Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chickenpox by Group 1b
Încărcat de
Venus MaglupayDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chickenpox by Group 1b
Încărcat de
Venus MaglupayDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
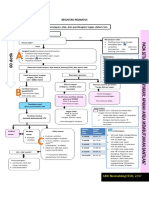
Is a common, acute, and highly contagiuos viral infection.
Can occur at any age but most common in children between 2-8 of age.
It is usually more severe in adults and very young infants than children.
It usually common during rainy season. Winter and spring in other countries.
Human (alpha) herpes virus 3 or also known as varicella-zoster virus.
And is often categorized with other common so-called viral exanthems (viral rashes):
Rubeola Rubella
Mumps Virus
5th disease (Parvovirus B13)
Roseola
Direct Contact Airborne droplets (coughing, sneezing, kissing, talking with an infected person)
Skin to skin (fluid from blisters and sores) Acute maternal infection in 1st or early 2nd semester of pregnancy Indirect Contact
> contact with articles of clothing and other items (fomites) exposed to fresh drainage from open sores.
Lasts from 13-17 days (2-3 wks) It is probably communicable from 1 day before lesions
erupt to 6 days after vesicle form Most contagious in early stages of skin lesions eruption.
Symptoms tend to appear 14 to 16 days after the initial
exposure but can occur anytime from 10 days to 21 days after contact with the virus. Two days of mild fever up to 102F (sometimes with cough and cold) General weakness and Headache
Nausea Anorexia And a rash (first sign of the disease)
* the rash of chicken pox develops in crops with raised red spots arriving first, progressing to blisters that burst, forming open sores, before crusting over. * blisters usually starts on the scalp, then the trunk, and finally the arms and the legs. Pruritus and pain on blisters that burst Sore throat Myalgia
Occurs worldwide and endemic in large cities Outbreaks are sporadic usually in areas with large
groups of susceptible children Affects all gender, races, and age groups. Second attacks are rare, probably 70% have the disease by the time they are 15 years of age.
Acute Pain Hyperthermia Altered Comfort Anxiety Imbalance Nutrition: Less than Body Requirement Impaired Skin Integrity Activity intolerance/Impaired Physical Mobility Ineffective Airway clearance/Impaired Gas Exchange/Ineffective Airway Clearance Disturbed Body Image Self-Care Deficit Risk For Infection Risk For Injury
^ aims to decrease symptoms and to prevent bacterial infection Acetaminophen (Tylenol) - to decrease fever and aches often associated with the initial presentation of the viral infection. Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or other anti histamine to control itching. Acyclovir (Zovirax) an antiviral that used to shorten the duration of the infection. To control the risk for secondary bacterial infection, nails are trimmed in young children.
Bacterial Infection related to an open pox sore. CNS: Cerebral Ataxia (with wobbliness, dizziness,
tremors, and altered speech). Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain with headache, seizures and decrease level of consciousness). Reyes Syndrome (fatal with combination of liver and brain disease). Patients taking cortisone-related medications are at risk patients with AIDS, SLE, Leukemia, and Cancer will have serious complications
Most people develop lifetime immunity to chickenpox
after the first occurrence and never experience it again. Shingles (zoster) vaccine. The vaccine requires 2 shots. 1st given at about 1 year of age. The second one (booster shot) is given at 4 years of age. If an older person has not had chickenpox, the shot may be given at any time. Vaccinations have been associated with a 90% decrease in the incidence of chickenpox and significantly lower complication rates in those who do develop the symptoms.
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus which
also causes shingle. Chickenpox is highly contagious and spreads by contact with someone with chickenpox. Fever, malaise, and a rash (red spot, blisters, and crusted lesions) are all symptoms and signs of chickenpox. Treatment for chickenpox is basically supportive. Although usually self-limited, chickenpox can also cause more serious complications, including pneumonia, encephalitis, and secondary skin infections. The chickenpox vaccine has resulted in a decrease in chickenpox incidence by 90% after two shots of zoster vaccine.
Sharmaine Coloma Tin Leyba
Cathreen Sause Michael cutedaw Zulueta
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- PPTDocument8 paginiPPTVenus MaglupayÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPTDocument8 paginiPPTVenus MaglupayÎncă nu există evaluări
- MVR Casepre XD (Repaired)Document65 paginiMVR Casepre XD (Repaired)Venus MaglupayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bites and Stings-10Document36 paginiBites and Stings-10Venus MaglupayÎncă nu există evaluări
- VenusDocument2 paginiVenusVenus MaglupayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insects and Spider Bites WordDocument4 paginiInsects and Spider Bites WordVenus MaglupayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latest Trend in Labor and DeliveryDocument6 paginiLatest Trend in Labor and DeliveryVenus MaglupayÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Publication 2022Document21 paginiPublication 2022zuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hoarseness-Causes and TreatmentsDocument33 paginiHoarseness-Causes and TreatmentsSatrio WisnugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar Pustaka Refrat Koas HoreDocument4 paginiDaftar Pustaka Refrat Koas HoreShinta Amalia KartikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Gestational DiabetesDocument2 paginiNCP - Gestational DiabetesKailah Rose CabantoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Snake Bite: Abhija Babuji. Crri. Department of Pediatrics. SmimsDocument76 paginiSnake Bite: Abhija Babuji. Crri. Department of Pediatrics. SmimsMeliani FranzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hospital Infections PDFDocument794 paginiHospital Infections PDFJOSEPH APPIAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pmls Finals ReviewerDocument72 paginiPmls Finals ReviewerIsiwjsbnwhshz Hshshzhbshs100% (1)
- ANC ModuleDocument103 paginiANC ModulePreeti ChouhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vasofix SafetyDocument6 paginiVasofix Safetydex99Încă nu există evaluări
- BIOLOGYDocument5 paginiBIOLOGYDiana NurulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Letting Go by Atul GawandeDocument18 paginiLetting Go by Atul Gawandetakoyakilovers100% (2)
- Sterile TechDocument85 paginiSterile TechBSN II - Tutor, Rel joshuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schizophrenia and Other Psychotic DisordersDocument85 paginiSchizophrenia and Other Psychotic DisordersEsraRamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 3 Acute TracheobronchitisDocument2 paginiWeek 3 Acute TracheobronchitisLu BeibeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- WeBSurg Winners 42 1Document129 paginiWeBSurg Winners 42 1Ana Adam100% (1)
- Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists: Fellowship ExaminationDocument11 paginiAustralian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists: Fellowship Examinationabazanhasan6705Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology Investigatory Project On Caffeine AddectionDocument5 paginiBiology Investigatory Project On Caffeine AddectionShivam SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- General DeclarationDocument1 paginăGeneral DeclarationPos SMB IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jcih 2007Document29 paginiJcih 2007Ankur BanerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Challenges and Uncertainties of Embolic Strokes of UndeterminedDocument4 paginiDiagnostic Challenges and Uncertainties of Embolic Strokes of UndeterminedDarliana Ospina DuarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Operating Procedure (Biochemistry - Diasys RESPONS - 910)Document17 paginiStandard Operating Procedure (Biochemistry - Diasys RESPONS - 910)Aniruddha ChatterjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resusitasi NeonatusDocument7 paginiResusitasi NeonatusIqbal Miftahul HudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Makalah Leigh Disease by Boys KDocument6 paginiMakalah Leigh Disease by Boys KAzizul HakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Caffeine? How Does Caffeine Work?Document16 paginiWhat Is Caffeine? How Does Caffeine Work?Agustinus SiswantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PrescriptionDocument2 paginiPrescriptionELvin LozandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Family Medicine Timeline 1Document6 paginiFamily Medicine Timeline 1api-259973261Încă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Manual - Part 2 - Drug Infusion Guidelines Revised - July 2015 - V7.11Document58 paginiClinical Manual - Part 2 - Drug Infusion Guidelines Revised - July 2015 - V7.11Jayaprakash KuppusamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burn Management by Tajuu Seid: Surgical WardDocument33 paginiBurn Management by Tajuu Seid: Surgical Wardelias adugnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016 Sep RECALLDocument49 pagini2016 Sep RECALLkyahuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 32 Oet Reading Summary 2.0-697-717Document21 pagini32 Oet Reading Summary 2.0-697-717Santhus100% (7)