Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Liver Cancer Intro
Încărcat de
Joeven HilarioDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Liver Cancer Intro
Încărcat de
Joeven HilarioDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
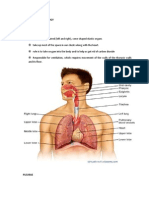
Largest gland in the body (1.
5 Kg) Under the diaphragm, within the rib cage in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen
Lobes Major: left and right Minor: caudate and quadrate Ducts Common hepatic Cystic Common bile Choledochus
From gallbladder
Joins pancreatic duct at hepatopancreatic ampulla
Liver lobules hexagonal structures consisting of hepatocytes Hepatocytes radiate outward from a central vein At each of the six corners of a lobule is a portal triad Liver sinusoids
Hepatocytes produce bile
Bile flows through canals called bile canaliculi to a bile duct
Bile ducts leave the liver via the common hepatic duct
BILE bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol, neutral fats, phospholipids and electrolytes
Liver produces 0.5-1 l of bile daily
Bile salts emulsify fats
LIVER
GALL BLADDER
Metabolic Synthesis Breakdown Other functions storage of vitamin A,D,B12,F Excretion of waste products from bloodstream into bile Vascular storage of blood
Protein metabolism Synthesis of amino acids Carbohydrate metabolism Gluconeogenesis Glycogenolysis Glycogenesis Lipid metabolism Cholesterol synthesis Lipogenesis Production of coagulation factors I, II, V, VII, IX, X and XI, and protein C, protein S and antithrombin Main site of red blood cell production Produces insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), a polypeptide protein anabolic effects Production of trombopoetin
Breaks down insulin and other hormones Breaks down hemoglobin Breaks down or modifies toxic substances (methylation) sometimes results in toxication Converts ammonia to urea
Produces albumin, the major osmolar component of blood serum Synthesizes angiotensinogen, the hormone responsible for raising blood pressure when activated by renin (enzyme released when the kidney senses low blood pressure)
Hepatic tumors maybe benign or malignant.
Benign liver tumors were uncommon until oral contraceptives were in wide spread
Now benign liver tumors occur most frequently in women in their reproductive years who are taking oral contraceptives
Primary liver tumors usually are associated with:
Chornic liver disease Hepatitis B and C infections Cirrhosis
is the most common type of primary liver cancer with more than half million cases diagnosed each year on a worldwide basis. HCC is the leading cause of cancer related to mortality worldwide.
1. LUNG CANCER 2. BREAST CANCER 3. LIVER CANCER 4. CERVICAL CANCER 5. COLORECTAL CANCER 6. THYROID CANCER 7. LEUKEMIA 8. GASTRIC CANCER 9. OVARIAN CANCER 10. PROSTATE CANCER
This cancer is more common among men than women and that the average age when liver cancer is diagnosed are between 50-60 years old. The common risk factors associated with this disease are chronic infection with hepatitis B and C, heavy alcohol use and cirrhosis or scarring of the liver, diabetes and obesity. STATISTICS: Most causes of liver cancer is secondary or metastatic, meaning it started elsewhere in the body. Primary liver cancer, which starts in the liver, accounts for about 2% of cancers in the U.S but up to 50% of all cancers in many undeveloped countries including the Philippines because of the predominance on infectious diseases. liver cancer accounts for 5,102 deaths (in every 100,000), according to the 2011 Phil Cancer Facts and Estimates.
Cirrhosis Chronic infection with Hepatitis B and C Exposure to some chemical toxins ( Vinyl Chloride, Arsenic) Cigarette Smoking especially when combined with alcohol
Cirrhosis
Exposure to some chemical toxins ( Vinyl Chloride, Arsenic)
A metabolite of the fungus Aspergillus flavus
Cholangiocellular carcinoma
Cholangiocellular carcinoma is a form of liver cancer that is composed of mutated epithelial cells (or cells showing characteristics of epithelial differentiation) that originate in the bile ducts which drain bile from the liver into the small intestine.
NEXT CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- Vi. Anatomy and Physiology The Lungs StructureDocument5 paginiVi. Anatomy and Physiology The Lungs StructureJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Ultimate Guide To Healthy Skin - LCONDocument26 paginiThe Ultimate Guide To Healthy Skin - LCONDenisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete Denture Case History ProformaDocument8 paginiComplete Denture Case History ProformaMrunal Doiphode100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Approach To HyponatremiaDocument47 paginiApproach To HyponatremiaRajiv MedankiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Fruit Sugar PDFDocument2 paginiUnderstanding Fruit Sugar PDFBobÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 Non-Vegetarian Weekly Diet Plan With Protein SupplementsDocument16 pagini1.1 Non-Vegetarian Weekly Diet Plan With Protein SupplementsAnil TalariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8-Gastroenterology and HepatologyDocument193 pagini8-Gastroenterology and HepatologythisarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chevron Safety Bulletin 2008Document12 paginiChevron Safety Bulletin 2008somayajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Food Poisoning Final Print!Document3 paginiFood Poisoning Final Print!Joeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiFamily Nursing Care PlanJoeven Hilario83% (6)
- Osteosarcoma Case StudyDocument17 paginiOsteosarcoma Case StudyJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osteosarcoma Case StudyDocument17 paginiOsteosarcoma Case StudyJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension Brochure Final 4-24-06Document2 paginiHypertension Brochure Final 4-24-06Norma J. Goodwin, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manage pain and inflammation with corticosteroid prednisoneDocument5 paginiManage pain and inflammation with corticosteroid prednisoneJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motives of the Spanish Conquistadors: God, Glory, and GoldDocument11 paginiMotives of the Spanish Conquistadors: God, Glory, and GoldJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Teachings: Post Turbt OperationDocument2 paginiHealth Teachings: Post Turbt OperationJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post-Surgical Pain Assessment and ManagementDocument2 paginiPost-Surgical Pain Assessment and ManagementJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historical Background and Trends in The Treatment of Infectious DiseasesDocument50 paginiHistorical Background and Trends in The Treatment of Infectious DiseasesJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitral Stenosis.. LatestDocument41 paginiMitral Stenosis.. LatestJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 TheraphyDocument2 pagini02 TheraphyJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motives of the Spanish Conquistadors: God, Glory, and GoldDocument11 paginiMotives of the Spanish Conquistadors: God, Glory, and GoldJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing MGT Oral Cav CancerDocument14 paginiNursing MGT Oral Cav CancerJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vi. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 paginiVi. Anatomy and PhysiologyJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ke MarcDocument3 paginiKe MarcJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypertension ManagementDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan for Hypertension ManagementJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- BibliographyDocument3 paginiBibliographyJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- CrisisDocument3 paginiCrisisJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vi. Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 paginiVi. Anatomy and PhysiologyJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugstudy Last DutyDocument5 paginiDrugstudy Last DutyJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- German MeaslesDocument16 paginiGerman MeaslesJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugstudy Last DutyDocument5 paginiDrugstudy Last DutyJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - FeverDocument2 paginiNCP - FeverJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluorescein Angiography 1Document2 paginiFluorescein Angiography 1Joeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP 2 LykaDocument1 paginăNCP 2 LykaJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecules: Antidiabetic Properties and Mechanism of Action of Diabetic RatsDocument16 paginiMolecules: Antidiabetic Properties and Mechanism of Action of Diabetic RatsJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lung CancerDocument20 paginiLung CancerJoeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Educ.11Document5 paginiHealth Educ.11Joeven HilarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading 1 What Do You Know About Giant PandasDocument4 paginiReading 1 What Do You Know About Giant PandasFadhla Diela100% (1)
- A 47 YearDocument12 paginiA 47 Yearwira rila zulma67% (3)
- Miriam's Must Haves: Dewey 600Document8 paginiMiriam's Must Haves: Dewey 600PRHLibraryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept Map PedsDocument6 paginiConcept Map Pedsapi-546398486Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3Document6 paginiUnit 3PAING PARAMIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pancretic Cancer Case Study - BurkeDocument52 paginiPancretic Cancer Case Study - Burkeapi-282999254Încă nu există evaluări
- Risk Factors of Diabetes in RawalpindiDocument29 paginiRisk Factors of Diabetes in RawalpindiFarrukh Ali BaigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Activity 2A - YGGN (GARBOSA, RM)Document3 paginiLaboratory Activity 2A - YGGN (GARBOSA, RM)Rej GarbosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dietabajaencarbohidratos Moreno Capponi 2020Document11 paginiDietabajaencarbohidratos Moreno Capponi 2020PerlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd G11 HOPE Module 2Document10 pagini2nd G11 HOPE Module 2Sheryl FaelnarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2 BodyDocument5 paginiAssignment 2 BodySindy Tan100% (2)
- Chap44 PDFDocument4 paginiChap44 PDFHerry SasukeÎncă nu există evaluări
- HypocalcemiaDocument2 paginiHypocalcemiaRachel Frances SorillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 THE USE OF PREMIUM YEAST EXTRACT PROSAF IN REDUCED FISHMEAL DIETS FOR THE WHITE LEG SHRIMP L. Vannamei Otavio Castro PDFDocument35 pagini5 THE USE OF PREMIUM YEAST EXTRACT PROSAF IN REDUCED FISHMEAL DIETS FOR THE WHITE LEG SHRIMP L. Vannamei Otavio Castro PDFtushar patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSG Khối 12 A 1314 PDFDocument9 paginiHSG Khối 12 A 1314 PDFDuc VinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Lesson Plan-1Document5 paginiNutrition Lesson Plan-1api-357196634Încă nu există evaluări
- Famine in China 1958-61Document34 paginiFamine in China 1958-61Agustín PineauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature Review - Makayla KleinerDocument7 paginiLiterature Review - Makayla Kleinerapi-609527702Încă nu există evaluări
- DR - Ashwin Porwal - Procto Surgeon in Pune - Healing Hands ClinicDocument15 paginiDR - Ashwin Porwal - Procto Surgeon in Pune - Healing Hands ClinicHealing Hands Clinic PuneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Month End WorksheetDocument5 paginiMonth End WorksheetMihaela RussellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrient Composition, Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Properties of Chilli and Tomato Cultivated by Fertigation and Conventional MethodsDocument25 paginiNutrient Composition, Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Properties of Chilli and Tomato Cultivated by Fertigation and Conventional MethodsMuhammad Fairuz Abdullah ShohimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bambalan ND738 At2 PDFDocument34 paginiBambalan ND738 At2 PDFMARIE GABRIELLE BAMBALANÎncă nu există evaluări