Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Bone Grafting
Încărcat de
aeruginoDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Bone Grafting
Încărcat de
aeruginoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
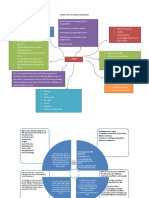
Bone grafting
Bone grafting
An operation whereby pieces of
bones taken from some part of
patients body are placed at another
site
Bone grafts are sometimes taken
from another person/ another
species
Indication
For 3 types of cases:
(a) non-union fracture- to promote
union
(b) arthrodesis of joints- to achieve
fusion between joint surface
(c) filling of bone defects/ cavities in
a bone
Types
3 types of bone grafting:
(a) autograft- from same person
(b) allograft- from another person of
same species
(c) xenograft- from different species
Autogenous grafting
Gold standard bone grafting technique
Human has lots of spare bone for such
use
Iliac crest is the commonest site
When graft is needed for osteogenic
purposes, cancellous bone grafts are
preferred
Its available from iliac crests & upper
end of tibia
When graft is used for providing
stability, (filling bone gaps), cortical
grafts are used (site:fibula)
Grafts described are free grafts
Primarily provides a scaffolding upon
which new bone is laid down
Bone stimulating protein/ BMP (bone
morphogenic protein) is liberated from
bone grafts
This helps in osteogenesis
Over a period of time, bone grafts are
replaced by new living bone
Newer techniques of autogenous bone-
grafting are such that while graft is being
placed on its receptor area, its blood
supply is maintained
2 ways of doing it:
(a) muscle pedicle bone grafting
(b) free vascularized grafting
Muscle pedicle bone grafting
Bone graft is taken along with a
pedicle of muscle
The muscle (with its intact blood
supply) continues to supply blood to
the graft
Commonly done for treating non-
union of fracture of neck of femur
(Baksi)
Free vascularized grafting
Bone (usually the fibula) is taken
along with vessels supplying it
It is placed at new site, & its vessels
anastomosed to a nearby vascular
bundle
Such a graft, therefore, remains as
it is & gets incorporated with the
parent bone
Microsurgical techniques are required
for free vascularized grafting
Allogenous grafting
Needed when not enough bone
available from the host (e.g. big defect
following a tumor resection)
Bone graft obtained from another
human being, live/ dead
The latter is called cadaveric graft
Allogenous graft from mother often
used when childs bone reserves are
not enough to fill a big gap
Another method of using allograft is by
preservation of bone from another
person
Allogenous grafting
Bone removed from a patient may be
preserved by deep freezing (at -
70degrees Celcius), by decalci-fying it/
by formalin preservation
Such a bone can be used for another
patient at a later date after due
processing
Hospitals performing tumor excision
surgery in a big way have regular
department procuring bones from
patient & cadavers, processing it &
storing it
These are called bone banks
Xenografting
Bone grafts from another species,
usually bovine
Available in tailor-made sizes
Use is not common yet
Artificial bone
Material derived from corals
Its hydroxyapetite with porous
structure
Its supposed to have
osteoconductive potential & being
used in some countries
Technique
A graft may be used as a solid slab
from a cortical bone (commonly a
segment from the fibula)/ as
cancellous bone slivers/ chips
(commonly from the iliac crest)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Maternity and Pediatric Nursing 3rd EditionDocument347 paginiMaternity and Pediatric Nursing 3rd EditionTaylor Talley80% (15)
- Knowing God: Prayer and Fasting 2013Document40 paginiKnowing God: Prayer and Fasting 2013ccforgph100% (4)
- Plaster of ParisDocument16 paginiPlaster of Parisaerugino100% (1)
- Orthopedic NursingDocument201 paginiOrthopedic NursingMitch Hellgirl Almonte100% (2)
- Bone Grafts and SubstitutesDocument85 paginiBone Grafts and Substitutessandeepvella100% (1)
- Bone Grafting and Bone Graft SubstitutesDocument12 paginiBone Grafting and Bone Graft Substitutesaiakoby100% (1)
- ArthroplastyDocument64 paginiArthroplastyAmit Kochhar75% (4)
- Stroke RecoveryDocument20 paginiStroke RecoveryVanessa SnowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Graft Harvesting From Distant Sites Concepts and TechniquesDocument16 paginiBone Graft Harvesting From Distant Sites Concepts and TechniquesGenesis Centeno100% (3)
- FAT Form Winch UnitDocument7 paginiFAT Form Winch UnitYadi KusmayadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- HANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Document40 paginiHANDOUTS Prelim CH 6Abia Annieson A. LorenzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Grape and WineDocument116 paginiAnalysis of Grape and WineElenaTrofimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pile Foundation As Per IRC 112Document59 paginiPile Foundation As Per IRC 112ARVIND SINGH RAWAT0% (1)
- Advanced Life Support (Training Manual)Document74 paginiAdvanced Life Support (Training Manual)Matt100% (25)
- Bonegrafting 180324163620Document105 paginiBonegrafting 180324163620Ankit Damor100% (1)
- Primary Healthcare Centre Literature StudyDocument32 paginiPrimary Healthcare Centre Literature StudyRohini Pradhan67% (6)
- Bone and Connective TissueDocument20 paginiBone and Connective TissueKarka PalmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peaditrician All IndiaDocument66 paginiPeaditrician All IndiaGIRISH JOSHIÎncă nu există evaluări
- OrifDocument13 paginiOrifAhmabelle Mara D. AbellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spxflow PDFDocument317 paginiSpxflow PDFAnonymous q2iHVf100% (3)
- A Presentation On Kit KatDocument9 paginiA Presentation On Kit KatRaju DoleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Report FinalDocument4 paginiMedical Report FinalaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Report FinalDocument4 paginiMedical Report FinalaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Graft AlternativesDocument6 paginiBone Graft Alternativesyudha anantha khaerul putraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic of Bone GraftingDocument29 paginiBasic of Bone GraftingdoctorniravÎncă nu există evaluări
- PIIS0030589809000881Document12 paginiPIIS0030589809000881dr. Joko WibowoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Almost FinalDocument38 paginiAlmost FinalPawan MarasiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone and Jont Surgery Engl2020Document86 paginiBone and Jont Surgery Engl2020Timbur IgorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Graft RefrDocument58 paginiBone Graft RefrAchmadPrihadiantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone grafting: A guide to bone graft procedures and typesDocument4 paginiBone grafting: A guide to bone graft procedures and typesAmbeel NasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Graft: A Patient's Guide To Bone GraftsDocument2 paginiBone Graft: A Patient's Guide To Bone Graftsirfan fadilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Substitutes and Growth Factors As An Alternative, Complement To Autogenous Bone For GrafDocument21 paginiBone Substitutes and Growth Factors As An Alternative, Complement To Autogenous Bone For GrafLuis HuaroteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Grafts BhanuDocument113 paginiBone Grafts BhanuBhanu Praseedha100% (1)
- Alveolarbone Graftingand Reconstruction Procedurespriorto ImplantplacementDocument10 paginiAlveolarbone Graftingand Reconstruction Procedurespriorto ImplantplacementKranti PrajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone GraftsDocument39 paginiBone GraftsyogeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Grafts 2006Document12 paginiBone Grafts 2006dhewienaraliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Musculoskeletal Tissue Bank Provides Orthopedic SolutionsDocument39 paginiMusculoskeletal Tissue Bank Provides Orthopedic SolutionsbasukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Grafting: Classification by OriginDocument4 paginiBone Grafting: Classification by OriginHerlangga Fadhillah AkbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aaid Joi D 17 00053Document11 paginiAaid Joi D 17 00053Yun De LinÎncă nu există evaluări
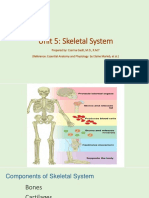
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument9 paginiMusculoskeletal SystemEduardson PHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tha - FinalDocument14 paginiTha - FinaldescalzotahÎncă nu există evaluări
- JAAOS - Volume 03 - Issue 01 January 1995Document63 paginiJAAOS - Volume 03 - Issue 01 January 1995kenthepaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Graft Harvesting From Distant Sites: Concepts and TechniquesDocument16 paginiBone Graft Harvesting From Distant Sites: Concepts and TechniquesguhanderÎncă nu există evaluări
- OSRG Assignment DR YehyaDocument5 paginiOSRG Assignment DR YehyaRouba Al hamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch6Bone StudentDocument67 paginiCh6Bone Studentbhattiareeba13Încă nu există evaluări
- Bone Graft AssingmentDocument4 paginiBone Graft AssingmentNyein Chan AungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 R Comparacion Materiales y Resultados Revision 2017Document11 pagini2 R Comparacion Materiales y Resultados Revision 2017feli.riam24Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Knowledge of Bone Grafting: March 2012Document29 paginiBasic Knowledge of Bone Grafting: March 2012Nadira NurinÎncă nu există evaluări
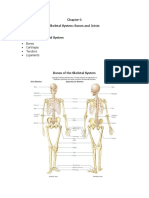
- BSN1 Unit 5 Skeletal SystemDocument101 paginiBSN1 Unit 5 Skeletal SystemCherub Chua100% (1)
- Treatment of Non-Unions With Bone Defects: Which Option and WhyDocument3 paginiTreatment of Non-Unions With Bone Defects: Which Option and Whylorena amorimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone GraftDocument91 paginiBone GraftHimanshu SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autogenous Bone GraftDocument10 paginiAutogenous Bone Graftprogramari maxiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Cartilage and BoneDocument5 paginiChapter 6 Cartilage and BoneSuperjunior8Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of Bone Graft Materials Jumping Gap (Distance)Document5 paginiTypes of Bone Graft Materials Jumping Gap (Distance)Mazen T. ShembeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fracture Fixation and ArthroplastyDocument39 paginiFracture Fixation and Arthroplastyzony khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal Structure of Bone & Biology of Fracture Healing: Dr. Aashish ChaudhryDocument22 paginiNormal Structure of Bone & Biology of Fracture Healing: Dr. Aashish ChaudhryPankaj VatsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch6Bone StudentDocument66 paginiCh6Bone Studentbhattiareeba13Încă nu există evaluări
- Transporte Oseo Postinfeccion en TibiaDocument7 paginiTransporte Oseo Postinfeccion en TibiaSusan Ly VillalobosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fibula Free Flap 2Document5 paginiFibula Free Flap 2Sanjay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Sassia Lecture Bone Histology Part II July 4 2023Document39 paginiDr. Sassia Lecture Bone Histology Part II July 4 2023Ali ELKARGHALYÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCAFFOLDS COMBINED WITH STEM CELLS AND GROWTH FACTORS IN RECONSTRUCTION OF LARGE BONE DEFECTS. Rodolfo Capanna, Pietro de BiaseDocument7 paginiSCAFFOLDS COMBINED WITH STEM CELLS AND GROWTH FACTORS IN RECONSTRUCTION OF LARGE BONE DEFECTS. Rodolfo Capanna, Pietro de BiaseNuno Craveiro LopesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Document3 paginiChapter 6 Content Review Questions 1-8Rhonique MorganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal Bone Anatomy and Physiology: Go ToDocument11 paginiNormal Bone Anatomy and Physiology: Go TotariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec BONE GRAFTING ZS 2023Document89 paginiLec BONE GRAFTING ZS 2023MohamedAliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5 - Skeletal System StudentDocument35 paginiModule 5 - Skeletal System StudentLaw HacksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone and Cartilage TissueDocument33 paginiBone and Cartilage TissueGIANG ĐẶNG DUY TRÚCÎncă nu există evaluări
- DO - DPM Bone Formation D2L 2014Document7 paginiDO - DPM Bone Formation D2L 2014snlee06Încă nu există evaluări
- Surgery - Lect.10Document17 paginiSurgery - Lect.10hatemmaraqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aps 39 345Document9 paginiAps 39 345isabelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liza RovDocument29 paginiLiza RovCarlos Taito TakahashiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ossification of Bone.Document22 paginiOssification of Bone.Shimmering MoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spine Surgery: Journal of Korean Society ofDocument10 paginiSpine Surgery: Journal of Korean Society ofkang soon cheolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument210 paginiMusculoskeletal SystemDr. Serin KuriakoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionDe la EverandAdvanced farriery knowledge: A study guide and AWCF theory course companionÎncă nu există evaluări
- ClerkingDocument3 paginiClerkingaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ClerkingDocument3 paginiClerkingaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of - Dengue Fever in ChildrenDocument27 paginiManagement of - Dengue Fever in Childrenumiraihana1Încă nu există evaluări
- Genu Valgum0Document4 paginiGenu Valgum0aeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- OSTEOMALACIADocument10 paginiOSTEOMALACIAaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmputationDocument40 paginiAmputationaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tana MeraDocument1 paginăTana MeraaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- KYPHOSIS1Document13 paginiKYPHOSIS1aeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal & External Fixation-NEWDocument23 paginiInternal & External Fixation-NEWaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cubitus Varus Deformity Causes Complications Diagnosis TreatmentDocument7 paginiCubitus Varus Deformity Causes Complications Diagnosis TreatmentaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neonatal SepsisDocument3 paginiNeonatal SepsisaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orthopedic Emergencies and Urgen CiesDocument49 paginiOrthopedic Emergencies and Urgen CiesaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Femoralfracturepresentation 130220092741 Phpapp02Document38 paginiFemoralfracturepresentation 130220092741 Phpapp02aeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For TreatmentDocument2 paginiGuidelines For TreatmentaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MissionDocument1 paginăMissionaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Symposium Pamplet Biogen Inno-Vision 2012 Intro To Usmle Based TLDocument4 paginiBio Symposium Pamplet Biogen Inno-Vision 2012 Intro To Usmle Based TLaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For TreatmentDocument2 paginiGuidelines For TreatmentaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SW 14 Passover DiagnosisDocument1 paginăSW 14 Passover DiagnosisaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntubationDocument90 paginiIntubationaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Messages AMI STEMIDocument9 paginiEssential Messages AMI STEMIaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential Messages AMI STEMIDocument9 paginiEssential Messages AMI STEMIaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntubationDocument90 paginiIntubationaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoma Care BasicsDocument40 paginiStoma Care Basicsaerugino100% (1)
- Viral Infections in Malaysia: Dengue, Influenza and MoreDocument37 paginiViral Infections in Malaysia: Dengue, Influenza and MoreaeruginoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Two-Headed Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia Mydas) Hatchling On Samandağ Beach, TurkeyDocument6 paginiA Two-Headed Green Sea Turtle (Chelonia Mydas) Hatchling On Samandağ Beach, TurkeysushiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chloe Kho - Assignment 5 - MTT PracticeDocument5 paginiChloe Kho - Assignment 5 - MTT PracticeanthonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vodafone Idea Limited: PrintDocument2 paginiVodafone Idea Limited: PrintPrakhar KapoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Face SerumDocument10 paginiFace SerumLiliana CojocaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Journal DNA PolymeraseDocument12 paginiResearch Journal DNA PolymeraseMauhibahYumnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Flyers / Answer Key G / Unit 4: GrammarDocument8 paginiHigh Flyers / Answer Key G / Unit 4: GrammarDian Novyta AriantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step by Step To The Perfect PedicureDocument6 paginiStep by Step To The Perfect PedicurepinkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of PharmaDocument4 paginiList of PharmaJamielle SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- ImpetigoDocument31 paginiImpetigoUmmu Insyirah100% (1)
- Mind Map Burn & BleedingDocument2 paginiMind Map Burn & BleedingUlfia KhoirinnissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eye, E.N.T. & Dental AnaesthesiaDocument22 paginiEye, E.N.T. & Dental AnaesthesiawellawalalasithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mulching Paper Laying Machine SynopsisDocument17 paginiMulching Paper Laying Machine SynopsisSiddhesh Zirpe50% (2)
- 2 - Electrical Energy Audit PDFDocument10 pagini2 - Electrical Energy Audit PDFPrachi BhaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology of Women Reproduction SystemDocument52 paginiPhysiology of Women Reproduction Systemram kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- XFY1548移动式筛分站术规格书Document16 paginiXFY1548移动式筛分站术规格书abangÎncă nu există evaluări
- LENZE E84AVxCx - 8400 StateLine-HighLine-TopLine 0.25-45kW - v9-0 - ENDocument291 paginiLENZE E84AVxCx - 8400 StateLine-HighLine-TopLine 0.25-45kW - v9-0 - ENClaudioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Navi Cure prospectus summaryDocument50 paginiNavi Cure prospectus summaryGaurav SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1644 CV Europass Daniel MatosDocument2 pagini1644 CV Europass Daniel MatosDaniel MatosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Face Port Port Retainer Nose Block HiDocument7 paginiFace Port Port Retainer Nose Block HiOzan EgemenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Silver Chloride Dissolution in ARDocument5 paginiSilver Chloride Dissolution in ARAFLAC ............Încă nu există evaluări