Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
4.. Water (Pollution and Prevention of Pollution) Act and Rules
Încărcat de
Sanjana GaneshTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
4.. Water (Pollution and Prevention of Pollution) Act and Rules
Încărcat de
Sanjana GaneshDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Introduction
70% of the Earths surface.
Precious natural resources. Essential for everything on this planet.
Polluted River
The pollution of rivers and streams with chemical contaminants has become one of the most crucial environmental problems within the 20th century.
How does Water Pollution Occur?
Contaminated water is returned again to the source like lakes, rivers etc. Sewage water without treated is discharged into waterways. Rain water runoff from urban and industrial areas and agricultural land and mining operations makes way back to receiving waters and into ground.
Pathways of Contamination
Types of Water Pollution
Microbiological Chemical Oxygen Depleting Substances Nutrients Suspended Matter
Water Pollution Control
The impact due to suspended solids may be minimized by controlling discharge of wastes that contain suspended solids; this includes sanitary sewage industrial wastes etc. Cooling towers can be used to convert oncethrough systems into closed systems. Treated wastewater (such as sewage, industrial wastes, or stored surface run-offs) can be used as a cooling water make up.
Water Pollution Control
All surface run-offs around mines or quarries should be collected, treated, and disposed. Waste containing radioactively should be treated separately by means of dewatering procedures, and solids or brine should be disposed off with special care.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Introduction
The problem of pollution of rivers and streams has assumed a greater importance and urgency as a result of increased industrialisation and tendency for urbanisation.
Thus necessity for treatment of discharged domestic and industrial effluents before sending to stream gains importance in this context. ( cont)
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
(cont..) If not, contaminated streams and water courses which becomes a major source of drinking water, posses a serious threat to human life and marine life. Also the irrigation ,thereby the economy of the country will be net sufferers.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
The purposes of the Act are: To provide for the Prevention and Control of Water Pollution, maintaining or restoring of the wholesomeness of water and to monitor and enforce the regulations. To establish Central and State Pollution Control Boards for the Prevention and Control of water Pollution.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
The purposes of the Act are: To provide for conferring and assigning to such Boards, the powers and functions relating thereto and for matters connected therewith, To impose penalties for contravention of provisions of the Act, and To establish central and State water testing laboratories to enable the Board to assess the extent of pollution, lay down standards and establish guilt or default.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Definitions..
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Definitions..
Sewage effluent means affluent from any sewerage system or sewage disposal works and includes sullage from open drains.
Sewer means any conduit pipe or channel, open or closed, carrying sewage or trade effluent. Outlet includes any conduit pipe or channel, open or closed carrying sewage or trade effluent or any other holding arrangement which causes or is likely to cause, pollution.
Occupier in relation to any factory or premises, means the person who has control over the affairs of the factory or the premises, and includes, in relation to any substance, the person in possession of the substance
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Definitions..
Board means the Central Board or a State Board.
Central Board means the Central Pollution Control Board Constituted under section 3. State Board means a State Pollution Control Board constituted under section 4. Trade effluent includes any liquid, gaseous or solid substance which is discharged from any premises used for carrying on any [Industry, operation or process, or treatment and disposal system], other than domestic sewage.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Definitions..
Stream includesRiver, inland water (whether natural or artificial), water course (whether flowing or for the time being dry), sub-terranean waters, sea or tidal waters to such extent or, as the case may be, to such point as the State Government may, by notification in the Official Gazette, specify in this behalf.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Indian scenario
In India,
matters, Coordinate with State govt for the purpose of technical assistance on abatements, Lay down safe standards in the state and central sectors, Plan and cause nation wide programmes .
CPCB advice Government on pollution related
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Indian scenario
Water (Prevention and control of water pollution ) Act 1974 & Rules 1975.
This act talks about, metering of the water used by the different entities including the industrial consumers, the returns that to furnished by every consumers
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Indian scenario
Standard of the meters to be used,
Functions and powers that can be exercised by the central board. Penalty clauses Appeal clauses (Section 25 or 27 )
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Functions and powers that can be exercised by the central board.
Advice central govt. on any matter concerning the prevention and control of water pollution.
Co-ordinate activities and resolve disputes among state boards. Provide technical assistance to state board to carry out research and investigations.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Plan and organise the training program of personnels involved in various activities concerning prevention and control of water pollution. Organize mass media awareness programmes.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
The acts & rules demands for the setting up of SPCBs in each state. The act provide the industry with permits called consents, which is to be taken by every industry (section 8) Consents are given for a specific period and are to be renewed every year.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
SPCBs has got rights to call off the consents
given to any industry if required.
SPCBs tests the standard of the effluents.
They may ask the concerned industry to set up laboratories for testing purpose and also the Effluent Treatment Plants.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
SPCBs are required by the Acts & Rules to evolve economical and reliable treatment methods and techniques depending up on the availability
SPCBs can modify and alter the present standards for sewage and trade effluents
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Salient features of the Consent.
Daily quantity of water utilized, source and purpose.
Daily maximum effluent generated, type of effluent and mode of disposal. Quality of effluents Monitoring arrangements
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Raw materials and chemicals used per month Process Description
Effluent Treatment process
Solid wastes generated in process and during waste treatment.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Emergency measures in case of pollution of stream or well: Under section 32 of Water Act, Where it appears to the State Board that any poisonous, noxious or polluting matter has entered into that stream or well due to any accident or other unforeseen act or event, and if the Board is of opinion that it necessary or expedient to take immediate action, it may for reasons to be recorded in writing, carry out such operations as it may consider necessary for all or any of the following purposes, that it to say.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Emergency measures in case of pollution of stream or well: Under section 32 of Water Act, Removing that matter from the [stream or well or on land] and disposing it off in such manner as the Board considers appropriate Remedying or mitigating any pollution caused by its presence in the stream or well. Issuing orders immediately restraining or prohibiting the person concerned from discharging any poisonous, noxious or polluting matter [into the stream or well or on land], or from making insanitary use of the stream or well.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
The Municipal Corporations, Companies, and Government departments are also prosecuted under the Water Act. [sections 47 and 48] Offences by Companies: Section 47, Offences by Government Departments Section 48.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
Procedures Legal sampling SPCB Officer to serve a notice to occupier or his agent, In the presence of Occupier or his agent, divide the sample into two parts. Each to be placed in a container marked and sealed and shall also be signed by both. Send one container to the laboratory established or recognised by SPCB On the request of the Occupier or his agent, send the second container to the laboratory established or specified by Central Government / State Government In case of willful absence of the Occupier or his agent Sealed, marked and signed sample container shall be sent to laboratory established or recognised by SPCB and then inform the Government appointed analyst about the willful absence of the Occupier or his agent. Government appointed analyst to submit the report in the prescribed form to SPCB in triplicate. CPCB / SPCB to send one copy of the report to the Occupier or his agent / second copy to be produced in court of law and third copy to be retained by SPCB. In case of any inconsistency or discrepancy between or variation in the results, the analyst carried out, the report of later shall prevail.
WATER ( PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLLUTION) ACT & RULES
The punishment under the Act may imprisonment for a term varying from 3 months to 7 years and / with a fine which may extend to Rs.10,000, with an additional fine which may extend to Rs. 5,000 for every day during which such failure continues after the conviction for the first such failure. If the failure continues beyond a period of one year after the date of conviction, the offender shall, on conviction, be punishable with imprisonment for a term which shall not be less than 2 years but which may extend to 7 years and with fine.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Water Act, 1974 Relevant Provisions IndiaDocument28 paginiWater Act, 1974 Relevant Provisions IndiaFaris MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4Document80 paginiUnit 4ANUSAYA SAHUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clean Water ActDocument27 paginiClean Water ActRonald MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Pollution Control Mechanism and Implementation of Water Pollution Schemes in IndiaDocument16 paginiWater Pollution Control Mechanism and Implementation of Water Pollution Schemes in IndiaLAW MANTRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water ActDocument15 paginiWater ActRadhaAnanthalekshmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fairfield Institute of Management and Technology 3Document10 paginiFairfield Institute of Management and Technology 3Devansh SethiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republic Act 9275: An Act Providing For A Comprehensive Water Quality Management and For Other PurposesDocument21 paginiRepublic Act 9275: An Act Providing For A Comprehensive Water Quality Management and For Other PurposesHercules OlañoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clean Water ActDocument5 paginiClean Water ActJexie Ann Gumiran AggabaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental LawsDocument6 paginiEnvironmental LawsYogesh GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Pollution Control Mechanism and Implementation of Water Pollution Schemes in IndiaDocument17 paginiWater Pollution Control Mechanism and Implementation of Water Pollution Schemes in IndiaLAW MANTRA100% (2)
- Salient Features Nat ResDocument15 paginiSalient Features Nat ResnilereverofÎncă nu există evaluări
- What You Should Know About The Clean Water ActDocument4 paginiWhat You Should Know About The Clean Water ActJazzel Avila ParadiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why The Need For The Clean Water Act?Document4 paginiWhy The Need For The Clean Water Act?Jerry Eduardo II BonaguaÎncă nu există evaluări
- China's 1984 Law on Prevention and Control of Water PollutionDocument8 paginiChina's 1984 Law on Prevention and Control of Water PollutionGlorie Mae BurerosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salient Features of Water ActDocument4 paginiSalient Features of Water Actnagarajan.cecriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Niveditha First DraftDocument20 paginiNiveditha First DraftVidit HarsulkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clean Water Act SummaryDocument2 paginiClean Water Act SummaryALJHON SABINOÎncă nu există evaluări
- EST Assignment 10Document5 paginiEST Assignment 10vivek rameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Sanitation and ConservationDocument20 paginiWater Sanitation and ConservationJasmine Erica Certeza100% (4)
- Philippine Clean Water Act of 2004Document7 paginiPhilippine Clean Water Act of 2004Joyce Lapuz100% (4)
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution)Document22 paginiWater (Prevention and Control of Pollution)Trupti JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Law - LongDocument21 paginiEnvironmental Law - LongCall DataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974Document27 paginiWater (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974KNOWLEDGE CREATORSÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.water Prevention and Control of Pollution Act (1974) of IndiaDocument5 pagini1.water Prevention and Control of Pollution Act (1974) of IndiaBiswa PattanaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republic Act 9275 Clean Water ActDocument9 paginiRepublic Act 9275 Clean Water ActkaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Clean Water Act OverviewDocument3 paginiPhilippine Clean Water Act OverviewJustine Louise Bravo FerrerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enviornmental LawDocument15 paginiEnviornmental LawAbhilasha SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Useful Notes On The Water Prevention and Control of Pollution Act, 1974Document6 paginiUseful Notes On The Water Prevention and Control of Pollution Act, 1974poonam sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974Document8 paginiWater (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974abhishek_moza100% (1)
- ENVIRONMENTAL LAW: THE WATER CESS ACTDocument16 paginiENVIRONMENTAL LAW: THE WATER CESS ACTAmit RawlaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republic Act No. 9275: The Philippine Clean Water Act of 2004Document6 paginiRepublic Act No. 9275: The Philippine Clean Water Act of 2004Hiroshi CarlosÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Da 2) Matulac, Reynee Shaira - Che423 Bsche4Document3 pagini(Da 2) Matulac, Reynee Shaira - Che423 Bsche4Reynee Shaira Lamprea MatulacÎncă nu există evaluări
- CET415 - M2 - Ktunotes - inDocument78 paginiCET415 - M2 - Ktunotes - initsnavani2002Încă nu există evaluări
- Notes On Environmental ActsDocument11 paginiNotes On Environmental ActsSukhmaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental ScienceDocument6 paginiEnvironmental ScienceMohit WadhwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Undersatnding Water Act, 1974Document40 paginiUndersatnding Water Act, 1974AanchalVidyasagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air and Water Pollution ActsDocument29 paginiAir and Water Pollution ActsRamen GogoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Royal Decree 115-2001 Law On Protection of Sources of Potable Water From PollutionDocument21 paginiRoyal Decree 115-2001 Law On Protection of Sources of Potable Water From Pollutionasex4uÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q. Explain Water Pollution and Function of State Pollution Control Board Under The Water Act 1974Document2 paginiQ. Explain Water Pollution and Function of State Pollution Control Board Under The Water Act 1974Adan HoodaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prevention and Control of Water PollutionDocument68 paginiPrevention and Control of Water PollutionProminceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Clean Water Act (CWA) of 2004Document20 paginiPhilippine Clean Water Act (CWA) of 2004ROLAND JOIE GELIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ordinance 2Document10 paginiOrdinance 2Jason GrohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Provisions of Clean Water ActDocument29 paginiProvisions of Clean Water ActJaypee EvangelistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Clean Water Act SummaryDocument106 paginiPhilippine Clean Water Act SummaryAngelika Calingasan100% (1)
- The Central Pollution Control BoardDocument7 paginiThe Central Pollution Control BoardGanapati Joshi SankolliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.7 Business Legal Systems: Mfa 1 SemesterDocument29 pagini1.7 Business Legal Systems: Mfa 1 SemesterSoumyaparna SinghaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Pollution BoardDocument3 paginiCentral Pollution BoardAAYUSHI VERMA 7AÎncă nu există evaluări
- India's Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974 - An Overview - Eco-Intelligent™Document9 paginiIndia's Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974 - An Overview - Eco-Intelligent™farhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reaction Paper NATRESDocument8 paginiReaction Paper NATRESMichael Angelo MemoracionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Pollution ControlDocument103 paginiWater Pollution ControlharshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Clean Water Act SummaryDocument44 paginiPhilippine Clean Water Act SummaryCDM100% (5)
- En - EnvStand17 - Industrial and Municipal Wastewater DischargesDocument17 paginiEn - EnvStand17 - Industrial and Municipal Wastewater DischargesWellfroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Act SummaryDocument9 paginiWater Act SummaryanonymousÎncă nu există evaluări
- Testing of WaterDocument5 paginiTesting of WaterVinod NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Law ProjectDocument20 paginiEnvironmental Law Projectabhishek choudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environment Final HardDocument24 paginiEnvironment Final Hardjay chandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Pollution and The LawDocument16 paginiWater Pollution and The LawKriti SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Model Environmental Code: The Dubai Environment LawDe la EverandA Model Environmental Code: The Dubai Environment LawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Securing Safe Water Supplies: Comparison of Applicable TechnologiesDe la EverandSecuring Safe Water Supplies: Comparison of Applicable TechnologiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urban Wastewater Management in Indonesia: Key Principles and Issues in Drafting Local RegulationsDe la EverandUrban Wastewater Management in Indonesia: Key Principles and Issues in Drafting Local RegulationsÎncă nu există evaluări
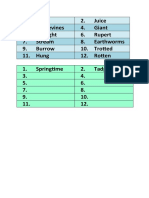
- Friday PPT Using Adverbs To Express TimeDocument18 paginiFriday PPT Using Adverbs To Express TimeSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Changes: Grade 2 Reading Comprehension WorksheetDocument4 paginiChanges: Grade 2 Reading Comprehension WorksheetSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- DictationDocument1 paginăDictationSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ant and Dove EnglishDocument29 paginiAnt and Dove EnglishSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hse LeadershipDocument4 paginiHse LeadershipSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Grasshopper and The Ants Fabel Power PointDocument12 paginiThe Grasshopper and The Ants Fabel Power PointSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Monkey & Crocodile A Wazoba Tribe StoryDocument8 paginiThe Monkey & Crocodile A Wazoba Tribe StorySanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- ButterflyDocument11 paginiButterflySanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thirsty CrowDocument7 paginiThirsty CrowSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- AesopDocument4 paginiAesopSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greedy DogDocument6 paginiGreedy DogSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 2 Reading about Mercury and the WoodsmanDocument7 paginiGrade 2 Reading about Mercury and the WoodsmanSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pronunciation Guide For EnglishDocument9 paginiPronunciation Guide For Englishkirank_11Încă nu există evaluări
- Accident Prevention: Health & Safety Management For QuarriesDocument19 paginiAccident Prevention: Health & Safety Management For QuarriesSanjana Ganesh100% (1)
- Sharks: Grade 2 Reading Comprehension WorksheetDocument4 paginiSharks: Grade 2 Reading Comprehension WorksheetSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crane HazardsDocument218 paginiCrane HazardsSanjana Ganesh100% (5)
- Actions Labour Inspector Should Take Following Workplace InjuryDocument12 paginiActions Labour Inspector Should Take Following Workplace InjurySanjana Ganesh67% (3)
- Multi Threading N NetworkingDocument40 paginiMulti Threading N NetworkingSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methods of TeachingDocument35 paginiMethods of TeachingSanjana Ganesh100% (10)
- IntroDocument14 paginiIntroSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health, Safety and Environment ProgramDocument35 paginiHealth, Safety and Environment ProgramSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Sets-NewDocument8 paginiChapter 1 Sets-NewSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety and Health ProgramDocument20 paginiSafety and Health ProgramSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scaffolding TrainingDocument81 paginiScaffolding TrainingSanjana Ganesh100% (1)
- Methods of TeachingDocument35 paginiMethods of TeachingSanjana Ganesh100% (10)
- Collective BargainingDocument35 paginiCollective BargainingSanjana Ganesh100% (1)
- Methods of TeachingDocument35 paginiMethods of TeachingSanjana Ganesh100% (10)
- Human Resource ManagementDocument144 paginiHuman Resource ManagementSuresh DevarajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automatic Sprinkler SystemDocument25 paginiAutomatic Sprinkler SystemSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refining Crude OilDocument20 paginiRefining Crude OilSanjana GaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 UEMX 3613 Topic2-1 R1Document50 pagini2015 UEMX 3613 Topic2-1 R1igantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- GrorudparkenDocument10 paginiGrorudparkenKuhu DhingraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deep Shaft ProcessDocument12 paginiDeep Shaft ProcessDevendra Sharma100% (1)
- Domestic Wastewater Management in Sri Lanka: A History of Sewerage WorksDocument23 paginiDomestic Wastewater Management in Sri Lanka: A History of Sewerage WorksweerasinghekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aqtesolv Manual 5Document1 paginăAqtesolv Manual 5Kevin Tang0% (1)
- Who Pulled The Plug On The Mediterranean? and Could It Happen Again? by Douglas MclnrrisDocument2 paginiWho Pulled The Plug On The Mediterranean? and Could It Happen Again? by Douglas MclnrrisQuang NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. Household DetailsDocument6 paginiA. Household DetailsTrex MarciiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- POME-Using 5mL PolymerDocument8 paginiPOME-Using 5mL PolymerParkavi KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zeus - AntipasDocument2 paginiZeus - AntipasPaw LabadiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE6605 Environmental Engineering IIDocument16 paginiCE6605 Environmental Engineering IIaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.4. Water Conservation LawsDocument49 pagini4.4. Water Conservation LawsBidhya SubediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Purification, Process by Which UndesiredDocument7 paginiWater Purification, Process by Which UndesiredRoshan Siddarth100% (1)
- Designing Septic Systems: Course DescriptionDocument0 paginiDesigning Septic Systems: Course DescriptionKhaled AbdelbakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urban Drainage Planning AssignmentDocument151 paginiUrban Drainage Planning AssignmentNaufal BariqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Environmental Engineering Lecture on Secondary Treatment MethodsDocument56 paginiBasic Environmental Engineering Lecture on Secondary Treatment MethodsRagib Nur Alam ShuvoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLANNING STORMWATER MANAGEMENT FOR URBAN AREASDocument94 paginiPLANNING STORMWATER MANAGEMENT FOR URBAN AREASMastura Binti HaronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faisal Fawaz Aljedaani - 2036389 - Engineering The Professional - PresentationDocument7 paginiFaisal Fawaz Aljedaani - 2036389 - Engineering The Professional - Presentationفيصل الجدعانيÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barangangay Development Plan 2023-25Document7 paginiBarangangay Development Plan 2023-25Blgu Lucog100% (6)
- CPCBDocument16 paginiCPCBSaurabh Mandal100% (2)
- Additional Tech Details For Polybond STP at DewasDocument2 paginiAdditional Tech Details For Polybond STP at DewasAnimesh JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joristown Piggery EISDocument55 paginiJoristown Piggery EISLinnel Faye C. MalibiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysing the Performance of Wastewater Treatment at Kitwe Nkana Sewage WorksDocument73 paginiAnalysing the Performance of Wastewater Treatment at Kitwe Nkana Sewage WorksPimpa MwiingaÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Is Wastewater Harmful?: BlackwaterDocument6 paginiHow Is Wastewater Harmful?: Blackwaterashutosh paridaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JD ReportsDocument9 paginiJD Reportsbendel_boyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NOC Request for 07 Small Dams in Khirthar National ParkDocument2 paginiNOC Request for 07 Small Dams in Khirthar National ParkArshad HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Status of Water Quality in India 2011Document211 paginiStatus of Water Quality in India 2011Zainy KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Pollution and DisasterDocument13 paginiWater Pollution and Disasterpratham sainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Star PVC Fitting List Yes 11111Document182 paginiStar PVC Fitting List Yes 11111SHIROMANY GadiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water and Wastewater Treatment - Design ConceptsDocument12 paginiWater and Wastewater Treatment - Design ConceptsBlessings HaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erosion and Deposition Action of Running Water and GroundwaterDocument12 paginiErosion and Deposition Action of Running Water and GroundwaterDevraj H SÎncă nu există evaluări