Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Git Physiology Part Iii
Încărcat de
dr.a.k.gupta6924100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
2K vizualizări9 paginiFor first year MBBS students on basics of GIT motiltiy -GIT Physiology
Titlu original
GIT PHYSIOLOGY PART III
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentFor first year MBBS students on basics of GIT motiltiy -GIT Physiology
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF sau citiți online pe Scribd
100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
2K vizualizări9 paginiGit Physiology Part Iii
Încărcat de
dr.a.k.gupta6924For first year MBBS students on basics of GIT motiltiy -GIT Physiology
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 9
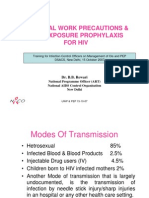
MOVEMENTS OF SMALL INTESTINE
Four Types of movements:
1. Mixing Movements (To mix CHYME
with juices):
c. Segmentation movements b.Pendular
movements
2. Propulsive Movements (to propel
food forward in GIT)
a. Peristalsis b. Peristalsis rush
8. Peristalsis in fasting- Migrating
Motor Complex
9. Movements of Villi
MIXING MOVEMENTS OF SMALL INTESTINE
1. SEGMENTATION COINTRACTIONS:
a. They occur rhythmically at regular spaced
intervals
along a part of intestine of length 1-5 cm. The
segments of intestine in between the
contracted
segments remain relaxed & are of equal
length to
contracted segment. So alternate segments of
Contraction & relaxation occurs giving
appearance of
a chain of sausages. See Diagram nxt slide
SEGMENTAL CONTRATIONS OF SMALL
INETESTINE
2. Pendular Movement:
Small portion of intestine sweep forward
and backward or upward & downward
resembling pendulum of a clock and help in
mixing chyme with digestive juices.
B. Propulsive Movements:
They are involved in pushing the chyme in the
aboral direction of intestine
3. Peristalsis:
d. It is defines as the wave of contraction
followed by wave of Relaxation, which
travel in aboral direction. It is caused by
stimulation of smooth muscles of small
intestine.
b. It travels from point of stimulation to both sides
but under
normal Conditions progress towards oral direction
is abolished
And Contractions Travel only in Anal direction.
d. The peristaltic contractions start at any
point and travel toward the anus at a
velocity of 0.5 to 2.0 cm/sec, faster in
the proximal intestine and slower in the
terminal intestine.
They normally are very weak and usually
die out after traveling only 3 to 5 cms,
so that forward movement of the
chyme is very slow, so slow in fact that
net movement along the small intestine
normally averages only 1 cm/min.
This means that 3 to 5 hours are
required for passage of chyme from
Peristaltic Rush:
Although peristalsis in the small
intestine is normally weak, intense
irritation of the intestinal mucosa, as
occurs in some severe cases of
infectious diarrhea, can cause both
powerful and rapid peristalsis, called
the peristaltic rush.
3.Movements of Villi:
Smooth muscle fibres extend from intestine
into villi so the villi also simultaneously
show movements when peristalsis occurs.
Movements of villi- Shortening &
elongation- & are under effect of hormone
Villikinin form small intestine.
Which help in
a. emptying Lymph from central lacteal of
villi into lymphatics
b. In increasing surface area of villi needed
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Regulation of GIT by gastrointestinal hormonesDocument13 paginiRegulation of GIT by gastrointestinal hormonesRaja Rashid IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- SGD 4 - Skeletal Muscle PhysiologyDocument3 paginiSGD 4 - Skeletal Muscle PhysiologyKriska Noelle0% (1)
- Small Intestine: DR Raghuveer ChoudharyDocument55 paginiSmall Intestine: DR Raghuveer ChoudharyPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPTDocument61 paginiPPTRheal P EsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
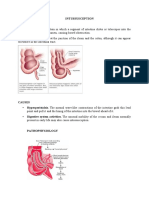
- INTUSSUSCEPTIONDocument3 paginiINTUSSUSCEPTIONS GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jaundice 03Document24 paginiJaundice 03kuldeep sainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glycogen Storage Disorders PDFDocument4 paginiGlycogen Storage Disorders PDFAHMEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inflammation CCDocument72 paginiInflammation CCmulatumeleseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal X RayDocument64 paginiAbdominal X RayabhishekbmcÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Kidney: Glomerular Diseases, Nephrotic Syndrome, and Acute Renal FailureDocument11 paginiThe Kidney: Glomerular Diseases, Nephrotic Syndrome, and Acute Renal FailureElina Drits100% (1)
- Yu - Git - Emb 2Document56 paginiYu - Git - Emb 2gtaha80Încă nu există evaluări
- Histology of The Digestive SystemDocument27 paginiHistology of The Digestive SystemHarnarayan Jeev Singh Bajaj100% (1)
- Renal 2 MTC PDFDocument55 paginiRenal 2 MTC PDFDrbee10Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 62: General Principles of GI Function-Motility, Nervous Control, and Blood CirculationDocument36 paginiChapter 62: General Principles of GI Function-Motility, Nervous Control, and Blood Circulationjackie funtanillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Vascular Disease GuideDocument46 paginiRenal Vascular Disease GuideCoy NuñezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biopolymers/Natural polymers structure and propertiesDocument78 paginiBiopolymers/Natural polymers structure and propertiesgautamahujaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 7 ThermoregulationDocument30 paginiLecture 7 ThermoregulationLouella Artates100% (1)
- Xray AbdominalDocument38 paginiXray Abdominalrizki sanÎncă nu există evaluări
- APOPTOSIS: Programmed cell death and its importance in development and diseaseDocument28 paginiAPOPTOSIS: Programmed cell death and its importance in development and diseasegull naz100% (1)
- Biliary DisoderDocument50 paginiBiliary DisoderZanida ZainonÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEDICAL CASE STUDIESDocument4 paginiMEDICAL CASE STUDIESDarryl John Pasamba67% (3)
- Fractures of The Upper LimbDocument20 paginiFractures of The Upper LimbWendy Francisca Borquez PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Introduction To The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument7 pagini1 Introduction To The Gastrointestinal SystemLinh Phan100% (1)
- Disorders of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismDocument20 paginiDisorders of Calcium and Phosphate MetabolismThirupathi Jakkani100% (1)
- Kholesistis & Kholelitiasis 30-11-14Document67 paginiKholesistis & Kholelitiasis 30-11-14Dian AzhariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipoprotein MetabolismDocument60 paginiLipoprotein MetabolismI MADE MIARTA YASAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 10 - Hemolytic Anemias - Extracorpuscular DefectsDocument28 paginiLecture 10 - Hemolytic Anemias - Extracorpuscular DefectsArif MaulanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Pathology GuideDocument71 paginiRenal Pathology GuideSuha AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatty Liver (1) - General PathologyDocument22 paginiFatty Liver (1) - General PathologyDarien LiewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal PhysiologyDocument43 paginiMaternal PhysiologyRaiza Love Caparas-PablicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIT & Urinary SystemDocument50 paginiGIT & Urinary SystemRenishya ManiarasuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology of Vomiting: A Guide to the PathophysiologyDocument24 paginiPhysiology of Vomiting: A Guide to the PathophysiologyKingWayne Tagatac BajoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 22 Bone and Joints (2nd Edition)Document23 paginiChapter 22 Bone and Joints (2nd Edition)Abhi KarmakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 - Sle, DMZ, PHSDocument157 pagini05 - Sle, DMZ, PHSG SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glomerular Disease Types and PresentationsDocument58 paginiGlomerular Disease Types and PresentationsJosa Anggi Pratama0% (1)
- PancreatitisDocument59 paginiPancreatitisAarif RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathanatomy Full MCQ SDocument47 paginiPathanatomy Full MCQ SAbhishek RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of Tuberculosis: International Standards 1-5Document51 paginiClinical Presentation and Diagnosis of Tuberculosis: International Standards 1-5Gilbert Solomon TantonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 17Document6 paginiChapter 17g_komolafe100% (1)
- Physiology of ANS Lecture 1 by Dr. Mudassar Ali RoomiDocument19 paginiPhysiology of ANS Lecture 1 by Dr. Mudassar Ali RoomiMudassar RoomiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apoptosis PPT, Pathological AnatomyDocument15 paginiApoptosis PPT, Pathological AnatomyN J3 CÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Destroying This RBC?Document28 paginiWhat Is Destroying This RBC?Putri Azka RinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cushings Syndrome and Addison Disease - BPTDocument45 paginiCushings Syndrome and Addison Disease - BPTAanchal GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQS CNS PathologyDocument14 paginiMCQS CNS PathologyFourth YearÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 paginiEndocrine SystemLen Len Ochinang OchinangÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQSDocument25 paginiMCQSkays30002403Încă nu există evaluări
- PELVISDocument68 paginiPELVISDevsya DodiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Fate of Metabolism Andmabolic PathwaysDocument25 paginiThe Fate of Metabolism Andmabolic PathwaysXuân Vi100% (1)
- Respiratory SystemDocument41 paginiRespiratory SystemNikkiAbbaNiColeCartagenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Studies in Pathomorphology. Self Assessment Textbook.: Ministry of Public Health of UkraineDocument93 paginiCase Studies in Pathomorphology. Self Assessment Textbook.: Ministry of Public Health of UkraineЯзан Мжарках - 2БÎncă nu există evaluări
- Git & Nutrition McqsDocument24 paginiGit & Nutrition McqsShahabuddin Shaikh100% (1)
- The Special Senses: Vision, Hearing, Taste, and SmellDocument31 paginiThe Special Senses: Vision, Hearing, Taste, and SmellDemuel Dee L. BertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guyton Respiration OverviewDocument6 paginiGuyton Respiration Overviewbahahahah100% (1)
- FCPS Pretest Series Golden File 3Document224 paginiFCPS Pretest Series Golden File 3Marsiano QendroÎncă nu există evaluări
- FBC Interpretation and Function of Blood ComponentsDocument7 paginiFBC Interpretation and Function of Blood ComponentsFrancesca LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gi SystemDocument73 paginiGi SystemSeema SachdevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology Cell InjuryDocument57 paginiPathology Cell InjuryMajd MustafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jugular Venous PressureDocument9 paginiJugular Venous Pressuremoh86-Încă nu există evaluări
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyDe la EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advances in Pathobiology and Management of Paget’s Disease of BoneDe la EverandAdvances in Pathobiology and Management of Paget’s Disease of BoneSakamuri V. ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Status of Orphan Vulnerable Children Infected or / Affected by HIV/AIDS in DelhiDocument32 paginiStatus of Orphan Vulnerable Children Infected or / Affected by HIV/AIDS in Delhidr.a.k.gupta6924Încă nu există evaluări
- Git Physiology Part Iv - Gi Motility by DR A.k.guptaDocument11 paginiGit Physiology Part Iv - Gi Motility by DR A.k.guptadr.a.k.gupta6924Încă nu există evaluări
- Post Exposure Prophylaxis For HivDocument21 paginiPost Exposure Prophylaxis For Hivdr.a.k.gupta6924Încă nu există evaluări
- Action Potential of Nerve FibreDocument2 paginiAction Potential of Nerve Fibredr.a.k.gupta6924Încă nu există evaluări
- GIT PHSYIOLOGY Part I BY DR A.K.GUPTADocument18 paginiGIT PHSYIOLOGY Part I BY DR A.K.GUPTAdr.a.k.gupta6924Încă nu există evaluări
- Blood Physiology Part II - Clotting of BloodDocument26 paginiBlood Physiology Part II - Clotting of Blooddr.a.k.gupta6924Încă nu există evaluări
- TranscriptionDocument15 paginiTranscriptiondr.a.k.gupta6924Încă nu există evaluări
- ElectrophoresisDocument2 paginiElectrophoresisdr.a.k.gupta6924Încă nu există evaluări
- Tracts of The Spinal CordDocument21 paginiTracts of The Spinal Corddr.a.k.gupta6924100% (10)
- Blood Physiology Part IV - Plasma Proteins, Hematocrit, ESR by DR A K GuptaDocument26 paginiBlood Physiology Part IV - Plasma Proteins, Hematocrit, ESR by DR A K Guptadr.a.k.gupta6924Încă nu există evaluări
- Physiology of Plasma ProteinsDocument21 paginiPhysiology of Plasma Proteinsdr.a.k.gupta6924100% (4)
- Post Exposure Prophylaxis & Universal Work Precautions - PPDocument43 paginiPost Exposure Prophylaxis & Universal Work Precautions - PPdr.a.k.gupta6924Încă nu există evaluări
- GIT Physiology Part II by DR A K GutaDocument11 paginiGIT Physiology Part II by DR A K Gutadr.a.k.gupta6924Încă nu există evaluări
- Blood Physiology Part I - CellsDocument119 paginiBlood Physiology Part I - Cellsdr.a.k.gupta6924100% (5)
- Coagulation of BloodDocument40 paginiCoagulation of Blooddr.a.k.gupta6924100% (8)
- HIV Intervention in College Youth by Red Ribbon ClubsDocument13 paginiHIV Intervention in College Youth by Red Ribbon Clubsdr.a.k.gupta6924100% (1)
- Epidemiology of HIV Infection by DR A.K. Gupta, Additional Project Director, Delhi State AIDS Control SocietyDocument26 paginiEpidemiology of HIV Infection by DR A.K. Gupta, Additional Project Director, Delhi State AIDS Control Societydr.a.k.gupta6924100% (2)
- Holistic Care of People Living With HIV/AIDS by DR A.K. Gupta, DSACSDocument36 paginiHolistic Care of People Living With HIV/AIDS by DR A.K. Gupta, DSACSdr.a.k.gupta6924100% (1)
- Natural History of HIV Infection by DR A K Gupta, Addl. Project Director, DSACSDocument29 paginiNatural History of HIV Infection by DR A K Gupta, Addl. Project Director, DSACSdr.a.k.gupta6924100% (3)
- Paediatric HIV Infection by DR A.K.Gupta, Additional Project Director, Delhi State AIDS Control SocietyDocument88 paginiPaediatric HIV Infection by DR A.K.Gupta, Additional Project Director, Delhi State AIDS Control Societydr.a.k.gupta6924Încă nu există evaluări
- MCQs of Digestive SystemDocument4 paginiMCQs of Digestive Systemالموعظة الحسنه chanel100% (10)
- Four Systems For Happy YogaDocument109 paginiFour Systems For Happy YogaAwanish PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PW Module-Digestion and AbsorptionDocument27 paginiPW Module-Digestion and AbsorptionadityaorhoneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect. 12 Digestive SystemDocument74 paginiLect. 12 Digestive Systemflex gyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy SharkDocument32 paginiAnatomy SharkKanwal RashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPP - 3 - MCQs Based On Intestine 1Document3 paginiDPP - 3 - MCQs Based On Intestine 1Dr-Atin Kumar SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology-Intestinal ObstructionDocument2 paginiAnatomy and Physiology-Intestinal ObstructionRaisa Robelle Quicho75% (8)
- Protein digestion in ruminants explainedDocument12 paginiProtein digestion in ruminants explainedJ Jesus Bustamante GroÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL q4 w1Document13 paginiDLL q4 w1Mayolita NavalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Px. Abdomen RadiologiDocument46 paginiPx. Abdomen RadiologiwagigtnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hsslive XI Zoology 05 Digestion and AsorptionDocument15 paginiHsslive XI Zoology 05 Digestion and AsorptionbnairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case of AmoebiasisDocument95 paginiCase of Amoebiasisdclaire_1886% (7)
- Ultrasonography of Gastrointestinal Foreign Bodies: DVM, Dominique G. Penninck, DVMDocument10 paginiUltrasonography of Gastrointestinal Foreign Bodies: DVM, Dominique G. Penninck, DVMrai jaine DarmantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Typhoid FeverDocument38 paginiTyphoid Fevermhamaenphapa27Încă nu există evaluări
- 9 Human NutritionDocument56 pagini9 Human NutritionSaamir SadmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- English - On Farm Post Mortem Guide For BroilersDocument72 paginiEnglish - On Farm Post Mortem Guide For BroilersMahjoubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Digestive System GuideDocument18 paginiHuman Digestive System Guidemark smithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive System NotesDocument11 paginiDigestive System NotesijustneedtheanswersÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Ăm'ə-Lāce ) or Ptyalin (Tī'ə-Lĭn) Is The Digestive Enzyme Found in Saliva. ItDocument5 pagini(Ăm'ə-Lāce ) or Ptyalin (Tī'ə-Lĭn) Is The Digestive Enzyme Found in Saliva. ItKyle Keen TaerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiological and Biological Psychology Group 7: Jerovel T. League Frances Mikaela Llorca JD Mommy MagnoDocument25 paginiPhysiological and Biological Psychology Group 7: Jerovel T. League Frances Mikaela Llorca JD Mommy MagnoJerovel T. LeagueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition in Plant and Animal 10 IDocument9 paginiNutrition in Plant and Animal 10 IKishan RÎncă nu există evaluări
- 38 AnswersDocument8 pagini38 AnswersJasmine Nicole EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Typhoid Fever (Mhine)Document20 paginiTyphoid Fever (Mhine)Donna Salamanca DomingoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestion 1 MCQDocument11 paginiDigestion 1 MCQgopodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive System 2Document7 paginiDigestive System 2SlaheddineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestion Test BiologyDocument3 paginiDigestion Test BiologyKatrīna SimanovskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive System: Dipali HarkhaniDocument83 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of The Digestive System: Dipali HarkhaniPatel archiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive System ModuleDocument16 paginiDigestive System ModuleLovelyjoy MarianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology 6093 (Text) - Principles of Biology + Nutrition & Transport in HumansDocument31 paginiBiology 6093 (Text) - Principles of Biology + Nutrition & Transport in HumansmahimaloveswaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestio NDocument27 paginiDigestio NSauban AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări