Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Liver
Încărcat de
sekiannTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Liver
Încărcat de
sekiannDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Liver Disease - What I will learn
Some basic liver anatomy, function and histology What are the common viral infections of the liver An understanding of Cirrhosis How gallstones are formed
Functions of the Liver
Metabolism of ingested carbohydrates, protein Fat delivered through the portal circulation Synthesis of proteins
plasma proteins Coagulation proteins
Functions of the Liver
Storage of vitamin B12 and other materials Detoxification and excretion of various substances
Liver Structure
Has a double blood supply from the hepatic artery and portal vein Portal tracts travel together
Hepatic artery Portal vein Bile ducts Lymphatic vessels
Liver, basic lobule, or acini
Bile
Bile pigment is derived from the breakdown of red blood cells Bile pigment is conjugated and excreted by the liver
Bile
An aqueous solution containing various dissolved substances
Conjugated bilirubin, bile salts, lecithin, cholesterol, water, minerals
Functions as a biologic detergent
Liver Injury
Manifestations
Cell necrosis Immune cell infiltration Fatty change Mixed necrosis and fatty change Later, fibrosis
Common Types of Liver Injury
Viral hepatitis
Hep A, B, C, etc
Alcoholic hepatitis Cirrhosis
Scarring, which is end result of acute injury
Hepatitis A
RNA virus Fecal-oral method of transmission, ie eating at the wrong place Self-limiting disease with no carriers and no chronic liver disease Hep A antibody appears at the time of symptoms Prevention after exposure Immunization available
Hepatitis B
DNA containing virus Blood or body fluid method of transmission 300 million carriers worldwide Most shed the virus, however, 10% become carriers and may develop chronic liver disease Prevention after exposure Immunization available
Hepatitis C
RNA containing virus Blood and body fluids method of transmission Most important cause of transfusion associated hepatitis 75% become carriers and many develop chronic liver disease HCV RNA detected for 1-3 weeks, but may persist No prevention of disease after exposure No immunization available
Alcoholic Liver Disease
Three stages of progression
fatty liver reversible Hepatitis - reversible The above two can lead to cirrhosis - irreversible
Cirrhosis of the Liver
Diffuse scarring (Cirrhosis) of the liver from any cause
Alcoholic liver disease Chronic hepatitis An episode of severe liver necrosis Other drugs and chemicals Longstanding bile duct obstruction
Manifestations of Cirrhosis of the Liver
Liver failure Liver unable to inactivate estrogen in males
Testicular atrophy, loss of sex drive, breast hypertrophy Ascites, collateral circulation formation
Portal hypertension
Manifestations of Cirrhosis of the Liver
Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
Incidence
Higher in women than men Higher in women who have borne several children Twice as high in women who use contraceptive pills Higher in obese women
Cholelithiasis
Cholesterol stones Cholesterol is soluble when mixed with water soluble bile salts and insoluble lecithins Once cholesterol exceeds the solubilizing capacity of bile, cholesterol crystalizes
Cholecystitis
Chronic disease common Gallstones may predispose to cholecystitis Impaction of a stone in the neck of the gallbladder may precipitate acute cholecystitis
Tumors of the Liver
Benign adenomas Primary carcinoma
Called Hepatocellular Carcinoma, related to Hep B Spread from primary sites most common type of tumors, Colonic cancer is common primary tumor
Metastatic carcinoma
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Liver CirrhosisDocument2 paginiLiver CirrhosisAzette Agpi100% (3)
- Liver: Created By: Group 3 Ashabul Kahfi M.Nanta.Z Shalsabila Qathrunnada Raihan RahmadhaniDocument29 paginiLiver: Created By: Group 3 Ashabul Kahfi M.Nanta.Z Shalsabila Qathrunnada Raihan RahmadhaniMuhammad Nanta ZachriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas ProblemsDocument95 paginiLiver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas ProblemsBav VAansoqnuaetzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesDe la EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirohsis of LiverDocument29 paginiCirohsis of LiverAnonymous L95gMHSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hepatobiliary System Functions of The Liver IncludeDocument19 paginiHepatobiliary System Functions of The Liver IncludeRacha MougharbelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disorders of The Hepatobiliary System: Dr. Mehzabin AhmedDocument27 paginiDisorders of The Hepatobiliary System: Dr. Mehzabin Ahmedbpt2100% (1)
- Chapter 8Document89 paginiChapter 8Harith AtrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- MetabolismDocument39 paginiMetabolismTiffany KnepperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hepatic Cirrhosis (肝硬化): Yu BaopingDocument62 paginiHepatic Cirrhosis (肝硬化): Yu BaopingKurbulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toxicity of The Liver Lecture 20-21Document28 paginiToxicity of The Liver Lecture 20-21h9g886qdnpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sirrhosis HatiDocument6 paginiSirrhosis HatikimokberusungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On Cirrhosis of LiverDocument34 paginiPresentation On Cirrhosis of LiverAnshu kumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 - Git2 'Document44 pagini8 - Git2 'ALNAKIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primary Biliary CholangitisDocument23 paginiPrimary Biliary CholangitisAbdul hadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver CirrohosisDocument157 paginiLiver CirrohosisSeema SachdevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Case Study of Liver CirrhosisDocument13 paginiMy Case Study of Liver Cirrhosisdysphile100% (1)
- PH Le BotomyDocument15 paginiPH Le BotomyPatty MenéndezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology - The LiverDocument66 paginiPathophysiology - The LiverMichelle BilayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Med Surg Test 4 Study GuideDocument29 paginiMed Surg Test 4 Study GuideJessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Askep SirosisDocument73 paginiAskep SirosisRisma Yuliana PratiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- With Ordinary Talent and Extraordinary Perseverance, All Things Are Attainable.Document72 paginiWith Ordinary Talent and Extraordinary Perseverance, All Things Are Attainable.Ainun JaariahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis 22008 Bajar Musica Gratis Descargar Musica Gratis Online Descargar Musica Gratis para CelularesDocument72 paginiCirrhosis 22008 Bajar Musica Gratis Descargar Musica Gratis Online Descargar Musica Gratis para CelularesYeni Chie Aneuk TuleutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Liver FailureDocument4 paginiChronic Liver FailureJasmine Faith SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocument35 paginiCirrhosis of LiverShazia Parveen100% (1)
- NCM Lecture (Liver and Gallbladder)Document76 paginiNCM Lecture (Liver and Gallbladder)beer_ettaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hepatic Cirrhosis and Hepatitis: Dr. Lubna DwerijDocument69 paginiHepatic Cirrhosis and Hepatitis: Dr. Lubna DwerijNoor MajaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 13 - Obesity and HepaticDocument91 paginiWeek 13 - Obesity and HepaticEditha LucasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case StudyDocument24 paginiCase StudyPatricia Marie BuenafeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Cirrhosis: A Case Study OnDocument31 paginiLiver Cirrhosis: A Case Study OnCharmaine del RosarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- LECTURES Liver PathophysiologyDocument118 paginiLECTURES Liver PathophysiologyTarik100% (1)
- Pediatric Renal & Genitourinary DisordersDocument72 paginiPediatric Renal & Genitourinary DisordersMarie Angelique Cruz CrestaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver CirrhosisDocument15 paginiLiver CirrhosisAngelica Mercado Sirot100% (1)
- Pathology of The Liver, Biliary Tract andDocument64 paginiPathology of The Liver, Biliary Tract andembeoyabarareÎncă nu există evaluări
- 97Document79 pagini97HATLERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis of The LiverDocument4 paginiCirrhosis of The LiverDaphineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Farmakologi Enterohepatal: Noor WijayahadiDocument134 paginiFarmakologi Enterohepatal: Noor WijayahadiYuni IsmulyatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Liver DiseaseDocument30 paginiChronic Liver Diseaseprajwal86% (7)
- Liver CirrhosisDocument4 paginiLiver CirrhosisromyÎncă nu există evaluări
- With Ordinary Talent and Extraordinary Perseverance, All Things Are Attainable.Document72 paginiWith Ordinary Talent and Extraordinary Perseverance, All Things Are Attainable.Darin MonerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sily MarinDocument6 paginiSily MarinBanc OanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis: On This PageDocument23 paginiCirrhosis: On This PageHasna FauziyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Liver FailureDocument25 paginiChronic Liver FailureMohamed Na3eemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 8-Liver Cirrhosis-DonghitDocument8 paginiActivity 8-Liver Cirrhosis-DonghitAllona Jane Beatrice DonghitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis Description Highlights Causes of CirrhosisDocument18 paginiCirrhosis Description Highlights Causes of Cirrhosisen-oleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fulminant Hepatic FailureDocument10 paginiFulminant Hepatic FailureAira Anne Tonee VillaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorDocument22 paginiLiver Cirrhosis: Precipitating Factors: Predisposing FactorJorie RocoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis of The Liver: GlossaryDocument21 paginiCirrhosis of The Liver: GlossaryNophÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alcoholic Liver Disease: Last Updated: January 19, 2024Document16 paginiAlcoholic Liver Disease: Last Updated: January 19, 2024Tselmeg TselmegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis of Liver: Shemil Clinical Instructor DmwimsDocument25 paginiCirrhosis of Liver: Shemil Clinical Instructor DmwimsSrihari DivyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12Document8 paginiChapter 12newmexicoomfsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 GallbladderDocument36 pagini1 Gallbladdercephas chinkoliÎncă nu există evaluări
- HepatitisDocument3 paginiHepatitisRosendo Dacuyan100% (1)
- What Is Sclerosis of The LiverDocument2 paginiWhat Is Sclerosis of The LiverLuinel PlasenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver CirrhosisDocument86 paginiLiver CirrhosisKenMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cirrhosis and ComplicationsDocument19 paginiCirrhosis and ComplicationsTogaju KuboyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Cirrhosis: Irish Nicole Dela Cruz Gessel Ann BoguenDocument79 paginiLiver Cirrhosis: Irish Nicole Dela Cruz Gessel Ann BoguenIrish Nicole DCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver NotesDocument2 paginiLiver NotesAnne IsheeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Askep HepaticDocument52 paginiAskep HepaticNia AnjarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. Primary GlaucomaDocument5 paginiA. Primary GlaucomasekiannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of NeuropathyDocument16 paginiClassification of NeuropathysekiannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definisi Shock, Klasifikasi Shock, Stadium ShockDocument8 paginiDefinisi Shock, Klasifikasi Shock, Stadium ShocksekiannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transverse Myelitis: Differential DiagnosisDocument14 paginiTransverse Myelitis: Differential DiagnosissekiannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ann Arbor Staging System For Hodgkin's DiseaseDocument3 paginiAnn Arbor Staging System For Hodgkin's DiseasesekiannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bowen's DiseaseDocument2 paginiBowen's DiseasesekiannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erythroplasia of QueyratDocument2 paginiErythroplasia of QueyratsekiannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tumor OtakDocument47 paginiTumor OtaksekiannÎncă nu există evaluări
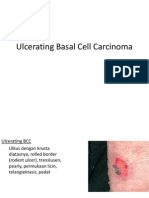
- Ulcerating Basal Cell CarcinomaDocument2 paginiUlcerating Basal Cell CarcinomasekiannÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carcinoma Gall BladderDocument25 paginiCarcinoma Gall Bladderrajan kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of GallbladderDocument14 paginiAnatomy of GallbladderSamridhi DawadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of The LiverDocument2 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of The LiverAldjen SetiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 177096869007065675Document371 pagini5 177096869007065675sillypolo100% (1)
- Stones in Galbladder - Pitay Ki Pathri - Homeopathic MedicineDocument4 paginiStones in Galbladder - Pitay Ki Pathri - Homeopathic MedicineParwaz KamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Qns v2Document37 paginiBiology Qns v2randomvidsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Presentation On - Jaundice NewDocument50 paginiCase Presentation On - Jaundice NewSara NoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Abscess Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDocument2 paginiLiver Abscess Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsAdi Kurnia100% (1)
- 13850bio Guess PaperDocument10 pagini13850bio Guess PaperJayaram GowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Checklist Mgu Sabtu 2016Document3 paginiChecklist Mgu Sabtu 2016dudi herlambangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDocument22 paginiAlcoholic Liver DiseaseMiraen MkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument33 paginiNeonatal JaundiceVaibhav Krishna100% (2)
- Data Mining UTS - KELOMPOK 4 (TI 3 A) - Resume Jurnal Internasional 2 BaruDocument10 paginiData Mining UTS - KELOMPOK 4 (TI 3 A) - Resume Jurnal Internasional 2 BaruFaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section D - Work BookDocument69 paginiSection D - Work BookMohamed AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument20 paginiUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationShivraj NaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pamphlet Liver BiopsyDocument8 paginiPamphlet Liver BiopsyManisha ShakyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- وظيفة الجهاز الهضميDocument4 paginiوظيفة الجهاز الهضمياحمد خالدÎncă nu există evaluări
- 100 Weird Facts About The Human BodyDocument11 pagini100 Weird Facts About The Human BodyramneetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive Disorders in Tortoises From Vetlexicon ReptileDocument4 paginiDigestive Disorders in Tortoises From Vetlexicon Reptilemomo689Încă nu există evaluări
- Nomzamo The Good Wife Part 2Document5 paginiNomzamo The Good Wife Part 2prayerntandwenhleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Owl NecropsyDocument3 paginiOwl Necropsykezia_stephanie_1Încă nu există evaluări
- Learn Nadi ParikshaDocument5 paginiLearn Nadi ParikshapjpropraveenssÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALF 418RLE Group1Document22 paginiALF 418RLE Group1PAOLA LUZ CRUZÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Role of Speaking in Academic ContextDocument16 paginiThe Role of Speaking in Academic ContextYoo ChenchenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Anatomy and Physiology MedicineDocument73 paginiLiver Anatomy and Physiology MedicineRobin TolentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy One LinersDocument10 paginiAnatomy One Linersridin007100% (2)
- Urinalysis How To Interpret Results PDFDocument3 paginiUrinalysis How To Interpret Results PDFАбу ДжудÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leptospirosis CompiledDocument76 paginiLeptospirosis CompiledTine Mendoza100% (1)
- 1994 Changing Body Composition Through Diet and Exercise GuidebookDocument250 pagini1994 Changing Body Composition Through Diet and Exercise GuidebookStef StenfordÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rabbit Soft Tissue Surgery: Zoltan Szabo,, Katriona Bradley,, Alane Kosanovich CahalaneDocument30 paginiRabbit Soft Tissue Surgery: Zoltan Szabo,, Katriona Bradley,, Alane Kosanovich CahalaneTayná P DobnerÎncă nu există evaluări