Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Power Point Presentation 1 Yr 10 SP
Încărcat de
api-206179362Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Power Point Presentation 1 Yr 10 SP
Încărcat de
api-206179362Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Understanding fitness and methods of training to improve sports performance
Physical fitness has been described as a capability of the heart, blood vessels, lungs and muscles to function at optimal efficiency.
Fitness is a state of well being that is made up of several components. Each of these components is achieved through the performance of different activities
Strength the capacity of a muscle to exert a force against a resistance. Muscular Endurance Is the capacity of a muscle to exert a force repeatedly over a period of time or to hold a fixed or static contraction Flexibility Static - The range of motion about a joint. Dynamic - the opposition or resistance of a joint to movement Agility Ability to change body position quickly and to control body movement
Speed How quickly you can perform a movement or cover a certain distance Cardiovascular Endurance Aerobic the capacity of the heart, blood vessels and lungs to deliver nutrients and oxygen and to remove wastes during exercise of a prolonged nature Anaerobic the capacity of the muscles to sustain high intensity activity or exercise for short periods of time, during which the supply of oxygen to the working muscles is insufficient.
Continuous Interval Circuit Resistance
Continuous This type of training requires the athlete to work continuously at an activity over a period of time of at least twenty minutes. During this time the body should be working aerobically. This means that the intensity of the work is lower than in other methods of training. Continuous training helps to develop general endurance which forms the foundation of all fitness. It helps to prepare the body so that it can cope with the increased intensity and effort of other training methods. It includes training activities like running, cycling, swimming and aerobics
Interval
During interval training the athlete alternates work periods with rest periods. The work is more intense than in continuous training and the work period is much shorter. Interval training is used to develop anaerobic fitness but can also help develop aerobic fitness. There are 3 main variables in interval training: Duration of work and rest Intensity of work Number of repetitions. These variables change so that the type of interval training is appropriate to the particular activity for which the athlete is training eg the anaerobic requirements of a field hockey player and a 10 000 m runner are different, although both athletes use interval training
Circuit
Circuit training is an extremely versatile form of training. It can be adapted to develop aerobic power, agility, flexibility, strength and skills. Circuits can be low impact or extremely intense so that not only can the type of exercise be varied but also the level at which people work. It involves at least 8 activities or stations. The athlete performs each of the exercises in the circuit to complete one lap. When you reach a station there are two ways of deciding how many of each exercise will be done:
A fixed number depending on their level
eg sit ups 20, 30 or 40 ! As many repetitions as possible in a set amount of time, trying to improve each time the complete the circuit
Resistance Resistance training involves the athlete working against a resistance or force in order to develop muscular strength, muscular power, muscular endurance and aerobic power. The resistance used can be the athletes own body weight or the types of weights found in a gym. You would use the overload principle in resistance training. Strength training heavy weights and few reps, 3 sets, 2-3 mins rest, increase kgs when you can complete comfortably, 3 days a week, day rest in between.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5jJoOLVE6vc
Progression As the level of fitness improves, the demands put on that person in training are increase to keep challenging them physically. It can be done by increasing the intensity and or the duration of the exercise. Week 1 :3 x 20 min runs Week 2 : 3 x 30 min runs
Overload Overload occurs when an athlete exercises at a level above that which she/he can normally work at comfortably. Eg Increase the load Increase the number of repitions Increase the number of sets Increase the speed of the work out Reduce the rest period
Specificity Make it specific to your sport Frequency How often? The average level of fitness can be maintained by training 3 to 4 times a week Intensity How hard you work during exercise. Eg,Percentage of maximum effort Duration The length of the training programme will depend type of exercise and the level of fitness, eg aerobic 20/60 min. The stage of the season off season , pres season , in season.
Remember
:- FITT
Frequency Intensity Time Type
Aerobic fitness 70% -80 % Through continuous, interval, circuit training Anaerobic 90 100 % Through, short/medium interval training Strength and power not measured Through resistance, circuit and plyometric training
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Musculoskeletal Disorders Sourcebook, First EditionDe la EverandMusculoskeletal Disorders Sourcebook, First EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report Princ Group 9 1Document32 paginiReport Princ Group 9 1raian claudeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Girls and Sport: Female Athlete Triad SimplifiedDe la EverandGirls and Sport: Female Athlete Triad SimplifiedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training Methods To Improve SpeedDocument5 paginiTraining Methods To Improve SpeedRizal Kundin100% (1)
- Factors A Ecting Performance: 400m RunDocument7 paginiFactors A Ecting Performance: 400m RunDharen MohanarajahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vrublevsky Strength Development in The 400mHDocument3 paginiVrublevsky Strength Development in The 400mHddtaxe100% (1)
- Fitness - ACE Fitness Center - Circuit TrainingDocument2 paginiFitness - ACE Fitness Center - Circuit TrainingdiegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Suslov How Much Strength Is Needed in Endurance EventsDocument6 paginiSuslov How Much Strength Is Needed in Endurance EventsAltec AlsingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerobic High-Intensity Intervals Improve 07Document7 paginiAerobic High-Intensity Intervals Improve 07Lindsay OrtizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tech - Speed Strength Endurance in 400Document7 paginiTech - Speed Strength Endurance in 400jeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sprint Programming: Long To Short Emphasis in Fall TrainingDocument31 paginiSprint Programming: Long To Short Emphasis in Fall TrainingArinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Warm-Up Exercises Instead of Traditional RoutinesDocument2 paginiDynamic Warm-Up Exercises Instead of Traditional RoutinespodamakriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Junior 400m SprintDocument8 paginiJunior 400m SprintLeehirzan LeehirzanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Szewinska A Years Training Program For Women Sprinters PDFDocument5 paginiSzewinska A Years Training Program For Women Sprinters PDFZachary LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bompa S Periodization For Sports TrainingDocument22 paginiBompa S Periodization For Sports TrainingNicolae Dragos-AlexandruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength EnduranceDocument27 paginiStrength EnduranceAdi HidayatÎncă nu există evaluări
- PowerDocument30 paginiPowerAndy RomeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Velocity and Stride Parameters in The 400 MetDocument8 paginiVelocity and Stride Parameters in The 400 MetjeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brian Mackenzie. - 400m TestingDocument2 paginiBrian Mackenzie. - 400m TestingIvanDamjanovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Energy Systems Primer 2011Document59 paginiAn Energy Systems Primer 2011Martin BeastallÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Fitness Test Protocol AND Functional Movement Screen Assessment (Development of A Baseline Data Norms)Document36 paginiPhysical Fitness Test Protocol AND Functional Movement Screen Assessment (Development of A Baseline Data Norms)Gemma AbadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interval TrainningDocument4 paginiInterval TrainningjimurgaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength For FootballDocument141 paginiStrength For Footballkc016Încă nu există evaluări
- The Effects of Eccentric Versus Concentric Resistance Training On Muscle Strength and Mass in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review With Meta-AnalysisDocument14 paginiThe Effects of Eccentric Versus Concentric Resistance Training On Muscle Strength and Mass in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review With Meta-AnalysisPerico PalotesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interval Training For The Fitness Professional.21Document6 paginiInterval Training For The Fitness Professional.21José Carlos Santos100% (1)
- 10.1007 S004210050402 Changes in Performance Muscle Metabolites Enzymes and Fibre Types After Short Sprint TrainingDocument7 pagini10.1007 S004210050402 Changes in Performance Muscle Metabolites Enzymes and Fibre Types After Short Sprint TrainingNaDer HamedChamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Season PlanDocument19 paginiSeason Planapi-403982187Încă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Aerobic Exercise (I)Document45 paginiPrinciples of Aerobic Exercise (I)Martha ChaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arm PlyometricsDocument5 paginiArm PlyometricsGhita Marius GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Athletics Project Science of Living ProjectDocument9 paginiAthletics Project Science of Living ProjectAnonymous 8HVq0DÎncă nu există evaluări
- Core Strength A New Model For Injury Prediction and PreventionDocument8 paginiCore Strength A New Model For Injury Prediction and PreventionYoh ChenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Changes in The STP Width, Step Length, and Step Frequency of The World's Top Sprinters During The 100 MetersDocument5 paginiChanges in The STP Width, Step Length, and Step Frequency of The World's Top Sprinters During The 100 MetersMarthinus Schultz100% (1)
- FIRST Training PacesDocument10 paginiFIRST Training PacesAndi YoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 100 Metres Training ProgramDocument8 pagini100 Metres Training ProgramNurulAdyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plyometric Training: Sumbul Ansari Ph.D. Scholar CPRS, JmiDocument27 paginiPlyometric Training: Sumbul Ansari Ph.D. Scholar CPRS, JmiIshant Kr AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerobic Conditioning IntensityDocument2 paginiAerobic Conditioning IntensityTabitha HandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinesiology 8 - PJJ Assgnment Movement AnalysisDocument64 paginiKinesiology 8 - PJJ Assgnment Movement AnalysispaegyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength & Conditioning Program Athlete HandbookDocument17 paginiStrength & Conditioning Program Athlete Handbookscorpion999Încă nu există evaluări
- Clinic Notes Arbogast2 PDFDocument6 paginiClinic Notes Arbogast2 PDFSanjeev KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mid Distance Ktps and DrillsDocument44 paginiMid Distance Ktps and Drillsapi-453393868Încă nu există evaluări
- Insanity - Dig Deeper!: Week 1 6-Jan 7-Jan 8-JanDocument3 paginiInsanity - Dig Deeper!: Week 1 6-Jan 7-Jan 8-JanCarlos RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Plyometrics - Converting Strength To PowerDocument4 paginiIntroduction To Plyometrics - Converting Strength To Powerapi-286237903Încă nu există evaluări
- Optimization of Performance Through Kinematic Analysis of The Different Phases of The 100 MDocument10 paginiOptimization of Performance Through Kinematic Analysis of The Different Phases of The 100 MChristine BrooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy System Breakdown For Hurdle EventsDocument1 paginăEnergy System Breakdown For Hurdle EventsDemetrio FrattarelliÎncă nu există evaluări
- High-Intensity Interval Training, Solutions To The Programming Puzzle: Part I: Cardiopulmonary EmphasisDocument29 paginiHigh-Intensity Interval Training, Solutions To The Programming Puzzle: Part I: Cardiopulmonary EmphasisОстојић СтрахињаÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technique and Speed Development For Running: What Contributes To Speed?Document4 paginiTechnique and Speed Development For Running: What Contributes To Speed?dambugÎncă nu există evaluări
- P Rehab For RunnersDocument4 paginiP Rehab For RunnerseretriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hamstring Rehabilitation in Elite Track and FieldDocument13 paginiHamstring Rehabilitation in Elite Track and FieldBarry DoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tmhs Speed Power Camp 2019Document1 paginăTmhs Speed Power Camp 2019api-330484228Încă nu există evaluări
- Locatelli The Importance of Anaerobic Glycolysis and Stiffness PDFDocument7 paginiLocatelli The Importance of Anaerobic Glycolysis and Stiffness PDFAltec AlsingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short-Term High Intensity Plyometric Training Program Improves Strength, Power and Agility in Male Soccer PlayersDocument10 paginiShort-Term High Intensity Plyometric Training Program Improves Strength, Power and Agility in Male Soccer PlayersChristine ViolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit Training HandoutsDocument4 paginiCircuit Training HandoutsGwyneth Bunda100% (1)
- E Arcelli Energy Production in The 800 MTDocument8 paginiE Arcelli Energy Production in The 800 MTDemetrio FrattarelliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod 01 Asca Level 02Document4 paginiMod 01 Asca Level 02Mayank Singh gariaÎncă nu există evaluări
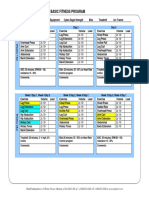
- EAGLE BasicFitnessProgramDocument2 paginiEAGLE BasicFitnessProgramzidanejason8Încă nu există evaluări
- Ozolin The Tech of The Sprint StartDocument5 paginiOzolin The Tech of The Sprint StartZachary LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Tension Hamstring TrainingDocument4 paginiHigh Tension Hamstring TrainingHüseyin KezerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Components of Energy ExpenditureDocument26 paginiThree Components of Energy ExpenditureDustin HarrisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Laws of Speed Development PDFDocument2 pagini3 Laws of Speed Development PDFtheghostinthepostÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fitness For Sport: Trevor DunneDocument36 paginiFitness For Sport: Trevor DunneHezron DamasoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hope 1Document17 paginiHope 1janssen.azagra.basalloteÎncă nu există evaluări
- QB High Intensity Weight Training 2006Document1 paginăQB High Intensity Weight Training 2006Алекс МалышевÎncă nu există evaluări
- Andrzejewski Et Al. (2012)Document25 paginiAndrzejewski Et Al. (2012)Callum BromleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Ultimate Badminton AthleteDocument48 paginiThe Ultimate Badminton AthleteSubbu PrashantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combined Strength and Endurance Training in Competitive SwimmersDocument10 paginiCombined Strength and Endurance Training in Competitive SwimmersSerban ValentinÎncă nu există evaluări
- SuperSlow Workout 3 Days Per WeekDocument1 paginăSuperSlow Workout 3 Days Per WeekMC100% (1)
- Establishing Strength Training Program FootballDocument6 paginiEstablishing Strength Training Program Footballzaid786786Încă nu există evaluări
- Intake of Carbohydrate-Protein Supplements by Recreational Users at Gym Body Composition ImprovedDocument9 paginiIntake of Carbohydrate-Protein Supplements by Recreational Users at Gym Body Composition ImprovedJuan Camilo MendietaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fitness RX For Women - August 2015 PDFDocument104 paginiFitness RX For Women - August 2015 PDFLucia Carolina Velasco Lopez100% (2)
- 20 Effective Tips To Lose Belly FatDocument17 pagini20 Effective Tips To Lose Belly FatAmer Gonzales100% (1)
- Cheer Dancing and CheerleadingDocument27 paginiCheer Dancing and CheerleadingCj CadondoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUPERHERO Suspension Training ManualDocument11 paginiSUPERHERO Suspension Training ManualCaleb Leadingham100% (5)
- Teenage Bodybuilding Guide - How To Workout, Eat & Grow - Muscle & StrengthDocument2 paginiTeenage Bodybuilding Guide - How To Workout, Eat & Grow - Muscle & StrengthJamie dobbinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wallis - Application and Assessment-2Document2 paginiWallis - Application and Assessment-2Martha Glorie Manalo WallisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Day StrengthDocument8 pagini3 Day Strengthmark100% (5)
- Routine PDFDocument3 paginiRoutine PDFBlack Sonichu NexionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Big Benchas: 3 Week Kickstart Bench ProgramDocument4 paginiBig Benchas: 3 Week Kickstart Bench ProgramDen KongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effective Methods of Grip Strength DevelopmentDocument10 paginiEffective Methods of Grip Strength DevelopmentDarnell GÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Day Male FinalDocument5 pagini4 Day Male FinalHey ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workout: 6-Week Women'S Full Body Strength and Conditioning WorkoutDocument1 paginăWorkout: 6-Week Women'S Full Body Strength and Conditioning Workoutmp3 RcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Sir AliDocument16 paginiJurnal Sir AliAhmad Sabarani Archery AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- U18 Rugby Specific Pre in Season ProgramDocument48 paginiU18 Rugby Specific Pre in Season Programde100% (1)
- Candito 6 Week ProgramDocument16 paginiCandito 6 Week ProgramSyed ArbabÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Belly Fat Diet John ChathamDocument92 paginiThe Belly Fat Diet John ChathamGurpreet Kaur100% (3)
- 3 - Day - Male - Final - 1 - OGDocument5 pagini3 - Day - Male - Final - 1 - OGuser240Încă nu există evaluări
- The Creatine ReportDocument31 paginiThe Creatine ReportBlackArmy88Încă nu există evaluări
- All About Program Design - A Ste - Tim Henriques (Croker2016)Document133 paginiAll About Program Design - A Ste - Tim Henriques (Croker2016)Leandro Aisa100% (1)
- Unlock Your Macro Types - Training PlansDocument21 paginiUnlock Your Macro Types - Training Plansrfzfwn8nf4Încă nu există evaluări
- 8 Week Blitz Duathlon Training Plan PDFDocument4 pagini8 Week Blitz Duathlon Training Plan PDFMatthew PettusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of Fitness Trainer.Document20 paginiRole of Fitness Trainer.Ajay Pal NattÎncă nu există evaluări