Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
01-06B - Introduction To Healthcare and Public Health in The US - Unit 06 - Regulating Healthcare - Lecture B
Încărcat de
Health IT Workforce Curriculum - 20120 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
27 vizualizări21 paginiThe Health IT Workforce Curriculum was developed for U.S. community colleges to enhance workforce training programmes in health information technology. The curriculum consist of 20 courses of 3 credits each. Each course includes instructor manuals, learning objectives, syllabi, video lectures with accompanying transcripts and slides, exercises, and assessments. The materials were authored by Columbia University, Duke University, Johns Hopkins University, Oregon Health & Science University, and University of Alabama at Birmingham. The project was funded by the U.S. Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. All of the course materials are available under a Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial ShareAlike (CC BY NC SA) License. The course description, learning objectives, author information, and other details may be found at http://archive.org/details/HealthITWorkforce-Comp01Unit06. The full collection may be browsed at http://knowledge.amia.org/onc-ntdc or at http://www.merlot.org/merlot/viewPortfolio.htm?id=842513.
Titlu original
01-06B - Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US - Unit 06 - Regulating Healthcare - Lecture B
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike (BY-NC-SA)
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe Health IT Workforce Curriculum was developed for U.S. community colleges to enhance workforce training programmes in health information technology. The curriculum consist of 20 courses of 3 credits each. Each course includes instructor manuals, learning objectives, syllabi, video lectures with accompanying transcripts and slides, exercises, and assessments. The materials were authored by Columbia University, Duke University, Johns Hopkins University, Oregon Health & Science University, and University of Alabama at Birmingham. The project was funded by the U.S. Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. All of the course materials are available under a Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial ShareAlike (CC BY NC SA) License. The course description, learning objectives, author information, and other details may be found at http://archive.org/details/HealthITWorkforce-Comp01Unit06. The full collection may be browsed at http://knowledge.amia.org/onc-ntdc or at http://www.merlot.org/merlot/viewPortfolio.htm?id=842513.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike (BY-NC-SA)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
27 vizualizări21 pagini01-06B - Introduction To Healthcare and Public Health in The US - Unit 06 - Regulating Healthcare - Lecture B
Încărcat de
Health IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012The Health IT Workforce Curriculum was developed for U.S. community colleges to enhance workforce training programmes in health information technology. The curriculum consist of 20 courses of 3 credits each. Each course includes instructor manuals, learning objectives, syllabi, video lectures with accompanying transcripts and slides, exercises, and assessments. The materials were authored by Columbia University, Duke University, Johns Hopkins University, Oregon Health & Science University, and University of Alabama at Birmingham. The project was funded by the U.S. Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. All of the course materials are available under a Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial ShareAlike (CC BY NC SA) License. The course description, learning objectives, author information, and other details may be found at http://archive.org/details/HealthITWorkforce-Comp01Unit06. The full collection may be browsed at http://knowledge.amia.org/onc-ntdc or at http://www.merlot.org/merlot/viewPortfolio.htm?id=842513.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial ShareAlike (BY-NC-SA)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 21
Introduction to Healthcare
and Public Health in the US
Lecture b
Regulating Healthcare
This material (Comp1_Unit6b) was developed by Oregon Health and Science University, funded by the Department of Health
and Human Services, Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology under Award Number
IU24OC000015.
Regulating Healthcare
Learning Objectives
Describe the role of accreditation, regulatory bodies, and
professional associations in health care in the US. (Lecture a)
Describe the basic concepts of law in the United States: the legal
system, sources of law, classification of laws, the court system, and
the trial process. (Lecture b)
Describe legal aspects of medicine involving the Affordable Care
Act, professional standards in health care, medical malpractice, Tort
reform, and Medicare and Medicaid Fraud and Abuse (Lecture c)
Describe key components of the Health Insurance Portability and
Accountability Act (HIPAA) and current issues of privacy and patient
safety in the US (Lecture d)
Discuss the need for quality clinical documentation for the use of the
health record as a legal document, communication tool and a key to
prove compliance for health care organizations. (Lecture e)
2
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
The Legal System in the US
Legislative
House of Representatives and the Senate
Executive
The president and numerous departments
and agencies
Judicial
Judges and courts
3
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Balance of Power
Separation of powers
Three branches of government
Designed to prevent any one branch from
becoming too powerful
Checks and balances
Legislative branch makes laws
Executive branch enforces laws
Judicial branch interprets laws
4
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Sources of Law
Legislative branch makes statutory laws
Executive branch makes administrative laws
Laws made by the courts are called common law
or case law
5
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
The Judicial System: Courts
Trial court
Hears evidence and hands down verdicts
Can be federal, state, or local
Appellate court
Losing party can appeal
Court usually does not hear new evidence
Reviews case to determine if the law was
properly applied to the facts as determined by
the trial court
6
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
The Judicial System: Jurisdiction
Federal courts
Constitutionality of a federal law
Disputes primarily involving federal law
Disputes between citizens of different states
State courts
Often called courts of common pleas or
county courts
City or municipal courts
7
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Comparing Court Systems:
An Example
US Government State of Ohio City of
Cleveland
Trial courts US District Court for the
Northern District of Ohio
Cuyahoga County
Court of Common
Pleas
Cleveland
Municipal Court
Appellate
courts
US Sixth Circuit
Court of Appeals
Ohio Eighth District Court of Appeals
Highest court US Supreme Court Ohio Supreme Court
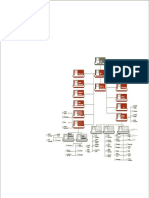
6.2 Table: Example of court jurisdiction on various levels of government.
8
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Classification of Laws
Civil or private law
Relationships between people
Relationships between people and
organizations
Relationships between organizations
Includes family, property, inheritance,
corporate, contract, and tort law
Public law
Relationships between people and the
government
9
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Two Kinds of Penalties
Civil lawexchange of money between the
private parties to the lawsuit
Public lawcan result in fines paid to the
government and/or imprisonment
The same action can result in both kinds of
penalties
10
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Example: Traffic Accident
Drunk driver crashes car, causing serious injury
to the driver of the other car
Criminal (public) penalty
State vs. drunk driver
Civil (private) damages
Injured driver vs. drunk driver
11
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
General Classification:
Private Law
6. 3 Figure: Two important sub classifications of civil law are contract law and tort law (OHSU, 2010).
12
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Contract Law
Contract elements
Offer
Acceptance
Consideration: something of value given in
exchange for a promise
Express contract
Written or oral
Implied contract
13
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Tort Law
Intentional torts
Battery
Defamation
Negligence
Does not act with a reasonable amount of
care
As a result, someone is injured
14
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
General Classification:
Public Law
6.4 Figure: The two types of Public Law that have the most effect on individuals are criminal law and administrative law (OHSU, 2010).
15
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Litigation: Parties
Adversary system
Each party presents his or her case
Facts determined by neutral fact-finder
Civil case: plaintiff and defendant
Criminal case: government and defendant
16
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Pre-trial Litigation: Discovery
Purpose is to fully develop the facts
Depositions are one kind of discovery
Sworn testimony recorded by court reporter
Parties
Witnesses
Expert witnesses
17
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Administrative Hearings
Sometimes an administrative agency has a
system of hearings that is outside the normal
court system
The agency may or may not have an appellate
level
Usually reviewable in a court of law
18
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Administrative Hearing Example
Social Security Administration (SSA)
Hearing officers
Social Security Appeals Council
Decisions of the SSA appeals board can be
further appealed to the US District Court
19
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Regulating Healthcare
Summary Lecture b
3 branches of government: legislative, executive,
judicial (the courts)
Courts are divided into:
Trial courts and appellate courts
Federal, state, city/municipal courts
The courts are neutral arenas where the parties
to a dispute face off in an adversarial process
2 main types of law: private and public
20
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
References
Administrative Office of the US Courts. The federal court system in the United States. 2010. 3rd ed.
http://www.uscourts.gov/uscourts/FederalCourts/Publications/English.pdf. Accessed April 8, 2011.
Administrative Office of the US Courts. Understanding federal and state courts.
http://www.uscourts.gov/EducationalResources/FederalCourtBasics/CourtStructure/UnderstandingFederalAndStateCourts.aspx.
Accessed April 8, 2011.
Administrative Office of the US Courts. United States Courts. http://www.uscourts.gov/Home.aspx. Accessed April 8, 2011.
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Guidance to laws and regulations: overview.
https://www.cms.gov/GuidanceforLawsAndRegulations. Accessed April 10, 2011.
Cornell University Law School Legal Information Institute. Tort. http://topics.law.cornell.edu/wex/tort. Accessed April 10, 2011.
Social Security Online. Information about Social Security's hearings and appeals process. http://www.ssa.gov/appeals. Accessed April 10,
2011.
The Library of Congress. Law Library of Congress. http://www.loc.gov/law. Accessed April 10, 2011.
US Citizenship and Immigration Services. Welcome to the United States: A guide for new immigrants.
ttp://www.uscis.gov/files/nativedocuments/M-618.pdf. Accessed April 8, 2011.
USA.gov. Federal executive branch. http://www.usa.gov/Agencies/Federal/Executive.shtml. Accessed April 10, 2011.
Charts, Tables and Images
6.2 Table: Example of court jurisdiction on various levels of government.
6. 3 Figure: Two important sub classifications of civil law are contract law and tort law. OHSU (2010).
6.4 Figure: The two types of Public Law that have the most effect on individuals are criminal law and administrative law. OHSU (2010).
21
Health IT Workforce Curriculum
Version 3.0/Spring 2012
Introduction to Healthcare and Public Health in the US
Regulating Healthcare
Lecture b
Regulating Healthcare
References Lecture b
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Future of Healthcare Reform in the United StatesDe la EverandThe Future of Healthcare Reform in the United StatesAnup MalaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Different Perspective on the Patient Protection and Affordable Care ActDe la EverandA Different Perspective on the Patient Protection and Affordable Care ActÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Rights Law Review-2015-Wang-hrlr - ngv025Document25 paginiHuman Rights Law Review-2015-Wang-hrlr - ngv025monÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Report On Health LawDocument21 paginiProject Report On Health LawAparna SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Health Care ReformDocument16 paginiThe Health Care ReformTowneMeadowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Law - Brief SummaryDocument202 paginiHealth Law - Brief Summaryhostel5knmuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Healthcare and Public Health in The USDocument28 paginiIntroduction To Healthcare and Public Health in The USHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - Health Law and EthicsDocument41 paginiChapter - Health Law and EthicsDr. philemon mwongeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Health 3 Student Guide To Group Activity No. 1Document4 paginiCommunity Health 3 Student Guide To Group Activity No. 1Aidenmee ConventoÎncă nu există evaluări
- (807439305) Health - LawDocument25 pagini(807439305) Health - LawIMRAN ALAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- V26 Young LemaitreDocument38 paginiV26 Young LemaitreVicky ChopraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 HSC Legal Studies MGDocument22 pagini2021 HSC Legal Studies MGzfp4dn5c86Încă nu există evaluări
- JohnPottow July2009 MedicalBankruptcyDocument8 paginiJohnPottow July2009 MedicalBankruptcyannualmedicalreport.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Law-Course Module-2019-20Document5 paginiHealth Law-Course Module-2019-20Harsh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Impacts of Bill C-10Document25 paginiHealth Impacts of Bill C-10The Criminalization and Punishment Education Project (CPEP)Încă nu există evaluări
- Mental Health LawsDocument55 paginiMental Health LawsCarmen Angela DusaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical MalpracticeDocument469 paginiMedical MalpracticeMuhammad Ali100% (1)
- Introduction To Healthcare and Public Health in The USDocument36 paginiIntroduction To Healthcare and Public Health in The USHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Hearing AidDocument9 paginiHearing AidporternovelliÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMC Anthology Medical Ethics For AMC and MCCQEDocument45 paginiAMC Anthology Medical Ethics For AMC and MCCQESana HameedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Berman: ForewordDocument7 paginiBerman: ForewordNew England Law ReviewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Law First DraftDocument10 paginiHealth Law First DraftNAYAN SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal Issues in Community Health NursingDocument22 paginiLegal Issues in Community Health NursingJune SavillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHCCOM005 Communication and Work in Health and Community Services 4Document13 paginiCHCCOM005 Communication and Work in Health and Community Services 4yESHEy TÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Health Information Technology in The U.S.: Payment-Related Issues and The Role of HITDocument22 paginiHistory of Health Information Technology in The U.S.: Payment-Related Issues and The Role of HITHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Healthcare and Public Health in The USDocument35 paginiIntroduction To Healthcare and Public Health in The USHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Healthcare and Public Health in The USDocument26 paginiIntroduction To Healthcare and Public Health in The USHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- 2022 HSC Legal Studies MGDocument21 pagini2022 HSC Legal Studies MGzfp4dn5c86Încă nu există evaluări
- Solution Manual For Health Care Management and The Law Principles and Applications 1st EditionDocument37 paginiSolution Manual For Health Care Management and The Law Principles and Applications 1st Editioneozoicjaggern2ni4100% (13)
- Answer To End of Chapter SolutionDocument98 paginiAnswer To End of Chapter SolutionTaher Jamil79% (19)
- Public Health Policies & LawsDocument41 paginiPublic Health Policies & LawsAYO NELSONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Download Community and Public Health Nursing 2nd Edition Harkness Demarco Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDocument36 paginiFull Download Community and Public Health Nursing 2nd Edition Harkness Demarco Test Bank PDF Full Chapterspicymeditate.ujqh2100% (15)
- Task 1Document12 paginiTask 1aries usamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meeting 5Document5 paginiMeeting 5Nadia ArviantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Health Care and T H E Principle of Fair Equality of OpportunityDocument21 paginiA Health Care and T H E Principle of Fair Equality of OpportunitydocsincloudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Negligence Liability in Medical Examination and Treatment in Vietnam in Comparision ReviewDocument22 paginiNegligence Liability in Medical Examination and Treatment in Vietnam in Comparision ReviewsimonpeternekesaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Proposal LawDocument5 paginiResearch Proposal Lawapi-352769442Încă nu există evaluări
- HCS 455 - Policy Process - Part 1 - Health Care Reform - Week 3Document8 paginiHCS 455 - Policy Process - Part 1 - Health Care Reform - Week 3Dawn Wrightington0% (1)
- Session 4Document76 paginiSession 4priyanshiraichada15Încă nu există evaluări
- History of Health Information Technology in The U.SDocument29 paginiHistory of Health Information Technology in The U.SHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Solution Manual For American Public Policy An Introduction 11th EditionDocument19 paginiSolution Manual For American Public Policy An Introduction 11th EditionScottWyattognje100% (42)
- Section 7 Master FileDocument7 paginiSection 7 Master FilesjsdiofjsoijÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01-04B - Introduction To Healthcare and Public Health in The US - Unit 04 - Financing Healthcare Part 1 - Lecture BDocument18 pagini01-04B - Introduction To Healthcare and Public Health in The US - Unit 04 - Financing Healthcare Part 1 - Lecture BHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Accommodation and Compliance Series: The ADA Amendments Act of 2008Document15 paginiAccommodation and Compliance Series: The ADA Amendments Act of 2008Barry BurijonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Paper FinalDocument19 paginiResearch Paper Finalapi-350383601100% (1)
- The Year in US Occupational Health & Safety 2012Document48 paginiThe Year in US Occupational Health & Safety 2012Celeste MonfortonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environment Protection Act in Relation To Health LawDocument25 paginiEnvironment Protection Act in Relation To Health LawNandini TarwayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Green Amendment Explainer - Fein Otterbein 3Document7 paginiGreen Amendment Explainer - Fein Otterbein 3Karlin RickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Green Amendment Explainer - Fein OtterbeinDocument7 paginiGreen Amendment Explainer - Fein OtterbeinKarlin RickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Green Amendment Explainer - Fein OtterbeinDocument7 paginiGreen Amendment Explainer - Fein OtterbeinKarlin RickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Green Amendment Explainer - Fein OtterbeinDocument7 paginiGreen Amendment Explainer - Fein OtterbeinKarlin RickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Healthy, Wealthy, and Wise: 5 Steps to a Better Health Care System, Second EditionDe la EverandHealthy, Wealthy, and Wise: 5 Steps to a Better Health Care System, Second EditionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Psle - Raise Your Voice, Each Vote CountDocument4 paginiPsle - Raise Your Voice, Each Vote CountHarsh SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vikas Gawai Right To HealthDocument7 paginiVikas Gawai Right To Healthrtjadhav158721804Încă nu există evaluări
- Beyond Earth Reseach Packet 2Document13 paginiBeyond Earth Reseach Packet 2Slaine Saazbaum TroyardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1Document4 paginiModule 1api-612975585Încă nu există evaluări
- Safe Practice - EditedDocument8 paginiSafe Practice - EditedSufyan MumtazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bloche-Health Law and Policy Exam Outline 2020Document70 paginiBloche-Health Law and Policy Exam Outline 2020Trevor RhodesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Code Red: An Economist Explains How to Revive the Healthcare System without Destroying ItDe la EverandCode Red: An Economist Explains How to Revive the Healthcare System without Destroying ItÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8sfnf Medical MalpracticeDocument469 pagini8sfnf Medical MalpracticeSana Khairi100% (2)
- 10 - Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign - Unit 6 - Process Redesign - Lecture CDocument23 pagini10 - Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign - Unit 6 - Process Redesign - Lecture CHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- 10 - Fundamentals of Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign - Unit 7 - Facilitating Meetings For Implementation DecisionsDocument23 pagini10 - Fundamentals of Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign - Unit 7 - Facilitating Meetings For Implementation DecisionsHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- 10 - Fundamentals of Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign - Unit 9 - Leading and Facilitating ChangeDocument31 pagini10 - Fundamentals of Workflow Process Analysis and Redesign - Unit 9 - Leading and Facilitating ChangeHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- 09 - Networking and Health Information Exchange - Unit 4 - Basic Health Data Standards - Lecture ADocument17 pagini09 - Networking and Health Information Exchange - Unit 4 - Basic Health Data Standards - Lecture AHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Health IT Workforce 10: Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and RedesignDocument87 paginiHealth IT Workforce 10: Fundamentals of Health Workflow Process Analysis and RedesignHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- 08 - SHC Relevant DataDocument3 pagini08 - SHC Relevant DataHealth IT Workforce Curriculum - 2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Prevention of Catheter Associated Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument61 paginiPrevention of Catheter Associated Urinary Tract Infectionsdex99Încă nu există evaluări
- LogiqC3 BrochureDocument2 paginiLogiqC3 BrochureMifaul AzmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific Programme (Tentative)Document2 paginiScientific Programme (Tentative)DivyaDeepthi18Încă nu există evaluări
- To Develop A Classification Model For Health Insurance SectorDocument5 paginiTo Develop A Classification Model For Health Insurance SectorAtulAtulKumarAgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aging Facial Skeleton PrsDocument10 paginiAging Facial Skeleton PrsJorge TreviñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Falls Risk InterventionsDocument1 paginăFalls Risk InterventionsPuja PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irrigation FluidDocument29 paginiIrrigation Fluidnestea42Încă nu există evaluări
- 999 257 Distalizer PEDocument6 pagini999 257 Distalizer PEOrtho OrganizersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Individual Health Insurance CoveragesDocument25 paginiIndividual Health Insurance Coveragesmannajoe70% (1)
- Hospital Detail As On 23 04 2021Document5 paginiHospital Detail As On 23 04 2021Ritu MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Austrilia Health CareDocument23 paginiAustrilia Health CarePandaman PandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hospital Organizational ChartDocument1 paginăHospital Organizational ChartAnonymous tDXlfJxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prognocis Meaningful Use GuidelinesDocument57 paginiPrognocis Meaningful Use GuidelinesKay MercadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ehr Poster 1 1Document1 paginăEhr Poster 1 1api-542441070Încă nu există evaluări
- Forensik KlinikDocument19 paginiForensik Klinikjoko_prasetio8268Încă nu există evaluări
- PPCA Impact On Medicare PayDocument21 paginiPPCA Impact On Medicare PaySupercoderÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPHRM Legal and Regulatory Version 2Document147 paginiCPHRM Legal and Regulatory Version 2Hosam GomaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Draft Sponsorship Application Form - For Hospital (PERNEFRI 2017)Document4 paginiDraft Sponsorship Application Form - For Hospital (PERNEFRI 2017)agustÎncă nu există evaluări
- Support Services Available in Greensboro, NCDocument1 paginăSupport Services Available in Greensboro, NCMote of Dust FilmsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Trial 28 FebDocument1 paginăFree Trial 28 FebByron Lu Morrell0% (1)
- Practice and Opinion Towards Disposal of Unused Medication in KuwaitDocument6 paginiPractice and Opinion Towards Disposal of Unused Medication in KuwaitAmirul AdamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding MedicareDocument4 paginiUnderstanding Medicare1224adhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Attendance and Treatment - 601.: Section A DefinitionsDocument1 paginăMedical Attendance and Treatment - 601.: Section A DefinitionsHari GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 10 18Document621 pagini3 10 18SumanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3A - Hospital PharmacyDocument13 pagini3A - Hospital PharmacyekramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric TMC Cover LetterDocument1 paginăPediatric TMC Cover Letterapi-383929607Încă nu există evaluări
- Telehealth: Review and Perspectives For SingaporeDocument33 paginiTelehealth: Review and Perspectives For Singaporesuhangmydoc100% (1)
- Pestel AnalysisDocument3 paginiPestel AnalysisfatimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WCASevereConditionsFAQs 0Document4 paginiWCASevereConditionsFAQs 0Gail Ward100% (1)
- Kokomo Perspective August 17Document30 paginiKokomo Perspective August 17kokomonewsÎncă nu există evaluări