Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Congenital Disease
Încărcat de
Ravi SharmaDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Congenital Disease
Încărcat de
Ravi SharmaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
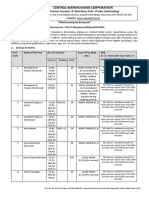
INTERNAL
EXTERNAL
Ones which are detected only through investigations Eg. congenital heart diseases, sickle cell disease
Can be diagnosed with naked eye. Eg. Flat foot syndrome, keratoconus
is a condition which is present at the time of birth which varies from the standard presentation. Etiology:Unknown,multifactorial inheritance, genetic factors implicated, high incidence in first degree relatives.
Congenital heart disease
Congenital hernia Congenital cataract
Pre auricular sinus
Hypospadias Flat foot syndrome
keratoconus
VENTRICULAR SEPTAL DEFECT
ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT
PATENT DUCTUS ARTERIOSIS
TETRALOGY OF FALLOT
Rapid breathing Cyanosis (a bluish tint to the skin, lips, and fingernails) Fatigue (tiredness) Poor blood circulation Congenital heart defects don't cause chest pain or other painful symptoms.
A Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) is a hole in the ventricular septum. most common forms of congenital heart disease, accounting for 21% of all cases. Treatment: Endocarditis prophylaxis,digoxin,diur etics. Surgical closure before pulmonary vascular changes become irreversible
An Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is a hole in the atrial septum Accounts for 1/3rd of CHD in adults Two to three times more common in women Surgical closure before age 20 associated with long-term survival same as general population Closure between ages 25-41 followed slightly shorter survival After age 41 closure associated with increase in late morbidity and mortality
Ventricular septal defect (hole between the right and left ventricles) Narrowing of the pulmonary outflow tract (the valve and artery that connect the heart with the lungs) Overriding aorta that is shifted over the right ventricle and ventricular septal defect, instead of coming out only from the left ventricle Thickened wall of the right ventricle (right ventricular hypertrophy)
In severe episodes, IV propranolol (Inderal) may be administered. Primary correction is the ideal operation for treatment of tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) and is usually performed under cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB).
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a condition in which the ductus arteriosus does not close ETIOLOGYidiopathic,congenital rubella syndrome,down syndrome results in irregular transmission of blood between two of the most important arteries close to the heart, the aorta and the pulmonary artery
medications such as indomethacin or a special form of ibuprofen are often the first choice percutaneous interventional method. Via the femoral vein or femoral artery, a platinum coil can be deployed via a catheter, which induces thrombosis (coil embolization) PDA occluder device
the inner area of the side of the feet do not form any arches giving the appearance of a flat foot instead of a curved appearance. ETIOLOGY-genetic, congenital bone malformation, chronic foot strain,injury Management-orthotic devices, Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs,surgery.
An abnormal protrusion of an organ or tissue through a defect in its surrounding walls Occur at sites where aponeurosis and fascia are not covered by striated muscle
Inguinal hernia: Makes up 75% of all abdominal wall hernias and occurring up to 25 times more often in men than women. Two types of inguinal hernias: indirect inguinal hernia and direct inguinal hernia.
Indirect inguinal hernia follows pathway that testicles made during prebirth development. This pathway normally closes before birth but remains a possible place for a hernia.
Umbilical hernia
These common hernias (10-30%) are often noted at
birth as a protrusion at the bellybutton (the umbilicus). This is caused when an opening in the abdominal wall, which normally closes before birth, doesnt close completely. Even if the area is closed at birth, these hernias can appear later in life because this spot remains a weaker place in the abdominal wall. They most often appear later in elderly people and middle-aged women who have had children.
Treatment of a hernia depends on whether it is reducible or irreducible and possibly strangulated.
Reducible
Can be treated with surgery but does not have to be.
Irreducible
All acutely irreducible hernias need emergency treatment because of the risk of strangulation. An attempt to push the hernia back can be made
Strangulation Operation
Prevention
You can do little to prevent areas of the
abdominal wall from being or becoming weak, which can potentially become a site for a hernia.
Strangulation Operation
Prevention
You can do little to prevent areas of the
abdominal wall from being or becoming weak, which can potentially become a site for a hernia.
Any condition in which the meatus occurs on the undersurface of the penis SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS-downward curve (ventral curvature or chordee) of the penis during an erection Abnormal spraying of urine Having to sit down to urinate Malformed foreskin that makes the penis look "hooded
MANAGEMENT- most urologists recommend repair before the child is 18 months old, tissue grafts are used to close the opening
Keratoconus is degeneration of the structure of the cornea. The cornea is the clear tissue covering the front of the eye. The shape of the cornea slowly changes from the normal round shape to a cone shape. Cause- The cause is unknown, but the tendency to develop keratoconus is probably present from birth. Keratoconus is thought to involve a defect in collagen, the tissue that makes up most of the cornea. SYMPTOMS- The earliest symptom is subtle blurring of vision that cannot be corrected with glasses
CONTACT LENSES CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATIO N INTRACORNEAL RING- the shape of the cornea can be changed so that vision with contact lenses is improved.
A congenital cataract is a clouding of the lens of the eye that is present at birth. ETIOLOGY- Intrauterine infections
SYMPTOMSGray or white cloudiness of the pupil (which is normally black), Infant doesn't seem to be able to see (if cataracts are in both eyes) "Red eye" glow of the pupil is missing in photos MANAGEMENT MILD FORM-no treatment required Severe form-surgical removal of cataract
Rubella Toxoplasmosis Cytomegalovirus Varicella
Metabolic disorders
Galactosaemia Hypoglycaemia Hypocalcaemia
Types of congenital cataract
Anterior polar Posterior polar Coronary Cortical spoke-like
Cryptorchidism/Empty scrotum/Monorchism/Vanished testes\Retractile testes Most of the time, children's testicles descend by the time they are 9 months old common in infants who are born early (premature infants). Management- Usually the testicle will descend into the scrotum without treatment during the child's first year of life. If this does not occur, the child may get hormone injections (B-HCG or testosterone) to try to bring the testicle into the scrotum. Surgery (orchiopexy) to bring the testicle into the scrotum
small dells adjacent to the external ear, usually at the anterior margin of the ascending limb of the inherited in an incomplete autosomal dominant pattern helix PRESENTATION--Most people with preauricular sinuses are asymptomatic.
May present with chronic intermittent drainage of purulent material. facial cellulitis or ulcerations located anterior to the ear. Management-Once a patient acquires infection of the sinus, he or she must receive systemic antibiotics. If an abscess is present, it must be incised and drained, and the exudate should be sent for Gram staining and culturing to ensure proper antibiotic coverage.
developmental congenital disorder caused by the incomplete closing of the embryonic neural tub SIGNS- Leg weakness and paralysis Orthopedic abnormalities (i.e., club foot, hip dislocation, scoliosis) Bladder and bowel control problems, including incontinence, urinary tract infections, and poor renal function
ETIOLOGY- results from the interaction of multiple genes and environmental factors(Medications such as some anticonvulsants, diabetes, having a relative with spina bifida, obesity, and an increased body temperature from fever or external sources such as hot tubs and electric blankets may increase the chances of conception of a baby with a spina bifida
There is no known cure for nerve damage caused by spina bifida To prevent further damage of the nervous tissue and to prevent infection, pediatric neurosurgeons operate to close the opening on the back.
Cleft palate is a condition in which the two plates of the skull that form the hard palate (roof of the mouth) are not completely joined If the cleft does not affect the palate structure of the mouth it is referred to as cleft lip
Cleft lip and palate is very treatable; however, the kind of treatment depends on the type and severity of the cleft. Often a cleft palate is temporarily covered by a palatal obturator Cleft palate can also be corrected by surgery, usually performed between 6 and 12 months
Thallasemia major Sickle cell disease Congenital hip dislocation Hypoplasia of tibia/femur Shortening of bones Anal atresia
Internal and external congenital diseases not covered in AMHI retail/corporate except few corporates
Internal congenital covered in PSU corporate EXTERNAL CONGENITAL NOT COVERED ANYWHERE
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- NCP - Group 1Document4 paginiNCP - Group 1Danica CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synthesis of FlavanoneDocument5 paginiSynthesis of FlavanonefikarisvitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory Interacting N Open System ModelDocument23 paginiTheory Interacting N Open System ModelBheru LalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hexose Monophosphate Shunt Pathway Generates NADPH and Ribose-5-PhosphateDocument7 paginiHexose Monophosphate Shunt Pathway Generates NADPH and Ribose-5-PhosphateElla BangalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amoebiasis: The Right Clinical Information, Right Where It's NeededDocument27 paginiAmoebiasis: The Right Clinical Information, Right Where It's NeededFhaJar PeluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treating and Preventing Chagas DiseaseDocument8 paginiTreating and Preventing Chagas DiseaseRade NikolajevicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Florence Nightingale's Nursing PhilosophyDocument12 paginiFlorence Nightingale's Nursing PhilosophyLuis LazaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inhibiting The Growth of Pathogens in Vivo Using Antimicrobial AgentsDocument1 paginăInhibiting The Growth of Pathogens in Vivo Using Antimicrobial AgentsLongyapon Sheena StephanieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory System: StructureDocument29 paginiRespiratory System: StructureDr. Abir Ishtiaq100% (1)
- Neonatal SeizuresDocument22 paginiNeonatal SeizuresKatrin Marcelina SihombingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs by ZebDocument40 paginiAntiarrhythmic Drugs by ZebFazl UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument27 paginiEndocrine Systemcardos cherry100% (1)
- CHF Drugs Guide: Key Medications for Treating Congestive Heart FailureDocument21 paginiCHF Drugs Guide: Key Medications for Treating Congestive Heart Failuremohsen mirdamadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 IntroDocument5 pagini1 IntroJeanjayannseptoemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 11 21 Antiviral AgentsDocument49 pagini13 11 21 Antiviral AgentsRahul LakhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pain Management: Kim L. Paxton MSN, ANP, APRN-BC Bro. Jim O'Brien, OFM, Conv. R.N., M.S.N., O.C.NDocument69 paginiPain Management: Kim L. Paxton MSN, ANP, APRN-BC Bro. Jim O'Brien, OFM, Conv. R.N., M.S.N., O.C.NsmusquizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distribution of DrugsDocument36 paginiDistribution of DrugsKashar SaeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flavonols and Phenolic Acids in Berries and Berry Products PDFDocument93 paginiFlavonols and Phenolic Acids in Berries and Berry Products PDFGopalaKrishnan SivaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2molting ProcessDocument22 pagini2molting ProcessGretz AnticamaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral Agents: Dr. Roshna Sh. Aziz Department of Pharmacology School of Medicine University of SulaimaniDocument72 paginiAntiviral Agents: Dr. Roshna Sh. Aziz Department of Pharmacology School of Medicine University of Sulaimaniheta aprianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Severe DehydrationDocument64 paginiManagement of Severe DehydrationIgbashioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iv TherapyDocument3 paginiIv TherapylovlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pepti C Ul Cer Dis Ea SeDocument36 paginiPepti C Ul Cer Dis Ea Segerald_ichigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genitourinary Tract InfectionsDocument80 paginiGenitourinary Tract Infectionsraene_bautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Renal FailureDocument30 paginiAcute Renal FailureJerinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiviral Agents: Viruses Are Obligate Cellular Parasites Composed of Nucleic AcidDocument47 paginiAntiviral Agents: Viruses Are Obligate Cellular Parasites Composed of Nucleic AcidhadeelÎncă nu există evaluări
- OT6 - Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocument19 paginiOT6 - Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisAnnbe BarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glaucoma Diagnosis & Treatment GuideDocument42 paginiGlaucoma Diagnosis & Treatment GuideSaha DirllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vitamin Deficiency DisordersDocument23 paginiVitamin Deficiency DisordersKibromWeldegiyorgisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presented By: DR Sharmila G SDocument76 paginiPresented By: DR Sharmila G SSharmila Shivakumar G SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anterior Pituitary HormonesDocument46 paginiAnterior Pituitary Hormonespramod bhaleraoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warfarin Therapy Management: ScopeDocument9 paginiWarfarin Therapy Management: ScopesastiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enzymes and Their ClassificationDocument30 paginiEnzymes and Their ClassificationSadia DinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of the female pelvisDocument24 paginiAnatomy of the female pelvisThrishia Jade IgotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension Disorder in PregnancyDocument42 paginiHypertension Disorder in Pregnancyholly girlchy JastinÎncă nu există evaluări
- OsmoregulationDocument3 paginiOsmoregulationLia Savitri Romdani0% (1)
- Pediatric Imperforate Hymen - Background, Anatomy, PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiPediatric Imperforate Hymen - Background, Anatomy, PathophysiologyAndry Ai Ryazen100% (1)
- Poisoning II FinalDocument45 paginiPoisoning II FinalBi PinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peptic UlcerDocument7 paginiPeptic UlcerMarielle Adey Magcawas RNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Initiating A Blood TransfusionDocument5 paginiInitiating A Blood TransfusionJoyce Kathreen Ebio LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Giardia lamblia in the Small IntestineDocument16 paginiGiardia lamblia in the Small IntestineRahul ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aluminum Hydroxide Antacids and Phosphate BindersDocument3 paginiAluminum Hydroxide Antacids and Phosphate BindersAP TOROBXÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coarctation of AortaDocument40 paginiCoarctation of Aortaaalok1903Încă nu există evaluări
- Tracheostomy CareDocument44 paginiTracheostomy CareJharaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Near DrowningDocument48 paginiNear DrowningS.m. TehseenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Shock ProteinsDocument98 paginiHeat Shock ProteinsAprianie Wiwin100% (1)
- CHP 1 CarbohydrateDocument79 paginiCHP 1 Carbohydrateستي نوراسيقينÎncă nu există evaluări
- LeprosyDocument22 paginiLeprosyKev Olaso ⎝⏠⏝⏠⎠Încă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord Injuries ExplainedDocument80 paginiSpinal Cord Injuries ExplainedMarah AbdulrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti Protozoal AgentsDocument19 paginiAnti Protozoal AgentsNithish SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disorders of The Kidneys and Ureters3962Document110 paginiDisorders of The Kidneys and Ureters3962Nikki M. ArapolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colostomy Care: A Guide For Home Care CliniciansDocument11 paginiColostomy Care: A Guide For Home Care Cliniciansdika franÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine System: THE Adrenal GlandsDocument50 paginiEndocrine System: THE Adrenal GlandsAbdel Aziz NazihÎncă nu există evaluări
- DengueDocument46 paginiDengueMuhammad Ayub KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malaria Prevention and TreatmentDocument20 paginiMalaria Prevention and TreatmentKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiprotozoal Agents: Pharmacology Group III Beguas, Beltran, Bejawada, Bingari, Cabrera, Cadawas, CaliwagDocument86 paginiAntiprotozoal Agents: Pharmacology Group III Beguas, Beltran, Bejawada, Bingari, Cabrera, Cadawas, CaliwagThakoon TtsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocument15 paginiAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosisyamie sulongÎncă nu există evaluări
- HOST-PARASITE RELATIONSHIP: NORMAL FLORA, SYMBIOSIS, AND PATHOGENICITYDocument6 paginiHOST-PARASITE RELATIONSHIP: NORMAL FLORA, SYMBIOSIS, AND PATHOGENICITYGrace ValenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toacs 5Document244 paginiToacs 5Mobin Ur Rehman Khan100% (2)
- Spina BifidaDocument33 paginiSpina BifidaRegine Prongoso DagumanpanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ta Da HirenDocument1 paginăTa Da HirenRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview Questions On AutomobileDocument13 paginiInterview Questions On AutomobileRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jess302 PDFDocument22 paginiJess302 PDFMita KunduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rotary Public School: I Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 paginiRotary Public School: I Multiple Choice QuestionsRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF To WordDocument1 paginăPDF To WordRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- R K Sharma) .IndustrialDocument3 paginiR K Sharma) .IndustrialRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SK Automatics ExperienceDocument1 paginăSK Automatics ExperienceRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- R K SHARMA (Resume) IndustrialDocument3 paginiR K SHARMA (Resume) IndustrialRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ravi K Sharma - Trainer - Acceptanc LetterDocument1 paginăRavi K Sharma - Trainer - Acceptanc LetterRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview Questions On AutomobileDocument13 paginiInterview Questions On AutomobileRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salary SlipDocument2 paginiSalary SlipRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Ravi SirDocument3 paginiFor Ravi SirRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ticket From GGGN To MehDocument1 paginăTicket From GGGN To MehRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ctsg-13 Attendance FormateDocument1 paginăCtsg-13 Attendance FormateRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Admit Card1Document4 paginiAdmit Card1Ravi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF To WordDocument1 paginăPDF To WordRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clutch Types and ConstructionDocument87 paginiClutch Types and Constructionaniket rautÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airless TyresDocument10 paginiAirless Tyresacharyasandeep100% (1)
- 3D Printing's Impact and Applications ExploredDocument6 pagini3D Printing's Impact and Applications ExploredRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ClutshesDocument15 paginiClutshesAmr Abd ElrahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airless TyresDocument10 paginiAirless Tyresacharyasandeep100% (1)
- BS VI Fuel Supply & Quality Up Gradation: Industry PerspectiveDocument14 paginiBS VI Fuel Supply & Quality Up Gradation: Industry PerspectiveSuvam PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro-Edm Overview and Recent DevelopmentsDocument16 paginiMicro-Edm Overview and Recent DevelopmentsRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12Document2 pagini12Ravi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Guide: HSSC Advt. No. 7/2016Document26 paginiUser Guide: HSSC Advt. No. 7/2016Ravi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Warehousing Corporation: (A Premier Schedule A' Mini Ratna Govt. of India Undertaking)Document42 paginiCentral Warehousing Corporation: (A Premier Schedule A' Mini Ratna Govt. of India Undertaking)darshitÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20 GSDocument12 pagini20 GSPankul BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical 3rd 4thsem 2010 11Document32 paginiMechanical 3rd 4thsem 2010 11Deepak RohillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSSC Recruitment 2018-6-2018Document25 paginiHSSC Recruitment 2018-6-2018TopRankersÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAD Lab Equipment Status ReportDocument3 paginiCAD Lab Equipment Status ReportRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cervical Disc Herniation Causing Rare Brown-Sequard SyndromeDocument6 paginiCervical Disc Herniation Causing Rare Brown-Sequard Syndromeida maryaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Report - ELISA LatestDocument8 paginiFull Report - ELISA LatestNik AmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 History of MassageDocument3 pagini4 History of MassageJoanna AaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selected Bibliography On DreamingDocument29 paginiSelected Bibliography On DreamingkayarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hospital Spaces PDFDocument65 paginiHospital Spaces PDFJamie TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doctor's Directory of Sri LankaDocument68 paginiDoctor's Directory of Sri LankaadithadharmasenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prospectus Ph.D. July 2021 SessionDocument5 paginiProspectus Ph.D. July 2021 SessiondamadolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Patients with Stroke: Assessment, Investigation, Immediate Management and Secondary PreventionDocument32 paginiManagement of Patients with Stroke: Assessment, Investigation, Immediate Management and Secondary Preventionvasarhely imolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preterm Prelabour Rupture of Membrane, Prelabour RuptureDocument14 paginiPreterm Prelabour Rupture of Membrane, Prelabour RuptureTengku NorshaherahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific TeamDocument4 paginiScientific TeampriyadikkalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetic Therapy in Eastern Europe A 30 Year ReviewDocument3 paginiMagnetic Therapy in Eastern Europe A 30 Year ReviewMichael McDonnough100% (2)
- Sepsis Power Point Slide Presentation - The Guidelines - Implementation For The FutureDocument25 paginiSepsis Power Point Slide Presentation - The Guidelines - Implementation For The Futuremontie13Încă nu există evaluări
- Update in Medicine - Newcastle - 0Document3 paginiUpdate in Medicine - Newcastle - 0drrudy2591Încă nu există evaluări
- Jose Rizal's TravelsDocument45 paginiJose Rizal's TravelsStephanie Ann Marie DueñasÎncă nu există evaluări
- KPPIA PERDATIN EXPO 2018 Anesthesiology ConferenceDocument33 paginiKPPIA PERDATIN EXPO 2018 Anesthesiology ConferenceMutia RahmatiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Merchant of DeathDocument9 paginiMerchant of DeathHowardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pulse Oximetry: Principles and Limitations: ReviewsDocument8 paginiPulse Oximetry: Principles and Limitations: ReviewsDavid González GamboaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Head Injury Management of PediatricDocument22 paginiHead Injury Management of PediatricIrma KusumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Sales RepresentativeDocument3 paginiMedical Sales Representativeapi-77860217Încă nu există evaluări
- ITLS 8e Advanced Pre-Test - Annotated Key PDFDocument10 paginiITLS 8e Advanced Pre-Test - Annotated Key PDFJohn E. Ibrahim100% (1)
- MMDSTDocument2 paginiMMDSTBianca MolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On Current Principles and Practices of Pediatric NursingDocument18 paginiPresentation On Current Principles and Practices of Pediatric Nursingmalleshwari athramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - The Berlin Definition.Document8 paginiAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome - The Berlin Definition.drschutterÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPR and First Aid PowerpointDocument21 paginiCPR and First Aid PowerpointZawawiIbnuRosyidÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnatoFisio VestibularDocument17 paginiAnatoFisio VestibularRocío YáñezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S0022347616004376 MainDocument7 pagini1 s2.0 S0022347616004376 MainRatih KusumawardaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duty Report 10 August 2016 EditedDocument5 paginiDuty Report 10 August 2016 EditedbloodsphereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Concepts: Scapular Dyskinesis: W Ben Kibler, Aaron SciasciaDocument7 paginiCurrent Concepts: Scapular Dyskinesis: W Ben Kibler, Aaron SciasciatomxtchÎncă nu există evaluări
- DMFT Index and Dental Caries DetectionDocument56 paginiDMFT Index and Dental Caries DetectionCarolinePiskeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular EmbryologyDocument10 paginiCardiovascular EmbryologyChristianus LeonardÎncă nu există evaluări