Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Fundamentals Mohrs Circle Dis
Încărcat de
Humberto Diomedi MirandaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fundamentals Mohrs Circle Dis
Încărcat de
Humberto Diomedi MirandaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
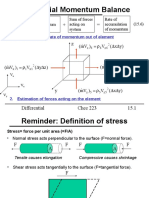
Review of fundamentals
Mohrs Circle
Stresses in a plane
( )
= 0 x F
( )
= 0 y F
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) u t u o o o o o
u
2 sin 2 cos
2
1
2
1
xy y x y x
+ + + =
( ) ( ) ( ) u o o u t t
u
2 sin
2
1
2 cos
y x xy
=
Assume that
xy
= 0, and let
x
=
1
and
y
=
2
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) u t u o o o o o
u
2 sin 2 cos
2
1
2
1
xy y x y x
+ + + =
( ) ( ) ( ) u o o u t t
u
2 sin
2
1
2 cos
y x xy
=
( ) ( ) ( ) u o o o o o
u
2 cos
2
1
2
1
2 1 2 1
+ + =
( ) ( ) u o o t
u
2 sin
2
1
2 1
=
( ) ( ) ( ) u o o o o o
u
2 cos
2
1
2
1
2 1 2 1
+ + =
( ) ( ) u o o t
u
2 sin
2
1
2 1
=
Analytical geometry for circles
Read the reading material:
Geometrical meaning of stress equations
Relationship between principal
stresses and max. shear stress
( ) ( )
2 2
max
4
2
1
2
1
) (
xy y x y x
P t o o o o o
u
+ + + = =
( ) ( )
2 2
min
4
2
1
2
1
) (
xy y x y x
Q t o o o o o
u
+ + = =
( )
2 2
min max,
4
2
1
xy y x
t o o t + =
2
max
Q P
= t
Mohrs
Circle
Procedure for plotting Mohrs Circle of
Stress (see pp. 16 18, Obert & Duvall)
1. Construct set of axes,
2. Plot
x
and
y
on
axis,
3. At
x
plot
xy
(if
xy
produces counter clockwise
couple, with shear diagonal positive, plot
xy
downwards)
4. At
y
plot
xy
(if
xy
produces clockwise couple, with
shear diagonal positive, plot
xy
up)
5. Join shear points A & B
6. Draw a circle at center C and diameter A B
7. P, Q,
max
, are as shown,
8. 2 is as shown
STUDY GUIDE:
Please try the following examples by yourself
Graphical meaning of principal
stresses and stress components
( ) ( )
2 2
max
4
2
1
2
1
) (
xy y x y x
P t o o o o o
u
+ + + = =
( ) ( )
2 2
min
4
2
1
2
1
) (
xy y x y x
Q t o o o o o
u
+ + = =
( )
2 2
min max,
4
2
1
xy y x
t o o t + =
2
max
Q P
= t
Graphical meaning of principal
stresses and stress components
( ) ( ) ( ) u o o o o o
u
2 cos
2
1
2
1
2 1 2 1
+ + =
( ) ( ) u o o t
u
2 sin
2
1
2 1
=
Invariants of stress
3 2 1 1
o o o o o o + + = + + =
z y x
I
STUDY GUIDE
The normal stresses change
with the direction at a point.
However, the summation of
the stresses in any three
perpendicular directions is a
constant.
Sketch the Mohr circles for the following stress
status.
1.
x
= 10,
y
= 2,
xy
= 3
2.
x
= 2,
y
= 10,
xy
= 3
3.
x
= 10,
y
= 2,
xy
= -3
4.
x
= 2,
y
= 10,
xy
= -3
5.
x
= -6,
y
= 2,
xy
= 3
6.
x
= -10,
y
= -2,
xy
= 3
Make sure you understand all the discusses
related to this example.
If you have difficult to understand the example,
you may want to study Study Guide 10 (down
below) and the associated slides and then go back
to this example.
STUDY GUIDE
Example
Given:
x
= 2000
y
= -800
xy
= -1000
Find:
P = ? Q = ? = ?
max/min
= ?
and
for = 22.5
( ) ( )
2 2
4
2
1
2
1
xy y x y x
P t o o o o + + + =
( ) ( ) ) 10 ( 4 2800
2
1
1200
2
1
6
2
+ + =
( )
6 6
10 * 4 10 * 84 . 7
2
1
600 + + =
2320 84 . 11 500 600 ~ + =
Using equations
( ) ( )
2 2
4
2
1
2
1
xy y x y x
Q t o o o o + + =
1140 ) ( = Q
( )
2 2
min max,
4
2
1
xy y x
t o o t + =
1740
min max,
= t
|
.
|
\
|
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
2800
) 1000 ( 2
tan
2
1
2
tan
2
1
1 1
1
y x
xy
o o
t
u
)
`
=
2800
2000
) ( tan
2
1
1
{ } 715 . 0 ) ( tan
2
1
1
=
Or
tan2 = (-) 0.715
tan2 = (-) 0.715
Angle will either be in 2
nd
or 4
th
quadrant
Simple stress diagram has told us
135 <
1
<180,
therefore
270 < 2
1
< 360
Looking up tangent in tables
2
1
= 36
2
1
= 360 36 = 324
1
= 162
Considering analytically the values of
and
on a plane at = 22.5
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) u t u o o o o o
u
2 sin 2 cos
2
1
2
1
xy y x y x
+ + + =
( ) ( ) ( ) 45 sin 1000 ) ( 45 cos 2800
2
1
1200
2
1
+ + =
283 600 ) 707 . 0 ( 1000 ) 707 . 0 ( 1400 600 + = + =
883 ~
u
o
( ) ( ) ( ) u o o u t t
u
2 sin
2
1
2 cos
y x xy
=
980 707 ) 707 . 0 )( 2800 (
2
1
) 707 . 0 )( 1000 ( = =
1687 ) ( =
u
t
The following two slides are used for further
demonstrating the importance of principle
stresses.
The example also demonstrates the concept of
invariants of stress discussed earlier
STUDY GUIDE 10
The four general steps discussed in the following
slides are extremely useful for plotting the Mohr
circle and for calculating the stresses and for
determining the directions of these stresses.
You will have no problem for Mohr circle plotting
and stress calculation if you follow these steps
exactly.
Using the example just discussed to practice
these steps. Using these steps as a guide to solve
your homework problems.
STUDY GUIDE
Step 1: Stress diagram
Mark the stresses: directions and magnitude
Mark the shear diagonal
Mark the directions for major and minor
principle stresses (the magnitude of the normal
stresses are measured algebraically)
Mohrs Circle and stress calculations
2
y x
o o +
=
2
2
min max,
4
) (
xy
y x
t
o o
t +
=
Step 2: Estimate the center and radius
of the Mohrs Circle
Radius: maximum shear stress, =
Center: average stress
Step 3: Drawing the Mohrs circle
Estimate the location and size of the Mohrs
circle
Mark two normal stresses ((the magnitude of
the normal stresses are measured
algebraically)
Mark two corresponding shear stresses
(using right-hand rule)
Drawing the circle
Mark the point representing x-plane, and then
the point for y-plane
Step 4: Principal stresses (P and Q)
and their directions
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
y x
xy
o o
t
u
2
tan 5 . 0
1
1
90
1
+ u
2
u
Calculating P and Q
and
one is corresponding to P.
Calculating
and determining which
Calculating
Homework 1
1) shear diagonal and approximate position of maximum
principal stress
2) major and minor principal stresses
3) angle
1
between the major principal stress and the x-
axis
4) maximum shear stress and angle
2
between the
maximum shear stress planes and the x-axis
5) normal and shear stress on a plane which makes an
angle of 30 with x-axis.
Verify the results using the Mohrs circle diagram.
2. Given the following state of stress,
1) determine 1 5 as in the previous
problem, and
2) verify the results using the Mohrs
circle diagram
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- FB AdsDocument1 paginăFB AdsHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- P Material Models Manual: LaxisDocument162 paginiP Material Models Manual: Laxismiquixtli4192Încă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Iaeg 189Document6 paginiIaeg 189Humberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- 2012 Body Application Guide Low ResDocument26 pagini2012 Body Application Guide Low ResHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Drawing1 Layout1Document1 paginăDrawing1 Layout1Humberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Geologic Mapping With Scaled 3D ImagesDocument5 paginiGeologic Mapping With Scaled 3D ImagesHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Limited Access: Geoprobe Model 420M: Strata Drilling Group: MachinesDocument1 paginăLimited Access: Geoprobe Model 420M: Strata Drilling Group: MachinesHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- V84-1 GenInfo PDFDocument18 paginiV84-1 GenInfo PDFJoão InácioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Lamina Iquique Arch D Horizontal-ModelDocument1 paginăLamina Iquique Arch D Horizontal-ModelHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- 2008 Journal of GeologyDocument14 pagini2008 Journal of GeologyHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rucker PDFDocument9 paginiRucker PDFHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rucker PDFDocument9 paginiRucker PDFHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Standard Penetration TestDocument8 paginiStandard Penetration TestRodneyXerri100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- CBR (Field) 1850 Triaxial Cell 2200 CBR Frame That You Include Free of Charge CBR Mould 85Document2 paginiCBR (Field) 1850 Triaxial Cell 2200 CBR Frame That You Include Free of Charge CBR Mould 85Humberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- ReferencesDocument1 paginăReferencesHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- HDS Black&White TargetDocument1 paginăHDS Black&White TargetHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VW Embedment Strain Gauge ManualDocument10 paginiVW Embedment Strain Gauge ManualHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Udc 505Document336 paginiUdc 505Humberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VW CrackmeterDocument9 paginiVW CrackmeterHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide To InstrumentationDocument52 paginiGuide To InstrumentationHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Iaeg 189Document6 paginiIaeg 189Humberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- D 2938 - 95Document3 paginiD 2938 - 95Humberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Straightline Rockeye Loaner ProgramDocument2 paginiStraightline Rockeye Loaner ProgramHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geo RobotDocument3 paginiGeo RobotHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Estimation of Rock Mass Properties of Heavily Sheared Flysch Using Data From Tunnelling ConstructionDocument12 paginiEstimation of Rock Mass Properties of Heavily Sheared Flysch Using Data From Tunnelling ConstructionHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReadmeDocument2 paginiReadmeHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iaeg 189Document6 paginiIaeg 189Humberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSIRO HI Cell Measures Rock & Concrete StressDocument2 paginiCSIRO HI Cell Measures Rock & Concrete StressHumberto Diomedi MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- What Happens When Warm Air RisesDocument30 paginiWhat Happens When Warm Air RisesCriselAlamag100% (1)
- Worksheet On Quantum NumbersDocument2 paginiWorksheet On Quantum NumbersJannah Mae IsioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zetex HandbookDocument8 paginiZetex HandbookbolermÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refractive Index of A Liquid (Theory) : Class 12: PhysicsDocument4 paginiRefractive Index of A Liquid (Theory) : Class 12: PhysicsAmartya AnshumanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radar Systems Range Equation PDFDocument6 paginiRadar Systems Range Equation PDFSanjid ElahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 85 Describing Motion OrganizerDocument10 pagini85 Describing Motion OrganizerFernando Sorto50% (2)
- PEGN 419 / GPGN 419 Spring 2017: Manika Prasad Mansur Ermila Expert Resource: Robert LieberDocument30 paginiPEGN 419 / GPGN 419 Spring 2017: Manika Prasad Mansur Ermila Expert Resource: Robert LiebertahermohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman Equation ExplainedDocument7 paginiHamilton-Jacobi-Bellman Equation ExplainedMakinita CerveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Planets Comparative Superlative - 87358Document2 paginiThe Planets Comparative Superlative - 87358Maria AdamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance-Based Plastic Design and Energy-Based Evaluation of Seismic Resistant RC Moment FrameDocument7 paginiPerformance-Based Plastic Design and Energy-Based Evaluation of Seismic Resistant RC Moment FrameARJafariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cooling Tower Pumping and Piping: LegendDocument46 paginiCooling Tower Pumping and Piping: LegendDenise Koh Chin HuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interactions and Incompatibilities of Pharmaceutical ExcipientsDocument24 paginiInteractions and Incompatibilities of Pharmaceutical ExcipientsEmmanuel Vachon LachanceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Linear Differential Equations Standard Form and Operator FormDocument10 paginiLinear Differential Equations Standard Form and Operator FormJoSaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norma Japonesa Aij-Rlb-1996Document36 paginiNorma Japonesa Aij-Rlb-1996AnaApcarianÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4363 111 Machine Design IDocument6 pagini4363 111 Machine Design Iyogesh_b_k100% (2)
- Basic Hazen Williams FormulaDocument28 paginiBasic Hazen Williams FormulaDhimas IriantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bedini's Free Energy Generator PDFDocument7 paginiBedini's Free Energy Generator PDFRafly Attila Al-Fiqri71% (7)
- CFD and Experimental Study of Wetting of Structured Packing ElementsDocument139 paginiCFD and Experimental Study of Wetting of Structured Packing ElementsahmedsalemyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch15 Differential Momentum BalanceDocument20 paginiCh15 Differential Momentum Balance89kkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astronomy Unit Resources SchoolpointeDocument17 paginiAstronomy Unit Resources SchoolpointeShekel DeninoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meteorology and Wind Resource Geostrophic BalanceDocument10 paginiMeteorology and Wind Resource Geostrophic BalanceSilvio NunesÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersDocument1 paginăRCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersArwin VillegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat and Temperature Unit3 - T4 - T6 PDFDocument28 paginiHeat and Temperature Unit3 - T4 - T6 PDFhiren_mistry55Încă nu există evaluări
- Stainless Steel PropertiesDocument3 paginiStainless Steel Propertieskiwanis_lamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choice of Steel Material To Avoid Brittle Fracture For Hollow Section StructuresDocument204 paginiChoice of Steel Material To Avoid Brittle Fracture For Hollow Section Structuresg1n2Încă nu există evaluări
- MIT Feedback Linearization LectureDocument5 paginiMIT Feedback Linearization LectureJosé Ignacio Fierro TravoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics of Weak Electrolytes Including H3PO4Document10 paginiThermodynamics of Weak Electrolytes Including H3PO4buhalnitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flight Equations of Motion for 6 DOF Aircraft ModelDocument24 paginiFlight Equations of Motion for 6 DOF Aircraft ModelNeetu SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Basics of General, Organic and Biological Chemistry - AttributedDocument1.421 paginiThe Basics of General, Organic and Biological Chemistry - AttributedAlfonso J Sintjago100% (2)