Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Care of The Newborn at Birth
Încărcat de
pppamm0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
344 vizualizări15 paginiBirth registration is important to avoid babies being handed to the wrong parents. Footprinting should be taken with care because it will be part of the child's permanent record. Infants must be screened for phenylketonuria and hyperthyroidism.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Care of the Newborn at Birth
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentBirth registration is important to avoid babies being handed to the wrong parents. Footprinting should be taken with care because it will be part of the child's permanent record. Infants must be screened for phenylketonuria and hyperthyroidism.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
344 vizualizări15 paginiCare of The Newborn at Birth
Încărcat de
pppammBirth registration is important to avoid babies being handed to the wrong parents. Footprinting should be taken with care because it will be part of the child's permanent record. Infants must be screened for phenylketonuria and hyperthyroidism.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 15
Care of the Newborn at Birth
Newborn Identification and
Registration
• It is important to avoid the babies
being handed to the wrong parents
• Also to avoid kidnapping of babies
Identification Band
• It is a plastic bracelet with
permanent locks that require cutting
to be removed
• It has the same number as the
mother’s hospital number, the
mother’s full name, date & time of
infant’s birth
• 2 bands should always be used
Birth Registration
• The physician or nurse-midwife who
delivered the infant must be certain
that a birth registration is filed to the
corresponding agency where the
infant was born
• It contains the correct infant’s name,
mother’s name, father’s name,
birthdate and place of birth.
Footprinting
• It should be taken with care because
it will be part of the child’s
permanent record
Birth Record Documentation
• Be certain that the birth record lists
the ff:
– Time of birth
– Time the infant breathed
– Whether respiration is spontaneous or
aided
– Apgar score at 1 and 5 minutes of life
– Whether eye prophylaxis was given
– Whether vitamin K was administered
Birth Record Documentation
– General condition of the infant
– Number of vessels in the umbilical cord
– Whether cultures were taken
– Whether the infant voided and passed
a stool
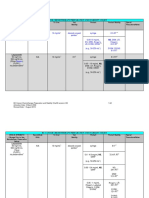
Apgar Scale
Sign 0 1 2
Heart rate Absent Slow (<100) >100
Respiratory effort Absent Slow, irregular, Good, strong cry
weak cry
Muscle tone Flaccid Some flexion of Well flexed
extremities
Reflex Irritability:
Response to No response Grimace Cough or sneeze
catheter in nostril
lap to sole of foot No response Grimace Cry and withdrawal
of foot
Color Blue, pale Body normal Normal skin
pigment, coloring
extremities blue
Initial Feeding
• May give breastfeeding immediately
after birth
• If formula feeding will be done, it
would be after 2-4 hours after birth
• Fed as often as every 2 hours
Metabolic Screening Test
• Every infant must be screened for
phenylketonuria (a disease of
defective protein metabolism) and
hyperthyroidism
• This is a simple blood test in which 3
drops of blood from the heel are
dropped onto a special filter paper
• The baby should have received milk
before the test for it to be accurate
Hepatitis B Vaccination
• All newborns received a 1st
vaccination against hepatitis B within
12 hours after birth
• Second dose: 1 month
• Third dose: 6 months
Vitamin K Administration
• Newborns are at risk for bleeding
disorders during the 1st week of life
because their gastrointestinal tract is
sterile at birth and unable to produce
Vitamin K, necessary for blood
coagulation
• Vitamin K stimulates the liver to
produce factors II, VII, IX and X
• A single dose of 0.5 to 1.0 mg of
Vitamin K is administered
intramuscularly within the first hour
of life
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Nursing ScheduleDocument1 paginăNursing SchedulepppammÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Defense MechanismsDocument2 paginiDefense MechanismspppammÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Bag Technique ChecklistDocument3 paginiBag Technique Checklistpppamm100% (9)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Signs and Symptoms of PregnancyDocument6 paginiSigns and Symptoms of Pregnancypppamm100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Pregnancy Discomforts and InterventionsDocument37 paginiPregnancy Discomforts and Interventionspppamm100% (3)
- InfluenzaDocument19 paginiInfluenzapppammÎncă nu există evaluări
- ImmunizationDocument12 paginiImmunizationpppammÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Supplementary Feeding For InfantsDocument50 paginiSupplementary Feeding For Infantspppamm0% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Case Study - DR EldaDocument3 paginiCase Study - DR EldaShashi KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Wmh-Cidi Papi Interview: Screening Section (SC)Document9 paginiWmh-Cidi Papi Interview: Screening Section (SC)Monia AzevedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Approved Moh Guidelines On Submission of Documentation For Registration of Human Pharmaceutical Products RwandaDocument436 paginiApproved Moh Guidelines On Submission of Documentation For Registration of Human Pharmaceutical Products RwandaAry Bima WinardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acticide Bac 50 M MSDS PDFDocument10 paginiActicide Bac 50 M MSDS PDFmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Parts of The Body and Health ProblemDocument13 paginiParts of The Body and Health ProblemSonia Tri AgustinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eccrine Sweat GlandsDocument5 paginiEccrine Sweat GlandssakuraleeshaoranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- BC CancerDocument42 paginiBC CancerIsal SparrowÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Training Table To The Battlefield: Protein Recommendations For WarfightersDocument4 paginiTraining Table To The Battlefield: Protein Recommendations For WarfightersLalu Reza AldiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Teknik MRI DasarDocument45 paginiTeknik MRI DasarDeki Kurnia JayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Case Study 103Document8 paginiCase Study 103Jonah MaasinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Nursing Practice IDocument45 paginiNursing Practice IWilmaBongotanPadawilÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Galvus (Vildagliptin) : How Does It Work?Document5 paginiGalvus (Vildagliptin) : How Does It Work?Radhakrishna KurupÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- 5z23. ED Crowding Overview and Toolkit (Dec 2015)Document33 pagini5z23. ED Crowding Overview and Toolkit (Dec 2015)Peter 'Pierre' RobsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antimicrobial Properties of Allicin From GarlicDocument3 paginiAntimicrobial Properties of Allicin From GarlicEdward Kenneth DragasÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Supine PositionDocument29 paginiThe Supine PositionKlaue Neiv CallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weeks Appellant BriefDocument54 paginiWeeks Appellant Briefthe kingfishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Précision P2D Par CalquesDocument1 paginăPrécision P2D Par CalquesamineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Read and Choose The Correct Answer From The Box Below.: Boys GirlsDocument1 paginăRead and Choose The Correct Answer From The Box Below.: Boys GirlsjekjekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive Revision Test - Basics 1Document16 paginiComprehensive Revision Test - Basics 1drpnnreddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nurse Writing 016 OET Practice Letter Darryl MahnDocument3 paginiNurse Writing 016 OET Practice Letter Darryl Mahnchoudharysandeep50163% (8)
- Sport Psychology ToolsDocument169 paginiSport Psychology Toolsfeldexxor100% (5)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- PackagingDocument29 paginiPackagingSagar TummaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dilip K. Ghosh, R. B. Smarta-Pharmaceuticals To Nutraceuticals - A Shift in Disease Prevention-Taylor & Francis - CRC Press (2017)Document274 paginiDilip K. Ghosh, R. B. Smarta-Pharmaceuticals To Nutraceuticals - A Shift in Disease Prevention-Taylor & Francis - CRC Press (2017)davidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disease Impact 2Document31 paginiDisease Impact 2Seed Rock ZooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionDocument3 paginiUpper Respiratory Tract Infectionmcvirgo014100% (1)
- Title: Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare An Integrated Approach To Healthcare DeliveryDocument13 paginiTitle: Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare An Integrated Approach To Healthcare DeliveryofhsaosdafsdfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recovery Road (Excerpt)Document13 paginiRecovery Road (Excerpt)I Read YA100% (1)
- List of Herbal Ingredients Which Are Prohibited or Restricted in MedicinesDocument12 paginiList of Herbal Ingredients Which Are Prohibited or Restricted in MedicinesEtra PublishingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intestinal Malrotation and VolvulusDocument14 paginiIntestinal Malrotation and VolvulusSaf Tanggo Diampuan100% (1)
- Evolution of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Cyclooxygenase (COX) Inhibition and BeyondDocument31 paginiEvolution of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) Cyclooxygenase (COX) Inhibition and BeyondAlexandru SavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)