Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
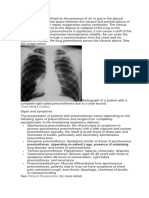
Barotrauma Radiology Images
Încărcat de
Anas Yahya0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
64 vizualizări15 paginibarotrauma
Titlu original
Baro Trauma
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentbarotrauma
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
64 vizualizări15 paginiBarotrauma Radiology Images
Încărcat de
Anas Yahyabarotrauma
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 15
BAROTRAUMA
Debi McCutcheon, MIV
Radiology Rotation
March 26, 2007
Barotrauma-Definition
Injury to air-containing structures, such as
the middle ears, sinuses, lungs, and
gastrointestinal tract, due to unequal
pressure differences across their walls .
Barotrauma-Etiologies
Mechanical Ventilation with or without
acute respiratory distress syndrome
Surgery
Asthma
COPD
Interstitial lung disease
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia
Barotrauma-Incidence
Seen most frequently in ICUs. In a study
published in American Journal of
Respiratory Critical Care Medicine in April
2002, 13% of patients with acute lung injury
and/or acute respiratory distress syndrome
developed early barotrauma within four
days and was noted to be directly related to
increased levels of PEEP.
Barotrauma-Pathophysiology
In mechanically ventilated patients,
ventilator induced lung injury (VILI) can
lead to barotrauma.
ARDS/ALI/Chronic Interstitial lung disease
have heterogeneous portions which
respond differently to pressure volume
introduced which leads to maldistribution of
tidal volume.
Barotrauma-Pathophysiology
Some alveoli become more distended than
others. Alveolar pressure increases and
forms a pressure gradient between the
alveoli and adjacent perivascular sheath.
Air dissects into the perivascular sheath
leading to perivascular interstitial
emphysema (PIE) and further moves into
areas of least resistance including
subcutaneous tissue and tissue planes.
Barotrauma-Complications
Pneumothorax
Interstitial emphysema
Pneumomediastinum-leads to PTX in 42%
of patients in one study
Pneumopericardium
Subcutaneous emphysema
Pneumoperitoneum
Barotrauma-radiographic images
Early-pulmonary interstitial emphysema and
subcutaneous emphysema
Barotrauma-Radiographic Images
Rt-mid lung-subpleural cyst
Barotrauma-Radiographic Images
One helluva Lft Pneumothorax
Barotrauma-Radiographic Images
Pneumomediastinum
Barotrauma-Radiographic Images
Pneumopericardium
Barotrauma-Radiographic Images
Pneumoperitoneum
Barotrauma-Treatments
Air must be evacuated with chest tube,
surgical evacuation, etc.
Lower tidal volumes are being used more
frequently to avoid this complication as
etiology appears to arise more from
increased volume as opposed to pressure.
Bibliography
http://www.emedicine.com. Barotrauma, July 10, 2006. Guy W Soo Hoo, MD,
Director, MICU, Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary and Critical
Care Section, West Los Angeles VA Healthcare Center
Airway Pressures and Early Barotrauma in Patients with Acute Lung Injury and Adult
Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Mark D. Eisner. American Journal of Respiratory
Critical Care Medicine, Vol 165, No 7, April 2002, 978-982.
Dr. Neuffer, the coolest radiologist I ever knew.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- BarotraumaDocument15 paginiBarotraumaEfa YusufÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax, Tension and TraumaticDocument29 paginiPneumothorax, Tension and TraumaticicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TBL Enfermedades de La Pleura - Lectura 2Document13 paginiTBL Enfermedades de La Pleura - Lectura 2Jose LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eumothorax: Assessment and Diagnostic TestingDocument4 paginiEumothorax: Assessment and Diagnostic TestingPANTS1Încă nu există evaluări
- Modern diagnosis and surgical management of pneumothoraxDocument8 paginiModern diagnosis and surgical management of pneumothoraxThia SanjayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumothoraxDocument13 paginiPneumothoraxRex NamudÎncă nu există evaluări
- TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX (Malav Shah)Document66 paginiTENSION PNEUMOTHORAX (Malav Shah)Sharath PsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventilator-Inducedlung Injury: Jeremy R. Beitler,, Atul Malhotra,, B. Taylor ThompsonDocument14 paginiVentilator-Inducedlung Injury: Jeremy R. Beitler,, Atul Malhotra,, B. Taylor ThompsonPaulHerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bullae, PneumothraxDocument20 paginiBullae, PneumothraxJim Albert PerlasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tension MedscapeDocument24 paginiTension MedscapeHandayaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest PainDocument15 paginiChest PainDwiky AmarullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest: Postgraduate Education CornerDocument8 paginiChest: Postgraduate Education CornerCristian LermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Review of Pneumothorax Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument5 paginiClinical Review of Pneumothorax Diagnosis and TreatmentAhmad SaifuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax and Pneumomediastinum: Dr. Emad EfatDocument89 paginiPneumothorax and Pneumomediastinum: Dr. Emad Efatinterna MANADOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax, Tension and TraumaticDocument24 paginiPneumothorax, Tension and TraumaticSatria WibawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax diagnosis and treatment guideDocument16 paginiPneumothorax diagnosis and treatment guideIbnu DharmajatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumothoraxDocument36 paginiPneumothoraxEira Lopez60% (5)
- Diagnosis and Management of Traumatic PneumothoraxDocument8 paginiDiagnosis and Management of Traumatic PneumothoraxsimcassÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Diagnosis and Management of Traumatic PneumothoraxDocument14 paginiPrinciples of Diagnosis and Management of Traumatic PneumothoraxEkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax: Classification and EtiologyDocument17 paginiPneumothorax: Classification and EtiologyPASMOXÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax Classification and Etiology: Clinics in Chest Medicine November 2021Document18 paginiPneumothorax Classification and Etiology: Clinics in Chest Medicine November 2021Maria Asri PranataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perioperative Pulmonary Atelectasis - Part II. Clinical Implications Anesthesiology American Society of AnesthesiologistsDocument78 paginiPerioperative Pulmonary Atelectasis - Part II. Clinical Implications Anesthesiology American Society of Anesthesiologistsrina yulianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- View Media GalleryDocument2 paginiView Media GalleryDhiya RahadianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Jesse B. Hall, MD, FCCPDocument12 paginiAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Jesse B. Hall, MD, FCCPMayun CacoellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Articulo Parcial 1 Urgencias Respiratorias Perros y GatosDocument23 paginiArticulo Parcial 1 Urgencias Respiratorias Perros y GatosYara Valentina Toledo ManriqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis of PneumothoraxDocument49 paginiClinical Presentation and Diagnosis of PneumothoraxisahÎncă nu există evaluări
- TensionDocument5 paginiTensionMutia FatinÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARDSDocument55 paginiARDSSandhya HarbolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pulmonary Trauma Emergency Department Evaluation and ManagementDocument23 paginiPulmonary Trauma Emergency Department Evaluation and ManagementPq PrissÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax Classification and Etiology: Clinics in Chest Medicine November 2021Document18 paginiPneumothorax Classification and Etiology: Clinics in Chest Medicine November 2021DesyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax Classification and Etiology: Clinics in Chest Medicine November 2021Document18 paginiPneumothorax Classification and Etiology: Clinics in Chest Medicine November 2021joaquinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tension Pneumothorax - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument9 paginiTension Pneumothorax - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfshinta damayantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventilatory Strategies in Obstructive Lung. Parrilla2014Document10 paginiVentilatory Strategies in Obstructive Lung. Parrilla2014EzeBorjesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treatment Options of Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Abdullah Al-QudahDocument10 paginiTreatment Options of Spontaneous Pneumothorax: Abdullah Al-QudahIneMeilaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alok Sinha Department of Medicine Manipal College of Medical Sciences Pokhara, NepalDocument46 paginiAlok Sinha Department of Medicine Manipal College of Medical Sciences Pokhara, NepalAnnushika PalanichamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.pneumothorax Imaging - Practice Essentials, Radiography, Computed TomographyDocument11 pagini4.pneumothorax Imaging - Practice Essentials, Radiography, Computed TomographyAchmadRizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bronchopleural Fistula in The Mechanically Ventilated Patient: A Concise ReviewDocument10 paginiBronchopleural Fistula in The Mechanically Ventilated Patient: A Concise Reviewronsua1966Încă nu există evaluări
- Hfo 3Document8 paginiHfo 3markus_danusantosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Primary Spontaneous PneumothoraxDocument6 paginiManagement of Primary Spontaneous PneumothoraxPendragon ArthurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax: From Definition To Diagnosis and Treatment: Review ArticleDocument5 paginiPneumothorax: From Definition To Diagnosis and Treatment: Review ArticleRiani NazilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Re Expansion Pulmonary EdemaDocument4 paginiRe Expansion Pulmonary EdemarendyjiwonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A PneumothoraxDocument4 paginiWhat Is A PneumothoraxCharyl Naganag ColanganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax Case FileDocument2 paginiPneumothorax Case Filehttps://medical-phd.blogspot.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manajemen VentiDocument2 paginiManajemen VentiBos AseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chest DrainDocument4 paginiChest DrainGALINDO PE?A JOSE EDUARDOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sep 1, 2011) Journal: Medscape Radiology: Radiological Society of North AmericaDocument19 paginiSep 1, 2011) Journal: Medscape Radiology: Radiological Society of North AmericaMohamad Rizki DwikaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Respiratory Distress John Rae 2019Document6 paginiAcute Respiratory Distress John Rae 2019yyullyyannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home - Clinical - Management - News - Products - Protocols/Guidelines - Research - Buyer's Guide - Expert Insight - ArchivesDocument8 paginiHome - Clinical - Management - News - Products - Protocols/Guidelines - Research - Buyer's Guide - Expert Insight - ArchivesDuvvuri SankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Ventilation To Minimize Progression of Lung Injury in Acute Respiratory FailureDocument5 paginiMechanical Ventilation To Minimize Progression of Lung Injury in Acute Respiratory FailureGenoveva Navarro SolorzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MECHANICAL VENTILATION ASSIGNMENTDocument14 paginiMECHANICAL VENTILATION ASSIGNMENTNeha ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr Chiranjib Bhattacharyya's Guide to Diagnosing and Treating Bronchopleural FistulaDocument40 paginiDr Chiranjib Bhattacharyya's Guide to Diagnosing and Treating Bronchopleural FistulaFadhli AzhimiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ventilation During Lung Resection and Critical Care ComparativeDocument11 paginiVentilation During Lung Resection and Critical Care Comparativeema moralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study For PneumothoraxDocument4 paginiCase Study For PneumothoraxGabbii CincoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumothotaxDocument32 paginiPneumothotaxAvishay ZoarÎncă nu există evaluări
- PneumothoraxDocument14 paginiPneumothoraxAsterlita WenasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Travel and PneumothorakDocument7 paginiAir Travel and PneumothorakRojullun TaufikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tension Pneumothorax: History and PhysicalDocument5 paginiTension Pneumothorax: History and PhysicalKenneth AndayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumothorax and Hemothorax GuideDocument32 paginiPneumothorax and Hemothorax GuideYan Sheng HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rare and Interesting Cases in Pulmonary MedicineDe la EverandRare and Interesting Cases in Pulmonary MedicineEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesDe la EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Lancet Volume 29 Issue 735 1837 (Doi 10.1016/s0140-6736 (02) 81169-2) Lambton, W - Strangulated Scrotal Hernia, Congenital. Operation,-CureDocument2 paginiThe Lancet Volume 29 Issue 735 1837 (Doi 10.1016/s0140-6736 (02) 81169-2) Lambton, W - Strangulated Scrotal Hernia, Congenital. Operation,-CureAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Groin Hernia: VZI, But It May Well Be That A Long Follow-UpDocument3 paginiGroin Hernia: VZI, But It May Well Be That A Long Follow-UpAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peripheral Arterial DiseaseDocument11 paginiPeripheral Arterial DiseaseAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cigarette Smoking: Information From TheDocument6 paginiCigarette Smoking: Information From TheAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cigarette Smoking: Information From TheDocument6 paginiCigarette Smoking: Information From TheAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stigma Palliative CareDocument5 paginiStigma Palliative CareAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SmileDocument1 paginăSmileAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2007 Cummings 1070 6Document8 paginiCancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2007 Cummings 1070 6Anas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benefit of Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis For Acute Iliofemoral DVT: Myth or Reality?Document2 paginiBenefit of Catheter-Directed Thrombolysis For Acute Iliofemoral DVT: Myth or Reality?Anas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cigarette Smoking: Information From TheDocument6 paginiCigarette Smoking: Information From TheAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pleural Effusions: Kara Lee Gallagher USC School of MedicineDocument20 paginiPleural Effusions: Kara Lee Gallagher USC School of MedicineAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cigarette Smoke and Adverse Health EffectsDocument7 paginiCigarette Smoke and Adverse Health EffectsAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervus Fasialis Files of DrsmedDocument19 paginiNervus Fasialis Files of DrsmedAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital MammographyDocument11 paginiDigital MammographyAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fractures: (On Which We Will Likely Be Pimped)Document66 paginiFractures: (On Which We Will Likely Be Pimped)Marivic DianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adult Sinusitis GuidelineDocument31 paginiAdult Sinusitis Guidelineralu33Încă nu există evaluări
- Status Epilepticus Treatment & Management: Julie L Roth, MD Chief Editor: Stephen A Berman, MD, PHD, MbaDocument2 paginiStatus Epilepticus Treatment & Management: Julie L Roth, MD Chief Editor: Stephen A Berman, MD, PHD, MbaAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Radiology CHFDocument13 paginiDiagnostic Radiology CHFAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SinusitusDocument14 paginiSinusitusAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bruno Mars - Marry YouDocument2 paginiBruno Mars - Marry YouAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- KATY PERRY ROAR LYRICSDocument2 paginiKATY PERRY ROAR LYRICSAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP Rewards Lucky Draw TNC April2013 Id-EnDocument4 paginiHP Rewards Lucky Draw TNC April2013 Id-EnAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP Rewards Lucky Draw TNC April2013 Id-EnDocument4 paginiHP Rewards Lucky Draw TNC April2013 Id-EnAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerumen ImpactionDocument7 paginiCerumen ImpactionAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complete Guide To ECGDocument78 paginiComplete Guide To ECGAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DreamDocument1 paginăDreamAnas YahyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOPs for Attestation of Educational and Personal DocumentsDocument10 paginiSOPs for Attestation of Educational and Personal DocumentsatifrjÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIDDLE ENGLISH TEST HEALTH VOCATIONAL HIGH SCHOOLDocument4 paginiMIDDLE ENGLISH TEST HEALTH VOCATIONAL HIGH SCHOOLZaenul WafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self ManagementDocument65 paginiSelf ManagementMusa Eve AikehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculate The Max Doses of Local Anesthesia in DentistryDocument13 paginiCalculate The Max Doses of Local Anesthesia in DentistryYasser MagramiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Hazards For The Nurse As A Worker - Nursing Health, & Environment - NCBI Bookshelf PDFDocument6 paginiEnvironmental Hazards For The Nurse As A Worker - Nursing Health, & Environment - NCBI Bookshelf PDFAgung Wicaksana100% (1)
- Part A Reading Task Playground Injuries Playground Surface MaterialDocument8 paginiPart A Reading Task Playground Injuries Playground Surface MaterialMitra NabizadehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cosmetic BrochureDocument4 paginiCosmetic BrochureDr. Monika SachdevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 22 The First Heart SoundDocument5 paginiChapter 22 The First Heart SoundAbhilash ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH 021 enDocument4 paginiPH 021 enjohnllenalcantaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report On Legal Medicine PowerpointDocument31 paginiReport On Legal Medicine PowerpointEdwin VillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- As 2550.5-2002 Cranes Hoists and Winches - Safe Use Mobile CranesDocument8 paginiAs 2550.5-2002 Cranes Hoists and Winches - Safe Use Mobile CranesSAI Global - APACÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Estimation of Rain Water Harvesting Scheme in VIVA Institute of TechnologyDocument4 paginiDesign and Estimation of Rain Water Harvesting Scheme in VIVA Institute of TechnologyVIVA-TECH IJRIÎncă nu există evaluări
- October 2022 Complete Month CA English - CompressedDocument117 paginiOctober 2022 Complete Month CA English - CompressedKing JÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anarchy RPG 0.2 Cover 1 PDFDocument14 paginiAnarchy RPG 0.2 Cover 1 PDFanon_865633295Încă nu există evaluări
- Remark: (Out Patient Department)Document7 paginiRemark: (Out Patient Department)Tmiky GateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dat IatDocument4 paginiDat Iatscribd birdÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Case of Eclectic Family TherapyDocument88 paginiA Case of Eclectic Family Therapygun gorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skema Jawapan Gerak Gempur 1Document5 paginiSkema Jawapan Gerak Gempur 1Cikgu RoshailaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labcorp: Patient ReportDocument4 paginiLabcorp: Patient ReportAsad PrinceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immersion Death: Dr. Rayyan Al-AliDocument42 paginiImmersion Death: Dr. Rayyan Al-AliRayyan AlaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Packaged Drinking Water Project ProfileDocument5 paginiPackaged Drinking Water Project ProfileArpna BhatiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legalizing abortion in the Philippines for women's health and rightsDocument2 paginiLegalizing abortion in the Philippines for women's health and rightsRosario Antoniete R. Cabilin100% (1)
- Week 6 - LP Modeling ExamplesDocument36 paginiWeek 6 - LP Modeling ExamplesCharles Daniel CatulongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Everything You Need to Know About Prenatal CareDocument5 paginiEverything You Need to Know About Prenatal Carelaura fernandiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Portal Hypertension Clinical Features and ManagementDocument29 paginiPortal Hypertension Clinical Features and ManagementPhilip LingÎncă nu există evaluări
- TuDocument382 paginiTuAndra NiculaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radiographic Cardiopulmonary Changes in Dogs With Heartworm DiseaseDocument8 paginiRadiographic Cardiopulmonary Changes in Dogs With Heartworm DiseaseputriwilujengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Municipal Ordinance No. 05-2008Document5 paginiMunicipal Ordinance No. 05-2008SBGuinobatan100% (2)
- Dapagliflozin Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, WarningsDocument8 paginiDapagliflozin Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, WarningspatgarettÎncă nu există evaluări
- IFCC Visiting LectureDocument3 paginiIFCC Visiting LectureMaruhum NurÎncă nu există evaluări