Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Fallas Direccionales - 2
Încărcat de
Arturo OsorioDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fallas Direccionales - 2
Încărcat de
Arturo OsorioDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fallas direccionales: Introduccin
Fallas que no crecen libremente, pero acomodan desplazamientos de fallas limitantes: Fallas de transferencia
Fallas que crecen libremente:
Fallas de transcurrencia
Fallas de transferencia ligadas a una tectnica de piel delgada
Fallas de transferencia entre dos fallas de una misma polaridad: Rampas laterales
Falla de transferencia entre dos fallas normales de polaridad opuesta
Fallas de transferencia ligadas a lmites de placa: Fallas de transformacin
Complicaciones estructurales relacionadas a saltos o terminaciones de una falla direccional (1)
Flexin relajante o constriccional (restraining / releasing bend)
Generacin de desplazamiento en el bloque SW de una falla del Valle Muerto
Complicaciones estructurales relacionadas a saltos o terminaciones de una falla direccional (2)
Regional-scale structures along a strike-slip fault. These structures can include restraining bends associated with thrusts and mountain building, releasing bends associated with basin development and rapid subsidence, and horsetail splays of either normal or reverse faults where deformation is spread over a broader zone. Right-stepping step-overs in a dextral shear zone (as shown here) create pull-apart basins as the fault tips curve toward the continuing fault trace and generate normal slip. Modified after
Negative flower structure related to downthrown side (or releasing bend).
Block diagrams showing negative and positive flower structures typical of large fault zones that are caused by transtension and transpression, respectively.
Positive flower structure related to upthrown side (or restraining bend).
Planos y pliegues secundarios que afectan una zona de dao o los alrededores de una falla direccional
A strain model explaining the subsidiary structures along a strike-slip fault.
(a) A map view of dextral simple shear. A square becomes a parallelogram, and a circle in the square becomes an ellipse. (b) A detail of the strain ellipse showing that folds and thrusts form perpendicular to the shortening direction, while normal faults and veins form perpendicular to the extension direction. R and R shears form at an acute angle to the shortening direction. (c) Note that R and R are similar to conjugate shear fractures formed in rock cylinder subjected to an axial stress.
Portrayal of the difference between bends and step-overs, both in right- and left-handed strikeslip systems (releasing and restraining bends).
Mechanisms of block rotation in a right-lateral strike-slip zone. (a) A map view of a grid being subjected to dextral simple shear. (b) The grid lines rotate. Further, fault-bounded blocks may rotate intact as slip on bounding faults increases (bookshelf model). (c) Alternatively, the fault zone may break into smaller blocks that rotate by different amounts. In this case, large rotations may occur locally. The amount of rotation is tracked by the paleomagnetic declination in each block (solid arrows) relative to a reference direction (dashed line).
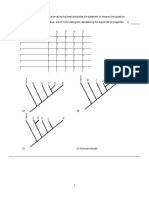
Fracture patterns in wrench zones. A. Part of Dasht-e Bayaz (Iran) earthquake fracture zone along left-lateral wrench. Western part shows development of synthetic en echelon faults; eastern end shows both antithetic and synthetic en echelon faults. B. Synthetic and antithetic en eche C. lon fractures (enlargement of east end of wrench zone in A above). D. Lake Basin fault zone, Montana, showing en echelon normal faults along indicated wrench zone. E. Cottage Grove fault zone, Illinois; note en echelon normal faults, parallel mafic dikes, and reversal of vertical separation sense on through-going strike-slip fault. Vertical components indicated in feet.
Ejemplos y ejercicios
Map-view models of fault bends along strike-slip faults. The edges of the crustal blocks are provided for reference. (a)Releasing bend at which normal faults and a pullapart basin have formed. (b)Restraining bend at which thrust faults have formed. (c)Application of this model to the San Andreas Fault north of Los Angeles (LA). The dashed lines outline imaginary reference blocks. The San Andreas Fault bends along the margin of the Mojave Desert.
La Falla Alpina de Nueva Zelandia
The transform system of the Alpine Fault, New Zealand, connects the west-dipping Tonga-Kermadec subduction zone to the east dipping Macquarie subduction zone. Note the tremendous displacement of major rock units on the Alpine Fault. The northern subduction zone dips east and the southern subduction zone dips west, as shown by the pattern of progressively deeper earthquakes.
La Falla Alpina de Nueva Zelandia: Transferencia entre dos zonas de subduccin
The Alpine Fault in New Zealand is a dextral transform fault that connects two subducting plate boundaries (see insert for larger field of view). Along this fault the geological units (various colored symbols) are displaced by several hundred kilometers.
The dextral North Anatolian Fault forms the plate boundary between the Anatolian and Eurasian plates; stars show epicenters of large earthquakes between 1939 and 1999. The numbers in brackets indicate the moment magnitudes of the earthquakes. The conjugated East Anatolian Fault has opposite sense of movement (sinistral). In the wedge between both faults the Anatolian Plate is pushed westwards (tectonic escape).
Fallas direccionales en los bordes de la Placa del Caribe
Marco tectnico de las fallas direccionales en los lmites de la Placa del Caribe
La falla de Motagua-Polochic
La falla de Bocon
La falla de Bucaramanga - Santa Marta
La Falla Palestina: Marco tectnico
Convergence between Nazca-Sam:
Highly oblique for the Pg and Ku Perpendicular for the Oligocene
Paleogene and earlier
La Falla Palestina: Marco cinemtico
Strain partitioning at a restraining bend of the Northandean block
Antioquia batholith
Structural markers along the southern segment of the Palestina fault illustrate an increase in displacement from 4 km to 26 km.
D
26,0 km
Cretaceous sediments Marble Diorite Gneiss Metamorphic basement
C D
27,3 km
SAN LUIS
B
26,4 km
B A
4,2 km
50 km
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Atlas of Structural Geological Interpretation from Seismic ImagesDe la EverandAtlas of Structural Geological Interpretation from Seismic ImagesAchyuta Ayan MisraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fault Zone Dynamic Processes: Evolution of Fault Properties During Seismic RuptureDe la EverandFault Zone Dynamic Processes: Evolution of Fault Properties During Seismic RuptureMarion Y. ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fallas DireccionalesDocument30 paginiFallas DireccionalesDubban AtseutaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Geology Seminar: A Presentation ONDocument35 paginiStructural Geology Seminar: A Presentation ONSergio Paucar MoreyraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strike: The Direction (Compass Bearing) of A Line Formed by The Intersection of A RockDocument16 paginiStrike: The Direction (Compass Bearing) of A Line Formed by The Intersection of A RockGanguli Tutor RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unconformities Joints Faults and FoldsDocument8 paginiUnconformities Joints Faults and FoldsTrue ConfessorÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 4 Faults 1Document42 pagini5 4 Faults 1Azman AzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Faults 2Document8 paginiTypes of Faults 2Living WoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Faults - LectDocument39 paginiFaults - LectMarshall NhodzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fault TerminologyDocument5 paginiFault Terminologypaul machariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fault Block Modeling LabDocument12 paginiFault Block Modeling Labapi-251355123100% (1)
- Seismic InterpretationDocument155 paginiSeismic InterpretationRafaelLlanos100% (1)
- Crider JSG 2001Document13 paginiCrider JSG 2001mhouskalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part XI Strike-Slip Systems: 1) Major Continental Transform FaultsDocument4 paginiPart XI Strike-Slip Systems: 1) Major Continental Transform Faultsmunaf afridiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fault-Lecture 4Document26 paginiFault-Lecture 4Tanim SyedÎncă nu există evaluări
- GY403 Faulting PDFDocument50 paginiGY403 Faulting PDFRonuelGreenidgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4 GEOLOGYDocument10 paginiLecture 4 GEOLOGYnattydreadfathelahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fault ScrapDocument24 paginiFault Scrapvishvincent5643Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 4 Tectonic and Structural LandformDocument50 paginiWeek 4 Tectonic and Structural LandformAndri ArrahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Galindo - Lonergan - 2020 - TCTNCS - Basin Evol - Shale Tectonics - Oblique Margin - Bahia Basin - LightDocument32 paginiGalindo - Lonergan - 2020 - TCTNCS - Basin Evol - Shale Tectonics - Oblique Margin - Bahia Basin - LightCarlos RomeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rock Deformation and Earthquake FinalDocument131 paginiRock Deformation and Earthquake Finalniaz ahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 5. Fault SystemsDocument91 paginiCH 5. Fault Systemselias assefaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tibaldi & Ferrari, 1993Document4 paginiTibaldi & Ferrari, 1993Ana Chiluisa GuamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ranalli 1974Document8 paginiRanalli 1974Som DevÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEQ-05 Faults & Folds Notes - ShortDocument15 paginiIEQ-05 Faults & Folds Notes - ShortShubham BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capitol7 Stike Slip FaultsDocument15 paginiCapitol7 Stike Slip FaultsgabrielamariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Sesar Normal-Naik & Mendatar PDFDocument49 pagini6 Sesar Normal-Naik & Mendatar PDFItTo MakinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.strike Slip, Transtension, TrasnpresionDocument33 pagini5.strike Slip, Transtension, TrasnpresionNicolas AlejandroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attribute DelineDocument4 paginiAttribute DelineMohamed Ibrahim ShihataaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Faults 3Document3 paginiTypes of Faults 3Eileen Joy NocedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Les Chaines de Montagnes Recentes Et Leur Relation Avec La Tectonique Des Plaques Cours 2Document18 paginiLes Chaines de Montagnes Recentes Et Leur Relation Avec La Tectonique Des Plaques Cours 2oussama Hm100% (1)
- Overview of Structural Geology and Geologic Map Interpretation PDFDocument26 paginiOverview of Structural Geology and Geologic Map Interpretation PDFMahmoud Eloribi100% (1)
- Transform Plate BoundariesDocument22 paginiTransform Plate BoundariesopulitheÎncă nu există evaluări
- McClay, 1992-Glossary of Thrust Tectonics TermsDocument15 paginiMcClay, 1992-Glossary of Thrust Tectonics TermsEvanz LazaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strike-Slip Basins - Nilson & Sylvester - 1995Document32 paginiStrike-Slip Basins - Nilson & Sylvester - 1995geoecologistÎncă nu există evaluări
- FaultsDocument74 paginiFaultsBS GeoPhysicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geologic Maps: For Example, The Ordovician Swan Peak Formation Is Labeled "Osp"Document8 paginiGeologic Maps: For Example, The Ordovician Swan Peak Formation Is Labeled "Osp"Yeremia PanggabeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rock Slope EngineeringDocument51 paginiRock Slope EngineeringbufaloteÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASSIGNMENT EGRS 2 NewDocument3 paginiASSIGNMENT EGRS 2 NewmstomarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 2BDocument9 paginiLab 2BalipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extensional Fault Arrays in Strike-Slip and Transtension: John W.F. WaldronDocument12 paginiExtensional Fault Arrays in Strike-Slip and Transtension: John W.F. WaldronIvan Hagler Becerra VasquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fault (Geology) - WikipediaDocument20 paginiFault (Geology) - WikipediaSubhrangshu Ray Sarkar IX B 34Încă nu există evaluări
- Shear Riedel StyleDocument20 paginiShear Riedel Style13092014Încă nu există evaluări
- Apotria 1995 Thrust Sheet Rotation and Out-Of-plane Strains Associated With Oblique Ramps An Example From The Wyoming Salient USADocument16 paginiApotria 1995 Thrust Sheet Rotation and Out-Of-plane Strains Associated With Oblique Ramps An Example From The Wyoming Salient USARICHARD REMY HUAYTA PACCOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tectonic and Structural Geomorphology - Terminology PDFDocument20 paginiTectonic and Structural Geomorphology - Terminology PDFVladimir AmorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acosta Et Al 2007 Strike Slip Deformation Within Colombian Andes CDocument17 paginiAcosta Et Al 2007 Strike Slip Deformation Within Colombian Andes CEdgar Castiblanco OrtizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plate Boundaries With Major Strike-Slip Components.Document11 paginiPlate Boundaries With Major Strike-Slip Components.anicetus namangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 07 Fault Folds Joint - 2 PDFDocument58 paginiLecture 07 Fault Folds Joint - 2 PDFMuhammad Inam ul HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- FaultsDocument5 paginiFaultsMarc Eleazar TaysonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Geology Chapter 7Document43 paginiStructural Geology Chapter 7Elijah IbsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1992 - Ring Al - Normal Vs Strike Slip in Malawi RiftDocument4 pagini1992 - Ring Al - Normal Vs Strike Slip in Malawi RiftDainerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Engineering Seismology: Earthquake Focal Mechanisms (Fault Plane Solutions)Document45 paginiFundamentals of Engineering Seismology: Earthquake Focal Mechanisms (Fault Plane Solutions)HarsanoJayadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fault-Fracture Network Development in Upper-Crustal, Strike-Slip Settings: A Case Study From The Atacama Fault SystemDocument5 paginiFault-Fracture Network Development in Upper-Crustal, Strike-Slip Settings: A Case Study From The Atacama Fault SystemJavier RetamalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grocott Taylor 2002 Magmatic Arc Complexes Northern Chile JGSLDocument20 paginiGrocott Taylor 2002 Magmatic Arc Complexes Northern Chile JGSLAle NuñezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strike-Slip and Oblique-Slip TectonicsDocument20 paginiStrike-Slip and Oblique-Slip TectonicsAlejandro MedranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument7 paginiTugas Bahasa InggrisGue Gitu LochÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Geometry of Strike-Slip Faulting: Structural GeologyDocument4 paginiThe Geometry of Strike-Slip Faulting: Structural GeologyFaishal Ahmad DarmawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- McClay, 1992-Glossary of Thrust Tectonics TermsDocument15 paginiMcClay, 1992-Glossary of Thrust Tectonics Termshazim_74Încă nu există evaluări
- Strike-Slip Fault PDFDocument20 paginiStrike-Slip Fault PDFAlejandro MedranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strike-Slip and Oblique-Slip TectonicsDocument21 paginiStrike-Slip and Oblique-Slip TectonicsAlbert StefenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bajaj Vs Hero HondaDocument63 paginiBajaj Vs Hero HondaHansini Premi100% (1)
- Asterisk NowDocument82 paginiAsterisk Nowkambojk100% (1)
- ALE Manual For LaserScope Arc Lamp Power SupplyDocument34 paginiALE Manual For LaserScope Arc Lamp Power SupplyKen DizzeruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stentofon Pulse: IP Based Intercom SystemDocument22 paginiStentofon Pulse: IP Based Intercom SystemCraigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bandhan Neft Rtgs FormDocument2 paginiBandhan Neft Rtgs FormMohit Goyal50% (4)
- Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures "ReadyDocument26 paginiEurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures "Readywazydotnet80% (10)
- Midi Pro Adapter ManualDocument34 paginiMidi Pro Adapter ManualUli ZukowskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artificial Intelligence Techniques For Encrypt Images Based On The Chaotic System Implemented On Field-Programmable Gate ArrayDocument10 paginiArtificial Intelligence Techniques For Encrypt Images Based On The Chaotic System Implemented On Field-Programmable Gate ArrayIAES IJAIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shelly e CommerceDocument13 paginiShelly e CommerceVarun_Arya_8382Încă nu există evaluări
- Walking in Space - Lyrics and Chord PatternDocument2 paginiWalking in Space - Lyrics and Chord Patternjohn smithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phylogeny Practice ProblemsDocument3 paginiPhylogeny Practice ProblemsSusan Johnson100% (1)
- How To Launch Remix OS For PCDocument2 paginiHow To Launch Remix OS For PCfloapaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organization Culture Impacts On Employee Motivation: A Case Study On An Apparel Company in Sri LankaDocument4 paginiOrganization Culture Impacts On Employee Motivation: A Case Study On An Apparel Company in Sri LankaSupreet PurohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical Modelling and Design of Electrical DevicesDocument69 paginiNumerical Modelling and Design of Electrical Devicesfabrice mellantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report FinalDocument48 paginiReport FinalSantosh ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Manual PM3250Document80 paginiUser Manual PM3250otavioalcaldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Эквивалентная Схема Мотра Теслы с Thomas2020Document7 paginiЭквивалентная Схема Мотра Теслы с Thomas2020Алексей ЯмаÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Design Fourth Edition William T Segui Solution Manual 1Document11 paginiSteel Design Fourth Edition William T Segui Solution Manual 1RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mahesh R Pujar: (Volume3, Issue2)Document6 paginiMahesh R Pujar: (Volume3, Issue2)Ignited MindsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sankranthi PDFDocument39 paginiSankranthi PDFMaruthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Security Notes International Security NotesDocument34 paginiInternational Security Notes International Security NotesBEeNaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smart Protein Plant Based Food Sector Report 2Document199 paginiSmart Protein Plant Based Food Sector Report 2campeon00magnatesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Draft JV Agreement (La Mesa Gardens Condominiums - Amparo Property)Document13 paginiDraft JV Agreement (La Mesa Gardens Condominiums - Amparo Property)Patrick PenachosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Famous Little Red Book SummaryDocument6 paginiFamous Little Red Book SummaryMatt MurdockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Switching Simulation in GNS3 - GNS3Document3 paginiSwitching Simulation in GNS3 - GNS3Jerry Fourier KemeÎncă nu există evaluări
- TESTDocument27 paginiTESTLegal CheekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Asimilasi Untuk PemulaDocument24 paginiData Asimilasi Untuk PemulaSii Olog-olog PlonkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Morfologi Dan Citra Kota Kawasan Kauman, Kecamatan Juwana, Kabupaten Pati The Morphology and Image of Kauman Town, Juwana Sub District, Pati RegencyDocument16 paginiMorfologi Dan Citra Kota Kawasan Kauman, Kecamatan Juwana, Kabupaten Pati The Morphology and Image of Kauman Town, Juwana Sub District, Pati RegencyRABIAH ARDIANTI TUM TOMAGOLAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Derebe TekesteDocument75 paginiDerebe TekesteAbinet AdemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Selection Criteria Tunnel Cons TraDocument32 paginiFinal Selection Criteria Tunnel Cons TraMd Mobshshir NayeemÎncă nu există evaluări