Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
BADMINTON Was Invented Long Ago A Form of Sport Played in Ancient Greece and
Încărcat de
janelaroxanDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
BADMINTON Was Invented Long Ago A Form of Sport Played in Ancient Greece and
Încărcat de
janelaroxanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
What is badminton Badminton is an indoor/outdoor game played with racket and shuttle cocks.
The game as such was started in PUNE (India) later the game was given a boost in England with the name of the hall as "Badminton" was used to give the game its official name. From then on Badminton was taken up as a recreational sport rather than competative before the game was picked up by the Asian giants like Indonesia, China, Malaysia, Korea, Hongkong etc... and countries like Denmark, Germany, Russia picked up the game later on
History of badminton BADMINTON was invented long ago; a form of sport played in ancient Greece and Egypt. Badminton came from a child's game called battledore and shuttlecock, in which two players hit a feathered shuttlecock back and forth with tiny rackets. The game was called "POONA" in India during the 18th Century, and British Army Officers stationed there took the Indian version back to England in the 1860's. The army men introduced the game to friends, but the new sport was definitely launched there at a party given in 1873 by the Duke of Beaufort at his country place, "Badminton" in Gloucestershire. During that time, the game had no name, but it was referred to as "The Game of Badminton," and, thereupon, Badminton became its official name. Until 1887 the sport was played in England under the rules that prevailed in India. They were, from the English viewpoint, somewhat contradictory and confusing. Since a small army of badminton players had been recruited, a group formed itself into the Bath Badminton Club, standardized the rules, made the game applicable to English ideas and the basic regulations, drawn up in 1887, still guide the sport. In 1895, the Badminton Association (of England) was formed to take over the authority of the Bath Badminton Club, and the new group made rules, which now govern the game throughout the world.
A shuttlecock (called bird or birdie in the USA)[1] is a high-drag projectile used in the sport of badminton. It has an open conical shape: the cone is formed from sixteen or so overlapping feathers, usually goose or duck and from the left wing only, embedded into a rounded cork base. The cork is covered with thin leather. The shuttlecock's shape makes it extremely aerodynamically stable. Regardless of initial orientation, it will turn to fly cork first, and remain in the cork-first orientation. The name shuttlecock is frequently shortened to shuttle. The "shuttle" part of the name was probably derived from its back-and-forth motion during the game, resembling theshuttle of a loom; the "cock" part of the name was probably derived from the resemblance of the feathers to those on a cockerel.
Badminton rackets are light, with top quality rackets weighing between about 70 and 100 grams (without strings). They are composed of carbon fiber composite (graphite reinforced plastic), which may be augmented by a variety of materials. Carbon fiber has an excellent strength to weight ratio, is stiff, and gives excellent kinetic energy transfer. Before the adoption of carbon fiber composite, rackets were made of light metals such as aluminum. Earlier still, rackets were made of wood. Cheap rackets are still often made of metal, but wooden rackets are no longer manufactured for the ordinary market, due to their excessive weight and cost. There is a wide variety of racket designs, although the racket size and shape are limited by the Laws. Different rackets have playing characteristics that appeal to different players. The traditional oval head shape is still available, but an isometric head shape is increasingly common in new rackets.
The 10 rules of badminton are as follows: 1. A game starts with a coin toss. Whoever wins the toss gets to decide whether they would serve or receive first OR what side of the court they want to be on. The side losing the toss shall then exercise the remaining choice. 2. At no time during the game should the player touch the net, with his racquet or his body. 3. The shuttlecock should not be carried on or come to rest on the racquet.
4. A player should not reach over the net to hit the shuttlecock. 5. A serve must carry cross court (diagonally) to be valid. 6. During the serve, a player should not touch any of the lines of the court, until the server strikes the shuttlecock. During the serve the shuttlecock should always be hit from below the waist. 7. A point is added to a player's score as and when he wins a rally. 8. A player wins a rally when he strikes the shuttlecock and it touches the floor of the opponent's side of the court or when the opponent commits a fault. The most common type of fault is when a player fails to hit the shuttlecock over the net or it lands outside the boundary of the court. 9. Each side can strike the shuttlecock only once before it passes over the net. Once hit, a player can't strike the shuttlecock in a new movement or shot. 10. The shuttlecock hitting the ceiling, is counted as a fault.
Different Badminton Strokes: 1. Serve - underhand stoke to start game play 2. Overhand Clear - overhand stroke driving the birdie high and deep into the opponent's court 3. Underhand Clear - underhand stroke driving the birdie high and deep into the opponent's court 4. Drop - a short shot in which just clears the net, and falls close to the net in the opponent's court. 5. Smash - an overhead stroke in which the birdie travels at a downward angle (spike).
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- BadmintonDocument20 paginiBadmintonJerrica Mae GalvezÎncă nu există evaluări
- BadmintonDocument55 paginiBadmintonJarapan LanggaÎncă nu există evaluări
- In The BeginningDocument7 paginiIn The BeginningJay Carlo BagayasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module Lesson 3 Equipments in BadmintonDocument8 paginiModule Lesson 3 Equipments in BadmintonJerald CañeteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basketball Fouls & Violations: Relozor, Tricia May M. BSN 2-3 N134 TH Pe4N (Sports)Document24 paginiBasketball Fouls & Violations: Relozor, Tricia May M. BSN 2-3 N134 TH Pe4N (Sports)Czarina Mae LomboyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE 1 GymnasticsDocument25 paginiPE 1 GymnasticsAngel Anne PadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BADMINTONDocument9 paginiBADMINTONFO&O PhilippinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- BadmintonDocument4 paginiBadmintonTrialhyn Yano0% (1)
- The Fundamentals of MovementsDocument21 paginiThe Fundamentals of MovementsJanfel TVÎncă nu există evaluări
- PEDocument46 paginiPEJhonsenn Escosio RudioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team Sport SyllabusDocument3 paginiTeam Sport SyllabusJayson MangueraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathfit 1Document9 paginiPathfit 1Minimi LovelyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pe4 NotesDocument7 paginiPe4 NotesCashy HannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rhythmic Gymnastics Exercise ProgramDocument28 paginiRhythmic Gymnastics Exercise Programlyra cosgafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 14 - Multiple ChoiceDocument34 paginiChapter 14 - Multiple ChoiceDance TagleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1Document5 paginiModule 1Cj Castillo100% (1)
- Physical Education 1 by Punzalan Et Al. 2019Document5 paginiPhysical Education 1 by Punzalan Et Al. 2019ANNA MARY GINTOROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 GymnasticsDocument3 paginiModule 1 GymnasticsElla Marie MostralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE2 Fundamentals of Rhythm and DanceDocument33 paginiPE2 Fundamentals of Rhythm and DancePiolo JazulÎncă nu există evaluări
- The History of VolleyballDocument3 paginiThe History of VolleyballaaryanjainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3PATH Fit 1 Activities WEEK1 8Document24 pagini3PATH Fit 1 Activities WEEK1 8Xxx100% (1)
- Rules and RegulationDocument4 paginiRules and RegulationIvanroy DiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bambang, Nueva VizcayaDocument19 paginiInstructional Module: Republic of The Philippines Nueva Vizcaya State University Bambang, Nueva VizcayaCJ M. Pablo100% (1)
- Physical Education: Leslie Anne M. FranciscoDocument37 paginiPhysical Education: Leslie Anne M. FranciscoKian GaboroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz in ArnisDocument1 paginăQuiz in ArnisGlen BeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Physical EducationDocument7 paginiIntroduction To Physical EducationLOVELYJEANBALBERO VALLESERA100% (1)
- Locomotor and Non Locomotor MovementsDocument6 paginiLocomotor and Non Locomotor MovementsRaymond Basilonia0% (1)
- Historical Foundation of PE and SportsDocument8 paginiHistorical Foundation of PE and SportsRowainneEichstadtBrittinghamSaracenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compilation of Philippine Traditional Games and Sports: Bachelor of Physical EducationDocument35 paginiCompilation of Philippine Traditional Games and Sports: Bachelor of Physical EducationRenz N. GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gymnastics: Brief History of GymnasticsDocument50 paginiGymnastics: Brief History of GymnasticsHillary Dwainee R. LorenzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety SwimmingDocument7 paginiSafety SwimmingNuhr Jean DumoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHMSC Preliminaries and Introduction To Physical FitnessDocument12 paginiCHMSC Preliminaries and Introduction To Physical FitnessDuex Mistry100% (1)
- Cheerdance PDF For ResearchDocument24 paginiCheerdance PDF For ResearchGon IslaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GymnasticsDocument32 paginiGymnasticsKimberly Gayle ChingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 008-Module 008-CheerdanceDocument12 paginiWeek 008-Module 008-CheerdanceJohnloyd LapiadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Athletic EventsDocument65 paginiAthletic EventsrusselldylanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE 4 - Topics and ReferencesDocument3 paginiPE 4 - Topics and ReferencesRea Angela Dealca100% (1)
- Universidad de Manila: Module #1 Pe 4: Basic Badminton FOCUS: History, Equipment, Basic Rules and RegulationDocument6 paginiUniversidad de Manila: Module #1 Pe 4: Basic Badminton FOCUS: History, Equipment, Basic Rules and RegulationYongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Fundamental Steps in Folk DanceDocument17 pagini5 Fundamental Steps in Folk DanceDuy100% (1)
- Outcomes-Based Teaching and Learning Plan in PHED 112: Movement EnhancementDocument6 paginiOutcomes-Based Teaching and Learning Plan in PHED 112: Movement EnhancementChristian Arnel Jumpay LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
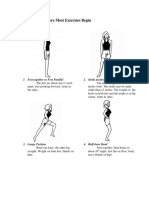
- Basic Positions Where Most Exercises Begin (STANDING AND SITTING POSITIONS)Document4 paginiBasic Positions Where Most Exercises Begin (STANDING AND SITTING POSITIONS)Marklein DumangengÎncă nu există evaluări
- P E2college-1stDocument24 paginiP E2college-1stREJ Vlogs100% (1)
- Reviewer in Physical Education 11Document2 paginiReviewer in Physical Education 11aeiaeiuaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- GRDocument1 paginăGRapi-350666556Încă nu există evaluări
- Appliedmotorlearning PPT No.1Document13 paginiAppliedmotorlearning PPT No.1Jojo JojoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TSTRAT 11 HandoutsDocument4 paginiTSTRAT 11 HandoutsP. Harrison100% (1)
- Pathfit Midterm 2Document6 paginiPathfit Midterm 2Xhejian EwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Module-Rhythmic-ActivitiesDocument112 paginiNew Module-Rhythmic-Activitiesromy imperialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Syllabus SCCPC 101 - Individual and Dual Sports (Any Racket Sports) Bsess FSCDocument11 paginiCourse Syllabus SCCPC 101 - Individual and Dual Sports (Any Racket Sports) Bsess FSCMena PotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic P.E Rhythmic ActvityDocument17 paginiBasic P.E Rhythmic ActvityJay R BayaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pe 3 Syllabus - AthleticsDocument7 paginiPe 3 Syllabus - AthleticsLOUISE DOROTHY PARAISOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam GRCDocument4 paginiExam GRCFrancis PJ BegasoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Badminton PowerpointDocument15 paginiBadminton PowerpointJave MontevirgenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pe101 GymnasticsDocument30 paginiPe101 GymnasticsAngelo100% (1)
- Brief History, Nature and Development of Volleyball: Lesson 1Document13 paginiBrief History, Nature and Development of Volleyball: Lesson 1Floyd Dimadim GayyedÎncă nu există evaluări
- PE 3 M3 T1 BadmintoDocument6 paginiPE 3 M3 T1 BadmintoMyle Trisha EstampaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dual Badminton-Porfolio 2Document31 paginiDual Badminton-Porfolio 2Ma.Cristy PedragozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Individual Sports: 1. BadmintonDocument32 paginiIndividual Sports: 1. BadmintonKrisleen GullasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pe AssignmentDocument22 paginiPe AssignmentSheina JavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- BadmintonDocument12 paginiBadmintonTahira KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Olympic Rio 2016: by John DoeDocument6 paginiOlympic Rio 2016: by John DoeJoey DingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Olimpic MascotsDocument23 paginiOlimpic MascotskatiamulikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grigg Ron 400 Meter TrainingDocument33 paginiGrigg Ron 400 Meter TrainingRayshawn Tiller100% (1)
- Farrell Invite 2012 ResultsDocument9 paginiFarrell Invite 2012 ResultsAnonymous ORdAVoBÎncă nu există evaluări
- I Stats Track 150313Document5 paginiI Stats Track 150313BernewsAdminÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1º Basics 1 Grammar Unit 6Document3 pagini1º Basics 1 Grammar Unit 6mariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best Books - English ListDocument3 paginiBest Books - English ListSenthilkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timex T5K588 Ironman Sleek 250 Lap - W279 PDFDocument70 paginiTimex T5K588 Ironman Sleek 250 Lap - W279 PDFGonzalo CeballosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Badminton TriviaDocument4 paginiBadminton TriviaGlenn Paul Villacruz BinaohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LINGAMDocument2 paginiLINGAMlingam balaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 800m Training Plan For Mando EmployeDocument7 pagini800m Training Plan For Mando EmployeSunder Veera Karthikeyan100% (1)
- BNP Paribas Open Main Draw SinglesDocument2 paginiBNP Paribas Open Main Draw SinglesdoblemixtoÎncă nu există evaluări
- FSI192315-INTEGRAL Física Geral II PDFDocument1 paginăFSI192315-INTEGRAL Física Geral II PDFGabriel ChagasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Walter Smith: The Ibrox Gaffer by Scott BurnsDocument40 paginiWalter Smith: The Ibrox Gaffer by Scott BurnsBlack & White PublishingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Swim Ireland Performance Coaching Conference 2018Document4 paginiSwim Ireland Performance Coaching Conference 2018yos_peace86Încă nu există evaluări
- Worldcup 2014Document8 paginiWorldcup 2014Tauhidur Rahman TanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Olympic QuizDocument7 paginiOlympic QuizrajeevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kasparov Losing The Title and AftermathDocument2 paginiKasparov Losing The Title and Aftermathanahata2014Încă nu există evaluări
- Black College Sports Page: Vol 20, No 35Document1 paginăBlack College Sports Page: Vol 20, No 35Eric MooreÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Men's National Association Football Teams - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument15 paginiList of Men's National Association Football Teams - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMelai Delos Reyes CelesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tokyo 2020 Olympic Programme Commission ReportDocument100 paginiTokyo 2020 Olympic Programme Commission ReportOvidiu JeleaÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Favorite Player EvidenceDocument13 paginiMy Favorite Player EvidenceJhon Jairo Umaña HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- SIAC Boys Golf Stats - April 30 2014Document2 paginiSIAC Boys Golf Stats - April 30 2014Johnny EversÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Table Tennis and BadmintonDocument3 paginiHistory of Table Tennis and BadmintonCatherine Nadulpit Soleybar33% (3)
- The Commonwealth Games ScamDocument5 paginiThe Commonwealth Games ScamAwdhoot BhagwatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sudirman CupDocument1 paginăSudirman Cuprahman2007Încă nu există evaluări
- April 2015Document84 paginiApril 2015Wanvisa Sanguansat100% (1)
- Yale Track Classic Accepted EntriesDocument36 paginiYale Track Classic Accepted EntriesBrandon MilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Purcell O Let Me WeepDocument11 paginiPurcell O Let Me WeepCecilia FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sportsfest ProposalDocument5 paginiSportsfest ProposalErica Dizon100% (5)