Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 11 Cell Communication
Încărcat de
Cleopatra AhmedDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 11 Cell Communication
Încărcat de
Cleopatra AhmedDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Yousef Abdelmotaal Dr.
Nina Lavlinskaia AP Biology
Phosphorylation cascades involving a series of protein kinases are useful for cellular signal transduction because A) They are species specific B) They always lead to the same cellular response C) They amplify the original signal manyfold D) They counter the harmful effects of phosphatases E) The number of molecules used is small and fixed Answer : C
Binding of a signal molecule to which type of receptor leads directly to a change in the distribution of anions and or cations on opposite sides of the membrane? A) Receptor tyrosine kinase B) G protein-coupled receptor C) Phosphorylated receptor tyrosine kinase dimer D) Ligand-gated ion channel E) Intracellular receptor Answer : D
1 Gate closed Ions
2 Gate open
3 Gate closed
Signaling molecule (ligand)
Plasma Ligand-gated membrane ion channel receptor
Cellular response
The activation of receptor tryosine kinases is always characterized by A) Dimerization and phosphorylation B) IP3 binding C) Phosphorylation cascade D) GTP hydrolysis E) Channel protein shape change
Answer : A
Synaptic signaling between adjacent neurons is like hormone signaling in which of the following ways? A) It sends its signal molecules through the blood. B) It sends its signal molecules quite a distance. C) It requires calcium ions. D) It requires binding of a signaling molecule to a receptor. E) It persists over a long period. Answer : D
Which of the following is true of the mating signal transduction pathway in yeast? A) The pathway carries an electrical signal between mating cell types. B) Mating type a secretes a signal called a factor. C) The molecular details of the pathway in yeast and in animals are very different. D) Scientists think the pathway evolved long after multicellular creatures appeared on Earth. E) The signal reception, transduction, and response occur in the nucleus. Answer : B
What could happen to the target cells in an animal that lack receptors for local regulators? A) They could compensate by receiving nutrients via an a factor. B) They could develop normally in response to neurotransmitters instead. C) They could divide but never reach full size D) They would not be able to multiply in response to growth factors from nearby cells. E) Hormones would not be able to interact with target cells. Answer : D
From the perspective of the cell receiving the message, the three stages of cell signaling are A) The paracrine, local, and synaptic stages. B) Signal reception, signal transduction, and cellular response. C) Signal reception, nucleus disintegration, and new cell generation. D) The alpha, beta, and gamma stages. E) Signal reception, cellular response, and cell division. Answer : B
The process of transduction usually begins A) When the chemical signal is released from the alpha cell. B) When the signal molecule changes the receptor protein in some way. C) After the target cell divides. D) After the third stage of cell signaling is completed. E) When the hormone is released from the gland into the blood. Answer : B
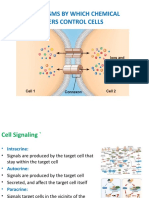
When a cell releases a signal molecule into the environment and a number of cells in the immediate vicinity respond, this type of signaling is A) Typical of hormones. B) Autocrine signaling. C) Paracrine signaling. D) Endocrine signaling. E) Synaptic signaling. Answer : C
A small molecule that specifically binds to another molecule, usually a larger one A) Is called a signal transducer. B) Is called a ligand. C) Is called a polymer. D) Seldom is involved in hormonal signaling. E) Usually terminates a signal reception.
Answer : B
Which of the following is (are) true of ligand-gated ion channels? A) They are important in the nervous system. B) They lead to changes in sodium and calcium concentrations in cells. C) They open or close in response to a chemical signal. D) Only A and B are true. E) A, B, and C are true. Answer : E
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- C8e 11 Test BankDocument11 paginiC8e 11 Test Bank123456789123456789hiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transduction Mechanisms in Cellular Signaling: Cell Signaling CollectionDe la EverandTransduction Mechanisms in Cellular Signaling: Cell Signaling CollectionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Life Sciences Cell CommunicationDocument21 paginiLife Sciences Cell CommunicationSadaf JavedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warrior Final ReviewDocument100 paginiWarrior Final ReviewKeVin Dean LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Lec 7Document5 paginiBio Lec 7Rowland OmorakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect. 10Document27 paginiLect. 10أحمدشريفÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell CommunicationDocument24 paginiCell Communicationanbuselvanselvan59Încă nu există evaluări
- CelltoCellComMC[1]Document3 paginiCelltoCellComMC[1]andersonmack047Încă nu există evaluări
- Structure and Function of The CellDocument39 paginiStructure and Function of The Cellglen_walker1687Încă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 7Document2 paginiQuiz 7JÎncă nu există evaluări
- SIGNALING QUIZZES: CELL SIGNALING PATHWAYSDocument8 paginiSIGNALING QUIZZES: CELL SIGNALING PATHWAYSignatiusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview: Cellular Messaging: © 2011 Pearson Education, IncDocument69 paginiOverview: Cellular Messaging: © 2011 Pearson Education, IncbbyiknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio 2 Study GuideDocument17 paginiBio 2 Study GuideJahnik KurukulasuriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacterial GeneticsDocument55 paginiBacterial GeneticsAme Grace DubeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology MadrasDocument11 paginiMolecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madrasapi-256504985Încă nu există evaluări
- BIO 345 S18 Chapter 6 S19 (Flipped) S20 - True of False Answers Included - S21Document94 paginiBIO 345 S18 Chapter 6 S19 (Flipped) S20 - True of False Answers Included - S21gaelle tannousÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer For First Quarter GENBIO1Document57 paginiReviewer For First Quarter GENBIO1Rshyron Crain GrospeÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP BIO: Cell Communication & Cell CycleDocument63 paginiAP BIO: Cell Communication & Cell Cyclemaitha91Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Signaling MechanismsDocument12 paginiCell Signaling Mechanismsmangesh1991Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions ManualDocument9 paginiBiology The Dynamic Science 3rd Edition Russell Solutions Manualfleakingpoutoz1k7v100% (29)
- Biology The Dynamic Science 3Rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument30 paginiBiology The Dynamic Science 3Rd Edition Russell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFCassieYangiosx100% (11)
- Intercellular Communication: Chemical Messengers and ReceptorsDocument30 paginiIntercellular Communication: Chemical Messengers and ReceptorsO'Brien AlfredÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Biotech (MCQS)Document22 paginiBasics of Biotech (MCQS)Hassaan Ahmad KaifiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch07 Test File-Cell Signaling and CommunicationDocument39 paginiCh07 Test File-Cell Signaling and CommunicationDollar'sCornerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Cell SignalingDocument35 paginiPlant Cell SignalingAmelia Sukma Wati325Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Signaling: Signaling Molecules and Their ReceptorsDocument49 paginiCell Signaling: Signaling Molecules and Their ReceptorsDeepanshu rawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Biology Chapter 11 Cell CommunicationDocument78 paginiAP Biology Chapter 11 Cell CommunicationRavider JadejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18 - Flow Cytometry and Introduction To Molecular PathologyDocument11 pagini18 - Flow Cytometry and Introduction To Molecular Pathologyhamadadodo7Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Signaling - ImpDocument11 paginiCell Signaling - Impkrishnarajagopal2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Bio Exam 2 Lecure QuizzesDocument42 paginiCell Bio Exam 2 Lecure QuizzesHafiza Dia Islam100% (4)
- Cell Communication and Signal TransductionDocument34 paginiCell Communication and Signal TransductionArina SafiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Review Session: Bio 99-Luo/Glabe Nathan Farrokhian Mai-Anh Vuong-DacDocument89 paginiFinal Review Session: Bio 99-Luo/Glabe Nathan Farrokhian Mai-Anh Vuong-Dacnate898989Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Signaling Problem SetDocument7 paginiCell Signaling Problem SetJohn WangÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 11 PPT Cell Communication 1Document77 paginiCH 11 PPT Cell Communication 1api-270681964Încă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Animal Physiology Canadian 3rd Edition Moyes Test BankDocument18 paginiPrinciples of Animal Physiology Canadian 3rd Edition Moyes Test Banktroyfernandezmpybjrasti100% (28)
- Recombinant DNA MCQDocument6 paginiRecombinant DNA MCQChaze WaldenÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSC 251 t2 QuestionsDocument38 paginiBSC 251 t2 QuestionssarahreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synaptic Signalling PDFDocument8 paginiSynaptic Signalling PDFHyunji KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multicellular Organisms Have BIG Communication Problems: Hey You - Divide Now!!! Oi! We Need Some Glucose!Document73 paginiMulticellular Organisms Have BIG Communication Problems: Hey You - Divide Now!!! Oi! We Need Some Glucose!kevin andrewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Signalling 1Document26 paginiCell Signalling 1Wubalem DestaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Your Results For "Matching Quiz"Document8 paginiYour Results For "Matching Quiz"Sebastian SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbial Genetics: DNA, Mutations, RecombinationDocument47 paginiMicrobial Genetics: DNA, Mutations, Recombinationminy1229Încă nu există evaluări
- Neurotransmitter Cell CommunicationDocument25 paginiNeurotransmitter Cell CommunicationOtnil DÎncă nu există evaluări
- ch9 SlidesDocument18 paginich9 Slidesapi-197124028Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Communication CH 11Document43 paginiCell Communication CH 11suryani yaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro 332Document7 paginiMicro 332Angelica VillarosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SampleQuiz-Ch11 18 PDFDocument2 paginiSampleQuiz-Ch11 18 PDFNguyễn Đức ÝÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Human Physiology 5Th Edition Stanfield Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument47 paginiPrinciples of Human Physiology 5Th Edition Stanfield Test Bank Full Chapter PDFotisphoebeajn100% (7)
- Principles of Human Physiology 5th Edition Stanfield Test BankDocument26 paginiPrinciples of Human Physiology 5th Edition Stanfield Test Banksiennaadelaideatknmp100% (26)
- Gene Transfer TechniquesDocument36 paginiGene Transfer TechniquesDrMumtaz F MusaliarÎncă nu există evaluări
- BioComp Exam 2014Document10 paginiBioComp Exam 2014martynapetÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEDBIO Base KROK-1 StudentsDocument54 paginiMEDBIO Base KROK-1 StudentsJack frimpongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Communication SignalsDocument27 paginiCell Communication Signalsbostonsox49Încă nu există evaluări
- Bacterial RecombinationDocument31 paginiBacterial Recombinationpnamdev018Încă nu există evaluări
- BS 161 QuizletDocument25 paginiBS 161 QuizletKaushik SridasyamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Communication Class Notes Presentation Topics 4.1 To 4.2 2020Document48 paginiCell Communication Class Notes Presentation Topics 4.1 To 4.2 2020Lavinia DonaldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eukaryotes: Base of Questions of Krok-1 Exam Medical BiologyDocument54 paginiEukaryotes: Base of Questions of Krok-1 Exam Medical BiologyKarla IngaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacterial Genetics: DR - Mohiruddin SK Senior Resident Dept of MicrobiologyDocument49 paginiBacterial Genetics: DR - Mohiruddin SK Senior Resident Dept of MicrobiologyAbcdefg HijklÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReceptorsDocument31 paginiReceptorsBareera NudratÎncă nu există evaluări
- Day 23 physics class notes and homeworkDocument3 paginiDay 23 physics class notes and homeworkCleopatra AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Biology Midterm Study GuideDocument3 paginiAP Biology Midterm Study GuideCleopatra AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lewis Structure of SO2Document1 paginăLewis Structure of SO2Cleopatra AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 26Document1 paginăWorksheet 26Cleopatra AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 VocabualryDocument3 paginiChapter 1 VocabualryCleopatra AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 15 Vocabulary APUSHDocument1 paginăChapter 15 Vocabulary APUSHCleopatra AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- VectorsDocument4 paginiVectorsCleopatra AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel GCSE Biology Specification (2016) PDFDocument60 paginiEdexcel GCSE Biology Specification (2016) PDFastargroup100% (1)
- Unnati Garg (ICH Guidelines)Document66 paginiUnnati Garg (ICH Guidelines)Unnati GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELI LILY Company Case StudyDocument15 paginiELI LILY Company Case Studykomaltagra100% (1)
- Biology Lab 1: Bioinformatic Report AnalysisDocument5 paginiBiology Lab 1: Bioinformatic Report AnalysisKasia DrewniakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 21 Reading GuideDocument3 paginiChapter 21 Reading GuideAnonymous RVfQZkvjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gbio 121 Week 11 19 by KuyajovertDocument11 paginiGbio 121 Week 11 19 by KuyajovertAnonymous DZY4MvzkuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacteria Cell StructureDocument4 paginiBacteria Cell StructureReyhan Audian Dwi PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetic Lab 2 CompiledDocument8 paginiGenetic Lab 2 CompiledNurul Iman Che AwangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceDocument36 paginiNon-Mendelian Patterns of InheritanceRhoda Mae CubillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disifin Evolving Importance in Health Okom Nkili F.C OfodileDocument12 paginiDisifin Evolving Importance in Health Okom Nkili F.C OfodilenassmargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Midterm Study GuideDocument5 paginiBiology Midterm Study GuidesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti-Neurocan Antibody (2Q174) Ab26003: 2 ReferencesDocument2 paginiAnti-Neurocan Antibody (2Q174) Ab26003: 2 Referenceskeven319hk4304Încă nu există evaluări
- Engelke1990 PDFDocument5 paginiEngelke1990 PDFDiego GarzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetic Diversity of Indonesian Cattle Breeds Based On Microsatellite MarkersDocument10 paginiGenetic Diversity of Indonesian Cattle Breeds Based On Microsatellite MarkersErik Angga SaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro History of BiochemDocument13 paginiIntro History of BiochemDan Christian BlanceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Cycle ModuleDocument28 paginiCell Cycle ModuleDuaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- CB Catalog 4thedition B PDFDocument192 paginiCB Catalog 4thedition B PDFDifermoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recombinant VaccinesDocument22 paginiRecombinant VaccinesjugesmangangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Importance of Herbs in MedicineDocument5 paginiImportance of Herbs in MedicineBrilian JelitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology 12 PaperDocument2 paginiBiology 12 PaperRakesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IAL - Biology - SB2 - Mark Scheme - 8BDocument3 paginiIAL - Biology - SB2 - Mark Scheme - 8BsalmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5 & 6 Mendel 'S Law LectureDocument18 paginiLecture 5 & 6 Mendel 'S Law Lectureakshay kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel IAL BIO October 2020 Mark SchemeDocument35 paginiEdexcel IAL BIO October 2020 Mark SchemeMeenakshie Chaudrie50% (4)
- PADER TrainingDocument20 paginiPADER Trainingisha jain100% (1)
- Chapter 5Document26 paginiChapter 5Kristine BaguinatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Theory-SongDocument2 paginiCell Theory-Songwdq5500Încă nu există evaluări
- 10 14Document12 pagini10 14Manoj KashyapÎncă nu există evaluări
- GC UNIVERSITY'S BS HONORS IN BOTANY SCHEMEDocument33 paginiGC UNIVERSITY'S BS HONORS IN BOTANY SCHEMEMuhammad Ahmad RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B2.5 InheritanceDocument35 paginiExampro GCSE Biology: B2.5 InheritanceMeera ParaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Andrade Martínez Et Al 2022 Computational Tools For The Analysis of Uncultivated Phage GenomesDocument26 paginiAndrade Martínez Et Al 2022 Computational Tools For The Analysis of Uncultivated Phage GenomesHuGo Castelán SÎncă nu există evaluări








![CelltoCellComMC[1]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/723475609/149x198/2c466f116e/1713246902?v=1)