Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Animal Cell
Încărcat de
Daryl De LeonDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Animal Cell
Încărcat de
Daryl De LeonDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
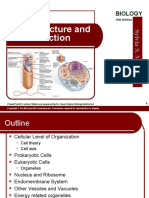
The cell is the basic unit of life.
All organisms are made up of cells (or in some cases, a single cell). Most cells are very small; most are invisible without using a microscope. Cells are covered by a cell membrane and come in many different shapes. The contents of a cell are called the protoplasm.
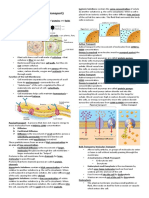
Centrioles - organize the assembly of microtubules during cell division. Cytoplasm - gel-like substance within the cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum - extensive network of membranes composed of both regions with ribosome's. Golgi Complex - responsible for manufacturing, storing and shipping certain cellular products. Lysosomes - sacs of enzymes that digest cellular macromolecules such as nucleic acids. Microtubules - hollow rods that function primarily to help support and shape the cell.
Mitochondria - power producers and the sites of cellular respiration. Nucleus - membrane bound structure that contains the cell's hereditary information.
Nucleolus - structure within the nucleus that helps in the synthesis of ribosomes.
Nucleopore - tiny hole within the nuclear membrane that allows nucleic acids and proteins to move into and out of the nucleus.
Ribosomes - consisting of RNA and proteins, ribosomes are responsible for protein assembly.
Comprising incorporating nutrition food inside the cell, the processing thereof and the assimilation of substances useful for forming the cell and its own material. Depending on your nutrition, cells are autotrophic and heterotrophic cells. Autotrophic cells make their own organic matter from inorganic matter of the physical environment that surrounds it, using ell or chemical energy contained in inorganic matter.
meiosis.
Through mitosis from a stem cell originate two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes and the genetic information same stem cell.
Through meiosis, from a stem cell form four daughter cells all having half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
The animal cell differs from other eukaryotes, mainly of plant cells which lack a cell wall and chloroplasts, and having smaller vacuoles. Due to the absence of a rigid cell wall, the animal cells may take a variety of shapes, and even a phagocyte cell may in fact surround and engulf other structures.
Broadly speaking, the major difference between plant and animal cell is that animals have no cell wall, which is the main component that provides rigidity to the plant cell. The number of vacuoles in the animal cell is minimal, while the plant cell vacuole has many groups. The animal cell has centrosome, no plant cell. The present animal cell liposome's, no plant cell. The animal cell has no photosynthesis plant cell if
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Document2 paginiCell Organelle Review Worksheet 14-15Kirsten Troupe100% (1)
- Bio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesDocument18 paginiBio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesMuhammad Mahi Nurul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibody Responses To Minor Histocompatibility Antigens After Solid Organ TransplantationDocument5 paginiAntibody Responses To Minor Histocompatibility Antigens After Solid Organ TransplantationBruna VoroniukÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 101 Essay 2 Final DraftDocument8 paginiEnglish 101 Essay 2 Final Draftapi-383935528Încă nu există evaluări
- The Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDocument13 paginiThe Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDiane CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structure, Processes, and Reproduction, Third EditionDe la EverandCell Structure, Processes, and Reproduction, Third EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDocument49 paginiEukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDaezel Deux100% (1)
- Plant Cell and Animal Cell - Docx YuvenDocument8 paginiPlant Cell and Animal Cell - Docx YuvenVikneswaran Gunahlan NeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 7 Postlab Frog External AnaDocument8 paginiActivity 7 Postlab Frog External Anaapi-3836574100% (1)
- Biodiversity and Conservation A Level NotesDocument8 paginiBiodiversity and Conservation A Level NotesNaseer SiddiquiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of Animal Tissue g12 BIODocument53 paginiStructure of Animal Tissue g12 BIOSimon A. Peter JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells Structure and Their Functions: Mary Winrose B. Tia, RNDocument60 paginiCells Structure and Their Functions: Mary Winrose B. Tia, RNFeah DaydayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Bio200 Chapter 11Document38 pagini6 Bio200 Chapter 11api-153638948Încă nu există evaluări
- Classes of Vertebrates (Comparative Analysis)Document173 paginiClasses of Vertebrates (Comparative Analysis)Vinci EbordeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structures and Functions 02Document22 paginiCell Structures and Functions 02YASMEROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taxonomy & Phylogeny: Classification Phylogeny Cladograms QuizDocument68 paginiTaxonomy & Phylogeny: Classification Phylogeny Cladograms QuizDorothy Yen EscalañaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 161S16 SystematicsDocument36 pagini161S16 SystematicsSamantha Jeka Bianca AsnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11.2 Domain Bacteria and ArchaeaDocument39 pagini11.2 Domain Bacteria and ArchaeaZkdlin SpaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument10 paginiClass: 8 Science Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsAmiteshwar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 1 The Cell 1Document6 paginiExercise 1 The Cell 1MJMadlangbayan100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Functions PPT 5Document24 paginiCell Structure and Functions PPT 5rajesh dua100% (1)
- New World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Document15 paginiNew World International School Biology Igcse Notes Chapter - 1Noor Samir100% (1)
- Biology DefinitionsDocument6 paginiBiology DefinitionsSixtine MorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Anatomy of The BoneDocument53 paginiComparative Anatomy of The BoneCherry SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- MeiosisDocument24 paginiMeiosisMuhammad HamzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology: The CellDocument8 paginiAnatomy and Physiology: The Celllourd nabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Use The Table Above To Fill in The ChartDocument5 paginiCell Organelles Worksheet Use The Table Above To Fill in The ChartRachel Ann EstanislaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sources of Stem CellsDocument13 paginiSources of Stem CellsAnshi AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant and Animal Cells PuzzleDocument3 paginiPlant and Animal Cells PuzzleLisa Ellis0% (1)
- Venn Diagram On Osmosis and DiffusionDocument1 paginăVenn Diagram On Osmosis and DiffusioncolacastellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Unit 2 Revision: Topic 3 - Voice of The GenomeDocument6 paginiBiology Unit 2 Revision: Topic 3 - Voice of The GenomeYasinKureemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Anatomy of Aortic ArchesDocument2 paginiComparative Anatomy of Aortic ArchesTibian_Mallick94% (16)
- Transport MechanismsDocument2 paginiTransport MechanismsErica GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CloningDocument6 paginiCloningkikkabuttigieg1466Încă nu există evaluări
- Stem Cells in HumansDocument4 paginiStem Cells in HumansSana NainaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal TissueDocument47 paginiAnimal TissueJoshua Verzosa PalconitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument5 paginiChapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDHAIRYA KASAR100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument20 paginiCell Structure and FunctionAPS UpdatesÎncă nu există evaluări
- HomeostasisDocument16 paginiHomeostasisDr M K GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells AssignmentDocument18 paginiCells AssignmentMuqadasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Guide For Cell Theory TestDocument2 paginiStudy Guide For Cell Theory Testchaine1Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet Summer ValliniDocument3 paginiCell Organelle Review Worksheet Summer ValliniSummer ValliniÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOPIC 2 - CellDocument9 paginiTOPIC 2 - CellAl Johan Atienza100% (1)
- Seed Germination Experiment Revised Final Copy 2Document8 paginiSeed Germination Experiment Revised Final Copy 2sally ngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structure and Function: BiologyDocument69 paginiCell Structure and Function: BiologyAsif Ali100% (1)
- Respiratory System: StructureDocument29 paginiRespiratory System: StructureDr. Abir Ishtiaq100% (1)
- ZOOL100. Endocrine SystemDocument10 paginiZOOL100. Endocrine SystemAyvi KeytÎncă nu există evaluări
- OCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision NotesDocument4 paginiOCR Biology F211 Cells, Exchange and Transport Revision Notes24wrightphilip100% (1)
- Unit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationDocument13 paginiUnit 8 The Reproductive System Bilingual EducationAntonio PrietoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 6 Variation HRADocument34 paginiLesson 6 Variation HRAAngel100% (1)
- Evol RelationshipsDocument15 paginiEvol RelationshipsCarla BanzuelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02a SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTSDocument35 pagini02a SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTSRitik Kumar NayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Practical 1Document21 paginiLab Practical 1randy_sanchez_10Încă nu există evaluări
- Biological Molecules: Prepared By: Mrs. Eden C. SanchezDocument50 paginiBiological Molecules: Prepared By: Mrs. Eden C. SanchezBernard D. Fajardo Jr.100% (1)
- Week 9 Topic 1 Types of TissueDocument60 paginiWeek 9 Topic 1 Types of TissueRoxanne Pastrana100% (1)
- Taenias IsDocument56 paginiTaenias Iseliwaja100% (1)
- Biology Chapter 4 Study Guide AnswersDocument3 paginiBiology Chapter 4 Study Guide AnswersEmma Frasier50% (2)
- 9aa Environmental Variation VLE V3Document32 pagini9aa Environmental Variation VLE V3syztqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Document4 paginiSheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Leo MatsuokaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocument74 paginiTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- A-P Chapter 3 Cell StructureDocument35 paginiA-P Chapter 3 Cell StructureMONIQUE VELASCOÎncă nu există evaluări
- ResourcesDocument166 paginiResourcesaeryll1305Încă nu există evaluări
- Algae, Fungi and ProtozoaDocument53 paginiAlgae, Fungi and ProtozoaMirza Salman BaigÎncă nu există evaluări
- REV Iavp AwardsDocument2 paginiREV Iavp AwardsIavp CongressÎncă nu există evaluări
- Certificate of Analysis No.: 1927745: CustomerDocument2 paginiCertificate of Analysis No.: 1927745: CustomerDimitris KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument4 paginiManagement of Diabetic Ketoacidosiscarla jazmin cortes rodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identifying Dispersive SoilsDocument2 paginiIdentifying Dispersive SoilsJhinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impak Bioteknologi PDFDocument24 paginiImpak Bioteknologi PDFlechumanan26Încă nu există evaluări
- Syarat KemasukanDocument13 paginiSyarat KemasukanLim ChintakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qdoc - Tips Topnotch Supplement Pharmacology HandoutDocument57 paginiQdoc - Tips Topnotch Supplement Pharmacology HandoutShehana MusahariÎncă nu există evaluări
- TMJ Anatomy and Biomechanics-14Document67 paginiTMJ Anatomy and Biomechanics-14erfan mohammadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Names For Trace Fossils A Uniform Approa PDFDocument22 paginiNames For Trace Fossils A Uniform Approa PDFcatfoulkrodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Print THE BARBARY DEERDocument1 paginăPrint THE BARBARY DEERBlâckmoon LîghtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bensons Microbiological Applications Laboratory Manual Complete Version 14th Edition Brown Solutions ManualDocument35 paginiBensons Microbiological Applications Laboratory Manual Complete Version 14th Edition Brown Solutions Manualfrustumslit.4jctkmÎncă nu există evaluări
- PTSD Recovery Group Therapist ManualDocument65 paginiPTSD Recovery Group Therapist ManualAnonymous Ax12P2sr100% (2)
- Allergic ConjunctivitisDocument16 paginiAllergic ConjunctivitisJose Antonio Fuentes VegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cecile Beguin Et Al - Synthesis and in Vitro Evaluation of Salvinorin A Analogues: Effect of Configuration at C (2) and Substitution at CDocument7 paginiCecile Beguin Et Al - Synthesis and in Vitro Evaluation of Salvinorin A Analogues: Effect of Configuration at C (2) and Substitution at CnnnnjwÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Project WorkDocument39 paginiMy Project WorkCharles OnandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensation & Perception - When We Smell A Fragrant Flower, Are We Experiencing A Sensation or ADocument8 paginiSensation & Perception - When We Smell A Fragrant Flower, Are We Experiencing A Sensation or AArūnė EinorytėÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecturer Des: College Preparation A.Y. '23-'24Document11 paginiLecturer Des: College Preparation A.Y. '23-'24Jemina PocheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phet Natural SelectionDocument6 paginiPhet Natural Selectionapi-316039932Încă nu există evaluări
- The Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument24 paginiThe Central Dogma of Molecular BiologybagyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Bachelor of Pharmacy Course StructureDocument4 paginiThe Bachelor of Pharmacy Course Structurekunalworldsingh1991Încă nu există evaluări
- BookDocument64 paginiBookPallaval VeerabramhachariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Double CirculationDocument2 paginiDouble CirculationMonika KanojiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report On Animal RightsDocument8 paginiReport On Animal RightsYashashvi Rastogi100% (1)
- Schulte Et Al 2009 Science 325 1124-1128 - Unprecendented Restoration of Native Oyster MetapopulationDocument7 paginiSchulte Et Al 2009 Science 325 1124-1128 - Unprecendented Restoration of Native Oyster MetapopulationYennifer Hoyos CazulúÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 12 (Nutrition) F.SC 1st Year Biology Helping NotesDocument11 paginiChap 12 (Nutrition) F.SC 1st Year Biology Helping NotesAbbas HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neural Dynamics For Landmark Orientation and Angular Path Integration - Seelig2015Document19 paginiNeural Dynamics For Landmark Orientation and Angular Path Integration - Seelig2015dagushÎncă nu există evaluări