Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
ICT in Education - Lesson 1
Încărcat de
tashadatTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ICT in Education - Lesson 1
Încărcat de
tashadatDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
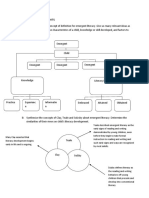
ICTs
In Education
DANIEL DANSO ESSEL
INDIVIDUALIZED INSTRUCTION
COLLABORATIVE LEARNING
How will this help you in your teaching and learning?
Recent advancement in communications technology has contributed immensely to minimize the effect of distance in the way we do business. Roblyer (2003) aptly describes the situation as the death of distance. She writes that the death of distance has given new life to education.
ICTs stand for information and communication technologies
diverse set of technological tools and resources used to communicate, and to create, disseminate, store, and manage information
Internet
These technologies include computers, the Internet, broadcasting technologies (radio and television), and telephony
e-learning
encompasses learning , that uses an information
networkthe Internet, an Intranet (LAN) or Extranet (WAN)whether wholly or in part, for course delivery, interaction and/or facilitation. Another term used for e-learning is online learning. Web-based learning is a subset of elearning and refers to learning using an Internet browser (such as Netscape or Internet Explorer).
blended learning (Hybrid Learning)
This refers to learning models that combine
traditional classroom practice with e-learning solutions. For example, students in a traditional class can be assigned both print-based and online materials, have online mentoring sessions with their teacher through chat, and are subscribed to a class email list.
Open and distance learning
Open and distance learning is defined by the
Commonwealth of Learning as a way of providing learning opportunities that is characterized by the separation of teacher and learner in time or place, or both time and place; learning that is certified in some way by an institution or agency; the use of a variety of media, including print and electronic; two-way communications that allow learners and tutors to interact; the possibility of occasional face-to-face meetings; and a specialized division of labour in the production and delivery of courses
ICTs provide powerful tools for extending educational opportunities to underserved communities
scattered and rural
Provides education Anywhere Anytime
On-line learning
populations groups traditionally excluded from education due to cultural or social reasons such as ethnic minorities, girls and women, persons with disabilities, and the elderly, as well as all others who for reasons of cost or because of time constraints are unable to enroll on campus.
material eLearning Distance Learning Enrolment in any world wide programs no temporal constraints
Provides Access to Remote Learning Resources
Computers are Everywhere
One of the most commonly cited reasons for using
ICTs in the classroom has been to better prepare the current generation of students for a workplace where ICTs, particularly computers, the Internet and related technologies, are becoming more and more ubiquitous
Global Job Market Requires 21st Century Skills
Technological literacy, or the ability to use ICTs
effectively and efficiently, is seen as representing a competitive edge in an increasingly globalizing job market.
Skills Needed in the Workplace of the Future Digital Age Literacy
Functional literacy - Ability to decipher meaning and express
ideas in a range of media; this includes the use of images, graphics, video, charts and graphs or visual literacy Scientific literacy -Understanding of both the theoretical and applied aspects of science and mathematics Technological literacy - Competence in the use of information and communication technologies Information literacy - Ability to find, evaluate and make appropriate use of information, including via the use of ICTs Cultural literacy - Appreciation of the diversity of cultures Global awareness - Understanding of how nations, corporations, and communities all over the world are interrelated
Inventive Thinking
Adaptability - Ability to adapt and manage in a
complex, interdependent world Curiosity - Desire to know Creativity - Ability to use imagination to create new things Risk-taking - Ability to take risks
Higher-Order Thinking
Creative problem-solving and logical thinking that
result in sound judgments
Effective Communication
Teaming - Ability to work in a team Collaboration and interpersonal skills - Ability to interact
smoothly and work effectively with others Personal and social responsibility - Be accountable for the way they use ICTs and to learn to use ICTs for the public good Interactive communication - Competence in conveying, transmitting, accessing and understanding information High Productivity - Ability to prioritize, plan, and manage programs and projects to achieve the desired results. Ability to apply what they learn in the classroom to real-life contexts to create relevant, high-quality products
The potential of ICTs to promote the acquisition of 21st Centuy skills is tied to its use as a tool for raising educational quality, including promoting the shift to a learnercentered environment
The National Research Council of the U.S. defines learner-centered environments as those that pay careful attention to the knowledge, skills, attitudes, and beliefs that learners bring with them to the classroom. The impetus for learner-centeredness derives from a theory of learning called constructivism
Knowledge is not out there, independent of the learner Learner does not passively receive knowledge Knowledge is created through an active process in which the learner transforms information, constructs hypothesis, and makes decisions using his/her mental models.
Learning is a process in which individuals construct meaning based on prior knowledge and experience. Experience enables individuals to build mental models or schemas, which in turn provide meaning and organization to subsequent experience. Social constructivism, learning must be active, contextual and social. It is best done in a group setting with the teacher as facilitator or guide.
ICTs can enhance the quality of education in several ways:
by increasing learner motivation and
engagement by facilitating the acquisition of basic skills by enhancing teacher training.
ICTs are also transformational tools which, when used appropriately, can promote the shift to a learner-centered environment.
Videos, television and multimedia computer software that combine text, sound, and colorful, moving images can be used to provide challenging and authentic content that engage the student in the learning process.
Networked computers with Internet connectivity can increase learner motivation as it combines the media richness and interactivity of other ICTs with the opportunity to connect with real people and to participate in real world events.
By use of television educational programs
By use of Computer-based instruction materials such as:
Tutorial programs Drill and practice
Simulations and,
Games
By improving access to and quality of teacher training:
Use of the Internet to provide better teacher
professional development opportunities to inservice teachers (Distance Learning) Deployment of Learning Management Systems to provide quality instruction.
By promoting Active Learning:
Provides a platform for student inquiry, analysis and
construction of new information. Learners therefore learn as they do and, whenever appropriate Learners work on real-life problems in-depth, making learning less abstract and more relevant to the learners life situation. In this way, and in contrast to memorization-based or rote learning, ICT-enhance learning Promotes increased learner engagement. ICTenhanced learning is also just-in-time learning in which learners can choose what to learn when they need to learn it.
By promoting Collaborative Learning: ICT-supported learning encourages interaction and cooperation among students, teachers, and experts regardless of where they are. Apart from modeling real-world interactions, ICT-supported learning provides learners the opportunity to work with people from different cultures, thereby helping to enhance learners teaming and communicative skills as well as their global awareness. It models learning done throughout the learners lifetime by expanding the learning space to include not just peers but also mentors and experts from different fields.
By promoting Creative Learning.
ICT-supported learning promotes the manipulation of
existing information and the creation of real-world products rather than the regurgitation of received information.
By promoting Integrative learning.
ICT-enhanced learning promotes a thematic,
integrative approach to teaching and learning. This approach eliminates the artificial separation between the different disciplines and between theory and practice that characterizes the traditional classroom approach.
By promoting Evaluative learning.
ICT-enhanced learning is student-directed and
diagnostic. Unlike static text- or print-based educational technologies, ICT-enhanced learning recognizes that there are many different learning pathways and many different articulations of knowledge. ICTs allow learners to explore and discover rather than merely listen and remember.
Aspect
Less Traditional Pedagogy
Activities prescribed by teacher Whole class instruction Little variation in activities Pace determined by the program Individual Homogeneous groups Each one for himself/herself
Emerging Pedagogy for the Information Society
Activities determined by learners Small groups Many different activities Pace determined by learners Working in teams Heterogeneous groups Supporting each other
Active
Collaborative
Aspect
Less Traditional Pedagogy
Emerging Pedagogy for the Information Society
Integrating theory and practice Relations between subjects Thematic Teams of teachers
Integrative
No link between theory and practice Separate subjects Discipline-based Individual teachers
Choose ICT according to educational outcome(s) being targeted !!!!!!
ICT uses in Education
presentation demonstration
drill and practice
interaction collaboration
ICTs: Print, Audio/Video Cassette, Radio and TV Broadcast, Computers or the Internet
Direct class teaching:
Broadcast radio lectures Winneba radio
lecture Broadcasting religious teachings
General educational programming over community, national and international stations
PSI radio/television broadcasts Educational game shows
Teleconferencing refers to an interactive electronic communication among people located at two or more different places. There are four types:
1) audio-conferencing 2) audio-graphic conferencing 3)videoconferencing; and 4) Web-based conferencing.
Use of ICTs is not a panacea to solving educational problems:
Roblyer (Integrating Educational Technology into
Teaching, 2003 p.8) Integrated Learning Systems have
taught that most current capable technology resources offer no quick, easy, or universal solutions.
Cuban (2001) technology was oversold.. and not
having the system changing impact many thought it would. more problems than it solves.
Trend (2001) overuse of distance learning can create
To what extent has use of ICT raised the quality of education?
The effect of radio and telivision broadcast on the
quality of basic education is under-researched but little research out there suggests that these interventions are as effective as classroom teaching. Assessments of use of computers,Internet and related technologies on test scores are equivocal in asserting that there is no significant difference between such interventions and traditional classroom teaching
Cost of Using ICT interventions in Education - Expensive
FIXED COSTS
Retrofitting of physical facilities Hardware and networking Software Upgrades and replacement (in about five years)
VARIABLE OR RECURRENT COSTS
Professional development Connectivity, including Internet access and telephone time Maintenance and support, including utilities and supplies
Is there equity of access to ICTs in education?
There are disparities between rich and poor
countries Absence of careful deliberation, can result in the further marginalization of those who are already underserved and/or disadvantaged.
Are ICT-enhanced educational projects sustainable?
History of development aid has shown that too
many projects and programs start with a bang but all too soon fade out with a whimper, to be quickly forgotten Economic sustainability: Schools are not able to find funds to finance ICT enabled programs
Social sustainability :
Results in lack of buy-in of parents, political
leaders, business leaders and other stakeholders
Political sustainability
refers to issues of policy and leadership. One of
the biggest threats to ICT- enabled projects is resistance to change.
What are the implications of ICT-enhanced education for educational policy and planning?
Ghana ICT for Accelerated Development (ICT4D)
seeks to transform education to produce citizens with requisite technology skills to enable them become functional participants in a technology-driven and information-rich global economy ICT introduced in curriculum of all teacher preparation institutions and at pre-tertiary and basic education levels
University of Education ICT policy
seeks to utilize ICT to enhance students skills and knowledge, improve curriculum delivery and enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the institution All students must pass, at least, a course in ICT
What are the infrastructure-related challenges in ICT-enhanced education?
Electricity
ICT equipment
Rooms and Buildings to house ICT
What are the challenges with respect to capacity-building?
Teacher professional development
Reading : e-primer ICT in Education by Victoria L. Tinio
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Creativity in Secondary EducationDocument143 paginiCreativity in Secondary Educationmariana henteaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Level of Readiness: Results and DiscussionDocument14 paginiLevel of Readiness: Results and DiscussionUchayyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Research 2 Chapter 1 Group11 Almost DoneDocument18 paginiPractical Research 2 Chapter 1 Group11 Almost DoneGin Ramos100% (1)
- SEVEN-PHILOSOPHIES ofDocument2 paginiSEVEN-PHILOSOPHIES ofJohn Lloyd DizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gitanjali Stevens - Philosophy of EducationDocument2 paginiGitanjali Stevens - Philosophy of Educationapi-251096761Încă nu există evaluări
- Formal Operational StageDocument7 paginiFormal Operational Stage933484100% (3)
- Topic 8 Collaborative SkillsDocument40 paginiTopic 8 Collaborative SkillsSegar Raja ManickamÎncă nu există evaluări
- ) Educational Phychology - 2022-2023Document27 pagini) Educational Phychology - 2022-2023JUSTINEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Second Language AcquisitionDocument3 paginiSecond Language AcquisitionHazel Abila0% (1)
- Career Counselling - Constructivist ApproachesDocument120 paginiCareer Counselling - Constructivist Approacheslareinalau66Încă nu există evaluări
- Prof Ed Let ReviewerDocument51 paginiProf Ed Let ReviewerLara Charisse BalonzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Page 31Document82 paginiPage 31AshutoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 GROUP 7 Home Based Learning Development Perception of Office Administration in PaterosDocument36 pagini2 GROUP 7 Home Based Learning Development Perception of Office Administration in Paterosnhenzkie ortilanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- E-Assessment Through The Moodle SystemDocument36 paginiE-Assessment Through The Moodle SystemVivian Dagohoy EchalicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fish Processing Technology-IDocument106 paginiFish Processing Technology-IKRISHNA KUMAR100% (1)
- Most Cited Papers PDFDocument429 paginiMost Cited Papers PDFMua Rai Rayna100% (2)
- UNIT1 Authentic AssessmentDocument18 paginiUNIT1 Authentic AssessmentHizzel De CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emotions in the Qur'an OverviewDocument40 paginiEmotions in the Qur'an OverviewKaisarDjafarMedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedagogy and Practice in EducationDocument13 paginiPedagogy and Practice in EducationJosias SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prof Ed Q&aDocument41 paginiProf Ed Q&aMaria Garcia Pimentel Vanguardia IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Impact of Internet Virtual Physics Laboratory Instruction On The Achievement in Physics, Science Process Skills and Computer Attitudes of 10th-Grade StudentsDocument11 paginiThe Impact of Internet Virtual Physics Laboratory Instruction On The Achievement in Physics, Science Process Skills and Computer Attitudes of 10th-Grade StudentsRandy YimooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genre Based ApproachDocument6 paginiGenre Based ApproachLow CscÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contextual LearningDocument11 paginiContextual Learningluck2ang100% (1)
- DLP Observation 1 EAPPDocument3 paginiDLP Observation 1 EAPPMaann KatJacobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emergent Literacy Theories and Child DevelopmentDocument50 paginiEmergent Literacy Theories and Child DevelopmentMaria Victoria Padro100% (3)
- Unit 3.3 Cognitive Process Module 14: Constructivism: Knowledge Construction/ Concept LearningDocument6 paginiUnit 3.3 Cognitive Process Module 14: Constructivism: Knowledge Construction/ Concept LearningMaria TML100% (1)
- Philosophy of Educationsample Isms With Answersclue KeywordpdfDocument16 paginiPhilosophy of Educationsample Isms With Answersclue KeywordpdfScribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erickson Concept - Based - Teaching - Learning PDFDocument13 paginiErickson Concept - Based - Teaching - Learning PDFjillysillyÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Grade Level 9 Teacher Learning Area Mapeh-Art Date Quarter FirstDocument3 paginiSchool Grade Level 9 Teacher Learning Area Mapeh-Art Date Quarter Firsthendrix obcianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Students' Problem Solving Skills in Mathematics With Peer Tutoring Math Pen-MateDocument5 paginiStudents' Problem Solving Skills in Mathematics With Peer Tutoring Math Pen-MateEuchel Pauline Doble RamosÎncă nu există evaluări