Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
01 Spinal Cord Injury
Încărcat de
Nurul Izzah Mat Sundari0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
93 vizualizări22 paginiThis document provides an overview of spinal cord anatomy and injury. It describes the 33 vertebrae that make up the vertebral column and how the spinal cord runs through the vertebral canal. The spinal cord extends from the foramen magnum to the L2 vertebra and gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves. The document outlines the protective layers surrounding the spinal cord as well as the anatomy of the spinal cord cross-section and roots of the spinal nerves. It also discusses upper motor neuron lesions versus lower motor neuron lesions and their distinguishing characteristics.
Descriere originală:
spinal cord injury
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThis document provides an overview of spinal cord anatomy and injury. It describes the 33 vertebrae that make up the vertebral column and how the spinal cord runs through the vertebral canal. The spinal cord extends from the foramen magnum to the L2 vertebra and gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves. The document outlines the protective layers surrounding the spinal cord as well as the anatomy of the spinal cord cross-section and roots of the spinal nerves. It also discusses upper motor neuron lesions versus lower motor neuron lesions and their distinguishing characteristics.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
93 vizualizări22 pagini01 Spinal Cord Injury
Încărcat de
Nurul Izzah Mat SundariThis document provides an overview of spinal cord anatomy and injury. It describes the 33 vertebrae that make up the vertebral column and how the spinal cord runs through the vertebral canal. The spinal cord extends from the foramen magnum to the L2 vertebra and gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves. The document outlines the protective layers surrounding the spinal cord as well as the anatomy of the spinal cord cross-section and roots of the spinal nerves. It also discusses upper motor neuron lesions versus lower motor neuron lesions and their distinguishing characteristics.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 22
Spinal cord injury
Mohd Hafiz Idlan Bin Radzali
0910683
Mr Zamzuri
outline
Anatomy
Pathophysiology
Diagnosis
Management
Complication
Anatomy
Spinal vertebrae
Composed of 33
vertebrae
7 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral
4 coccygeal
Vertebral columns
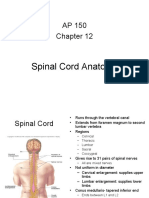
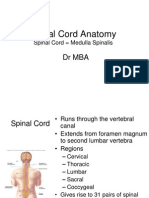
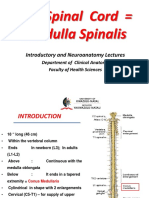
Spinal cord
Runs through the vertebral canal
Extends from foramen magnum to
second lumbar vertebra
Regions
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
Coccygeal
Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal
nerves
All are mixed nerves
Not uniform in diameter
Cervical enlargement: supplies
upper limbs
Lumbar enlargement: supplies
lower limbs
Conus medullaris- tapered inferior
end
Ends between L1 and L2
Cauda equina - origin of spinal
nerves extending inferiorly from
conus medullaris.
Protective layers
Connective tissue membranes
Dura mater: outermost layer; continuous with epineurium of the spinal nerves
Arachnoid mater: thin layer
Pia mater: bound tightly to surface
Forms the filum terminale
anchors spinal cord to coccyx
Forms the denticulate ligaments that attach the spinal cord to the dura
Spaces
Epidural: external to the dura
Anesthestics injected here
Fat-fill
Subdural space: serous fluid
Subarachnoid: between pia and arachnoid
Filled with CSF
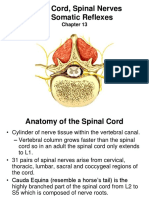
Cross section
Anterior median fissure and posterior median sulcus
deep clefts partially separating left and right halves
Gray matter: neuron cell bodies, dendrites, axons
Divided into horns
Posterior (dorsal) horn
Anterior (ventral) horn
Lateral horn
Intermediate column
White matter
Myelinated axons
Divided into three columns (funiculi)
Ventral
Dorsal
lateral
Each of these divided into sensory or motor tracts
Root of spinal nerves
Roots
31 pairs of Spinal nerves arise as rootlets then combine to form dorsal
and ventral roots
Dorsal and ventral roots merge laterally and form the spinal nerve
Ventral(Motor) roots
Each Joint: typically by 4 spinal nerves
Hip flexion: L2,L3 extension: L4,L5
Knee extension: L3,L4 flexion: L5, S1
Dorsiflexion: L4, L5 plantar flexion: S1,S2
Inversion: L4 Eversion: L5, S1
Shoulder Abd: C5 Adduction: C6, C7
Elbow flexion: C5, C6 Extension: C6, C7
Wrist: C6, C7 Fingers: C7, C8
Pronation
& Supination: C6
Dorsal(sensory)
Blood supply
Anterior spinal artery
Posterior spinal artery
Radicular artery
Internal vertebral
venous plexus
Neurological injuries
UMNL vs LMNL
UMNL
Cerebral cortex (pyramidal tract) > Precentral gyrus (motor
strip) internal capsule (posterior limb) brainstem
spinal cord
Interruption of the corticospinal and corticonuclear tract
along its course
LMNL
Anterior horn cells in spinal cordnerve rootsnerve plexus
peripheral nerves
Degeneration of the motor neuron & peripheral nerves
UMNL vs LMNL
UMNL
Weakness in all muscle
group
Very little muscle wasting
No fasciculation
Hypertonia
Hyperreflexia
Positive Babinski
LMNL
Weakness of individual
muscles
Muscle wasting prominent
feature
Fasciculation
Hypotonia
Hyporeflexia
Normal or absent babinski
Thank you
References
Apleys System of Orthopaedics and Fractures,
9
th
edition.
Pocketbook of Ortho and Fractures,McRae, 2
nd
Edition
Netters Concise Ortho Anatomy
Clinical Anatomy by regions 8
th
edition
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument57 paginiIntroduction To Human AnatomyJomari Kilantang100% (2)
- Caudal Medulla: Midbrain Inferior ColliculusDocument5 paginiCaudal Medulla: Midbrain Inferior ColliculusKiana TehraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy - Nervous System - Spinal Cord and Motor and Sensory PathwaysDocument43 paginiAnatomy - Nervous System - Spinal Cord and Motor and Sensory PathwaysYAMINIPRIYAN100% (1)
- 16 Back Spinal CordDocument27 pagini16 Back Spinal CordAnonymous lsnDTjvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urinary SystemDocument9 paginiUrinary SystemCailah Sofia SelausoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy SpineDocument31 paginiAnatomy SpineCodillia CheongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesDocument67 paginiSpinal Cord and Spinal NervesRAVISHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skin SCC Guide: Causes, Types, Risks & Treatment of Squamous Cell CarcinomaDocument18 paginiSkin SCC Guide: Causes, Types, Risks & Treatment of Squamous Cell CarcinomaNurul Izzah Mat SundariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord AnatomyDocument20 paginiSpinal Cord AnatomyrooparawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord Injury, DisordersDocument54 paginiSpinal Cord Injury, DisordersChananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 Module 1 The Menstrual CycleDocument20 paginiUnit 3 Module 1 The Menstrual CycleMARIANNE SORIANO100% (2)
- Routes & Mechanisms of MetastasisDocument26 paginiRoutes & Mechanisms of MetastasisNeetu GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arch Width and Form - A ReviewDocument9 paginiArch Width and Form - A ReviewMafe SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Spinal Cord,, and Blood Supply To The BrainDocument78 paginiThe Spinal Cord,, and Blood Supply To The BrainMartha MulusaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord AnatomyDocument22 paginiSpinal Cord AnatomyAbdallah ElshayahÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASSIGNMEN1Document11 paginiASSIGNMEN1Muhammad HuzaifaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 13 14Document63 paginiLab 13 14Gabriel BotezatuÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPINEDocument27 paginiSPINEMadhavarao MaddisettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord: DR Ganesh Khemnar Assistant Professor Dept. of Anatomy BVDUMC, PuneDocument43 paginiSpinal Cord: DR Ganesh Khemnar Assistant Professor Dept. of Anatomy BVDUMC, PunePraneetha NouduriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Anatomy & Physiology: Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic ReflexesDocument41 paginiHuman Anatomy & Physiology: Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic ReflexesSyarif MaulanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPINAL NERVE Presentation Completed-2Document51 paginiSPINAL NERVE Presentation Completed-2Sheikh Muhammad MuhallilÎncă nu există evaluări
- DrMBA Medulla SpinalisDocument25 paginiDrMBA Medulla SpinalisAyu FadhilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord Injury IntroductionDocument243 paginiSpinal Cord Injury Introductionfahad100% (1)
- Brain Anatomy: Diencephalon, Brain Stem and Medulla SpinalisDocument36 paginiBrain Anatomy: Diencephalon, Brain Stem and Medulla SpinalisAngela FovinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord: Prof DR Nasaruddin Abdul AzizDocument54 paginiSpinal Cord: Prof DR Nasaruddin Abdul Azizkyoko08Încă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord: Prof DR Nasaruddin Abdul AzizDocument54 paginiSpinal Cord: Prof DR Nasaruddin Abdul AzizBJKines BjmcÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.spinal CordDocument62 pagini5.spinal CordNishanth LakshmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Spinal CordDocument22 paginiThe Spinal Cordcy lifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essentials of the Spinal Cord and Nervous SystemDocument24 paginiEssentials of the Spinal Cord and Nervous Systemأمال داودÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.spinal CordDocument46 pagini3.spinal CorddenekeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Spinal Cord: DR - SatyaDocument61 paginiThe Spinal Cord: DR - SatyacheckmateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal CordDocument60 paginiSpinal CordPiyush KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous tissue functions and cell typesDocument34 paginiNervous tissue functions and cell typesSameer MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 - BrainstemDocument33 pagini4 - Brainstemb.ozyurek84Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 6Document4 paginiLecture 6A-Naeem To'mah Al-sawaieÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Spinal Cord Medulla Spinalis: Introductory and Neuroanatomy LecturesDocument24 paginiThe Spinal Cord Medulla Spinalis: Introductory and Neuroanatomy LecturesHumaira BadatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord Anatomy and FunctionsDocument5 paginiSpinal Cord Anatomy and FunctionsTida TpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal CordDocument38 paginiSpinal CordUrwah KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.spinal CordDocument29 pagini2.spinal CordPraneethaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Spinal CordDocument59 paginiThe Spinal CordbegeerizikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revit of Blood Supply of BrainDocument41 paginiRevit of Blood Supply of Brainepic sound everÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 Spinal CordDocument87 paginiChapter 5 Spinal CordOsman abdilahi nuurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-Spinal CordDocument57 paginiChapter-Spinal Cordsimi yÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 3 Spinal Cord, Spinal NervesDocument53 paginiWeek 3 Spinal Cord, Spinal NervesHephzibah JaporÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 3 Spinal Cord, Spinal NervesDocument53 paginiWeek 3 Spinal Cord, Spinal NervesCyril Jay G. OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal CordDocument27 paginiSpinal CordRashid DayaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord and Nerve Plexii: by Dr. TDocument20 paginiSpinal Cord and Nerve Plexii: by Dr. TthwisemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gross Anatomy of Spinal Cord: Dr. Normaizatul Afizah Ismail Normaizatul@unishams - Edu.myDocument48 paginiGross Anatomy of Spinal Cord: Dr. Normaizatul Afizah Ismail Normaizatul@unishams - Edu.mykalppena naiduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sci and Other Disease of The Spinal Cord: Slide 1Document9 paginiSci and Other Disease of The Spinal Cord: Slide 1Dyoan UhhmiitÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nervous System: Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument30 paginiThe Nervous System: Anatomy & PhysiologyDrAvinash NandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- تشريح فاينل جميع المحاضراتDocument167 paginiتشريح فاينل جميع المحاضراتحجيه X5Încă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord and Nerve Anatomy and Disorders/TITLEDocument21 paginiSpinal Cord and Nerve Anatomy and Disorders/TITLESiddharth SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord, Nerve Roots, Peripheral Nerves, and SynapsesDocument97 paginiSpinal Cord, Nerve Roots, Peripheral Nerves, and SynapsesLynx Kee BayatingÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves: - Together With Brain Forms The CNS - FunctionsDocument36 paginiThe Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves: - Together With Brain Forms The CNS - FunctionsJeannie LongoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal ReflexesDocument43 paginiThe Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal ReflexesSyed Irfan ArifÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 BMC Lecture Spinal Cord (Autosaved)Document63 pagini4 BMC Lecture Spinal Cord (Autosaved)Hoang Nhu NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal ReflexesDocument43 paginiChapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal ReflexesEzekiel ArtetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument60 paginiNervous SystemFiraol DiribaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal CardDocument10 paginiSpinal CardAsawara NoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy Fisiologi Spine LumbosacralDocument27 paginiAnatomy Fisiologi Spine LumbosacraloyomziicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Cord Embryology, Neuroanatomy & NeurophysiologyDocument60 paginiSpinal Cord Embryology, Neuroanatomy & NeurophysiologyNadia Vinka LisdiantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain Stem: - Located BTWN The Cerebrum and The SCDocument41 paginiBrain Stem: - Located BTWN The Cerebrum and The SCnkuligowskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuro 3 Brainstem and Spinal Cord BriefDocument68 paginiNeuro 3 Brainstem and Spinal Cord BriefYasimini Ramadhani100% (1)
- Spinal Cord Anatomy and FunctionsDocument22 paginiSpinal Cord Anatomy and Functionsno lifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anesthesia Seminar 1 (PE)Document11 paginiAnesthesia Seminar 1 (PE)Nurul Izzah Mat SundariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decline of Ottoman EmpireDocument23 paginiDecline of Ottoman EmpireNurul Izzah Mat Sundari100% (1)
- Decline of Ottoman EmpireDocument23 paginiDecline of Ottoman EmpireNurul Izzah Mat Sundari100% (1)
- Male Genitals and Inguinal AreaDocument33 paginiMale Genitals and Inguinal AreabianqueeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1Document6 paginiDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1warren macraisinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iyengar Yoga For The Respiratory System-2020 PDFDocument13 paginiIyengar Yoga For The Respiratory System-2020 PDFSlice LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Integumentary System NotesDocument3 paginiThe Integumentary System NotesJose Enrico SumayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 - TissuesDocument103 pagini4 - TissuesAngel Alexis BiasonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manage Endocrine DisordersDocument2 paginiManage Endocrine DisordersJan Cyrel ColomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBBS Assignment on Histology of Spleen and Lymph NodesDocument3 paginiMBBS Assignment on Histology of Spleen and Lymph NodesAbhishek PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Thyroid ExaminationDocument6 paginiBasic Thyroid ExaminationPalwasha MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oesophagus Maag DuodenographyDocument49 paginiOesophagus Maag DuodenographyEvan DionesiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UOW BIOMD301 2 - Cells, Tissues and MembranesDocument40 paginiUOW BIOMD301 2 - Cells, Tissues and Membranesnandani ramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanisms of Coagulation and Fibrinolysis (Autosaved)Document60 paginiMechanisms of Coagulation and Fibrinolysis (Autosaved)Tom Anthony TonguiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class HolothuroideaDocument2 paginiClass HolothuroideaSecretsoushiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apraxia PDFDocument13 paginiApraxia PDFAndré CantanhedeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrene Disorders Kel. 11 (B.inggris)Document16 paginiEndocrene Disorders Kel. 11 (B.inggris)Arif WahyuÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANCFGBLOODBANK 0216 FinalDocument5 paginiANCFGBLOODBANK 0216 FinalShan AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Terminology Blood Lymph SystemsDocument29 paginiMedical Terminology Blood Lymph Systemsapi-268199514100% (1)
- Coreection Du TD D'anglais 21-22Document13 paginiCoreection Du TD D'anglais 21-22Issouf BertheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overhead Transparency Human AtlasDocument34 paginiOverhead Transparency Human Atlasdr tamerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestion and Absorption: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsDocument9 paginiDigestion and Absorption: Fact/Definition Type QuestionsNayan BhardwazÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Bodys Defence - MechanismDocument74 paginiThe Bodys Defence - Mechanismagarwaljenish2005Încă nu există evaluări
- Ubogu - Inflammatory NeuropathiesDocument24 paginiUbogu - Inflammatory NeuropathiesMarcelo BedoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immunochemistry: Frederick A. Bettelheim William H. Brown Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellDocument41 paginiImmunochemistry: Frederick A. Bettelheim William H. Brown Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellShereen AlobinayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homeostasis 2Document31 paginiHomeostasis 2Khayelihle WakaDingiswayo NtshakalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro 7Document2 paginiIntro 7QUIZANA, Ceazairenee P.Încă nu există evaluări
- Dental AnatomyDocument215 paginiDental AnatomyJAPINDERPREET KAURÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pes 2023Document1 paginăPes 2023dr_yasserÎncă nu există evaluări