Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Steady State Stabiblity
Încărcat de
koolmanoj27Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Steady State Stabiblity
Încărcat de
koolmanoj27Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Equilibrium speed of motor-load
Steady State Stability
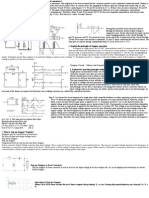
system can be obtained when motor torque equals the load torque. Electric drive system will operate in steady state at this speed, provided it is the speed of stable state equilibrium. Concept of steady state stability has been developed to readily evaluate the stability of an equilibrium point from the steady state speed torque curves of the motor and load system. Now, consider the steady state equilibrium point A shown in figure below.
Steady State Stability
The equilibrium point will be termed as stable state when the operation will restore to it after a small departure from it due to disturbance in the motor or load. Let a disturbance causes reduction in speed & at new speed, electrical motor torque becomes greater than the load torque, consequently motor will accelerate and operation will be restored to point A. Similarly an increase in speed caused by a disturbance will make load torque greater than the motor torque, resulting into deceleration and restoring operation to point A.
Steady State Stability
Now consider equilibrium point B which is obtained when the same motor drives another load as shown in the figure. A decrease in speed causes the load torque to become greater than the motor torque, electric drive decelerates and operating point moves farther away from point B. Similarly when working at point B and an increase in speed will make motor torque greater than the load torque, which will move the operating point farther away from point B. Thus point B is unstable .
From the above discussions, an equilibrium point will be stable when an increase in speed causes load torque to exceed the motor torque. (i.e.) When at equilibrium point following conditions is satisfied.
Inequality in the above equation can be derived by an alternative approach. Let a small perturbation in speed m results in T and Tl perturbations in T and Tl respectively. Therefore the general load torque equation becomes
The basic equation of motion is Subtracting (3) from (2) and rearranging
For small perturbations, the speed torque curves of the motor and load can be assumed to be straight lines, thus
Where dT and dTl are respective slopes of the steady state d m d m speed torque curves of motor and load at operating point under considerations. Substituting (5) and (6) in (4) we get,
This is a first order linear differential equation. If initial deviation in speed at t=0 be then the solution of equation (7) is
m 0
An operating point will be stable when approaches zero as t approaches infinity. For this to happen exponential term in equation (8) should be negative. Thus we have the condition of stability as described in equation (1) above, that is
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- HW1 ADocument3 paginiHW1 Adrizzle8433% (3)
- Rectifier ControlDocument3 paginiRectifier ControlatharvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Problems: 1. A, B, C, and DDocument4 paginiTutorial Problems: 1. A, B, C, and DOmar Zamalkawy100% (1)
- Lecture 14 Memory InterfaceDocument19 paginiLecture 14 Memory Interfacenjpar0% (2)
- Assig 1Document4 paginiAssig 1atharvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Commutation in DC Machines PDFDocument2 paginiCommutation in DC Machines PDFTom0% (1)
- MODULE 1 - Introduction To Electrical DrivesDocument34 paginiMODULE 1 - Introduction To Electrical DrivesAshraf FauzanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Flexible Link ProjectDocument15 pagini1 Flexible Link Projectprasaad08Încă nu există evaluări
- Line Following Robot ReviewDocument9 paginiLine Following Robot ReviewSree Krishna Nimmagadda ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem StatementDocument9 paginiProblem StatementTauseef Gillani100% (1)
- ILC - Online ImplementationDocument11 paginiILC - Online ImplementationHoàng HứaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics and Bifurcations-HaleDocument577 paginiDynamics and Bifurcations-Halealaa alqurasheyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuzzy Logic Control: Lect 5 Fuzzy Logic Control Basil Hamed Electrical Engineering Islamic University of GazaDocument96 paginiFuzzy Logic Control: Lect 5 Fuzzy Logic Control Basil Hamed Electrical Engineering Islamic University of GazaFLOWERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ied Unit VDocument8 paginiIed Unit VRudra Kumar MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Machinery PrinciplesDocument51 paginiChapter 1 - Introduction To Machinery PrinciplesGopinath SubramaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Theorms ProblemsDocument14 paginiNetwork Theorms ProblemsVinod Shanker ShringiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE664 Prob Set1Document3 paginiEE664 Prob Set1Shubham YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Drives Notes Lecture 1Document4 paginiElectrical Drives Notes Lecture 1Kunal TanwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 - Dynamic AnalysisDocument16 paginiChapter 4 - Dynamic AnalysisDimple Sharma100% (1)
- Electrical Machine Design Question Bank - As Per VTU SyllabusDocument20 paginiElectrical Machine Design Question Bank - As Per VTU SyllabusManjunathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stack and SubroutinesDocument19 paginiStack and Subroutinesapi-372408293% (14)
- Experiment 3 Economic Load DispatchDocument12 paginiExperiment 3 Economic Load DispatchMahesh KambleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Load Flow Matrices IIT Roorkee Notes NPTELDocument88 paginiLoad Flow Matrices IIT Roorkee Notes NPTELconsultrail100% (1)
- 8086 Microprocessor Linking and RelocationDocument18 pagini8086 Microprocessor Linking and RelocationSasirekha KosalramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unsymmetrical Fault AnalysisDocument49 paginiUnsymmetrical Fault AnalysisabdulbabulÎncă nu există evaluări
- CTRL Sys Lab ManualDocument46 paginiCTRL Sys Lab Manualabixek100% (2)
- Communication Engineering Cycle Test 1 AnDocument2 paginiCommunication Engineering Cycle Test 1 AnsamÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBPSD-lab Manual PDFDocument40 paginiCBPSD-lab Manual PDFShiv Rajput80% (10)
- Electrical Engineering Laboratory V Course Code: Epo662: Simulation of Three-Phase Inverter With A PWM Control EPO662Document5 paginiElectrical Engineering Laboratory V Course Code: Epo662: Simulation of Three-Phase Inverter With A PWM Control EPO662Danial AkramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microcontroller Based System Design Question BankDocument2 paginiMicrocontroller Based System Design Question BankVishal KottarathilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integrator and DifferentiatorDocument7 paginiIntegrator and DifferentiatorManoj KavediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEE Viva QuestionsDocument2 paginiBEE Viva Questionsyash.patil16431Încă nu există evaluări
- Transfer Function of The DC Motor (Yaser Rahmati)Document4 paginiTransfer Function of The DC Motor (Yaser Rahmati)Farag AlargtÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC-DC Converter - DDocument39 paginiAC-DC Converter - DBishnu100% (1)
- EDC Question BankDocument6 paginiEDC Question BankSudershan DolliÎncă nu există evaluări
- PWM Based DC Motor Speed Control Using MicrocontrollerDocument8 paginiPWM Based DC Motor Speed Control Using MicrocontrollertazebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Representation of Power System ComponentsDocument14 paginiRepresentation of Power System ComponentsRume EmujekarohwoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes: Digital Logic DesignDocument66 paginiLecture Notes: Digital Logic DesignJyoti GroverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synchronous Motor Working PrincipleDocument6 paginiSynchronous Motor Working PrincipleHemraj Singh RautelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Working Principle of A Tube LightDocument3 paginiWorking Principle of A Tube LightYassir ButtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tut 3Document3 paginiTut 3mohanrajgupta1950% (2)
- Lab Manual 1-8Document31 paginiLab Manual 1-8Vengat Raman Manohar100% (1)
- Fuzzy Control: Lect 4 Fuzzy Logic ProcessDocument89 paginiFuzzy Control: Lect 4 Fuzzy Logic ProcessAjayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frog Leg WindingDocument9 paginiFrog Leg WindingAbhijeet RedekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8051 Interrupt and SerielDocument52 pagini8051 Interrupt and SerielVenkatasamy VijayarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of DrivingDocument2 paginiProperties of DrivingDina GaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- QUBE-Servo DC Motor ModelingDocument5 paginiQUBE-Servo DC Motor Modelingandres guerreroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cmps Paper Objective PaperDocument27 paginiCmps Paper Objective PaperJeetu Bhardwaj0% (2)
- Homework Assignment 3Document6 paginiHomework Assignment 3Preserve Oladipo0% (1)
- 15 - Conclusion and Future ScopeDocument5 pagini15 - Conclusion and Future ScopeMel Vin PinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers of Power Electronics NewDocument9 paginiAnswers of Power Electronics NewSyed ZabiullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- MINOR REPORT ON Energy Meter Using ADE7757Document55 paginiMINOR REPORT ON Energy Meter Using ADE7757Himanshu Patidar100% (5)
- FCS Lab2Document36 paginiFCS Lab2muhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 Induction Machines-EEE301Document96 paginiChapter 7 Induction Machines-EEE301DilekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic Load Dispatch: Submitted byDocument12 paginiEconomic Load Dispatch: Submitted byDev Kumar100% (1)
- Lecture 14 Chopper Fed DC DrivesDocument6 paginiLecture 14 Chopper Fed DC DrivesNadjÎncă nu există evaluări
- MICROPORCESSOR 8085 Lab ManualDocument53 paginiMICROPORCESSOR 8085 Lab ManualAjay PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mosfet (J.B Gupta)Document13 paginiMosfet (J.B Gupta)rik banerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Interview Questions & Answers - Lab Viva QuestionsDocument2 paginiElectrical Interview Questions & Answers - Lab Viva QuestionsLaxman Naidu NÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase Rectifier Fed DC Motor DriveDocument11 paginiSingle Phase Rectifier Fed DC Motor DriveNitesh kumar singh100% (1)
- Steady State StabiblityDocument6 paginiSteady State StabiblitybalajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Load: Classification of Load Torque: A) Active Load Torque B) Passive Load TorqueDocument29 paginiMechanical Load: Classification of Load Torque: A) Active Load Torque B) Passive Load TorqueIndira RawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appointment RecieptDocument3 paginiAppointment Recieptkoolmanoj27Încă nu există evaluări
- Cognizant ResultDocument2 paginiCognizant Resultkoolmanoj27Încă nu există evaluări
- 89s52 DatasheetDocument30 pagini89s52 DatasheetAnkit TakleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exchange RateDocument3 paginiExchange Ratekoolmanoj27Încă nu există evaluări
- Solar Tracking SystemDocument12 paginiSolar Tracking SystemSrinivas MudhirajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless ChargingDocument18 paginiWireless Chargingkoolmanoj27Încă nu există evaluări
- Flexible Link WorkbookDocument51 paginiFlexible Link Workbookialvarez75Încă nu există evaluări
- Transient Stability of Power Systems With Embedded VSC HVDC Links Stability Margins Analysis and Control Juan Carlos GONZALEZDocument12 paginiTransient Stability of Power Systems With Embedded VSC HVDC Links Stability Margins Analysis and Control Juan Carlos GONZALEZChristian MárquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interconnection and Damping Assignment Passivity-Based Control: A SurveyDocument19 paginiInterconnection and Damping Assignment Passivity-Based Control: A SurveyAntonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kundur Word Pequeña SeñalDocument72 paginiKundur Word Pequeña SeñalJhonathan IzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics of Fitzhugh-Nagumo Excitable Systems With Delayed CouplingDocument15 paginiDynamics of Fitzhugh-Nagumo Excitable Systems With Delayed Couplingneel1237Încă nu există evaluări
- Stabilidad de Keller-Segel ModeloDocument7 paginiStabilidad de Keller-Segel ModeloJose Fabian Beltran JoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec6405 - Control System Engineering Questions and Answers Unit - IV Stability Analysis Two MarksDocument6 paginiEc6405 - Control System Engineering Questions and Answers Unit - IV Stability Analysis Two MarksShailaja UdtewarÎncă nu există evaluări
- LMMDocument10 paginiLMMSaad KhalisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why To Use An Articulated Vehicle in Underground Mineing OperationsDocument6 paginiWhy To Use An Articulated Vehicle in Underground Mineing OperationsalpesmergulÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW2 SolDocument5 paginiHW2 SolMouliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Control Systems, Modeling, Analysis and DesignDocument262 paginiLinear Control Systems, Modeling, Analysis and DesignEduardo Valencia100% (2)
- Role of Automatic Generation Control (AGC) in Energy Management SystemDocument49 paginiRole of Automatic Generation Control (AGC) in Energy Management Systemhodeegits9526Încă nu există evaluări
- Power System Stability: Prof. M Venkateswara RaoDocument56 paginiPower System Stability: Prof. M Venkateswara RaochinnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ODE StabilityDocument20 paginiODE Stabilitybaraksh4Încă nu există evaluări
- Ce 579: Structral Stability and DesignDocument16 paginiCe 579: Structral Stability and DesignMarinos GiannoukakisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Space TrussDocument74 paginiSpace Trussomer1299Încă nu există evaluări
- Routh Criterion - Tutorial 7 - Co - 12Document3 paginiRouth Criterion - Tutorial 7 - Co - 12Haelu KuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPS SyllabusDocument105 paginiCPS SyllabusabishekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Controlling Unstable Equilibrium Point Theory For Stability Assessment of Two-Time Scale Power System ModelsDocument9 paginiControlling Unstable Equilibrium Point Theory For Stability Assessment of Two-Time Scale Power System ModelsRony AimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 00mar WeissenfelsDocument112 pagini00mar WeissenfelsSebastian CotinghiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME 534 - 03 Stability (Rev. 1.2)Document7 paginiME 534 - 03 Stability (Rev. 1.2)Michael PalmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09 Fall 501 LyapDocument10 pagini09 Fall 501 LyapAnonymous XKlkx7cr2IÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stabilization With Relaxed ControlsDocument11 paginiStabilization With Relaxed Controlsfx_amvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Delay in CSDocument173 paginiTime Delay in CSDineshkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Script PDEDocument127 paginiScript PDEcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Truncation Error, Consistency, and Convergence: J.K. Ryan@tudelft - NLDocument54 paginiTruncation Error, Consistency, and Convergence: J.K. Ryan@tudelft - NLisele1977Încă nu există evaluări
- Sohan OkDocument46 paginiSohan OkSohan SinghÎncă nu există evaluări