Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Poster: Measuring Human Memory
Încărcat de
Khamis AlarabiTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Poster: Measuring Human Memory
Încărcat de
Khamis AlarabiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Measuring Effectiveness of Memory through Affect
Khamis Faraj Alarabi , Abdul Wahab
Department of Computer Science, KICT, IIUM P.O. Box 10, 50728 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Kf_alarabi@yahoo.com abdualwahab@iium.edu.my
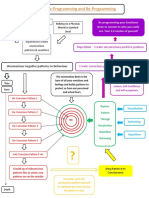
ABSTRACT The efforts to measure memory effectiveness have been since years on the top of research not only in psychology but in cognitive science and engineering as well. Much work has been done to measure both types of memory, explicit and implicit. According to H. Roediger III, explicit memory can be measured by explicit (or direct) tests such as free recall and recognition, which reflect conscious recollection of the past, while implicit (or indirect) tests such as word-stem completion and word fragment completion are used to test implicit memory, where they can measure the transfer (or priming) from past experience on tasks that do not need Conscious recollection of recent task to perform. Since emotions have a great influence on effectiveness of memory and they could be measured using EEG signals in terms of valence and arousal, this poster paper proposes new techniques that focus on how TITLE HEADER memory effectiveness can be measured through dynamic emotions. In this experimental study, four postgraduate students from KICT were chosen to participate in the experiments to measure their memory effectiveness during memory tests. Participants brain signals were collected using EEG machine. Digital signal processing techniques were applied to EEG data to detect participants TEXT emotions and emotion trajectory that reflects effectiveness of their memories. Preliminary results of the experiments showed potential of using electroencephalogram (EEG) in measuring the effectiveness of memory through affect. Key words: Implicit memory, Memory test, Emotion recognition, Affect, Memory effectiveness. Human memory Memory is divided into: 1- Sensory memory, which has limited capacity and last for 0.3 sec. 2- STM, which has limited 5+/-2 capacity and last for 3 sec. 3- LTM, which has unlimited capacity/time and divided into: Declarative (explicit or conscious) memory. Non-declarative ( implicit or unconscious) memory. Memory tests There are two types of memory tests: 1- Direct ( or explicit) test, such as Free recall, that used to measure explicit memory. 2- Indirect (or implicit) test, such as word-stem completion, that used to measure implicit memory. Emotion recognition & emotion impact on memory
Arousal-Valence model
Arousal-Performance curve
Emotions can be mapped using two-dimensional (valencearousal ) scaling to classify the emotion experience. Using such model, four emotions (Fear, Happy, Sad and Calm) can be recognized.
Results Preliminary results of this work showed that memory effectiveness is notably influenced by emotions. The emotion trajectory over valence-arousal map is related to memory effectiveness, which is reflected in subjects response. The highest arousal the highest memory effectiveness . Conclusion Preliminary results of our experiments showed a potential of using electroencephalogram (EEG) in measuring the effectiveness of memory through affect.
References
1- Frank, J.& C. Tomaz, Enhancement of declarative memory associated with emotional content in Brazilian sample, Brazilian Journal of medical and biological research, 33:1483-1489, 2000. 2- Lewis, M. et al., Handbook of emotion, the Guilford press, London, 3rd ed., 2008. 3- Roediger, H., Implicit memory: retention without remembering , American psychologist, 45, 1043-1056.1990.
Postgraduate Students Colloquium (PGSC) 2013
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Chapter14 From Book Psychology 2005 ISBN 978-0-631 20678 1Document22 paginiChapter14 From Book Psychology 2005 ISBN 978-0-631 20678 1Khamis AlarabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Moon 1996Document25 paginiMoon 1996Khamis AlarabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- MemoryPaper 1991Document19 paginiMemoryPaper 1991Khamis AlarabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Personality and The Eeg: Arousal AND Emotional ArousabtlityDocument17 paginiPersonality and The Eeg: Arousal AND Emotional ArousabtlityKhamis AlarabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Khamis CS Template 2013Document1 paginăKhamis CS Template 2013Khamis AlarabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Organizational Behaviour: AttitudesDocument16 paginiOrganizational Behaviour: AttitudesgswetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Research Proposal Critical Thinking and Metacognitive Learning-RelationshipDocument2 paginiResearch Proposal Critical Thinking and Metacognitive Learning-RelationshipLuis Fernando Santos MenesesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- 1 - Understanding Our Brain - Chris OsbornDocument1 pagină1 - Understanding Our Brain - Chris OsbornChris Osborn100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions On Historical Evolution of OBDocument9 paginiMultiple Choice Questions On Historical Evolution of OBAnjali Kumari100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Zimmerman. Self Efficacy An Essential Motive To LearnDocument10 paginiZimmerman. Self Efficacy An Essential Motive To LearnAlejandroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Journal of Experimental Social Psychology: Kathleen D. Vohs, Roy F. Baumeister, Brandon J. SchmeichelDocument5 paginiJournal of Experimental Social Psychology: Kathleen D. Vohs, Roy F. Baumeister, Brandon J. SchmeichelAlejandro GarcíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Informatics - It's Scope and Met - A - I. Mikhailov PDFDocument15 paginiInformatics - It's Scope and Met - A - I. Mikhailov PDFMaria Cristina MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- UTSDocument3 paginiUTSDio NolascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Expressionism Surrelaishm ExistentalismDocument2 paginiExpressionism Surrelaishm ExistentalismzahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Social Structure Interaction Assignment by Sana Aslam and Weiming ZhanDocument3 paginiSocial Structure Interaction Assignment by Sana Aslam and Weiming Zhanapi-377156107Încă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Case Study (Behavioral Fianance Can Teach Investors)Document2 paginiCase Study (Behavioral Fianance Can Teach Investors)luvnehaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identity: An International Journal of Theory and ResearchDocument13 paginiIdentity: An International Journal of Theory and ResearchIgnacio VeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum PlanningDocument17 paginiCurriculum PlanningUmaimah Mohd IdrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Terror Barrier by Bob Proctor PDFDocument3 paginiTerror Barrier by Bob Proctor PDFWyn Christian RebanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abstrak Skripsi Semiotics Analysis On FilmDocument2 paginiAbstrak Skripsi Semiotics Analysis On FilmRifaldi AdlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 108 BioethicsDocument5 paginiNCM 108 BioethicsMIA JHENN PAULENE PARRA75% (8)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Science Concept PlannerDocument1 paginăScience Concept Plannerapi-399270132Încă nu există evaluări
- Total Quality Management: Aireen Y. CloresDocument51 paginiTotal Quality Management: Aireen Y. CloresaireencloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Action Research 1.0Document10 paginiAction Research 1.0Dan MarshallÎncă nu există evaluări
- Culturally Relevant UsaDocument14 paginiCulturally Relevant UsaNitin BhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neo Behaviorism FFDocument27 paginiNeo Behaviorism FFRother JoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- 4 PDFDocument6 pagini4 PDFDr.V.Bastin JeromeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Counselling NotesDocument925 paginiCounselling Notesrina_singh47796200% (1)
- Theoretical Framework For Thesis DesignDocument1 paginăTheoretical Framework For Thesis DesignRenz Christian PadiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Price and Feinman 1995Document297 paginiPrice and Feinman 1995Kepa Martinez Garcia100% (1)
- Simplifying Complexity-A Review of Complexity TheoryDocument10 paginiSimplifying Complexity-A Review of Complexity TheoryIndra Budhi KurniawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nommon Solutions and Technologies PDFDocument53 paginiNommon Solutions and Technologies PDFNommon Solutions and TechnologiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- DeRosnay TheSymbioticManDocument308 paginiDeRosnay TheSymbioticMancrisgthomas100% (1)
- Social Preference and Social Behaviour of Adolescents: A Comparative StudyDocument4 paginiSocial Preference and Social Behaviour of Adolescents: A Comparative StudyAnonymous CwJeBCAXpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Freud's Psychoanalytic TheoryDocument17 paginiFreud's Psychoanalytic TheorySathish Rajamani100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)