Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
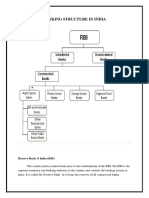
Development Banks
Încărcat de
khatiwada2005Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Development Banks
Încărcat de
khatiwada2005Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Development banks are the institutions engaged in the promotion and development of industry, agriculture and other key
sectors.
National or regional financial institution designed to provide mediumand long-term capital for productive investment. Such investment is usually accompanied by technical assistance.
Some development banks are government-owned, while others are private. Many have been established under the auspices of the World Bank.
Among the largest are the Inter-American Development Bank, the Asian
Development Bank, and the African Development Bank.
A development bank does not accept deposits from the public like commercial banks and other financial institutions who entirely depend upon saving mobilization. It is a specialized financial institution which provides medium term and long-term lending facilities.
It is a multipurpose financial institution. Besides providing
financial help it undertakes promotional activities also. It helps an enterprises from planning to operational level.
It provides financial assistance to both private as well as
public sector institutions.
The role of a development bank is of gap filler, when assistance from other sources is not sufficient then this channel helps. It does not compete with normal channels of finance.
Development banks primarily aim to accelerate the rate of growth. It helps industrialization specific and economic development in general.
The objective of these banks is to serve public interest rather than earning profits.
Development banks react to the socio-economic needs of development.
Lay Foundations for Industrialization
Meet Capital Needs
Need for Promotional Activities
Help Small and Medium Sectors'
Financial Gap Fillers Undertake Entrepreneurial Role Joint Finance
Refinance Facility
Credit Guarantee Underwriting of Securities
The recommendation for setting up industrial financing institutions was made in 1931 by Central Banking Enquiry Committee but no concrete steps were taken.
In 1949, Reserve Bank had undertaken a detailed study to find out the need for
specialized institutions.
It was in 1949 that the first development bank i.e. Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI) was established.
In 1951, Parliament passed State Financial Corporation Act. Under this Act state governments could establish financial corporations for their respective regions.
The IFCI and state financial corporations served only a limited purpose. There was
a need for dynamic institutions which could operate as true development agencies.
The Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI) were established in 1955 as a Joint Stock Company. Though ICICI was established in private sector but its pattern of shareholding and methods of raising funds gives it the characteristic of a public sector financial institution.
Another institution ,Refinance Corporation for Industry Ltd. (RCI) was set up in 1958
by Reserve Bank of India, LIC and Commercial Banks.
In 1964, Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI) was set up as an apex institution in the area of industrial finance, RCI was merged with IDBI. IDBI was a wholly owned subsidiary of RBI and was expected to co-ordinate the activities of the
institutions engaged in financing, promoting or developing industry.
The State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDC's) were established in the sixties to promote medium scale industrial units.
8
The State Small Industries Development Corporations (SSIDC's) were also set up to cater to the needs of industry at state level.
The Unit Trust of India (UTI) established in 1964, Life Insurance Corporation of India (1956) and General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC) set up in 1973 also finance industrial activities at all India level.
In 1982 the Export-Import Bank of India (Exim Bank) was established to provide financial assistance to exporters and importers.
In order to meet credit needs of agriculture and rural sector, National' Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) was set up in 1982.
9
Providing Funds
Infrastructural Facilities
Promotional Activities Development of Backward Areas Planned Development Accelerating Industrialization Employment Generation
10
Set-up in 1948 to provide institutional credit to medium and large industries. Project financing: Medium/Long term credit for setting up new project, expansion schemes, financial assistance by way of rupee loans, loans in foreign currencies, underwriting of direct subscription of shares/debentures. Financial Services and corporate advisory services.
Established in 1964 for coordinating the working of institutions at national level and state levels engaged in financing, promoting and developing industries. Provides merchant banking & corporate advisory services as a part of its fee based activities. Provide advice & services for issue management, private placement of equity/debt instrument, project evaluation, corporate restructuring etc.
Set up in 1990, the principal financial institution for the promotion, financing and development of industries in the small sector and to co-ordinate the functions of other institutions engaged in similar activities. An apex institution, SIDBI makes use of the network of the banks and state financial institutions. Financial Products- Micro finance, venture capital, project finance, assistance for technology development, export finance etc.
An apex institution which promotes foreign trade. Creating export capability by arranging competitive financing at various stages of export cycle. Bank provides export credit on deferred payment terms on exports of indian machinery, manufactured goods and technology services.
An apex institution set up for providing & regulating credit and other facilities for the promotion & development of agriculture, small scale industries, cottage & village industries, handicrafts and other rural crafts and other allied economic activities in rural areas.
First development bank in the world to be set up in the private sector Objective is to provide medium-term & long-term financing to Indian business. ICICI Securities & Finance Co. Ltd. ICICI Venture Funds Management Co. Ltd. ICICI Prudential Life Insurance ICICI Home Finance Co. Ltd. ICICI Investment Management Co. Ltd.
The Infrastructure Development Finance Company Limited (IDFC ) India's leading integrated infrastructure finance player providing end-to-end infrastructure financing and project implementation services
Discount and Finance House of India Ltd. a unique institution of its kind, was set up in April 1988. The discount has been established to deal in money market instruments in order to provide liquidity in the money market.
The Sub-Group on Housing Finance for the Seventh Five Year Plan (1985-90) identified the non-availability of long-term finance to individual households
It is responsible for the development of industries in the state by formulating policies that help industry growth, and also by establishing Industrial Estates.
There are three investment institutions:
Life Insurance Corporation of India Ltd.,
Unit Trust of India and
General Insurance Corporation of India.
At state level there are 18 State Finance Corporations and 28 state industry development corporations.
21
Survey of Backward Areas Inter institutional Groups (IIGs) Establishment technical Consultancy Organizations (TCOs) Entrepreneurial Development Programs (EPPs) Technological Improvements
23
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Brief History of RBI: Hilton Young CommissionDocument24 paginiBrief History of RBI: Hilton Young CommissionharishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction of RbiDocument63 paginiIntroduction of RbiAshley BakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Banking Sector in IndiaDocument29 paginiBanking Sector in Indiahahire0% (1)
- SEBIDocument29 paginiSEBISanjana Sen100% (1)
- Project Role of RBI Word Doc.3Document66 paginiProject Role of RBI Word Doc.3nilesh dhivreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regulatory Framework For Banking in IndiaDocument12 paginiRegulatory Framework For Banking in IndiaSidhant NaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organizational Structure, Development of Banks in IndiaDocument54 paginiOrganizational Structure, Development of Banks in Indiaanand_lamani100% (1)
- RBI Credit Control Objectives & MethodsDocument10 paginiRBI Credit Control Objectives & MethodsRishi exportsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bhavna Patil (NBFC)Document55 paginiBhavna Patil (NBFC)BHAVNA PATIL100% (3)
- University of Mumbai: "75 Years of Reserve Bank of India"Document109 paginiUniversity of Mumbai: "75 Years of Reserve Bank of India"Harshal Chavan100% (1)
- A STUDY OF ACCOUNTING AND STATUTORY REQUIREMENT OF SAI KRUPA C.H.S (Nerul East)Document29 paginiA STUDY OF ACCOUNTING AND STATUTORY REQUIREMENT OF SAI KRUPA C.H.S (Nerul East)Pankaj Rathod67% (3)
- LIQUIDATION CASE STUDIES ON COMPANIESDocument7 paginiLIQUIDATION CASE STUDIES ON COMPANIESsuresh100% (1)
- Difference Between A Private LTD and Public LTDDocument4 paginiDifference Between A Private LTD and Public LTDShoaib Shaik0% (1)
- Commercial BankDocument13 paginiCommercial BankVedant JhunjhunwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of RBI in Indian EconomyDocument4 paginiRole of RBI in Indian EconomySubhashit SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Banking Financial CompanyDocument39 paginiNon Banking Financial Companymanoj phadtareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report On Sutex BankDocument55 paginiReport On Sutex Bankjkpatel221Încă nu există evaluări
- Finanial Analysis of HDFC BankDocument15 paginiFinanial Analysis of HDFC BankShweta SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emerging Issues of MicrofinanceDocument2 paginiEmerging Issues of MicrofinanceAthira VenugopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On Government (Gilt Edged) SecuritiesDocument22 paginiPresentation On Government (Gilt Edged) Securitieshiteshnandwana100% (1)
- A Comparative Study of NBFCs in IndiaDocument28 paginiA Comparative Study of NBFCs in IndiaGuru Prasad0% (1)
- Lead Bank SchemeDocument8 paginiLead Bank Schemebistamaster100% (2)
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument10 paginiReserve Bank of Indiatejaskamble45Încă nu există evaluări
- Evolution of Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument6 paginiEvolution of Reserve Bank of IndiamotherfuckermonsterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial AccountingDocument36 paginiFinancial Accountingkhanafsha100% (1)
- Sutex Co-Op Bank ProjectDocument49 paginiSutex Co-Op Bank ProjectHinal Prajapati100% (4)
- Project On NBFCDocument67 paginiProject On NBFCkumar12925359Încă nu există evaluări
- PPT of Role of Rbi Policies Functions and ProhibitoryDocument17 paginiPPT of Role of Rbi Policies Functions and Prohibitoryr.vani75% (4)
- Investment Banking ProjectDocument16 paginiInvestment Banking Projectdevarakonda shruthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foreign BanksDocument9 paginiForeign Banks1986anuÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCA & RD Bank PDFDocument86 paginiPCA & RD Bank PDFmohan ks100% (2)
- Merchant Banking Meaning - Functions of Merchant Banking PDFDocument3 paginiMerchant Banking Meaning - Functions of Merchant Banking PDFkadalarasane83% (6)
- Various Types of Companies Under Companies Act, 1956-11Document54 paginiVarious Types of Companies Under Companies Act, 1956-11Upneet Sethi67% (3)
- Role of RBI in Indian Financial MarketsDocument5 paginiRole of RBI in Indian Financial MarketsBiswajit Paul100% (2)
- Banking Structure in IndiaDocument49 paginiBanking Structure in IndiaAjay RapelliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reserve Bank of IndiaDocument21 paginiReserve Bank of IndiaAcchu BajajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synopsis On The Study of Home LoansDocument5 paginiSynopsis On The Study of Home LoansRajul Rkg0% (1)
- The Industrial Finance Corporation of India (Ifci)Document15 paginiThe Industrial Finance Corporation of India (Ifci)manumadhu0% (1)
- Presentation on Amalgamation and Merger of BanksDocument14 paginiPresentation on Amalgamation and Merger of BanksKrishnakant Mishra100% (1)
- RBI's Role and FunctionsDocument51 paginiRBI's Role and Functionspadmavathi mandry100% (1)
- Financial Ratio Analysis of SBI and ICICI BankDocument32 paginiFinancial Ratio Analysis of SBI and ICICI BankDeepika KalimuthuÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Analysis of The Customers' Attitude, Preference and Satisfaction Level Towards Investment in Icici Prudential Life Insurance Company Limited, Adyar, Chennai.Document73 paginiA Study On Analysis of The Customers' Attitude, Preference and Satisfaction Level Towards Investment in Icici Prudential Life Insurance Company Limited, Adyar, Chennai.Srisudharsana Giri Kpr100% (1)
- A Research Project On Credit Risk and Liquidity RiskDocument86 paginiA Research Project On Credit Risk and Liquidity RiskEkam JotÎncă nu există evaluări
- IFCI (Industrial Finance Corporation of India)Document12 paginiIFCI (Industrial Finance Corporation of India)sapnasingh55576Încă nu există evaluări
- Functions of Commercial Banks ReportDocument14 paginiFunctions of Commercial Banks ReportAryan Khan50% (2)
- Sip Project of UbiDocument75 paginiSip Project of UbiArgha MondalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Banking Sector ReformsDocument131 paginiIndian Banking Sector Reformsanikettt50% (2)
- ConclusionDocument2 paginiConclusionezekiel50% (2)
- Co Operative BankDocument52 paginiCo Operative BankDevendra SawantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution and Organizational Structure of SBIDocument6 paginiEvolution and Organizational Structure of SBIpandisivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- State Co-Operative Bank LatestDocument29 paginiState Co-Operative Bank LatestAhana SenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development BanksDocument24 paginiDevelopment Bankssumit_garg_93Încă nu există evaluări
- INSTITUTION PROVIDING FINANCIAL HELP TO ENTREPRENEURSDocument24 paginiINSTITUTION PROVIDING FINANCIAL HELP TO ENTREPRENEURSjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Small Industrial Development Bank of IndiaDocument32 paginiSmall Industrial Development Bank of IndiahariniariesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development Banks FinalDocument13 paginiDevelopment Banks Finalsamritigoel67% (6)
- Importance of Financial Instituitions in EntrepreneurshipDocument7 paginiImportance of Financial Instituitions in EntrepreneurshiphimanshuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development Banking in IndiaDocument10 paginiDevelopment Banking in IndiaAkshay SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development Banking in IndiaDocument39 paginiDevelopment Banking in IndiaMonika RaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entrepreneurship 03 InstitutionsDocument8 paginiEntrepreneurship 03 InstitutionsManganÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASSIGNMENTDocument18 paginiASSIGNMENTeldhopaul19894886Încă nu există evaluări
- Abdhini Biswas Product CannibalisationDocument45 paginiAbdhini Biswas Product Cannibalisationabdhini biswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polar Sports, IncDocument15 paginiPolar Sports, IncJennifer Jackson91% (11)
- Indian Money Market: An Overview of Key Components and CharacteristicsDocument13 paginiIndian Money Market: An Overview of Key Components and CharacteristicsSachin MethreeÎncă nu există evaluări
- AVEVA CoW BrochureDocument8 paginiAVEVA CoW BrochureerikestrelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICS: INTEREST RATES, INVESTMENT, AND AGGREGATE DEMANDDocument4 paginiINTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICS: INTEREST RATES, INVESTMENT, AND AGGREGATE DEMANDCördïî X Cördïî100% (1)
- CRM challenges in investment banking and financial marketsDocument16 paginiCRM challenges in investment banking and financial marketssarferazul_haqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- MFC-I Syllabus for 2011-2012 and 2012-2013 SessionsDocument11 paginiMFC-I Syllabus for 2011-2012 and 2012-2013 SessionsangelagarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Accounting 2Document4 paginiPractical Accounting 2RajkumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Study Resource Was: The Cost of Capital For Hubbard Computer, IncDocument5 paginiThis Study Resource Was: The Cost of Capital For Hubbard Computer, IncErro Jaya RosadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial PlanningDocument7 paginiFinancial PlanningLieza Jane AngelitudÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALFI and ABBL Guidelines and Recommendations For Depositaries Safekeeping of Other AssetsDocument62 paginiALFI and ABBL Guidelines and Recommendations For Depositaries Safekeeping of Other AssetsludivineÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoalAsia 66 LowresDocument122 paginiCoalAsia 66 LowresDery Oktory NofendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Andex Wall CANENGDocument1 paginăAndex Wall CANENGhyporÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Sector ReformsDocument14 paginiFinancial Sector ReformsMinisha GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Manulife ProposalDocument7 paginiSample Manulife ProposalRicci MelecioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13 International FinanceDocument35 paginiChapter 13 International FinanceDivyesh GandhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Railway Rates in Re 032634 MBPDocument358 paginiRailway Rates in Re 032634 MBPdegiuseppeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Detective Case AnalysisDocument11 paginiFinancial Detective Case AnalysisBrian AlmeidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article StockbasedcompensationDocument29 paginiArticle StockbasedcompensationКостя КомаровÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions To A2StudyPack2012Document21 paginiSolutions To A2StudyPack2012Juncheng WuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1211Document201 pagini1211Angel CapellanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter9 - FinalDocument17 paginiChapter9 - FinalbraveusmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Luxury Consumer MarketDocument9 paginiLuxury Consumer MarketVicente J. CasanovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paytm crisisDocument6 paginiPaytm crisisrishikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equity Pick-Up Module & Customized Intercompany Matching: Fusion 11.1.1.2, HFM & ReportsDocument20 paginiEquity Pick-Up Module & Customized Intercompany Matching: Fusion 11.1.1.2, HFM & Reportssagiinfo1Încă nu există evaluări
- Legal Aspects of Finance: Case 1 Matti RudankoDocument19 paginiLegal Aspects of Finance: Case 1 Matti RudankoRahul RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report On Banking IndustryDocument91 paginiReport On Banking IndustrySachin MittalÎncă nu există evaluări
- KOMATSU Case SolutionDocument6 paginiKOMATSU Case SolutionSujeeth BharadwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To BacktestingDocument20 paginiAn Introduction To BacktestingwhitecrescentÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Decoupling Creates Win-Win For Power Companies and CustomersDocument11 paginiHow Decoupling Creates Win-Win For Power Companies and CustomersClutha Mata-Au River Parkway GroupÎncă nu există evaluări