoud Handase35Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5Document45 paginiChapter 5Rajesh KannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-Iii: (Q) Explain Network Layer Design Issues? (2M/5M)Document28 paginiUnit-Iii: (Q) Explain Network Layer Design Issues? (2M/5M)karthik vaddiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hwk3 4 Su10 SolDocument11 paginiHwk3 4 Su10 SolKun LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.225 Transportation Flow SystemsDocument12 pagini1.225 Transportation Flow Systemsknsmanto-1Încă nu există evaluări
- Exam #1 For Computer Networks SOLUTIONSDocument4 paginiExam #1 For Computer Networks SOLUTIONS87bbÎncă nu există evaluări
- 311 FinalDocument4 pagini311 Finalapi-358841842Încă nu există evaluări
- CST 311introduction To Computer Networks Final: in Your Answer Sheet Please Remember To Write Your NameDocument6 paginiCST 311introduction To Computer Networks Final: in Your Answer Sheet Please Remember To Write Your Nameapi-360110588Încă nu există evaluări
- Data Networks Summer 2007 Midterm ExamDocument10 paginiData Networks Summer 2007 Midterm ExamKerem CelikÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Optional) Assignment-4 (50 Points) : General InstructionsDocument2 pagini(Optional) Assignment-4 (50 Points) : General InstructionsBhoomika MandloiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blanc Comp Net Exam Fall 09Document20 paginiBlanc Comp Net Exam Fall 09jerome_bovay5831Încă nu există evaluări
- Practice Exam 1-SolutionsDocument10 paginiPractice Exam 1-SolutionsBlack MelekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 3 (SEE 312) : Part ADocument3 paginiAssignment 3 (SEE 312) : Part ANaveen SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Discrete-Time Event Simulator For Distance Vector RoutingDocument3 paginiA Discrete-Time Event Simulator For Distance Vector RoutingAsad HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brianbegun FinalexamDocument4 paginiBrianbegun Finalexamapi-357413467Încă nu există evaluări
- hw4 SolDocument4 paginihw4 SolIkhtear SharifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fixed-Point Approximations For TCP Performance Over Bandwidth On Demand GEO Satellite LinksDocument6 paginiFixed-Point Approximations For TCP Performance Over Bandwidth On Demand GEO Satellite LinkskirkbdavisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee132b Hw3 SolDocument7 paginiEe132b Hw3 SolDylan Ler100% (1)
- Csem 107 (Old)Document7 paginiCsem 107 (Old)Rituparna MajumdarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mob Net 2011 Exam SolutionDocument13 paginiMob Net 2011 Exam Solutionمحيي الدين الكميشىÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comp Net Midterm Fall 09Document19 paginiComp Net Midterm Fall 09Shiva MohammadzadehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Holistic Exam2005-1 PDFDocument6 paginiHolistic Exam2005-1 PDFEnyew100% (1)
- Frame Acq For SatDocument7 paginiFrame Acq For SatkidusÎncă nu există evaluări
- QADocument9 paginiQAkiet eduÎncă nu există evaluări
- COSC 328 Lab 8-Link-LayerDocument4 paginiCOSC 328 Lab 8-Link-LayerAbhishek DashÎncă nu există evaluări
- 434 HW 3 SolDocument5 pagini434 HW 3 SolSweet AliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMPT 371: Midterm 2: 1 Short Answer QuestionsDocument4 paginiCMPT 371: Midterm 2: 1 Short Answer QuestionsNeil HolmesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercícios - Parte 1 - Só PerguntasDocument4 paginiExercícios - Parte 1 - Só PerguntasMarcos PereiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abc DOCUUCOD1109902Document4 paginiAbc DOCUUCOD1109902santoshchapaneriÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACN - Full QBDocument5 paginiACN - Full QBshabacutipieÎncă nu există evaluări
- CN Manual Sliding WindowDocument6 paginiCN Manual Sliding WindowSneha KanwadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELEN E6951 - Wireless & Mobile Networking II Problem Set #3Document2 paginiELEN E6951 - Wireless & Mobile Networking II Problem Set #3Abdullah AlGhamdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport AnswersDocument5 paginiTransport AnswersPebo GreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 1 SolutionDocument3 paginiQuiz 1 SolutionAli AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final 6711 F07 SolsDocument4 paginiFinal 6711 F07 SolsSongya PanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee132b Hw4 SolDocument11 paginiEe132b Hw4 SolDylan LerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mob Net 2012 Exam SolutionDocument16 paginiMob Net 2012 Exam SolutionMohammad IrsheadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework Title / No.: 3 Course CodeDocument10 paginiHomework Title / No.: 3 Course CodeSurendra Singh Chauhan0% (1)
- Exam SS15 SPASDocument11 paginiExam SS15 SPASkcikdmywgouxzgafghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Modeling of Wireless Communication SystemsDe la EverandAnalytical Modeling of Wireless Communication SystemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesDe la EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Paper ScienceDocument28 paginiTest Paper ScienceRamin ShokuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistics 3 Revision of Linear Combinations of Random VariablesDocument4 paginiStatistics 3 Revision of Linear Combinations of Random VariablesnicholasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differentiation MsDocument3 paginiDifferentiation MsnicholasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PureMathDocument494 paginiPureMathElvis100% (5)
- Modul Perfect Score SBP 2009Document124 paginiModul Perfect Score SBP 2009Jia HuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arimethric ks3Document4 paginiArimethric ks3nicholasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRIAL MATE SPM 2010 Perak Paper 1 AnswerDocument1 paginăTRIAL MATE SPM 2010 Perak Paper 1 AnswerwaichunkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9709 w11 Ms 63Document6 pagini9709 w11 Ms 63Mushfiqur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integration Formulas: 1. Common IntegralsDocument5 paginiIntegration Formulas: 1. Common IntegralssiegherrÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9709 w11 Ms 63Document6 pagini9709 w11 Ms 63Mushfiqur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hybrid Electric and Battery Electric Vehicles - Measures To Stimulate UptakeDocument43 paginiHybrid Electric and Battery Electric Vehicles - Measures To Stimulate UptakeAndrew DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 paginiHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- 2011-07!18!1 All IT Hyper MarketDocument3 pagini2011-07!18!1 All IT Hyper MarketDefriman DjafriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 paginiHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- IoT Security Checklist Web 10 17 r1Document39 paginiIoT Security Checklist Web 10 17 r1SubinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using Your Digital Assets On Q-GlobalDocument3 paginiUsing Your Digital Assets On Q-GlobalRemik BuczekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Batron: 29 5 MM Character Height LCD Modules 29Document1 paginăBatron: 29 5 MM Character Height LCD Modules 29Diego OliveiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science9 Q4 Week2Document16 paginiScience9 Q4 Week2Maria Josie Lopez TumlosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essay On Stem CellsDocument4 paginiEssay On Stem CellsAdrien G. S. WaldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Handbook Arendal 1961 Series SubwoofersDocument44 paginiProduct Handbook Arendal 1961 Series SubwoofersDomagoj KovacevicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2396510-14-8EN - r1 - Service Information and Procedures Class MDocument2.072 pagini2396510-14-8EN - r1 - Service Information and Procedures Class MJuan Bautista PradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Download University Physics With Modern Physics 14th Edition Young Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDocument13 paginiFull Download University Physics With Modern Physics 14th Edition Young Test Bank PDF Full Chapterpoetrycloudyzjm12q100% (19)
- 한국항만 (영문)Document38 pagini한국항만 (영문)hiyeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- CryptogrophyDocument37 paginiCryptogrophyFarah EssidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grua Grove 530e 2 Manual de PartesDocument713 paginiGrua Grove 530e 2 Manual de PartesGustavo100% (7)
- Immobilization of Rhodococcus Rhodochrous BX2 (An AcetonitriledegradingDocument7 paginiImmobilization of Rhodococcus Rhodochrous BX2 (An AcetonitriledegradingSahar IrankhahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entrepreneurial MotivationDocument18 paginiEntrepreneurial MotivationRagavendra RagsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taylorism vs. FordismDocument2 paginiTaylorism vs. FordismLiv Maloney67% (3)
- Chapter 5 IppDocument24 paginiChapter 5 IppRoseann EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defining The Standards For Medical Grade Honey PDFDocument12 paginiDefining The Standards For Medical Grade Honey PDFLuis Alberto GarcíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kursus Jabatan Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Sesi Jun 2014Document12 paginiKursus Jabatan Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Sesi Jun 2014ihsanyusoffÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Ghana: This Paper Contains Two Parts (PART I and PART II) Answer All Questions From Both PARTSDocument3 paginiUniversity of Ghana: This Paper Contains Two Parts (PART I and PART II) Answer All Questions From Both PARTSPhilip Pearce-PearsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- AVEVA LFM - Data Summary v2Document6 paginiAVEVA LFM - Data Summary v2Joshua HobsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Masking Conventional Metallic Cast Post For Enhancing EstheticsDocument5 paginiMasking Conventional Metallic Cast Post For Enhancing EstheticsleilyanisariÎncă nu există evaluări
- UserProvisioningLabKit 200330 093526Document10 paginiUserProvisioningLabKit 200330 093526Vivian BiryomumaishoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 1 Computer Science ASDocument194 paginiPaper 1 Computer Science ASLailaEl-BeheiryÎncă nu există evaluări
- RS-All Digital PET 2022 FlyerDocument25 paginiRS-All Digital PET 2022 FlyerromanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cummins: ISX15 CM2250Document17 paginiCummins: ISX15 CM2250haroun100% (4)
- Details Philippine Qualifications FrameworkDocument6 paginiDetails Philippine Qualifications FrameworkCeline Pascual-RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Some Studies On Structure and Properties of Wrapped Jute (Parafil) YarnsDocument5 paginiSome Studies On Structure and Properties of Wrapped Jute (Parafil) YarnsVedant MahajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panera Bread Case StudyDocument28 paginiPanera Bread Case Studyapi-459978037Încă nu există evaluări
- Ec 0301Document25 paginiEc 0301Silvio RomanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENSC1001 Unit Outline 2014Document12 paginiENSC1001 Unit Outline 2014TheColonel999Încă nu există evaluări
- God Reproducing Himself in UsDocument6 paginiGod Reproducing Himself in UsLisa100% (1)