Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Penyakit Jantung Pada Anak
Încărcat de
Anatasya PriharyayuDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Penyakit Jantung Pada Anak
Încărcat de
Anatasya PriharyayuDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
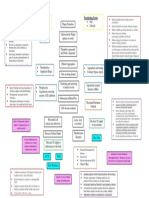
PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN
PADA ANAK
Deteksi dini penyakit jantung
pada anak
Biru
Aktifitas kurang
Sesak
Batuk berulang
Berat badan tidak meningkat
Structures of the heart
Penyakit Jantung Bawaan
A. PJB Asianotik
ASD
VSD
PDA
b. PJB Sianotik
- TF
- TGA
Normal Heart
Atrial Septal defect
( ASD )
Insidence : + 10 %
: ratio = 2 : 1
Anatomy :
Defect on foramen ovale : Secundum ASD
Defect at SVC and RA junction: sinus
venosus ASD
Defect at ostium primum : primum ASD
RA
RV
LA
LV
RA
RV
LA
LV
Atrial septal Defect
Clinical findings
Asymptomatic
Auscultation :
Normal 1st HS or loud
Widely split and fixed
2
nd
HS
Ejection systolic murmur
Atrial septal Defect
Atrial Septal defect
Management
Surgery : Preschool age
Recent treatment: transcatheter closure using
ASO (Amplatzer septal occluder)
Ventricular septal defect
Insidence
20 % of all CHD
No sex influence
RA
RV
RA
LA
LA
RV LV LV
Ventricular septal defect
Ventricular Septal Defect
Clinical findings
Day 1
st
after birth: murmur (-)
After 2-6 weeks : murmur (+)
Murmur : pansystolic grade 3/6 or higher
at LSB 3
Small muscular defect: early systolic murmur
Significant defect: Mid diastolic murmur at apex
Ventricular septal defect
Management:
Definitive : VSD closure
Surgery
Transcatheter closure
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Insidence
+ 10%
Female : Male = 1.2 to 1.5 : 1
Premature and LBW higher
Anatomy
Fetus: ductus arteriosus connects PA and aorta.
If ductus does not closs Patent Ductus arteriosus
RA
RV
LA
LV
RA
LA
RV LV
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Clinical findings
Small defect:
Symptom (-)
Growth and development normal
Significant defect:
Decreased exercise tolerant
Weigh gained not good
Frequent URTI
Specific case: pulsus seler at 4
th
extremities
Tetralogy Fallot
Insidence
5-8% from all CHD
Sindroma consist of 4 items:
VSD
pulmonary stenosis
aortic over-riding
RVH
Tetralogy Fallot
Hemodynamic acyanotic
Hemodynamic cyanotic
Tetralogy Fallot
Diagnosis
Clinically : cyanosis
Single 2
nd
HS, ejection systolic murmur
CXR :
Boot-shaped
Tetralogy Fallot
Transposition of Great
Artery
Insidence
5% of CHD
Anatomy
Abnormality of formation of trunkal septum that cause
aorta arising from RV and PA arising from LV
Transposition of Great artery
Hemodynamic normal
Hemodynamic of TGA
series parallel
Transposition of Great artery
TGA with large VSD TGA with VSD and PS
Transposition of Great artery
Clinical aspects
More frequent in male
Birth weight usually normal normal or bigger
Cyanotic vary from mild to severe
Auscultation : single 2
nd
HS and loud
Murmur vary from silent to pansystolic murmur or
continuous murmur
Transposition of Great artery
Diagnosis
Clinically :
Suspicious if neonates presents with cyanotic
with birth weight normal or bigger
Murmur (-)
Single 2
nd
HS and loud
Transposition of Great artery
Transposition of Great artery
CXR :
Cardiomegaly
Egg-on-side
heart
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Chapter - 014 Student HandoutsDocument16 paginiChapter - 014 Student Handoutsebiniyam2021Încă nu există evaluări
- Post PartumDocument22 paginiPost PartumShaira Mae Yante RomeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual Long Bone DissectionDocument2 paginiVirtual Long Bone Dissectionapi-438665079Încă nu există evaluări
- Small Animals - Advances - in - Fluid, - Electrolyte, - and - Acid-Base - DisordersDocument323 paginiSmall Animals - Advances - in - Fluid, - Electrolyte, - and - Acid-Base - Disordersprolixe108100% (1)
- Degnala DiseaseDocument12 paginiDegnala DiseaseSantosh Bhandari100% (1)
- CH 11 Admission, Discharge, Transfers & ReferralsDocument14 paginiCH 11 Admission, Discharge, Transfers & ReferralsNilakshi Barik Mandal100% (1)
- Fitzgerald AnnInternMed 1999 130 70 Curiosity PDFDocument3 paginiFitzgerald AnnInternMed 1999 130 70 Curiosity PDFPaulinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatric HistoryDocument63 paginiPsychiatric HistoryStarlet Rhonadez Bito-onon Oriel0% (1)
- Recovery From Tactile AgnosiaDocument12 paginiRecovery From Tactile AgnosiaIsaac Saucedo FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lastearthdistro PDFDocument24 paginiLastearthdistro PDFleonabrahamzapruderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary Syndrome - Concept MapDocument1 paginăAcute Coronary Syndrome - Concept MapWyen CabatbatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1908 Character and Anal ErotismDocument4 pagini1908 Character and Anal ErotismFutile Hurling100% (1)
- Dosage and SolutionsDocument3 paginiDosage and SolutionsNicole PageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radiologi Kedaruratan & Traumatologi-Prof. Dr. Bachtiar MDocument55 paginiRadiologi Kedaruratan & Traumatologi-Prof. Dr. Bachtiar MMonazzt AsshagabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carte PsihiatrieDocument9 paginiCarte PsihiatrieInna CazacliuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machupo VirusDocument15 paginiMachupo VirusiggyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sds Methode LimitationsDocument8 paginiSds Methode LimitationsorinadeesfuerzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AbortionDocument39 paginiAbortionMerielLouiseAnneVillamilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Screenshot 2564-04-16 at 09.45.04Document95 paginiScreenshot 2564-04-16 at 09.45.04Sarunpong ImampaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chin Chong MinDocument3 paginiChin Chong MinSHine PukurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 paginiUntitled Documentapi-388763698Încă nu există evaluări
- Doctor Mi Kay Khau Nandini DhargalkarDocument51 paginiDoctor Mi Kay Khau Nandini Dhargalkarabmopalhvac0% (1)
- Primary Awards 2012-2014 - CaribbeansDocument7 paginiPrimary Awards 2012-2014 - CaribbeansGuillaume PrefolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Johns Hopkins Dean - Reflections On Medical School AdmissionsDocument4 paginiJohns Hopkins Dean - Reflections On Medical School AdmissionstheintrepiddodgerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Program of Instruction First Aid With MciDocument10 paginiProgram of Instruction First Aid With MciShan Dave TupasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demystifying The Diagnosis and Classification of Lymphoma - Gabriel C. Caponetti, Adam BaggDocument6 paginiDemystifying The Diagnosis and Classification of Lymphoma - Gabriel C. Caponetti, Adam BaggEddie CaptainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sales Account Manager Biotechnology in Boston MA Resume Cynthia SmithDocument2 paginiSales Account Manager Biotechnology in Boston MA Resume Cynthia SmithCynthiaSmith2Încă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine PathologyDocument13 paginiEndocrine Pathologysarguss14100% (1)
- What Is Personal HygieneDocument4 paginiWhat Is Personal HygieneAnonymous 0FWhoTu100% (1)
- KVG Medical CollegeDocument11 paginiKVG Medical CollegepentagoneducationÎncă nu există evaluări