Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Dams
Încărcat de
Meggy VillanuevaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Dams
Încărcat de
Meggy VillanuevaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
DAMS:
Dams are structures that block the flow of a river, stream, or
other waterway.
Purpose of a Dam:
Dams are built for the following purposes:
1. Irrigation and drinking water
2. Power generation (hydroelectric)
3. Navigation
4. Flood Control
5. Multi purposes
TYPES OF DAMS:
1. Gravity Dams use only the force of gravity to resist water
pressure that is, they hold back water by the sheer force of
their weight pushing downward.
>>> Grand Coulee Dam, Grand
Coulee, Washington, USA
TYPES OF DAMS:
2. Embankment Dam is a gravity dam formed out of loose
rock, earth, or a combination of these materials.
>>> Ambuklao Dam, Bokod, Benguet, Philippines
TYPES OF DAMS:
2. Embankment Dam is a gravity dam formed out of loose
rock, earth, or a combination of these materials.
>>> Magat Dam, Cagayan, Isabela, Philippines
TYPES OF DAMS:
2. Embankment Dam is a gravity dam formed out of loose
rock, earth, or a combination of these materials.
>>> San Roque
Dam, Pangasinan,
Philippines
TYPES OF DAMS:
2. Embankment Dam is a gravity dam formed out of loose
rock, earth, or a combination of these materials.
>>> San Roque Dam, Pangasinan, Philippines
TYPES OF DAMS:
3. Arch Dams are concrete masonry structures that curve
upstream into a reservoir, stretching from one wall of a river
canyon to the other.
>>> Glen Canyon Dam, Colorado River, Arizona, USA
TYPES OF DAMS:
4. Buttress Dam consists of a wall, or face, supported by
several buttresses on the downstream side.
>>> Buttress Dam, France
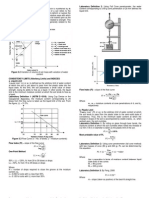
ANALYSIS OF GRAVITY DAM:
Dams are structures whose purpose is to raise the water level on the
upstream side of river, stream, or other waterway. The rising water
will cause hydrostatic force which will tend the dam to slide
horizontally and overturn about its downstream edge or toe.
ANALYSIS OF DAMS:
The raised water level on the upstream edge or heel will also cause
the water to seep under the dam. The pressure due to this seepage is
commonly called hydrostatic uplift and will reduce the stability of the
dam against sliding and against overturning.
ANALYSIS OF DAMS:
Step 1: Consider 1 unit length (1 m
length) of dam perpendicular to the
cross section.
With reference to the figure :
ANALYSIS OF DAMS:
Step 2: Determine all the forces acting:
A. Vertical Forces
1. Weight of the dam
W
1
=
c
V
1
; W
2
=
c
V
2
; W
3
=
c
V
3
2. Weight of water in the upstream
side (if any)
W
4
=V
4
3. Weight of permanent structures on
the dam
4. Hydrostatic Uplift
U
1
=V
u1
U
2
=V
u2
Where:
= unit wt. of water
c
= unit wt. of concrete
c
= 2.4 (usually taken as 23.5 kN/m
3
)
With reference to the figure:
ANALYSIS OF DAMS:
Step 2: Determine all the forces acting:
B. Horizontal Force
1. Total Hydrostatic Force acting at
the vertical projection of the
submerged portion of the dam.
2. Wind Pressure
3. Wave Action
4. Floating Bodies
5. Earthquake Load
With reference to the figure:
ANALYSIS OF DAMS:
Step 3: Solve for the Reaction
A. Vertical Reaction, R
y
R
y
= F
v
R
y
= W
1
+ W
2
+
W
3
+
W
4
-
U
1
-
U
2
B. Horizontal Reaction, R
x
R
x
= F
h
R
x
= F
With reference to the figure:
ANALYSIS OF DAMS:
Step 4: Solve for the Reaction
A. Righting Moment, RM (rotation
towards the upstream side)
RM=W
1
x
1
+W
2
x
2
+W
3
x
3
+W
4
x
4
B. Overturning Moment, OM (rotation
towards the downstream side)
OM = F(y)+ U
1
z
1
+U
2
z
2
With reference to the figure:
ANALYSIS OF DAMS:
With reference to the figure:
Step 5: Location of R
y
, ( )
FACTORS OF SAFETY:
1. Factor of safety against sliding, FS
s
:
2. Factor of safety against overturning, FS
o
:
Where:
= coefficient of friction between the base of the dam and
the foundation
FOUNDATION PRESSURE:
1. For eccentricity, e B/6:
Note: Use (+) to get the stress
at point where R
y
is nearest.
In this figure, use (+) to get q
T
and (-) to get q
H
A negative stress indicates
compressive stress and a
positive stress indicates tensile
stress.
FOUNDATION PRESSURE:
2. For eccentricity, e > B/6:
SAMPLE PROBLEMS:
A gravity dam of trapezoidal cross-section with one face vertical and
horizontal base id 22 m high and has a thickness of 4m at the top. Water
upstream stands 2m below the crest of the dam. The unit weight of concrete
is equal to 23.5 kN/m
3
and the coefficient of friction between the base of the
dam and the foundation is 0.5.
SAMPLE PROBLEMS:
Neglecting hydrostatic uplift, determine the following:
1. Factor of safety against sliding
2. Factor of safety against overturning
3. Overturning moment acting against the dam
4. Foundation Pressure
SAMPLE PROBLEMS:
Considering uplift pressure to vary uniformly from full hydrostatic pressure
at the heel to zero at the toe.
1. Factor of safety against sliding
2. Factor of safety against overturning
3. Overturning moment acting against the dam
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Group 6 (Central Market KL) PDFDocument81 paginiGroup 6 (Central Market KL) PDFAmirul Hakim Sabri100% (2)
- Season of The PhilippinesDocument35 paginiSeason of The PhilippinesKharl Fullo94% (17)
- Key Assumptions of Darcy's LawDocument19 paginiKey Assumptions of Darcy's LawFah EemÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE6405 Soil Mechanics Solved QB PDFDocument112 paginiCE6405 Soil Mechanics Solved QB PDFcivildept maamallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1 Specific Gravity Determination Objective:: P P y yDocument8 paginiExperiment 1 Specific Gravity Determination Objective:: P P y yJoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nga - Sig.0012 2.0.0 UtmupsDocument86 paginiNga - Sig.0012 2.0.0 UtmupsMohammad Ibna AnwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. Hydrostatic Force On Plane Surface: 1. FormulaDocument20 paginiA. Hydrostatic Force On Plane Surface: 1. FormulaKim Kelley AngÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE140 Lecture 02Document46 paginiCE140 Lecture 02eric labordoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3: Calculating Hydrostatic Forces on Plane and Curved SurfacesDocument19 paginiModule 3: Calculating Hydrostatic Forces on Plane and Curved SurfacesJohn GaviolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 425 - Engineering HydrologyDocument32 paginiCE 425 - Engineering HydrologyCiel RonquilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conjugate Beam Method PDFDocument7 paginiConjugate Beam Method PDFdada100% (1)
- Analyzing Gravity DamsDocument38 paginiAnalyzing Gravity DamsMerwin Andrew UyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic - 7 - Permeability & SeepageDocument32 paginiTopic - 7 - Permeability & Seepagejimmys45Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab. Exp. 10 Alternate Stages of FlowDocument4 paginiLab. Exp. 10 Alternate Stages of FlowCamille Andrea Sequitin100% (1)
- Masonry Dam Pressure CalculationsDocument3 paginiMasonry Dam Pressure CalculationsJems Mansueto0% (1)
- HydrologyDocument34 paginiHydrologyMichaelViloria100% (1)
- EXPERIMENT 1 HYDROSTATIC FORCEDocument6 paginiEXPERIMENT 1 HYDROSTATIC FORCENor Farah AlwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrology (Precipitation)Document12 paginiHydrology (Precipitation)Aj AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- HYDRAULICS - Module 1 Lesson 2Document57 paginiHYDRAULICS - Module 1 Lesson 2Rey Angelo Carbilledo Jr.100% (2)
- Assignment 1Document1 paginăAssignment 1Tushar GautamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1-Flow RatesDocument8 paginiChapter 1-Flow RatesJeisther Timothy GalanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus 2017 Numerical Methods For Civil EngineeringDocument3 paginiSyllabus 2017 Numerical Methods For Civil EngineeringNyikolajev100% (1)
- Doubly Reinforced BeamDocument9 paginiDoubly Reinforced BeamBaharulHussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Mindanao College of Engineering EducationDocument42 paginiUniversity of Mindanao College of Engineering EducationLi LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prefi Calculus DraftDocument2 paginiPrefi Calculus Draftralph crucilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geotechnical EngineeringDocument3 paginiGeotechnical EngineeringJesus Ray M. Mansayon67% (3)
- Wells and Well HydraulicsDocument110 paginiWells and Well HydraulicsSaqalain HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two Dimensional Flow of Water Through SoilDocument28 paginiTwo Dimensional Flow of Water Through SoilMinilik Tikur SewÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIE5450 Hydrology PrecipitationDocument121 paginiCIE5450 Hydrology PrecipitationZaTaSaraMeenaKomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn Key Soil PropertiesDocument7 paginiLearn Key Soil PropertiesAljon AvilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1003 Return in 10 Seconds - Rectilinear Translation - Engineering Mechanics ReviewDocument3 pagini1003 Return in 10 Seconds - Rectilinear Translation - Engineering Mechanics ReviewKristin Brienne Leander-RenomeronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Theory 1 (Part 2)Document11 paginiStructural Theory 1 (Part 2)GinoOcampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1Document33 paginiTopic 1Nur HananiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EVAPORATIONDocument52 paginiEVAPORATIONRica Marie MarilaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- KFUPM CE331 Engineering Statics & Hydrology NotesDocument92 paginiKFUPM CE331 Engineering Statics & Hydrology NotesEry100% (1)
- Ch2 Fluid StaticsDocument131 paginiCh2 Fluid StaticsAsif SunnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slides 1 Flow in Open ChannelDocument30 paginiSlides 1 Flow in Open ChannelTing Wee KietÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 10 (Shear and Moment Diagram, EtAl)Document29 paginiLecture 10 (Shear and Moment Diagram, EtAl)francisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stormwater Modeling GuideDocument71 paginiStormwater Modeling GuidesmrtnickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Fluid Flow: A. Path Lines, Streamlines and Stream TubesDocument3 paginiFundamentals of Fluid Flow: A. Path Lines, Streamlines and Stream TubesMegan MontibonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deflection of Beams - NoteDocument12 paginiDeflection of Beams - NoteJackÎncă nu există evaluări
- InfiltrationDocument22 paginiInfiltrationTsumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertical Stress in The GroundDocument12 paginiVertical Stress in The GroundRabindraSubediÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE505 Structures Theory Exam QuestionsDocument2 paginiCE505 Structures Theory Exam QuestionsKamlesh GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions BedientDocument47 paginiSolutions BedientRaul Cordova Alvarado100% (1)
- Module 3 EvaporationDocument22 paginiModule 3 EvaporationPrince VinceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geoteknikal EngiineeringDocument3 paginiGeoteknikal EngiineeringDea LestariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec3 - Ce131p-2 - Double Integration Method PDFDocument26 paginiLec3 - Ce131p-2 - Double Integration Method PDFThe BluemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Channel Flow Hydraulics BesavillaDocument4 paginiOpen Channel Flow Hydraulics BesavillagabinuangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5: Runoff Questions and Key ConceptsDocument20 paginiChapter 5: Runoff Questions and Key ConceptsEmily Shum100% (1)
- Introductions 1Document132 paginiIntroductions 1Mariz Ellaine Baltazar100% (2)
- Unit Hydrograph Analysis and DerivationDocument36 paginiUnit Hydrograph Analysis and DerivationRas Mekonnen100% (1)
- FLOW OF WATER THROUGH SOILDocument76 paginiFLOW OF WATER THROUGH SOILRichie BobbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 - Historical Background and Early Fathers On Structural Engineering PDFDocument8 paginiAssignment 1 - Historical Background and Early Fathers On Structural Engineering PDFArteezy BabaevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple - Stress-Strain and TrussDocument131 paginiSimple - Stress-Strain and Trussdarshan100% (3)
- P5 Effective StressDocument28 paginiP5 Effective StressMiguel TabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flow of Open ChannelDocument61 paginiFlow of Open Channelmr_sam91100% (1)
- Engineering Hydrology Lecture on Branches and the Hydrological CycleDocument18 paginiEngineering Hydrology Lecture on Branches and the Hydrological CycleAsadullah Khan GhalibÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10-Flow in AquifersDocument20 pagini10-Flow in AquifersFachmi ZainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Celebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985De la EverandCelebrating Literacy in the Rwenzori Region: Lest We Forget: a Biographical Narrative of Uganda’S Youngest Member of Parliament, 1980-1985Încă nu există evaluări
- 3 2 PDFDocument10 pagini3 2 PDFJohn GaviolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Gravity DamsDocument10 paginiAnalysis of Gravity DamskerbyreyesmanaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Windblatt 0310 EnglDocument16 paginiWindblatt 0310 EnglMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME Elective 3. Exercise 1Document4 paginiME Elective 3. Exercise 1Meggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OSOSOSOSOSOSOSODocument4 paginiOSOSOSOSOSOSOSOMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FY15 - Autodesk Education Expert - Points GuideDocument8 paginiFY15 - Autodesk Education Expert - Points GuideMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Villanueva - Christian Meguel - Me Laws Finals - ReportDocument2 paginiVillanueva - Christian Meguel - Me Laws Finals - ReportMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geothermal Energy Development in The Philippines: Country UpdateDocument9 paginiGeothermal Energy Development in The Philippines: Country UpdateMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Geothermal Energy Production and UseDocument55 paginiBasics of Geothermal Energy Production and UseBruno Andrade Freitas FalcãoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Average Solar Radiation by Month 2015Document9 paginiAverage Solar Radiation by Month 2015Meggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Potential of Geothermal EnergyDocument28 paginiPotential of Geothermal EnergyMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Geothermal Energy Production and UseDocument55 paginiBasics of Geothermal Energy Production and UseBruno Andrade Freitas FalcãoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terms in IPEDocument73 paginiTerms in IPEMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering LawDocument20 paginiMechanical Engineering Lawnepaulo100% (1)
- Environmental GuideDocument86 paginiEnvironmental GuideRavinder RandhawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geothermal Development in The Philippines: Atty. Marissa P. CerezoDocument22 paginiGeothermal Development in The Philippines: Atty. Marissa P. CerezoMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ansi ListDocument293 paginiAnsi ListMeggy Villanueva67% (6)
- Part 3 - Experiment 1Document2 paginiPart 3 - Experiment 1Meggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Villanueva AdvmathDocument5 paginiVillanueva AdvmathMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 16 PDFDocument97 paginiSection 16 PDFherrerafaridÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC MotorsDocument2 paginiDC MotorsMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine Tool & MachiningDocument75 paginiMachine Tool & Machiningasim12975% (4)
- ME Elective 3. Exercise 1Document4 paginiME Elective 3. Exercise 1Meggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRF Mini4WD Technical Race Rules and Regulations 2014Document12 paginiTRF Mini4WD Technical Race Rules and Regulations 2014Meggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmcakmDocument428 paginiAmcakmMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maxima and Minima ProblemsDocument44 paginiMaxima and Minima ProblemsMeggy Villanueva100% (2)
- Workshop Safety RulesDocument5 paginiWorkshop Safety RulesMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Cloning - For Better or For WorseDocument4 paginiHuman Cloning - For Better or For WorseMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- KusamakuraDocument3 paginiKusamakuraMeggy Villanueva0% (1)
- Simple Hitches for Ropes and LinesDocument13 paginiSimple Hitches for Ropes and LinesMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MisnomersDocument2 paginiMisnomersMeggy VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWE - 2020 - 03 - Sources of WaterDocument32 paginiWWE - 2020 - 03 - Sources of WaterGHANTASALA VARUNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceng 5163Document2 paginiCeng 5163Dagim GelawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Most Essential Learning CompetenciesDocument16 paginiMost Essential Learning Competenciesjovito13Încă nu există evaluări
- Design HydrographDocument50 paginiDesign HydrographSyamil DzulfidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CY 2023 Annual Investment PlanDocument14 paginiCY 2023 Annual Investment PlanMadel EmpuertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 98 220 1 SMDocument26 pagini98 220 1 SMRachma YudhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Darcy's Law and Groundwater FlowDocument72 paginiDarcy's Law and Groundwater FlowMarianne EncaboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Africa Water AtlasDocument326 paginiAfrica Water AtlasJavier Martínez EscamillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sites Where Volcanoes Are FoundDocument9 paginiSites Where Volcanoes Are FoundAdrienne BarrogaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 9 Natural DisastersDocument17 paginiUnit 9 Natural DisastersbohucÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 The Role and Purpose of IrrigationDocument11 pagini1.1 The Role and Purpose of IrrigationsubxaanalahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes DRRR 6.2Document2 paginiNotes DRRR 6.2Noella may de MesaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characterization of Aquifer System of Different Geological Formations Is Based OnDocument13 paginiCharacterization of Aquifer System of Different Geological Formations Is Based Oninternational journal of modern chemistry and applied scienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Watershed-Based Systems ExplainedDocument17 paginiWatershed-Based Systems Explainedali_loraineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guevara Et Al, 2018Document14 paginiGuevara Et Al, 2018Adriana CaballeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ocean Acidification: Jumanah Amoudi College Preparation Program English 036, 3002 March 3, 2022Document10 paginiOcean Acidification: Jumanah Amoudi College Preparation Program English 036, 3002 March 3, 2022chum chumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bab 6 Flow Measurement StructureDocument41 paginiBab 6 Flow Measurement StructureReinhart HadithyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL 8 2. DemoDocument2 paginiDLL 8 2. DemoKate EvangelistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal English 2Document20 paginiJurnal English 2Mimma MonicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Map Projections and Map TermsDocument20 pagini4 Map Projections and Map TermsKristine Dahang MabalosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Build storm water drainage systemDocument4 paginiBuild storm water drainage systemJessa Mae CatabayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lichenometry in IndiaDocument1 paginăLichenometry in IndiashonapinkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Secondary 1 Chapter 4 - Sustainable Water ManagementDocument4 paginiSecondary 1 Chapter 4 - Sustainable Water ManagementKrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan 7e's Sea BreezeDocument3 paginiLesson Plan 7e's Sea BreezeMark Joel Macaya GenoviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meteorology QuestionDocument52 paginiMeteorology QuestionMahesh MahajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report To The Portfolio Committee On The Pollution of The Umgeni RiverDocument13 paginiReport To The Portfolio Committee On The Pollution of The Umgeni RiverSundayTimesZAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes in Physical Oceanography (Inglés) Autor Odd Henrik Saelen and Eyvind AasDocument108 paginiLecture Notes in Physical Oceanography (Inglés) Autor Odd Henrik Saelen and Eyvind Aasfranzs ezra rojas delgadoÎncă nu există evaluări