Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Drug Cards 3
Încărcat de
p_dawgDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Drug Cards 3
Încărcat de
p_dawgDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
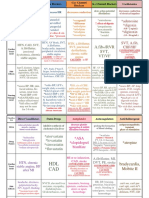
Classification acetaminophen Nonopioid analgesic (Pain medication for mild to moderate pain), antipyretic (prevent or reduce fever).
PO/RECT 325-650 mg q46hr prn, max 4g/day.
Indications Mild to moderate pain or fever, arthralgia (pain in a joint), dental pain, dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation or abdominal cramps), headache, myalgia (pain in a muscle), osteoarthritis. Adverse Effects drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, GI bleeding, seizure, renal failure, leukopenia, rash, hypersensitivity, cyanosis, jaundice, coma, death, CNS stimulation, delirium followed by vascular collapse.
Contraindications Hypersenstivity, intolerance to tartrazine, alcohol, table sugar, saccharin, depending on product.
Mechanism of Action May block pain impulses peripherally that occur in response to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis; does not possess anti-inflammatory properties; antipyretic action results from inhibition of prostaglandins in the CNS.
Nursing Considerations Assess health status and alcohol usage before administering. Assess for pain (type and location), use pain scale. Allergic reactions like rash, if it occurs product may have to discontinued. Decreasing output may indicate renal failure.
Classification Simvastin antilipemics
Indications Reduce the risk of death from CV To reduce total and LDL cholesterol in patients
Contraindications Allergy Hypoglycemia Some antacids Iodine containing contrast mediums Nursing Considerations Strict diet with restricted saturated fat Obtain liver function test results at start of therapy and periodically.
Mechanism of Action
Adverse Effects
Inhibits HMG-CoA an early Asthenia step in cholestrol biosynthesis. Headache Syspepsia Upper respiratory tract infection.
Classification Loop Diuretics furosemide (Lasix)
Indications Congestive Heart Failure Mitral Regurgitation Hypertension
Contraindications Steroids (may lead to hypokalemia) Digoxin (may lead to hypokalemia) Anuria Kidney failure
PO/IV
Mechanism of Action
Acts on loop of Henle to block chloride and sodium reabsorption (reduces fluid volume and removes fluid from the body) Help to decrease preload and central venous pressures
Adverse Effects
Dizziness N/V/D Tinnitus Headache Hypokalemia Hyperglycemia Muscle cramping Dehydration Urinary frequency
Nursing Considerations
Thorough cardiovascular assessment is required prior to administration Monitor potassium levels Monitor glucose levels Instruct client to decrease diet of sodium-rich foods Client should report a weight loss of more than 2 lb/week Serum electrolytes should be closely monitored r/t frequent changes in kidney function Tinnitus can be avoided by dividing oral doses Greater risk for hypotension and excessive diuresis
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 14 Fun Facts About Your Heart: Educational VersionDe la Everand14 Fun Facts About Your Heart: Educational VersionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharm ExamDocument293 paginiPharm ExamTrish HồÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsDe la EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug CardsDocument6 paginiDrug Cardsp_dawgÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideDe la EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 paginiClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Pharm Exam ReviewDocument13 paginiPharm Exam ReviewAshleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nclex-Pn Cram Sheet: General Test Information Normal Lab ValuesDocument2 paginiThe Nclex-Pn Cram Sheet: General Test Information Normal Lab Valuesroboat96Încă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular System Acronyms and MnemonicsDocument18 paginiCardiovascular System Acronyms and Mnemonicsdecsag06Încă nu există evaluări
- DRUGS Flash CardsDocument9 paginiDRUGS Flash Cardsdrp2011Încă nu există evaluări
- 1430 Drug CardsfinalDocument7 pagini1430 Drug CardsfinalLizSherman100% (1)
- Exam 3 Review Med SurgDocument18 paginiExam 3 Review Med SurgCarol ReidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocument9 paginiCongestive Heart Failure PDFSheryl Ann Mae BombalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunity 1Document6 paginiImmunity 1Tori RolandÎncă nu există evaluări
- 50 Most Commonly Prescribed MedicationsDocument2 pagini50 Most Commonly Prescribed MedicationsGloryJane67% (3)
- Nursing Pharmacology Drug Study GuideDocument15 paginiNursing Pharmacology Drug Study GuideChelsea SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug CardsDocument11 paginiDrug CardsLizShermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCLEXstudyguidevmDocument31 paginiNCLEXstudyguidevmAnonymous vqG0paWG100% (1)
- Medical Surgical NotesDocument18 paginiMedical Surgical NotesshalomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Drugs ChartDocument15 paginiCommon Drugs Chartforminsko100% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolyte DisturbancesDocument7 paginiFluid and Electrolyte DisturbancesMarie Antionette MondragonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy Test Q&ADocument5 paginiAnatomy Test Q&ARoze PetalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology-ATI 150 Drug Cards PDFDocument4 paginiPharmacology-ATI 150 Drug Cards PDFhollyÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-T-I Endocrine NotesDocument3 paginiA-T-I Endocrine NotesKelseyAnnBarnesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ati Live 2Document6 paginiAti Live 2VanessaMUellerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ams 11Document702 paginiAms 11CrazyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nero Drugs To KnowDocument14 paginiNero Drugs To KnowGina Giammalvo100% (2)
- Pharm RemediationDocument5 paginiPharm RemediationAudrey WatsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharm 2013Document13 paginiPharm 2013Shae Thomas100% (6)
- Lecture NotesDocument56 paginiLecture NotesLalaine April E. Ortiola100% (13)
- Cardiology & Ekgs: Archer Nclex ReviewDocument59 paginiCardiology & Ekgs: Archer Nclex Reviewdaphne farleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hematologic System2Document70 paginiHematologic System2Jesus Mario LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Nclex ExamDocument11 paginiNursing Nclex ExamDenisa Viviana MaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Pharmacology Perfusion Study GuideDocument9 paginiNursing Pharmacology Perfusion Study GuideChelsea SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nclex Disease: 4. Oral ContraceptivesDocument7 paginiNclex Disease: 4. Oral ContraceptivesMeijia SongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infection Control For NclexDocument9 paginiInfection Control For NclexMadora SamuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequently Asked ECG & X-Ray QuestionsDocument9 paginiFrequently Asked ECG & X-Ray Questionsزكريا عمرÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluids and Electrolytes: Irene L. Gardiner, MDDocument48 paginiFluids and Electrolytes: Irene L. Gardiner, MDGabriel Carlo FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology OutlineDocument11 paginiCardiovascular Pharmacology OutlineLhay de OcampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 50 Most Commonly Prescribed Medications PDFDocument2 pagini50 Most Commonly Prescribed Medications PDFChantelle Houston100% (1)
- CardionotesDocument5 paginiCardionotesNichole Coletta100% (1)
- Medsurg ATIDocument7 paginiMedsurg ATIloveoverpride12% (17)
- Nclex RN Sata CompilationDocument10 paginiNclex RN Sata CompilationJanna mae PatriarcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MedicalSurgical Nursing ReviewDocument86 paginiMedicalSurgical Nursing ReviewPopa D. SilviuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medsurge RationaleDocument8 paginiMedsurge RationaleRose Anne AbivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prof. Sandra M. Covarrubias - September 24, 2021: 5.2fluid & Electrolytes ImbalancesDocument5 paginiProf. Sandra M. Covarrubias - September 24, 2021: 5.2fluid & Electrolytes ImbalancesIvy VillalobosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bullets Nclex Terms 50Document48 paginiBullets Nclex Terms 50ShazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCLEX Study GuideDocument2 paginiNCLEX Study GuideLogin Nurse100% (1)
- NCLEX Practice QuestionsDocument12 paginiNCLEX Practice QuestionsDane WrightÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top Meds To Know For NCLEX - The NCLEX TutorDocument5 paginiTop Meds To Know For NCLEX - The NCLEX Tutorbaharada1979Încă nu există evaluări
- Med Surg: GI - Gastrointestinal: PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăMed Surg: GI - Gastrointestinal: PathophysiologyTori RolandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ati Medication Template CodeineDocument1 paginăAti Medication Template CodeineSharee HaywoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Significant Labs WorksheetDocument3 paginiCommon Significant Labs Worksheetapi-508954625100% (2)
- NCLEXDocument95 paginiNCLEXrikkapupuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine MedicationsDocument47 paginiEndocrine MedicationsAamir AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- N53 ATI PHARM 207637583-Ati-PharmacologyDocument26 paginiN53 ATI PHARM 207637583-Ati-PharmacologyWMWrian100% (3)
- Chapter 09: Photo Atlas of Drug Administration Test Bank: Multiple ChoiceDocument8 paginiChapter 09: Photo Atlas of Drug Administration Test Bank: Multiple ChoicePrettygirl716Încă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive Nclex Notes Easy To Read PDFDocument97 paginiComprehensive Nclex Notes Easy To Read PDFKenia GeorgesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Med CardsDocument26 paginiClinical Med CardsLila DanielsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ati Funds ReviewDocument11 paginiAti Funds Reviewmrsfelic08Încă nu există evaluări
- Crisis Intervention Ppt-1Document26 paginiCrisis Intervention Ppt-1p_dawg100% (3)
- Drug Cards 2Document6 paginiDrug Cards 2p_dawgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Teaching Plan - Wound Care and DressingDocument6 paginiHealth Teaching Plan - Wound Care and Dressingp_dawg100% (2)
- Surgical Client CareDocument58 paginiSurgical Client Carep_dawg100% (1)
- Drug CardsDocument16 paginiDrug Cardsp_dawg100% (7)
- Pharmacology Nursing ReviewDocument19 paginiPharmacology Nursing Reviewp_dawg50% (2)
- Annotated BibliographyDocument6 paginiAnnotated Bibliographyp_dawg100% (1)
- Generic Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: ActionDocument22 paginiGeneric Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: Actionp_dawg100% (14)
- Generic Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: ActionDocument22 paginiGeneric Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: Actionp_dawg100% (14)
- BloodDocument64 paginiBloodp_dawgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treatment of PainDocument5 paginiTreatment of PainMarrauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Progesterone (Crinone 8% Gel Vaginal)Document7 paginiProgesterone (Crinone 8% Gel Vaginal)ddandan_2Încă nu există evaluări
- Recipes (Pharmacology Prescriptions)Document6 paginiRecipes (Pharmacology Prescriptions)tianallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- KSSM SCIENCE Form 4 Chapter 10 10.1 StudentsDocument36 paginiKSSM SCIENCE Form 4 Chapter 10 10.1 StudentsTSEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cis 2018 PDFDocument3 paginiCis 2018 PDFTara Oliveros Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synthroid (Levothyroxine)Document2 paginiSynthroid (Levothyroxine)E100% (2)
- Pantosec 40mg HeteroDocument2 paginiPantosec 40mg Heteroopto careÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brimonidine TartrateDocument2 paginiBrimonidine TartrateAlain SoucotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Field Apraisal Report Final 11Document10 paginiField Apraisal Report Final 11Raja100% (1)
- Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Different Generic Paracetamol 500mg TabletDocument4 paginiQuantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Different Generic Paracetamol 500mg TabletEileen Eika Dela Cruz-LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Illegal DrugsDocument5 paginiIllegal DrugsJOCELYN VARGASÎncă nu există evaluări
- MaxminrptDocument38 paginiMaxminrptMeta JuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver TransplantDocument16 paginiLiver TransplantNephrology On-DemandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rosuvastatin A Review of Its Use in The.5Document18 paginiRosuvastatin A Review of Its Use in The.5urbanincultureÎncă nu există evaluări
- Format Rko Program 2020Document18 paginiFormat Rko Program 2020Anonymous ItXYBoaC1CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti TB DrugsDocument2 paginiAnti TB DrugsdhaineyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Week 7 Quiz NURS 6521N 26 Advanced PDFDocument10 paginiTest Week 7 Quiz NURS 6521N 26 Advanced PDFmary011danielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sandoz Sertraline: Sertraline Hydrochloride 25 MG, 50 MG and 100 MG CapsulesDocument1 paginăSandoz Sertraline: Sertraline Hydrochloride 25 MG, 50 MG and 100 MG Capsulesm3510Încă nu există evaluări
- Albendazole, Mebendazole and Praziquantel. Review of Non-Clinical Toxicity and PharmacokineticsDocument19 paginiAlbendazole, Mebendazole and Praziquantel. Review of Non-Clinical Toxicity and PharmacokineticsGianmarcoSugarAventureroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 AntihyperlipidemicsDocument6 pagini1 AntihyperlipidemicsChristian VillacruzesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fac Thrombolysis 2007Document36 paginiFac Thrombolysis 2007Tri Harjono0% (1)
- OsteoporosisDocument15 paginiOsteoporosisWil LesterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simvastatin Drug StudyDocument3 paginiSimvastatin Drug StudyCheezy BreadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baclofen (Drug Study)Document2 paginiBaclofen (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Unit 6 Drugs Acting On The CNS and PNSDocument43 paginiUnit 6 Drugs Acting On The CNS and PNSTherese Margarette SantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steroid Tapering and Supportive Treatment Guidance V1.0 PDFDocument1 paginăSteroid Tapering and Supportive Treatment Guidance V1.0 PDFAulia AzahrahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anasthesia in Obese PatientDocument4 paginiAnasthesia in Obese PatientWaNda GrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric IVFDocument37 paginiPediatric IVFLarr SumalpongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clobazam For The Treatment ofDocument3 paginiClobazam For The Treatment ofpronto4meÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluasi Keterseiaan Obat TRHP FormulariumDocument96 paginiEvaluasi Keterseiaan Obat TRHP FormulariumAsetianiÎncă nu există evaluări