Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
EIGRP
Încărcat de
Jeton AhmetiDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
EIGRP
Încărcat de
Jeton AhmetiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
EIGRP
EIGRP is an advanced distance vector routing protocol developed by Cisco. EIGRP is an advanced distance vector or hybrid routing protocol that includes the following features: Rapid convergence: EIGRP uses the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) to achieve rapid convergence. A router that uses EIGRP stores all available backup routes for destinations so that it can quickly adapt to alternate routes. Reduced bandwidth usage: EIGRP does not make periodic updates. Instead, it sends partial updates when the path or the metric changes for that route. Classless routing: EIGRP supports discontiguous subnetworks and variable-length subnet masks (VLSM). Less overhead: EIGRP uses multicast and unicast rather than broadcast Load balancing: EIGRP supports unequal metric load balancing
Easy summarization:
In EIGRP, the best route is called a successor route while a backup route is called the feasible successor. To determine the best route (successor) and the backup route (feasible successor) to a destination, EIGRP uses the following two parameters: Advertised distance: The EIGRP metric for an EIGRP neighbor to reach a particular network Feasible distance: The advertised distance for a particular network learned from an EIGRP neighbor plus the EIGRP metric to reach that neighbor
Five types of EIGRP packets exist, further categorized as reliable packets and unreliable packets. The reliable EIGRP packets are as follows: Update Update packets contain EIGRP routing updates sent to an EIGRP neighbor. Query Queries are sent to neighbors when a route is not available and the router needs to ask the status of the route for fast convergence. Reply Reply packets to the queries contain the status of the route being queried for. The unreliable EIGRP packets are as follows: Hello Hello packets are used to establish EIGRP neighbor relationships across a link. Acknowledgment Acknowledgment packets ensure reliable delivery of EIGRP packets. All the EIGRP packets are sent through EIGRP multicast address 224.0.0.10.
EIGRP default administrative distances Summary routes = 5 Internal routes = 90 Imported routes = 170
The formula for calculating EIGRP metric is:
Metric = 256*((K1*Bw) + (K2*Bw)/(256-Load) + (K3*Delay)*(K5/(Reliability + K4)))
k1=bandwidth k2=load k3=delay k4=reliability k5=MTU K1 = 1 and K3 = 1 and rest all are Zero.
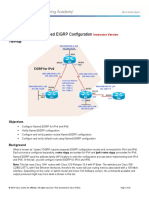
Configuring and Verifying EIGRP Use the router eigrp and network commands to create an EIGRP routing process. Note that EIGRP requires an autonomous system (AS) number. The AS number does not have to be registered as is the case when routing on the Internet with the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) routing protocol. However, all routers within an AS must use the same AS number to exchange routing information with each other. Figure 5-3 shows the EIGRP configuration of a simple network.
Troubleshooting commands:
show ip eigrp interfaces: Lists the working interfaces on which EIGRP is enabled (based on the network commands); it omits passive interfaces. show ip protocols: Lists the contents of the network configuration commands for each routing process, and a list of neighbor IP addresses. show ip eigrp neighbors: Lists known neighbors; does not list neighbors for which some mismatched parameter is preventing a valid EIGRP neighbor relationship. show ip eigrp topology: Lists all successor and feasible successor routes known to this router. It does not list all known topology details. show ip route: Lists the contents of the IP routing table, listing EIGRP-learned routes with a code of D on the left side of the output.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- ENARSI 300-410 September 2020-v1.1Document75 paginiENARSI 300-410 September 2020-v1.1Pak ChannÎncă nu există evaluări
- BGP TutorialDocument157 paginiBGP Tutorialbhavik_babariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enterprise Network AssignmentDocument56 paginiEnterprise Network AssignmentSeemab Kanwal100% (1)
- Khawar Butt CCIE Security v3 0Document191 paginiKhawar Butt CCIE Security v3 0kamleg100% (1)
- Lab8 Sequential Lab Router ConfigDocument6 paginiLab8 Sequential Lab Router ConfigmedjacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pass4sure CCIE 350-080 DumpsDocument216 paginiPass4sure CCIE 350-080 DumpsRhiannon444Încă nu există evaluări
- Cisco Press Ccie Security PracticeDocument618 paginiCisco Press Ccie Security PracticeRobert BradyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNP Lead 2 PassDocument194 paginiCCNP Lead 2 PassPisotonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNPv7 ROUTE Lab2-4 EIGRP-Named-Configuration InstructorDocument23 paginiCCNPv7 ROUTE Lab2-4 EIGRP-Named-Configuration InstructorNiko SB FSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Singh, J., Mahajan, R. (2013) Simulation Based Comparative Study of RIP, OSPF and EIGRPDocument4 paginiSingh, J., Mahajan, R. (2013) Simulation Based Comparative Study of RIP, OSPF and EIGRPLee HeaverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer DocumedddddddddddddddddddddddddntDocument12 paginiAnswer DocumedddddddddddddddddddddddddntAzaj IkbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA5 ScaN EIGRP Practice Skills Assessment - PTDocument14 paginiCCNA5 ScaN EIGRP Practice Skills Assessment - PTDanny HpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topics Weightage: Status LeftDocument15 paginiTopics Weightage: Status LeftGhayas AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dangi, V., Shrimali, T. (2014) Comparative Performance Analysis of Link Recovery Between EIGRP and OSPF Protocols Based On SimulationDocument5 paginiDangi, V., Shrimali, T. (2014) Comparative Performance Analysis of Link Recovery Between EIGRP and OSPF Protocols Based On SimulationLee HeaverÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA4 Challenge LabsDocument32 paginiCCNA4 Challenge LabsDavor BudimirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examen FinalDocument43 paginiExamen FinalClaudio Aliste Requena83% (18)
- CCNA 2 Chapter 7 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100Document7 paginiCCNA 2 Chapter 7 v5.0 Exam Answers 2015 100ovidiu0702Încă nu există evaluări
- Configuration and Troubleshooting CommandsDocument5 paginiConfiguration and Troubleshooting CommandsAmeen Hashim Farhan 363TEGYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acn NotesDocument79 paginiAcn NotesShubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Redistribute EIGRP and OSPF - GNS3 LabDocument11 paginiRedistribute EIGRP and OSPF - GNS3 LabErnesto PanellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7.3.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge InstructionsDocument3 pagini7.3.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge Instructionsyair cedillo jaramilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- On The Interaction of Multiple Routing AlgorithmsDocument12 paginiOn The Interaction of Multiple Routing AlgorithmsLee HeaverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab EIGRP 2Document15 paginiLab EIGRP 2Danny Ricce EnriqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab - Configure and Verify eBGP: TopologyDocument4 paginiLab - Configure and Verify eBGP: TopologyjohnathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Karan Singh R10Document5 paginiKaran Singh R10Arun KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Configuring MPLS VPNs - Troubleshooting Any Transport Over MPLS Based VPNsDocument19 paginiConfiguring MPLS VPNs - Troubleshooting Any Transport Over MPLS Based VPNsAnonymous 6PurzyegfXÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNP ENARSI v8 Scope and SequenceDocument9 paginiCCNP ENARSI v8 Scope and SequenceMeriem OultacheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Thesis of ReazDocument66 paginiFinal Thesis of ReazNahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- EIGRP Whitepaper - C11-720525Document17 paginiEIGRP Whitepaper - C11-720525mad maranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Desktop Support Engineer Materials 2Document20 paginiDesktop Support Engineer Materials 2kapishkumar100% (1)