Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Important Definitions in BRM
Încărcat de
Samir SidDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Important Definitions in BRM
Încărcat de
Samir SidDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Business Research- Research is the process of systematic and in-depth study or search for a solution to a problem or an answer to a question
backed by collection, compilation, presentation, analysis and interpretation of relevant details, data and information. Exploratory Study: The information known on a particular subject matter is little. Hence, a study is conducted to know more about it so as to formulate the problem and procedures of the study. Such a study is called exploratory/ formulative study. Descriptive Study: The major purpose of descriptive research is the description of a person, situation, institution or an event as it exists. Generally fact finding studies are of this type. Experiment - manipulation of an independent variable to see how it affects a dependent variable, while controlling the effects of additional extraneous variables Extraneous variables are those that may have some effect on a dependent variable but yet are not independent variables A field experiment is a research study in a realistic situation in which measurements of the dependent variable are made on subjects (test units) in their natural setting Lab Experiment- contrived, artificial setting for the purpose of controlling the many possible extraneous variables that may affect the dependent variable. Internal Validity - The ability of an experiment to answer the question whether the experimental treatment was the sole cause of changes in a dependent variable. An experiment is internally valid if the observed changes in the dependent variable is, in fact, due to the independent variable External Validity- If the results of the experiment apply to the real world outside the experimental setting, refers to - External validity Observation Method Observation means seeing or viewing. It is not a casual but systematic viewing. Observation may therefore be defined as a systematic viewing of a specific phenomenon in its proper setting for the purpose of gathering information for the specific study. Experimental Method Experimentation is the basic tool for establishing cause and effect relationship and for verifying inferences.
Experience Surveys Analysis: A form of exploratory research is experience surveys. Experience surveys involve talking with knowledgeable individuals, both inside and outside the organization, who may provide insights into the problem. Secondary Data Analysis: Secondary data analysis is another form of exploratory research. Secondary data are data that have been gathered for some purpose other than the one at hand. Focus Groups: Focus groups are in-depth discussions, usually consisting of 8 to 12 participants, which are led by a moderator and are generally limited to one particular concept, idea, or theme. The general idea is to have what one person says generate thoughts and comments by others, therefore creating group dynamics. A hypothesis is a conjectural statement about a relationship between two or more variables that can be tested with empirical data The research design is a plan for addressing the research objectives or hypotheses. In essence, the researcher develops a structure or framework to answer a specific research problem/opportunity. There is no single best research design. Instead, different designs offer an array of choices, each with certain advantages and disadvantages. Causal Studies In causal studies, the researcher investigates whether the value of one variable causes or determines the value of another variable, in an attempt to establish linkage between them. A dependent variable is a symbol or concept expected to be explained or affected by an independent variable. In contrast, an independent variable is a variable that the market researcher can, to some extent, manipulate, change, or alter.
SOURCES OF SECONDARY DATA Sometimes, it is not possible to collect primary data due to time, cost and human resource constraints. Therefore, researchers have to take the help of secondary data. Now let us discuss, (a) various sources from where, one can get secondary data, (b) precautions while using secondary data, its merits and demerits and some documentary and electronic sources of data in India. Documentary Sources of Data
This category of secondary data source may also be termed as Paper Source. The main sources of documentary data can be broadly classified into two categories: a) Published sources, and b) Unpublished sources. A) Published Sources There are various national and international institutions, semi-official reports of various committees and commissions and private publications which collect and publish statistical data relating to industry, trade, commerce, health etc. These publications of various organizations are useful sources of secondary data. These are as follows: 1) Government Publications: Central and State Governments publish current information along with statistical data on various subjects, quarterly and annually.
For example, Monthly Statistical Abstract, National Income Statistics, Economic Survey, Reports of National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER), Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI), Indian
Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Central Statistical Organization (CSO), etc. 2)International International Publications: Labor The United Nations Organization Monetary Fund (UNO), (IMF),
Organization
(ILO),
International
World Bank, Asian Development Bank (ADB) etc., also publish relevant data and reports. 3) Semi-official Publications: Semi-official organizations like Corporations, District Boards, Panchayat etc. publish reports. 4) Committees and Commissions: Several committees and commissions appointed by State and Central Governments provide useful secondary data. For example, the report of the 10th Financial Commission or 6th Pay Commissions etc. 5) Private Publications: Newspapers and journals publish the data on different fields of Economics, Financial Commerce Express etc. and and Trade. like For example, Economic and Times, Political
Journals
Economist,
Economic
Weekly, Indian Journal of Commerce, Journal of Industry and Trade, Business Today etc. Some of the research and financial institutions also publish their
reports annually like Indian Institute of Finance. In addition to this, reports prepared by research scholars, universities etc. also provide secondary source of information
Unpublished Sources It is not necessary that all the information/data maintained by the institutions or individuals are available in published form. Certain research institutions, trade associations, universities, research scholars, private firms, business institutions etc., do collect data but they normally do not publish it. We can get this information from their registers, files etc.
Electronic Sources The secondary data is also available through electronic media (through Internet). You can download data from such sources by entering web sites like google.com; yahoo.com; msn.com; etc., and typing your subject for which the information is needed. You can also find secondary data on electronic sources like CDs, and the following online journals:
http://businessstandard.com
Electronic Journal http://www.businessworldindia.com
Electronic Journal http://www.business-today.com
Electronic Journal http://www.india-invest.com
Census of India http://www.censusindia.net
Union Budget and Economic Survey http://www.indianbudget.nic.in
Directory of Government of India http://goidirectory.nic.in
Institutions Indian Council of Agricultural Research http://www.icar.org.in
Ministry of Commerce and Industry http://www.commin.nic.in
Indian Institute of Foreign Trade http://www.iift.edu
Khadi and Village Industries http://www.kvic.org.in
Board for Industrial & Financial Reconstruction http://www.bifr.nic.in
The Associated Chamber of Commerce and Industry http://www.assochm.org
Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry http://www.ficiofindia.com
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Confrontation Meeting and Third Party Intervention - GauravDocument11 paginiConfrontation Meeting and Third Party Intervention - Gauravaninia100% (1)
- BM Handbook HRMDocument52 paginiBM Handbook HRMMarcus McGowanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016 ARC SurveyDocument99 pagini2016 ARC SurveyThe Statesman100% (1)
- Definition EmploymentDocument5 paginiDefinition EmploymentconsaldradooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Innovative Rural Retail Marketing Strategies in IndiaDocument10 paginiInnovative Rural Retail Marketing Strategies in IndiasamuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer KeyDocument15 paginiAnswer KeyBiancaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Resource Management ProjectDocument22 paginiHuman Resource Management ProjectVikram AdityaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SWOT Analysis of the Software Development IndustryDocument28 paginiSWOT Analysis of the Software Development IndustrySindhuja VijayakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The American Approach To HRMDocument18 paginiWhat Is The American Approach To HRMkiranaishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Staff Profile B.edDocument2 paginiStaff Profile B.edgarima kathuriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Satisfaction towards RTGS & NEFTDocument70 paginiCustomer Satisfaction towards RTGS & NEFTRajibKumar100% (1)
- Inter-Group InterventionsDocument8 paginiInter-Group InterventionsSowmyaRajendran100% (1)
- Training Manual On SHG For Micro-Enterprise DevelopmentDocument77 paginiTraining Manual On SHG For Micro-Enterprise DevelopmentGeeta VenkadakrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corporations: Unique Selling Proposition: Axis Provides Tourism, Corporate TransportationDocument1 paginăCorporations: Unique Selling Proposition: Axis Provides Tourism, Corporate TransportationPro Business PlansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Voter ListDocument57 paginiVoter Listhari1221Încă nu există evaluări
- Production Manager Details Labor Payments Overtime PlanDocument1 paginăProduction Manager Details Labor Payments Overtime PlanMano_Bili89Încă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of HRMand Payroll Cycle in BDUDocument13 paginiAssessment of HRMand Payroll Cycle in BDUSolomon MollaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CVP Analysis ExplainedDocument2 paginiCVP Analysis ExplainedjawadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 ConceputalDocument16 paginiUnit 5 ConceputalGangadhara RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uses of Financial Reporting Accountability and Interperiod EquityDocument4 paginiUses of Financial Reporting Accountability and Interperiod EquityTekaling NegashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Netiquette QuizletDocument1 paginăNetiquette QuizletLemuel CondesÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSC Mock Test Paper - 155 66Document22 paginiSSC Mock Test Paper - 155 66ShikharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Littlefield Technologies: Overview: Stanford University Graduate School of BusinessDocument5 paginiLittlefield Technologies: Overview: Stanford University Graduate School of BusinessarchitbumbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q4 Week6-ModuleDocument10 paginiQ4 Week6-Moduleyojchie de villÎncă nu există evaluări
- Absorption (Variable) Costing and Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDocument41 paginiAbsorption (Variable) Costing and Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisPapsie PopsieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Precautions of Writing A Research ReportDocument2 paginiPrecautions of Writing A Research Reportkarishmapatel9375% (4)
- AEV Balance Sheet: Total Current AssetsDocument5 paginiAEV Balance Sheet: Total Current AssetsJoyce Ann Agdippa BarcelonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBA-513 Management of Financial InstitutionsDocument140 paginiMBA-513 Management of Financial InstitutionsVasudev SurendranÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRM Global ViewDocument3 paginiHRM Global Viewditidube100% (3)
- Resume of Trang NguyenDocument2 paginiResume of Trang NguyenTrang NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management FunctionsDocument1 paginăManagement Functionsrajesh nagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competition Policy in Romania After The Eu AccessionDocument7 paginiCompetition Policy in Romania After The Eu AccessionAndreea OancaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HR DictionaryDocument75 paginiHR Dictionarydave_kool2002Încă nu există evaluări
- Cash Flow Statement and Cash BudgetingDocument14 paginiCash Flow Statement and Cash Budgetingsk0033610Încă nu există evaluări
- Yume SDN BHD - Sample Business PlanDocument96 paginiYume SDN BHD - Sample Business PlanNur Afifah Shahrizal0% (2)
- HRM - Basic Concepts and TrensdDocument14 paginiHRM - Basic Concepts and Trensdshiiba22Încă nu există evaluări
- Asyad Holding Company Balance Sheets and Income Statements 2007-2010Document9 paginiAsyad Holding Company Balance Sheets and Income Statements 2007-2010shawktÎncă nu există evaluări
- Employment Offer 'Salahudin'Document6 paginiEmployment Offer 'Salahudin'knight1729Încă nu există evaluări
- Article 03 Impact of HRM Practices On Employees PerformanceDocument8 paginiArticle 03 Impact of HRM Practices On Employees Performanceshwetauttam00562960% (1)
- Folio Assignment 1 InstructionsDocument6 paginiFolio Assignment 1 Instructionscody bankerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis For DefenseDocument52 paginiThesis For DefenseDebbie Diane Ditching Severino0% (1)
- Talent Management Information SystemDocument7 paginiTalent Management Information SystemAnkita BhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidance Hotels PDFDocument4 paginiGuidance Hotels PDFearlturnerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing A Research Report: Various FieldsDocument7 paginiWriting A Research Report: Various FieldsAyen DivineÎncă nu există evaluări
- HR Practices SurveyDocument7 paginiHR Practices SurveybuddysmbdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internship Format Mba HRM - LatestDocument3 paginiInternship Format Mba HRM - LatestSadia ShahzadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sap HCM Pa Tcodes ListDocument3 paginiSap HCM Pa Tcodes ListSupriyo DuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Career Preparation and ContinuityDocument17 paginiCareer Preparation and ContinuityJorge Luis Villacís NietoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Elements of a Good Feasibility StudyDocument2 paginiThe Elements of a Good Feasibility Studyutcm77Încă nu există evaluări
- Study Performance Appraisal QuestionnaireDocument4 paginiStudy Performance Appraisal QuestionnaireAkhtar AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Partners Key Activity Value Propositions Customer Relationship Customer SegmentDocument1 paginăKey Partners Key Activity Value Propositions Customer Relationship Customer SegmentKhairinÎncă nu există evaluări
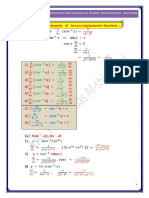
- Derivative and Integral of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument7 paginiDerivative and Integral of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsBashar JassimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive Exam Masters HRM Study GuideDocument23 paginiComprehensive Exam Masters HRM Study GuidePÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concepts & Theories of Crime & DevianceDocument62 paginiConcepts & Theories of Crime & DevianceRobert EdwardsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Employee Appraisal FormsDocument6 paginiEmployee Appraisal Formsarmaya33Încă nu există evaluări
- FINALconceptG 5Document20 paginiFINALconceptG 5Prime ZibheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Small BusinessDocument29 paginiSmall Businessrayhan555Încă nu există evaluări
- Management Consulting Development From Historical Perspective - AftandilyantsDocument9 paginiManagement Consulting Development From Historical Perspective - AftandilyantsVadym AftandilyantsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Human in Human ResourceDe la EverandThe Human in Human ResourceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air FightersDocument1 paginăAir FightersSamir SidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Definitions in BRMDocument5 paginiImportant Definitions in BRMSamir SidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air FightersDocument1 paginăAir FightersSamir SidÎncă nu există evaluări
- A26 CitmDocument12 paginiA26 CitmSamir SidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Oil Prices Hike in Airline IndustryDocument3 paginiImpact of Oil Prices Hike in Airline IndustrySamir SidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oracle Warehouse Management System Rules Engine: An Oracle White Paper October 2000Document22 paginiOracle Warehouse Management System Rules Engine: An Oracle White Paper October 2000Ron DeLongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linux Lab 02 Command LineDocument1 paginăLinux Lab 02 Command Linesmile4ever54Încă nu există evaluări
- LESSON PLAN GRAPH OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTION (Recovered)Document6 paginiLESSON PLAN GRAPH OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTION (Recovered)Jolina Bagwisa LptÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4: Benefit EstimationDocument12 paginiUnit 4: Benefit EstimationRaj ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.abhijith Be (Mech) 2021Document2 pagini3.abhijith Be (Mech) 2021MudduKrishna shettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- FPGA Implementation of OFDM PDFDocument6 paginiFPGA Implementation of OFDM PDFFausto Paco ValenzuelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 PG MTEC 2 Presentation Vote TemplateDocument25 pagini2019 PG MTEC 2 Presentation Vote Templatekholofelo letsoaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reactive Distillation For Producing N-Butyl Acetate: Experiment and SimulationDocument8 paginiReactive Distillation For Producing N-Butyl Acetate: Experiment and SimulationHemant RathvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistical Process Control Study: Data Collection: - Sample D2 A2 D4Document1 paginăStatistical Process Control Study: Data Collection: - Sample D2 A2 D4sa_arunkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Bassoon StopDocument16 paginiAnalysis of Bassoon StopashockleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Portfolio 2021-2022 UnayDocument40 paginiPortfolio 2021-2022 UnayAngelo Aniag UnayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instabilities, Chaos, and Turbulence - Manneville PDFDocument406 paginiInstabilities, Chaos, and Turbulence - Manneville PDFFinalDanishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer MappingDocument11 paginiCustomer MappingVenkat Subramanian RÎncă nu există evaluări
- IFC Investment Analyst ProgramDocument2 paginiIFC Investment Analyst Programthava477cegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exponential smoothing for time series forecastingDocument12 paginiExponential smoothing for time series forecastingNageshwar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- JOEL Microscopio UntitledDocument2 paginiJOEL Microscopio UntitledFrancisco_Patt_9809Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 3 PDFDocument15 paginiAssignment 3 PDFPArk100100% (1)
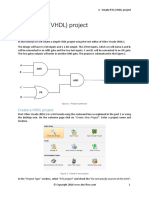
- 4 Simple RTL (VHDL) Project With VivadoDocument6 pagini4 Simple RTL (VHDL) Project With VivadoNarendra BholeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vpci PMC NCR 0026 PDFDocument51 paginiVpci PMC NCR 0026 PDFDarrel Espino AranasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Project Management Module 3Document14 paginiBasic Project Management Module 3Ajaya KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3D PDF Converter Product Data Sheet RelDocument2 pagini3D PDF Converter Product Data Sheet RelMradul YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Como Criar Micromarcas PDFDocument28 paginiComo Criar Micromarcas PDFJoséÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 01 - Introduction To Project ManagementDocument82 paginiWeek 01 - Introduction To Project ManagementtaribÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macro Environment of The Mobile IndustryDocument2 paginiMacro Environment of The Mobile IndustryAbhinandanMalhotraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 245 Q4 AR Extra PracticeDocument9 pagini245 Q4 AR Extra PracticeKausarAtiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unfamiliar Text - Violence ComprehensionDocument1 paginăUnfamiliar Text - Violence ComprehensionjazminecoxofficialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instruction Manual: Digital CameraDocument187 paginiInstruction Manual: Digital CameraalelendoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Path IntegralsDocument6 paginiPath IntegralsSourav Sen ChoudhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP Note Explains Merge Process for Authorization DataDocument5 paginiSAP Note Explains Merge Process for Authorization Dataakash_sky51Încă nu există evaluări