Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
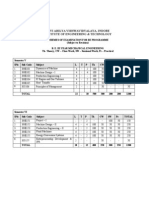
Me 2203 Kinematics of Machinery 3 1 0 4
Încărcat de
Maharaja KanthasamyDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Me 2203 Kinematics of Machinery 3 1 0 4
Încărcat de
Maharaja KanthasamyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ME 2203 KINEMATICS OF MACHINERY 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVE To understand the concept of machines, mechanisms and related terminologies.
To analyse a mechanism for displacement, velocity and acceleration at any point in a moving link To understand the theory of gears, gear trains and cams To understand the role of friction in drives and brakes. UNIT I BASICS OF MECHANISMS 7(L) Definitions Link, Kinematic pair, Kinematic chain, Mechanism, and Machine. -Degree of Freedom Mobility - Kutzbach criterion (Grueblers equation) -Grashoff's lawKinematic Inversions of four-bar chain and slider crank chain - Mechanical AdvantageTransmission angle. Description of common Mechanisms - Offset slider mechanism as quick return mechanisms, Pantograph, Straight line generators (Peaucellier and Watt mechanisms), Steering gear for automobile, Hookes joint, Toggle mechanism, Ratchets and escapements - Indexing Mechanisms. UNIT II KINEMATIC ANALYSIS 10(L)+5(T) Analysis of simple mechanisms (Single slider crank mechanism and four bar mechanism) - Graphical Methods for displacement, velocity and acceleration; Shaping machine mechanism - Coincident points Coriolis acceleration - Analytical method of analysis of slider crank mechanism and four bar mechanism. Approximate analytical expression for displacement, velocity and acceleration of piston of reciprocating engine mechanism. UNIT III KINEMATICS OF CAMS 8(L)+3(T) Classifications - Displacement diagrams - Parabolic, Simple harmonic and Cycloidal motions Graphical construction of displacement diagrams and layout of plate cam profiles - circular arc and tangent cams - Pressure angle and undercutting. UNIT IV GEARS 10(L)+4(T) Classification of gears Gear tooth terminology - Fundamental Law of toothed gearing and involute gearing Length of path of contact and contact ratio - Interference and undercutting - Gear trains Simple, compound and Epicyclic gear trains - Differentials. UNIT V FRICTION 10(L)+3(T) Dry friction Friction in screw jack Pivot and collar friction - Plate clutches - Belt and rope drives - Block brakes, band brakes. Total Number of Periods: L= 45 T= 15 60
8
TEXT BOOKS 1. Ambekar A. G., Mechanism and Machine Theory, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2007. 2. Uicker J.J.,Pennock G.R., Shigley J.E., Theory of Machines and Mechanisms(Indian Edition), Oxford University Press, 2003. REFERENCE BOOKS 1. Thomas Bevan, Theory of Machines, CBS Publishers and Distributors, 1984. 2. Ramamurti,V., Mechanism and Machine Theory, Second Edition, Narosa Publishing House, 2005 3. Ghosh A and A.K.Mallick, Theory of Mechanisms and Machines, Affiliated EastWest Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 1998. 4. Rao J.S and Dukkipati R.V, Mechanism and Machine Theory, Wiley-Eastern Ltd., New Delhi, 199 2.
5. John Hannah and Stephens R.C, Mechanics of Machines, Viva Low-Prices Student Edition, 1999 BIS Codes of Practice/Useful Websites 1. IS 2458 : 2001, Vocabulary of Gear Terms Definitions Related to Geometry 2. IS 2467 : 2002 (ISO 701: 1998), International Gear Notation Symbols for Geometric Data. 3. IS 5267 : 2002 Vocabulary of Gear Terms Definitions Related to Worm Gear Geometry. 4. IS 5037 : Part 1 : 2004, Straight Bevel Gears for General Engineering and Heavy Engineering - Part 1: Basic Rack. 5. IS 5037 : Part 2 : 2004, Straight Bevel Gears for General Engineering and Heavy Engineering - Part 2: Module and Diametral Pitches. WEBSITE: www.howstuffworks.com
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- ME2203 KOM SyllabusDocument1 paginăME2203 KOM SyllabusrkumaravelanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me6401 KomDocument128 paginiMe6401 KomThomas LafontaineÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1151au105 - Mechanics of Machines: SyllabusDocument1 pagină1151au105 - Mechanics of Machines: SyllabusSriramulu JaichandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mee215 Kinematics-Of-machinery TH 2.00 Ac26Document2 paginiMee215 Kinematics-Of-machinery TH 2.00 Ac26yashvantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me6401 NotesDocument115 paginiMe6401 NotesAkhil Rajagopal100% (1)
- Me6401 Kinematics of Machinery L T P CDocument2 paginiMe6401 Kinematics of Machinery L T P CThiru Moorthy100% (1)
- Me2203 Kom 2011Document4 paginiMe2203 Kom 2011sumikannuÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME9203 Kinematics of Machines SyllabusDocument1 paginăME9203 Kinematics of Machines SyllabusJayasundar Mithunraj JÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10.kom Guide Book MvreddyDocument41 pagini10.kom Guide Book MvreddyVenkateswar Reddy MallepallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- KOM Tutorial Book-2019-20 VK Es1Document12 paginiKOM Tutorial Book-2019-20 VK Es1Vinoth KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus - 3rd & 4thmechanical EngineeringDocument35 paginiSyllabus - 3rd & 4thmechanical EngineeringSalman KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME8492 NotesDocument76 paginiME8492 NotesYa Hya SahalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ae1253 Mechanics of Machines 3 1 0 100Document2 paginiAe1253 Mechanics of Machines 3 1 0 100sivaaero41Încă nu există evaluări
- KOM Tutorial Book-2019-20 VK Es2Document12 paginiKOM Tutorial Book-2019-20 VK Es2Vinoth KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of MachinesDocument1 paginăMechanics of MachinesmaniaeronauticalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kom Lecture NotesDocument163 paginiKom Lecture NotesgvnagamaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinematics of Machinery: II B.Tech IV SemesterDocument2 paginiKinematics of Machinery: II B.Tech IV SemesterPraveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 Te Tom-IiDocument3 pagini03 Te Tom-Iikiran_wakchaureÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mee301 Dynamics-Of-machinery Eth 1.10 Ac26Document2 paginiMee301 Dynamics-Of-machinery Eth 1.10 Ac26yashvantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinematics of MachinesDocument2 paginiKinematics of MachinesBhavesh J MakwanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinematics of Machines ME 207 E: B.Tech (Mechanical Engg.) 3RD SemesterDocument2 paginiKinematics of Machines ME 207 E: B.Tech (Mechanical Engg.) 3RD SemesterparmodrtkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Printing Iii To Viii PDFDocument62 paginiPrinting Iii To Viii PDFRaja PrabhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME6401-SCAD-MSM - by WWW - LearnEngineering.in PDFDocument123 paginiME6401-SCAD-MSM - by WWW - LearnEngineering.in PDFYenigalla GamanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME8492 Kinematics of Machinery 03 - by LearnEngineering - inDocument76 paginiME8492 Kinematics of Machinery 03 - by LearnEngineering - inPrasanna SekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinematics of Machinery: Lecture NotesDocument3 paginiKinematics of Machinery: Lecture NotesPraveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering B.techDocument35 paginiMechanical Engineering B.techRamBabuInkolluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me2302 Dynamics of Machinery L T P CDocument3 paginiMe2302 Dynamics of Machinery L T P Ckumar kmÎncă nu există evaluări
- KDM SyllabusDocument2 paginiKDM SyllabusmehercetbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mech-Iv-Kinematics of Machines (10me44) - Notes PDFDocument196 paginiMech-Iv-Kinematics of Machines (10me44) - Notes PDFgopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machines and Mechanism PDFDocument3 paginiMachines and Mechanism PDFPradeepvenugopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- CurriculummitmDocument2 paginiCurriculummitmPrasad PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinematics of Machinery Anna University Question Papers CompiledDocument77 paginiKinematics of Machinery Anna University Question Papers CompiledNatesha SundharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- KMDocument120 paginiKMsady1967Încă nu există evaluări
- KOM Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiKOM Lesson PlanFarhan Shah Sarani100% (1)
- Theory of Machine (9050)Document7 paginiTheory of Machine (9050)Candice Andrews25% (4)
- Theory of MachineDocument2 paginiTheory of MachineBikash ChoudhuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Objectives:: Me3262:Dynamics of MachinesDocument4 paginiCourse Objectives:: Me3262:Dynamics of Machinesgiriaj kokareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mech Sylabus 21Document1 paginăMech Sylabus 21Honey SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rtmnu Mechanical Engineering SyllabusDocument85 paginiRtmnu Mechanical Engineering SyllabusShobit JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 4-Kom PDFDocument90 pagini2 4-Kom PDFpiocasmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final TOM Lab Manual New PDFDocument10 paginiFinal TOM Lab Manual New PDFdab111Încă nu există evaluări
- Thomas Bevan-Theory of Machine IIDocument3 paginiThomas Bevan-Theory of Machine IIShiyam Raj11% (9)
- 6 Sem SyllabusDocument7 pagini6 Sem SyllabusAjinkya NawghareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Read This First MechanicalDocument5 paginiRead This First MechanicalAnimesh RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Basic Concepts v2Document29 pagini01 Basic Concepts v2Shashank SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anna University Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli - 620 024Document59 paginiAnna University Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli - 620 024Siva KumaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Affiliated Institutions Anna University of Technology Chennai:: Chennai 600 113 Curriculum 2010Document12 paginiAffiliated Institutions Anna University of Technology Chennai:: Chennai 600 113 Curriculum 2010Gowri ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME6401 SCAD MSM by EasyEngineering - Net 1Document122 paginiME6401 SCAD MSM by EasyEngineering - Net 1shankar0% (1)
- ME214 Theory of MachinesDocument2 paginiME214 Theory of Machinesnandan144Încă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Theory of Constraint and Motion Analysis for Robot MechanismsDe la EverandAdvanced Theory of Constraint and Motion Analysis for Robot MechanismsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tom SyllabusDocument1 paginăTom SyllabusavantikasankhyainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinematics of Machinery Question BankDocument92 paginiKinematics of Machinery Question BankNatesha Sundharan100% (2)
- Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, I Dore I Stitute of E Gi Eeri G & Tech OlogyDocument20 paginiDevi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, I Dore I Stitute of E Gi Eeri G & Tech OlogySonal MahajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME211 Mechanics of Solids and Mechanics of MachinesDocument2 paginiME211 Mechanics of Solids and Mechanics of Machinesnandan144Încă nu există evaluări
- Btmel205 Kinematics of MacinesDocument3 paginiBtmel205 Kinematics of MacinesVinayak DakreÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Tech. Second Year (Mechanical Engineering) : (Batch 2009)Document11 paginiB.Tech. Second Year (Mechanical Engineering) : (Batch 2009)Faiz AkhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus (New2013 Pattern) - TOM-IDocument14 paginiSyllabus (New2013 Pattern) - TOM-IAkshayÎncă nu există evaluări
- FeaturesDocument9 paginiFeaturesMaharaja KanthasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic SolidWorks LayoutDocument8 paginiBasic SolidWorks LayoutMaharaja KanthasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine Design Article On Stiffness Vs StrengthDocument3 paginiMachine Design Article On Stiffness Vs StrengthMaharaja KanthasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anna University Chennai SyllabusDocument95 paginiAnna University Chennai SyllabusRAAM MECHÎncă nu există evaluări
- GearDocument19 paginiGearArul DossÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spur Gear DesignDocument15 paginiSpur Gear DesignMaharaja KanthasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Collage Lab PDFDocument145 paginiCollage Lab PDFmaa siddhi92% (12)
- Calculate Cable Size and Voltage Drop Electrical Notes Articles PDFDocument10 paginiCalculate Cable Size and Voltage Drop Electrical Notes Articles PDFRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuromuscular Diseases. ALSDocument7 paginiNeuromuscular Diseases. ALSjalan_zÎncă nu există evaluări
- TA1515VDocument4 paginiTA1515VLeo LeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wic ReflectionDocument3 paginiWic Reflectionapi-307029735Încă nu există evaluări
- BLANCHARD-The Debate Over Laissez Faire, 1880-1914Document304 paginiBLANCHARD-The Debate Over Laissez Faire, 1880-1914fantasmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ra Wah Night Shift - Word Format FiniDocument17 paginiRa Wah Night Shift - Word Format FiniREHOBOTH YAMBO KAHILUÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Quarter: 5 Grade Benchmark Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide 2015-2016Document3 pagini1 Quarter: 5 Grade Benchmark Scope and Sequence Pacing Guide 2015-2016api-292307509Încă nu există evaluări
- Calabano Clinical Bacteriology Exercise 1Document5 paginiCalabano Clinical Bacteriology Exercise 1MarkJasperCalabanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 28701-FGC+101+3441+Router+6471+Datasheet+Rev+FDocument2 pagini1 28701-FGC+101+3441+Router+6471+Datasheet+Rev+FВладимир ЕгоровÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acer AIO Z1-752 System DisassemblyDocument10 paginiAcer AIO Z1-752 System DisassemblySERGIORABRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polynomial Transformations of Tschirnhaus, Bring and Jerrard4s++Document5 paginiPolynomial Transformations of Tschirnhaus, Bring and Jerrard4s++wlsvieiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feature Writing EnglishDocument2 paginiFeature Writing EnglishAldren BababooeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Output Process Input: Conceptual FrameworkDocument4 paginiOutput Process Input: Conceptual FrameworkCHRISTINE DIZON SALVADORÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daphne Alpha Cleaner Series: Lubricant Product InformationDocument2 paginiDaphne Alpha Cleaner Series: Lubricant Product InformationChart ChÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signals and Systems: Dr. Shurjeel WyneDocument3 paginiSignals and Systems: Dr. Shurjeel Wynemarryam nawazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertical Isolation VCBEnglishDocument1 paginăVertical Isolation VCBEnglishdip461Încă nu există evaluări
- S.V. Kulkarni, S.A. Khaparde Transformer and Inductor Design Handbook 2004Document532 paginiS.V. Kulkarni, S.A. Khaparde Transformer and Inductor Design Handbook 2004Gianpiero Boccato0% (1)
- Theology of Work and Practical ImplicationsDocument28 paginiTheology of Work and Practical ImplicationsVinicius CardosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noxim MANUALDocument5 paginiNoxim MANUALSAI NRUSIMHA DEEPAK BURRA SAI NRUSIMHA DEEPAK BURRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faujifood Pakistan PortfolioDocument21 paginiFaujifood Pakistan PortfolioPradeep AbeynayakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Pen MountDocument17 paginiNon-Pen MountT BagÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Failed Rotator CuffDocument307 paginiThe Failed Rotator Cufforthofitness2017Încă nu există evaluări
- General Anaesthesia MCQsDocument5 paginiGeneral Anaesthesia MCQsWasi Khan100% (3)
- Article Unleashing The Power of Your StoryDocument17 paginiArticle Unleashing The Power of Your StoryAnkit ChhabraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tempera 2018 AbstractsDocument45 paginiTempera 2018 AbstractsGerard Emmanuel KamdemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art and Geography: Patterns in The HimalayaDocument30 paginiArt and Geography: Patterns in The HimalayaBen WilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ketu in 12th HousesDocument10 paginiKetu in 12th HousesSanket MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monk - Way of The Elements RevisedDocument3 paginiMonk - Way of The Elements Revisedluigipokeboy0% (1)
- Annual Report 2022-23 (Eng.)Document326 paginiAnnual Report 2022-23 (Eng.)Gaurav DurejaÎncă nu există evaluări