Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Ch14 Intro To Motor Controls
Încărcat de
s.b.v.seshagiri14070 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
55 vizualizări90 paginiThe document provides an overview of electric motors and motor control. It discusses the basic components and functions of electric motors, including the stator, rotor, electromagnets, and how reversing current direction reverses magnetic polarity. Common types of electric motors are described such as permanent magnet DC motors, stepper motors, and brushless DC motors. The document also explains what motor control is and how it is used to control speed, torque, position and other motor functions through electronics. An agenda outlines topics to be covered, including introductions to electromagnets, motors, motor control, and specific motor types.
Descriere originală:
Introduction to Motor controls
Titlu original
Ch14 Intro to Motor Controls
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe document provides an overview of electric motors and motor control. It discusses the basic components and functions of electric motors, including the stator, rotor, electromagnets, and how reversing current direction reverses magnetic polarity. Common types of electric motors are described such as permanent magnet DC motors, stepper motors, and brushless DC motors. The document also explains what motor control is and how it is used to control speed, torque, position and other motor functions through electronics. An agenda outlines topics to be covered, including introductions to electromagnets, motors, motor control, and specific motor types.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
55 vizualizări90 paginiCh14 Intro To Motor Controls
Încărcat de
s.b.v.seshagiri1407The document provides an overview of electric motors and motor control. It discusses the basic components and functions of electric motors, including the stator, rotor, electromagnets, and how reversing current direction reverses magnetic polarity. Common types of electric motors are described such as permanent magnet DC motors, stepper motors, and brushless DC motors. The document also explains what motor control is and how it is used to control speed, torque, position and other motor functions through electronics. An agenda outlines topics to be covered, including introductions to electromagnets, motors, motor control, and specific motor types.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 90
Bridging Theory in Practice
Transferring Technical Knowledge
to Practical Applications
Introduction to Motor Control
Introduction to Motor Control
Intended Audience:
Individuals with an interest in learning about electric motors and how they are
controlled
A simple understanding of magnetics is assumed
Topics Covered:
What is an electric motor?
What are some common types of electric motors?
How do these electric motors work?
How these motors are controlled.
Expected Time:
Approximately 90 minutes
Introduction to Motor Control
Agenda
Introduction to Electromagnets and Electric
Motors
What Is Motor Control?
What Are Some Common Types of
Motors?
Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Stepper Motors
Brushless DC Motors
Summary of Motors and Motor Control
Circuits
Agenda
Introduction to Electromagnets and Electric
Motors
What Is Motor Control?
What Are Some Common Types of Motors?
Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Stepper Motors
Brushless DC Motors
Summary of Motors and Motor Control Circuits
What Is a Permanent Magnet?
A piece of iron or steel which produces a magnetic
field
Found in nature as magnetite (Fe
3
O
4
) lodestones
Magnetic field causes the permanent magnet to
attract iron and some other materials
Two ends of the permanent magnet are usually
designated North and South
Opposite magnet ends attract and like magnet ends
repel
What Is an Electromagnet?
Electromagnets behave like permanent
magnets
but their magnetic field is not
permanent
Magnetic field is temporarily induced by an
electric current
How Do You Make an
Electromagnet?
Start with an iron bar
How Do You Make an
Electromagnet?
Start with an iron bar
Wrap a wire around the iron bar
How Do You Make an
Electromagnet?
Start with an iron bar
Wrap a wire around the iron bar
Connecting a battery causes a current to flow
in the wire
Current
+
-
How Do You Make an
Electromagnet?
Start with an iron bar
Wrap a wire around the iron bar
Connecting a battery causes a current to flow in the wire
The current induces a magnetic field creating an
electromagnet
Current
SOUTH
NORTH
+
-
How Do You Make an
Electromagnet?
Reversing the current direction, reverses the
polarity
Current
+
-
NORTH
SOUTH
How Do You Make an
Electromagnet?
Reversing the current direction, reverses the
polarity
If the current is stopped, the induced magnetic field
decays to 0
Current
+
-
NORTH
SOUTH
Electromagnets and
Electric Motors
We can use electromagnets in electric motors to convert
electrical energy to mechanical work
+
Electric Motor
12V
-
Electric
Energy
Electric motors are used to
perform a mechanical task by
using electricity
Open a sunroof
Lift a power antenna
Control windshield wiper
What Is an Electric Motor?
STATOR
ROTOR
An electric motor has two basic parts:
The stationary part is called the stator.
The rotating part of the electric motor is called the
rotor.
What Is an Electric Motor?
STATOR
Electrical energy creates a rotating magnetic field
inside the motor causing the rotor to rotate,
creating mechanical motion
ROTOR
Where Are
Electric Motors Used?
Electric motors are used in many different automotive applications:
Power windows
Power seats
Power mirrors
Fans
Windshield wipers
Windshield washer pumps
Starter motor
Electric radio antennae
Door locks
Information gauges
Sunroof
Brakes
Power steering
Fuel pump
Water pump
Hybrid and electric vehicles
Cruise control
Throttle plate control
Air vents
Others
Agenda
Introduction to Electromagnets and Electric Motors
What Is Motor Control?
What Are Some Common Types of Motors?
Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Stepper Motors
Brushless DC Motors
Summary of Motors and Motor Control Circuits
The controlled application of electrical energy to a motor to
elicit a desired mechanical response
Start / Stop
Speed
Torque
Position
Significant amount of electronics may be required to
control the operation of some electric motors
What Is Motor Control ?
Control of Electromagnetics
Much of the physical design of an electric motor and its control
system are related to the switching of the electromagnetic field
There is a mechanical force which acts on a current carrying wire
within a magnetic field
The mechanical force is perpendicular to the wire and the magnetic
field
The relative magnetic fields between the rotor and stator are
arranged so that a torque is created, causing the rotor to rotate
about its axis
Agenda
Introduction to Electromagnets and Electric Motors
What Is Motor Control?
What Are Some Common Types of Motors?
Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Stepper Motors
Brushless DC Motors
Summary of Motors and Motor Control Circuits
There are many different types and classifications of electric
motors:
Permanent magnet DC motor
Stepper motor
Brushless DC motor
Wound field motor
Universal motors
Three phase induction motor
Three-phase AC synchronous motors
Two-phase AC Servo motors
torque motors
Shaded-pole motor
split-phase induction motor
capacitor start motor
Permanent Split-Capacitor (PSC) motor
Repulsion-start induction-run (RS-IR) motor
Repulsion motor
Linear motor
Variable reluctance motor
Unipolar stepper motor
Bipolar stepper
Full step stepper motor
Half step stepper motor
Micro step stepper motor
Switched reluctance motor
Shaded-pole synchronous motor
Induction motor
Coreless DC motor
Others......
Types of Electric Motors
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Similar in construction to the introductory example
Metallic contacts (brushes) are used to deliver electrical energy
Rotational speed proportional to the applied voltage
Torque proportional to the current flowing through the motor
Advantages:
+ Low cost (high volume demand)
+ Simple operation
Disadvantages:
Medium efficiency
Poor reliability (brush, commutator wear out)
Strong potential source of electromagnetic interference
Stepper Motor
Full rotation of electric motor divided into a number of "steps"
For example, 200 steps provides a 1.8
o
step angle
A stepper motor controller can move the electric motor one step (in
either direction) by applying a voltage pulse
Rotational speed is controlled by changing the frequency of the
voltage pulses
Advantages:
+ Low cost position control (instrument gauges)
+ Easy to hold position
Disadvantages:
Poor efficiency
Requires digital control interface
High motor cost
Brushless DC Motor
Similar to a permanent magnet DC motor
Rotor is always the permanent magnet (internal or external)
Design eliminates the need for brushes by using a more
complex drive circuit
Advantages:
+ High efficiency
+ High reliability
+ Low EMI
+ Good speed control
Disadvantages:
May be more expensive than "brushed" DC motors
More complex and expensive drive circuit than
"brushed" DC motors
Agenda
Introduction to Electromagnets and Electric Motors
What Is Motor Control?
What Are Some Common Types of Motors?
Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Stepper Motors
Brushless DC Motors
Summary of Motors and Motor Control Circuits
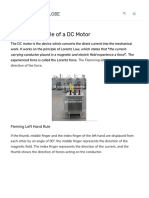
How Does a Permanent Magnet
DC Motor Work?
"DC Motors" use magnets to produce motion
Permanent magnets
NORTH SOUTH
"DC Motors" use magnets to produce motion
Permanent magnets
An electromagnet armature
How Does a Permanent Magnet
DC Motor Work?
NORTH SOUTH
NORTH SOUTH
Electromagnet armature is mounted on axle so that
it can rotate
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Rotating Armature
NORTH SOUTH
Electromagnet armature is mounted on axle so that
it can rotate
A commutator makes an electrical contact with the
motor's brushes
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Commutator and Brushes
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Commutator Structure
Commutator is comprised of two "near-
halves" of a ring
Commutator is comprised of two "near-halves" of a ring
Mounted on the armature's axle to rotate with the rotor
Armature
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Commutator Structure
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Commutator Structure
Armature's windings are connected to the
commutator
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Commutator and Brushes
Armature's windings are connected to the commutator
Brushes connect the commutator to the battery
NORTH SOUTH
Current flows through the armature's windings,
which polarizes the electromagnet
+
-
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Electromagnet Polarization
NORTH SOUTH
The like magnets (NORTH-NORTH and SOUTH-SOUTH) repel
As the like magnets repel, the armature rotates, creating mechanical
motion
+
-
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Rotation
NORTH SOUTH
What direction will the armature spin?
Clockwise? Counterclockwise?
Clockwise ?
Counterclockwise ?
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Rotation Direction?
+
-
To determine the direction of the motor's rotation, we need
to use the "Left Hand Rule"
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Rotation Direction?
Left Hand Rule
Start with two opposite
ends of a magnet
NORTH
SOUTH
Left Hand Rule:
Magnetic Field
NORTH
SOUTH
The magnetic field (B) is from
the NORTH pole to the
opposite SOUTH pole
The pointing finger
follows B into
screen
B
Left Hand Rule:
Current Flow
NORTH
SOUTH
Current flows in a wire through
the magnetic field from left to
right
The middle finger follows I
1
right, or I
2
left
I
1
I
2
Left Hand Rule:
Force
NORTH
SOUTH
The force, F, acting on each wire
is in the direction of the
thumb
The wire with I
1
is pushed up,
I
2
down
I
1
I
2
F
1
F
2
Left Hand Rule:
Force
NORTH
SOUTH
The magnitude of F is give by:
| F | = | I | * * | B |
where is the length of the
wire in B
I
1
I
2
F
1
F
2
Left Hand Rule:
Current Loop
NORTH
SOUTH
If the current flows in a loop,
the force(s) will cause the
loop to rotate
I
F
F
NORTH SOUTH
Magnetic field is from right to left
Imagine current flows out of the screen in this cross
section
+
-
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Rotation
NORTH SOUTH
Magnetic field is from right to left
Imagine current flows out of the screen in this cross section
The force causes the armature to rotate clockwise
+
-
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Rotation
NORTH SOUTH
+
-
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Rotation
At some point, the commutator halves will rotate away
from the brushes
Momentum keeps the electromagnet and the commutator
ring rotating
NORTH SOUTH
+
-
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Rotation
When the commutator halves reconnect with the
other brush, the current in the windings is reversed
NORTH SOUTH
+
-
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Rotation
When the commutator halves reconnect with the
other brush, the current in the windings is reversed
The polarity is reversed and the armature continues
to rotate
+
-
NORTH SOUTH
Magnetic field is from right to left
Imagine current flows out of the screen in this cross section
The force causes the armature to rotate clockwise
+
-
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
Rotation
Controlling a Permanent Magnet
DC (PMDC) Motor
Bi-directional PM DC motors are controlled with an "H-Bridge"
circuit consisting of the motor and four power switches
Current
Turning On a PMDC Motor
One switch is closed in each leg of the "H"
One switch is open in each leg of the "H"
Current
One switch is closed in each leg of the "H"
One switch is open in each leg of the "H
Turning On a PMDC Motor
in the Other Direction
Current
Unidirectional motors are controlled by a half-H
bridge circuit
Controlling a Permanent Magnet
DC (PMDC) Motor
Controlling a PMDC Motor
Options
DC operation
Rotational speed of the DC motor is fixed at a given voltage
and load
PWM Operation
Average voltage (and rotational speed) can be controlled
by opening/closing the switches quickly
Braking
Shorting the terminals or momentarily reversing the drive
Others
Agenda
Introduction to Electromagnets and Electric Motors
What Is Motor Control?
What Are Some Common Types of Motors?
Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Stepper Motors
Brushless DC Motors
Summary of Motors and Motor Control Circuits
Why a Stepper Motor ?
Unlike the permanent magnet DC motor, stepper
motors move in discrete steps as commanded by the
stepper motor controller
Because of their discrete step operation, stepper
motors can easily be rotated a finite fraction of a
rotation
Another key feature of stepper motors is their ability
to hold their load steady once the require position is
achieved
An example application for stepper motors is for
implementing traditional "analog" instrumentation
gauges on a dashboard
How Does a
Stepper Motor Work ?
A stepper motor often has an internal rotor with a large number of
permanent magnet teeth
A large number of electromagnet "teeth" are mounted on an
external stator
Electromagnets are polarized and depolarized sequentially, causing
the rotor to spin one "step"
Full step motors spin 360
o
/(# of teeth) in each step
Half step motors spin 180
o
/(# of teeth) in each step
Microstep motors further decrease the rotation in each step
Full Step Motor Operation
`
Half Rotate
and Hold
`
Half Step Motor Operation
Half Rotate
and Hold
Stepper Motor Control
The stepper motor driver receives square wave pulse
train signals from a controller and converts the
signals into the electrical pulses to step the motor
This simple operation leads stepper motors to
sometimes be called "digital motors"
To achieve microstepping, however, the stepper
motor must be driven by a (quasi) sinusoidal current
that is expensive to implement
Agenda
Introduction to Electromagnets and Electric Motors
What Is Motor Control?
What Are Some Common Types of Motors?
Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Stepper Motors
Brushless DC Motors
Summary of Motors and Motor Control Circuits
Many of the limitations of the classic permanent magnet "brushed"
DC motor are caused by the brushes pressing against the rotating
commutator creating friction
As the motor speed is increased, brushes may not remain in
contact with the rotating commutator
At higher speeds, brushes have increasing difficulty in maintaining
contact
Sparks and electric noise may be created as the brushes
encounter flaws in the commutator surface or as the commutator
is moving away from the just energized rotor segment
Brushes eventually wear out and require replacement, and the
commutator itself is subject to wear and maintenance
Brushless DC motors avoid these problems with a modified design,
but require a more complex control system
Why a Brushless DC Motor ?
How Does a Brushless DC Motor
Work ?
A brushless DC motor uses electronic sensors to detect the
position of the rotor without using a metallic contact
Using the sensor's signals, the polarity of the electromagnets
is switched by the motor control drive circuitry
The motor can be easily synchronized to a clock signal,
providing precise speed control
Brushless DC motors may have:
An external PM rotor and internal electromagnet stator
An internal PM rotor and external electromagnet stator
This example brushless DC motor has:
An internal, permanent magnet rotor
Example Brushless DC Motor
Operation
This example brushless DC motor has:
An external, electromagnet stator
Example Brushless DC Motor
Operation
This example brushless DC motor has:
An external, electromagnet stator, with magnetic
field sensors
Example Brushless DC Motor
Operation
Brushless DC Motor
Construction
A
a
a
com
com
b
b
B
com
c
c
C
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
A
a
a
com
com
b
b
B
com
c
c
C
1
Brushless DC Motor Operation
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
A
a
a
com
com
b
b
B
com
c
c
C
2
Brushless DC Motor Operation
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
A
a
a
com
com
b
b
B
com
c
c
C
3
Brushless DC Motor Operation
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
A
a
a
com
com
b
b
B
com
c
c
C
4
Brushless DC Motor Operation
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
A
a
a
com
com
b
b
B
com
c
c
C
5
Brushless DC Motor Operation
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
A
a
a
com
com
b
b
B
com
c
c
C
6
Brushless DC Motor Operation
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
A
a
a
com
com
b
b
B
com
c
c
C
1
Brushless DC Motor Operation
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
A1 B1 C1
A2 B2 C2
Brushless DC Motor
Control Circuit
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
1
A1 B1 C1
A2 B2 C2
Brushless DC Motor
Control Circuit
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
2
A1 B1 C1
A2 B2 C2
Brushless DC Motor
Control Circuit
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
3
A1 B1 C1
A2 B2 C2
Brushless DC Motor
Control Circuit
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
4
A1 B1 C1
A2 B2 C2
Brushless DC Motor
Control Circuit
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
5
A1 B1 C1
A2 B2 C2
Brushless DC Motor
Control Circuit
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
6
A1 B1 C1
A2 B2 C2
Brushless DC Motor
Control Circuit
Brushless DC Motor
Control Circuit
A
a
b
B
c
C
com
1
A1 B1 C1
A2 B2 C2
Agenda
Introduction to Electromagnets and Electric Motors
What Is Motor Control?
What Are Some Common Types of Motors?
Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Stepper Motors
Brushless DC Motors
Summary of Motors and Motor Control Circuits
+
An electric motor converts electric energy into
mechanical motion
Electric Motor
12V
-
Electric
Energy
Electric motors are used to
perform a mechanical task by
using electricity
Open a sunroof
Lift a power antenna
Control windshield wiper
What Is an Electric Motor?
Permanent Magnet Stepper Brushless DC
DC Motor Motor Motor
Advantages: + Low cost + Position control + High efficiency
(high volume) (low cost + High reliability
+ Simple operation control circuits) + Low EMI
+ Speed control
Disadvantages: - Medium efficiency - Poor efficiency - Maybe higher cost
- Poor reliability - Digital interface - Complex control
- Bad EMI - High cost
Types of Electric Motors
Agenda
Introduction to Electromagnets and Electric Motors
What Is Motor Control?
What Are Some Common Types of Motors?
Permanent Magnet DC Motors
Stepper Motors
Brushless DC Motors
Summary of Motors and Motor Control Circuits
Introduction to Motor Control
Thank you!
www.btipnow.com
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Bridging Theory in Practice: Transferring Technical Knowledge To Practical ApplicationsDocument90 paginiBridging Theory in Practice: Transferring Technical Knowledge To Practical Applicationskali_eee05100% (1)
- Electric MachineDocument45 paginiElectric MachineravihbtiÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEC - 05 (DC Machines)Document23 paginiLEC - 05 (DC Machines)zain malik100% (1)
- MotorDocument19 paginiMotorRabi khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNCDocument63 paginiCNCSahil Bangia100% (1)
- Mod5 - MECHATRONICS IN ROBOTICSDocument34 paginiMod5 - MECHATRONICS IN ROBOTICSDeepa Ragav RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actuators: Department of E&E EngineeringDocument14 paginiActuators: Department of E&E Engineeringmanavi naikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric MotorsDocument20 paginiElectric MotorsJulie Ann CortezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Motors: ECE131 Basic Electrical & Electronics EnggDocument58 paginiElectrical Motors: ECE131 Basic Electrical & Electronics EnggVinamra MittalÎncă nu există evaluări
- MotorsDocument36 paginiMotorsscorpionarnold100% (1)
- MCT 5.1Document70 paginiMCT 5.1Alfred CheriyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ActuatorsDocument88 paginiActuatorsMrs. Prabha Niranjan NMAMIT E & EÎncă nu există evaluări
- AGK - Electrics 16 DC Motors 16 S2Document16 paginiAGK - Electrics 16 DC Motors 16 S2Cemalettin öztoprakÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Fundamentals of Electric Motors v2Document21 pagini1 Fundamentals of Electric Motors v2Daejoong KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Ac MotorsDocument14 paginiOn Ac Motorspurna reddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-3 Robot Drive MechanisamDocument82 paginiUNIT-3 Robot Drive MechanisamChetuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sigma Institute of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering Bakrol, VadodaraDocument52 paginiSigma Institute of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering Bakrol, VadodaraBhavik PrajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction Motors: Presentation by S.R.Paraskar Electrical Dept SSGMCEDocument22 paginiInduction Motors: Presentation by S.R.Paraskar Electrical Dept SSGMCEdoss mÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase Induction MotorDocument24 paginiSingle Phase Induction MotorKh Muhammad MashoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2: Electrical Actuation SystemsDocument47 paginiUnit 2: Electrical Actuation SystemsHariprasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- BLDC & PMDC MotorDocument29 paginiBLDC & PMDC MotorxfgngfbhsehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase Induction MotorDocument25 paginiSingle Phase Induction Motordumpy100% (1)
- Single Phase Induction MotorDocument25 paginiSingle Phase Induction MotorKh Muhammad Mashood0% (1)
- Electrical Motors EPDI2013Document51 paginiElectrical Motors EPDI2013neocentricgeniusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 14 - 1Document13 paginiWeek 14 - 1M. HamzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actuation SystemsDocument52 paginiActuation SystemsJkl MahanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5 Notes MTRDocument14 paginiModule 5 Notes MTRAbhijith JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 6 - DC Motors PDFDocument22 paginiGroup 6 - DC Motors PDFRashen DilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture#5Document35 paginiLecture#520pwmct0739Încă nu există evaluări
- Working Principle of DC Motor & Back EMFDocument13 paginiWorking Principle of DC Motor & Back EMFsatyammishra1907Încă nu există evaluări
- Lec 18Document29 paginiLec 18Asher RizviÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC MotorDocument10 paginiDC MotorNagesh KolteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Motors Year 8Document25 paginiElectric Motors Year 8M Rameez Ul HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnimatedDocument18 paginiAnimatedfieraminaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Type of NC SystemDocument20 paginiType of NC Systemamit kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Electrical Machines Acm 03 - DC and Ac MachineryDocument14 paginiChapter 1: Introduction To Electrical Machines Acm 03 - DC and Ac MachineryGlaze GregorioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase Induction Motor and Special Electrical MachinesDocument22 paginiSingle Phase Induction Motor and Special Electrical MachinesRajesh Babu100% (2)
- DC MotorsDocument45 paginiDC Motorstristan jeff bautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechatronics MotorsDocument39 paginiMechatronics MotorsSanskar AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- EM CH-4-5-6 Ac MachinesDocument80 paginiEM CH-4-5-6 Ac Machinesmuhammad.anas2007Încă nu există evaluări
- Beee-Unit 3Document54 paginiBeee-Unit 3Sano ManjiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction MotorDocument15 paginiInduction MotorgireeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- DownloadfileDocument16 paginiDownloadfilemadanacharjya449Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To DC Machine: by Dr. Shubhobrata RudraDocument129 paginiIntroduction To DC Machine: by Dr. Shubhobrata RudraBhabani sankar KishanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5 ElectricalDocument22 paginiModule 5 ElectricalSKANDAN BHARADWAJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 3b PPT - Series MotorDocument23 paginiLab 3b PPT - Series MotorLiaqat AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Ac GeneratorDocument17 paginiSimple Ac GeneratorRishi singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To DC Electric MotorsDocument31 paginiIntroduction To DC Electric MotorsJames Adrian Abalde SaboÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC and DC Electric MotorsDocument6 paginiAC and DC Electric Motorsroco_rasim100% (1)
- Induction MotorDocument29 paginiInduction Motordumpy100% (1)
- DC MotorDocument2 paginiDC MotorShailesh RanawareÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC Motors: AC Motors Convert AC Electrical Energy To Mechanical EnergyDocument18 paginiAC Motors: AC Motors Convert AC Electrical Energy To Mechanical EnergyIslam FouadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bee Unit-4Document49 paginiBee Unit-4Aarush PitlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brushless DC MotorDocument19 paginiBrushless DC MotorAnonymous M8PzfJmÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEE (21EEE15A) Module 3BDocument49 paginiBEE (21EEE15A) Module 3BG46Anand P KÎncă nu există evaluări
- PMBLDC Motor DriveDocument55 paginiPMBLDC Motor DriveSushant SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- G10 Science Q2-Week 9-ELECTRIC MOTORS - GENERATORSDocument29 paginiG10 Science Q2-Week 9-ELECTRIC MOTORS - GENERATORSKarina GentonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics and Working of AC Motors & Basics of Power GeneratorDocument37 paginiBasics and Working of AC Motors & Basics of Power GeneratorYasir ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4Document37 paginiChapter 4Atul Jaysing PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pmic Safety Detroit TechdayDocument61 paginiPmic Safety Detroit Techdays.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- ZD 007 Sample Definition Project Management ENDocument1 paginăZD 007 Sample Definition Project Management ENs.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- Gowda2019 ECU Inter - Processor Data CommunicationDocument11 paginiGowda2019 ECU Inter - Processor Data Communications.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- QEP en Quality Requirements For SamplesDocument3 paginiQEP en Quality Requirements For Sampless.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- AURIX MultiCore Lauterbach HandoutDocument56 paginiAURIX MultiCore Lauterbach Handouts.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- Adc Student: Andrew Brown Jonathan Warner Laura StricklandDocument51 paginiAdc Student: Andrew Brown Jonathan Warner Laura Stricklands.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- H Da Barth Functional Safety On MulticoreDocument23 paginiH Da Barth Functional Safety On Multicores.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Electronic DesignDocument18 paginiIntroduction To Electronic Designs.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Study of Sense AmplifierDocument5 paginiAnalytical Study of Sense Amplifiers.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- 07 DRITSANOS IoT-Conference Schneider-ElectricDocument13 pagini07 DRITSANOS IoT-Conference Schneider-Electrics.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- L17 FET DC AnalysisDocument19 paginiL17 FET DC Analysiss.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Stability Control: NHTSA's Notice of Proposed RulemakingDocument18 paginiElectronic Stability Control: NHTSA's Notice of Proposed Rulemakings.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Electronic DesignDocument18 paginiIntroduction To Electronic Designs.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- Robot Chassis and Drivetrain FundamentalsDocument65 paginiRobot Chassis and Drivetrain Fundamentalss.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- Software Testing and ReliabilityDocument77 paginiSoftware Testing and Reliabilitys.b.v.seshagiri1407Încă nu există evaluări
- Em1 2marksDocument9 paginiEm1 2marksSuryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SEEA1601Document104 paginiSEEA1601skrtamilÎncă nu există evaluări
- BMW Starting SystemsDocument15 paginiBMW Starting Systemsgraig27Încă nu există evaluări
- 115826010Document166 pagini115826010ashvinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 16.5 Simple D.C. MotorDocument13 paginiSection 16.5 Simple D.C. Motortwy113Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit-2 - DC Machines PDFDocument123 paginiUnit-2 - DC Machines PDFsujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- CARBOTECH - Technical PresentationDocument37 paginiCARBOTECH - Technical PresentationpiojeziorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromechanical Systems CH 4Document64 paginiElectromechanical Systems CH 4fabrice mellantÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 S Sankaran Energy Eff DesignDocument64 pagini03 S Sankaran Energy Eff DesignVignesh BalajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions On Electrical Machine Applications Armature Reaction and CommutationDocument12 paginiQuestions On Electrical Machine Applications Armature Reaction and Commutationkibrom atsbhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Working Principle of A DC Motor - Circuit GlobeDocument6 paginiWorking Principle of A DC Motor - Circuit GlobeHumair AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTS-231 Actuating Systems: Kanwal NaveedDocument21 paginiMTS-231 Actuating Systems: Kanwal NaveedARSLAN FALAKÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEEE STD ANSI-IEEE STD 116-1975Document12 paginiIEEE STD ANSI-IEEE STD 116-1975abdou samiÎncă nu există evaluări
- AN BLDC Sensorless Control ENG MCUMON-0 PDFDocument37 paginiAN BLDC Sensorless Control ENG MCUMON-0 PDFDoDuyBacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of DC GeneratorDocument10 paginiSummary of DC GeneratorChristopher YsitÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 CNC PPT Lecture 2 DoneDocument38 pagini3 CNC PPT Lecture 2 DoneSidhant AryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vapour Compression Refrigeration CycleDocument44 paginiVapour Compression Refrigeration CycleSayaliRewaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines: DC GeneratorDocument34 paginiElectrical Machines: DC GeneratorMarc Joshua MACATANGAYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer For WorksheetDocument4 paginiAnswer For Worksheetabene danÎncă nu există evaluări
- (04-01) - StarterDocument3 pagini(04-01) - StartereduardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANSUMAN SHARMA 109ee0305 Department of ELECTRICAL Engineering, NIT RourkelaDocument1 paginăANSUMAN SHARMA 109ee0305 Department of ELECTRICAL Engineering, NIT RourkelaAnsuman Sharma100% (1)
- GEQParts CatalogDocument7 paginiGEQParts CatalogIRWIN_DSOUZAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19 - Galvanometers & Electric MotorsDocument3 pagini19 - Galvanometers & Electric MotorsgavinilaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalog Switchboard InstrumentsDocument42 paginiCatalog Switchboard InstrumentsFlo MircaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group Number - 17: Prof. Saifullah PayamiDocument7 paginiGroup Number - 17: Prof. Saifullah PayamiMayank SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pitanja Iz Engleskog-PrevodDocument1 paginăPitanja Iz Engleskog-PrevodZvonimirDelićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salminen NikoDocument26 paginiSalminen Nikohashem AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 45 16255 EE321 2015 1 1 1 Week 9 10Document22 pagini45 16255 EE321 2015 1 1 1 Week 9 10Zakaria MaazazÎncă nu există evaluări
- BTech EE 20211Document127 paginiBTech EE 20211Anurag DavesarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 ConceptsDocument5 paginiChapter 3 ConceptsEzequiel Posadas BocacaoÎncă nu există evaluări