Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
ONTAP p2-2009
Încărcat de
Batisxuta MichaelDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ONTAP p2-2009
Încărcat de
Batisxuta MichaelDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
NOUNS
COUNTABLE NOUNS
UNCOUNTABLE NOUNS
Countable used with:
a/an or numbers (one, two,
three, etc.), or plural forms
Ex: a cat; eleven matches
Many; several; various;
few; a few; how many;
fewerthan
Ex: several jumbo jets; a
few jokes
Uncountable
CANNOT be used with
a/an; numbers; in plural
forms
BUT: They ordered a wine
that wasnt included in our
list. (a kind of wine)
much; how much;
little; a little;
lessthan
Ex: There was less
rainfall last year.
a number of/ the number
of
Ex:- A number of people
decided to withdraw a lot of
money from their account.
- The number of people
who decided to withdraw a
lot of money from their
account was low.
A great number of/ a
large number of/ the
majority of
Ex:- A great number of
whales were killed for meat
Each (of)+ N
Every (of)+N+ Verb (sing.)
the amount of/ a
large amount of/ a
great deal of
Ex: A large amount of
food was taken to the
north.
Expressions used with both count. &
uncount. nouns
Some (of)
Any (of)
A lot of
Lots of
Plenty (of)
Almost (of)
All (of)
None (of)
Ex: - Some of the food in the fridge was spoiled.
- Some children are overindulged and spoiled by
their parents
Some expressions used with uncount.
1. A bar of chocolate / two bars of
chocolate
2. A kilo/ a cube/ a spoon/ a jar of sugar
3. A tube of toothpaste / two tubes of .
4. A glass/ a carton/ a liter of milk
5. A packet/ a cup of flour
Notes
Some of
All of
Any of + the/ possessive adj.+ Noun
Most of
None of
One of
Ex: - Some comments are helpful.
- Some of her comments are helpful.
- Some of the comments are helpful.
IRREGULAR NOUNS
A. IS -> ES
SINGULAR PLURAL
axis axes
analysis analyses
basis bases
crisis crises
diagnosis diagnoses
ellipsis ellipses
hypothesis hypotheses
oasis oases
paralysis paralyses
parenthesis parentheses
synthesis syntheses
synopsis synopses
thesis theses
B. IX -> ICES
SINGULAR PLURAL
appendix appendices
index indeces /indexes
matrix matrices /matrixes
C. OUSE -> ICE
SINGULAR PLURAL
louse lice
mouse mice
D. EAU -> EAUX
SINGULAR PLURAL
beau beaux
bureau bureaus/bureaux
tableau tableaux/tableaus
E. -> EN
SINGULAR PLURAL
child children
man men
ox oxen
woman women
F. UM A
SINGULAR PLURAL
bacterium bacteria
corpus corpora
criterion criteria
curriculum curricula
datum data
genus genera
medium media
memorandum memoranda
phenomenon phenomena
stratum strata
G. OO -> EE
SINGULAR PLURAL
foot feet
goose geese
tooth teeth
H. A -> AE
SINGULAR PLURAL
antenna antennae/antennas
formula formulae/formulas
nebula nebulae
vertebra vertebrae
vita vitae
I. UNCHANGED
SINGULAR PLURAL
deer deer
fish fish
means means
offspring offspring
series series
sheep sheep
species species
A hour ago
An hour ago
A honest man
An honest man
An university
A university
A one-eyed man
(correct)
An SAT test
(correct)
A MP
An PM
A member of Parliament
(correct)
ARTICLES
A+ nouns beginning with a consonant.
An+ nouns beginning with a vowel.
BUT:
A + uniform/ one-dollar coin/
/ju/ /wn/
An+ honest person/ honorable prize
SOS signal/ MP/ an SAT test
BUT: a member of Parliament
Indefinite articles
When the person/ thing is not yet
mentioned before or not definite.
Ex: I saw a poor child begging for food in the
streets.
To talk about a job or profession
Ex: Jenny is a taxi driver.
As a synonym of per
Ex: 200km per hour/ an hour
To mention the quantity of people or things
EX: Theres a/ one slice of bread in the toaster
oven.
DEFINTE ARTICLES
When the person/ thing has already been
mentioned before or definite.
Ex: The child was about 6 years old.
The only/ unique things: the moon, the sun
The first, the second, etc.
The corner of/ the top of / the middle of
Before a class/ species of animal:
Ex: The whale is in danger of becoming extinct.
( Or: X Whales are in danger of extinction.)
The+ adj: as a group of people
Ex: the poor, the rich
Before familys last name: The Smiths
Before rivers, channels, seas, oceans,
mountain ranges, deserts, hotels,
Ex: The Alps, the English Channel, The Pacific
Ocean
BUT X Everest (as a single mountain)
A people:
Ex: The Vietnamese/ X Vietnamese people
Names of newspapers/ magazines
Ex: The Far Eastern Economic Review.
Superlatives:
Ex: The most complicated problem
With decades, centuries
Ex: in the 1960s, in the 20th century
Before names of places+ of + Nouns
Ex: the Gulf of Mexico
Musical instruments
Ex: Play the violin
Go to the cinema/ the theatre/the opera
listen to the radio
BUT: watch X TV
Have a cold/ a headache/ a backache
have the flu/ the measles
DO NOT use the before an illness:
Ex: have cancer/ have pneumonia
Abbreviations and organizations:
"the UN", "the USA", "the IMF/ the World
Health Organization
The + university/ college of
Ex: the university of Technology
BUT: X Saigon University
The university of Saigon
The of
Ex: - the top of the mountain
Tittle
Ex: - the Queen of England //
- x Queen Elizabeth
Names of countries which contain the
words "union" or "united":
The Soviet Union
The United Kingdom
But: France, Japan.
NO ARTICLES
Nouns in general
Singular uncount.N:
Ex: Milk is good.
Plural count. N:
Ex: - Bananas are good.
- Whales are in danger of becoming
extinct.
BUT: Man and woman were created equal.
Countries
X Vietnam/ The Socialist Republic of Vietnam
To/at/ in/ from school (/university/ church/ prison/
college)
Ex: - James is in hospital right now to have his eyes
checked.
- Go to university
By + means of transportation
Ex: He often went there on foot.
Some expressions
make friends, shake hands, have faith, take part in
something, pay attention, take advantage of
something/someone, etc.
Sports
school subjects
languages
professions
vacations
meals of days
streets, towns, cities
Ex: - Play golf/
- Spend Christmas in the country
- Live on X LTK street.
- Hes going to take an evening course in X
accounting.
SUBJECT-VERB Agreement
Singular Verb:
Clause + Verb +
Ex:- What hes saying is unbelievable.
- Who hes making friends with makes
his parents very worried.
Indefinite pronouns as the subject (
someone, something, anything,
nothing, etc)
Ex: Someone is standing outside.
A sum of money/a duration of time
Ex: Ten dollars isnt a big sum of money.
Some nouns (of illnesses/ subjects,
etc.) ending ins
Ex:- Physics is my favorite subject.
None of/ neither of/ either of + N (count/
uncount.)
Ex: - None of the dogs belongs to us.
- Neither of the employees has agreed
with me.
The number of + Nouns (plural) + verb
Ex: The number of tenants without heat is
increasing.
When all parts of a compound subject are
singular and refer to the same person or
thing:
Ex: The head of the expedition and the
major of the village was the same person.
PLURAL VERBS
(both) N1 + and N2
Ex: Both Jim and John like football.
Subjects such as
People/ those/ police/ cattle/glasses /etc.
Ex: Those who register at this hotel can
get a discount.
A number of + N (plural) + Verb
Ex: A number of tenants are in the building.
The rich/ the poor/... + Verb (plural)
Ex: The sick are taken to hospital immediately.
Trousers/ pliers/ binoculars/ etc.+ Verb
(plural)
Ex: The binoculars which John bought were brand-
new.
Ex: These trousers cost him $100.
But: A pair of + + V (singular)
Ex: This pair of trousers costs him $100.
SINGULAR or PLURAL
N1 + together with/ with/ as well as/
accompanied by + N2 + V (N1)
Ex: John together with his children is
coming here.
Either + N1 or + N2 + V (N2)
Neither nor
Ex: Either John or his children are coming
here.
All of N (plural) + Verb-Plural
Some of +
Most of N (sing.) + Verb- singular
Ex: - All of the cake has been eaten.
- All of the cakes on the plate have been
eaten.
Collective nouns + Verb (plural or
singular)
family, jury, majority, minority, etc.
Ex: The committee has been working for 3
hours.
The committee have been working for three
hours.
When the subject is a fraction or a word
(half, part, plenty, rest, etc.):
Ex: Three fourths of the enemys army was
wounded.
Ex: Three fourths of the enemys soldiers
were wounded.
ONE THE OTHER
ONE ANOTHER THE OTHERS
SOME OTHER
Mentioning 2 people or things: ONE- THE OTHER
(the rest singular meaning)
Ex: - Pat offered us two options- one is to stay at
his home during the vacation, the other is to stay in a
very comfortable but cheap inn.
Mentioning at least three people or things
ONE ANOTHER THE OTHERS (the rest-
plural meaning)
Ex: - I saw a lot of cars in their garage- one is a
Mercedes, another a Honda, and the others
Fords.
(the other cars were Fords)
Some Other
Ex: Some people are calm, others are quite easily
to lose their temper.
(others means other people, doesnt mean the rest)
I or ME
It was she who made those loud noises.
It was I who broke the promise.
Preposition + Obj pronoun
Ex: Between you and me, I can share with
you some of her secrets.
NOTES about PRONOUNS
Reflexive pronouns
Did you compose the song by yourself/ on your own?
EMPHASIS
I myself wrote that song.
Indefinite Pronouns
Indef.pron.+ adj
Ex: I had expected something new from this article but I
couldnt
Indef.Pron.+ Verb-Sing.
Ex: Somebody is knocking at the door.
EMPHASIS
On Verbs
Phil made the announcement about his wedding.
Phil did make the announcement about his wedding.
You have certainly grown.
You certainly have grown.
On Adverb
I seldom call them.
Seldom do I call them.
We go off.
Off we go.
Pete and Jane go off.
Off go Pete and Jane.
Cleft structures
John paid for the next drink.
It was John who paid for the next drink.
I need a good rest.
What I need is a good rest.
SUBJUNCTIVES
WISH
I wish you were here now.(present)
I wish you would be here tomorrow.(future)
I wish Jack had not said anything insulting to
his colleagues. (Past)
(in fact, he did say something.)
Some structures used with subjunctives
Wish that
Would rather that
If only
As if
As though
Its (high) time that
It is advisable that
Subj. + recommend/ propose/ that
Ex: If only Phil had told me about the
schedule changes. (He didnt say
anything)
Ex: Jane would rather that we came to
help her now. (We cant come now.)
Ex: Laura talked to us as if she had been
our boss.( She was not our boss)
I would rather / Id rather that you would
come to help me.
Id rather do it on my own than ask John
for help.
Its time (that) we stopped for lunch.
Its time to stop for lunch.
NOTES on CONDITIONALS
Ex1:- If you had helped me do that, I would
have finished it on time.
= Had you helped me do that, I would have
finished it on time.
Ex2: If she were my daughter, she wouldnt
behave as a cheater.
= Were she my daughter,.
Ifnot = Unless
Ex: If she doesnt come, well leave without
her.
= Unless she comes, well leave without
her.
Ex: Ill take the job unless the pay is too low.
= If the pay isnt too low,
COMPARISONS
Ex: Im trying to work harder for the
coming examination.
Im trying to work much harder for the
coming exam.
The test was more difficult than I had
expected.
The test was far more difficult than I had
expected.
Ex: Alain is two years younger than I am.
Jack earns three times as much as I do.
Or: Jack earns twice as much as /three
times more than I do.
PASSIVE
Ex: They asked us for help.
We were asked for help.
Passive form:
S + Verb-BE (tense) + Verb-main (past part.)
Ex: She has been doing the test for three hours.
The test (be) done for three hours.
Ex: Sarah is writing a postcard.
The postcard (be) written by
Sarah.
Ex: They will be discussing this issue at this
time tomorrow.
This issue (be) discussed at
this time tomorrow.
PASSIVES
Formation of Passive structures
Subj + Be (tenses) + Verb (past participle)
Ex: Sarah (has) returned the books to me.
The books were/ have been returned to me.
Verb + Sb + to-infinitive (v2)
Verb + to be past participle (v2)
Ex1: I wanted them to inform me of the
conference.
I wanted to be informed of the conference.
Verb + Sb +V-ing (v2)
Verb + Being- past participle (v2)
Ex2: Pete disliked them discriminating himself.
Pete disliked being discriminated.
Verb (v1) + sb + bare-inf
Verb-past part. (v1) + to-inf.
Ex2: I saw him come out of the house.
He was seen to come out of the house.
S1+ V1- that S2 +V2 +
It + be + V1-past part.+ that S2+V2+
S2 + be + V1 + to-infinitive V2
Ex: They said that Joe was a doctor.
It was said that Joe was a doctor.
Joe was said to be doctor.
This structure is often used with some verbs:
say, tell, think, believe, expect, consider,
rumor, etc.
Verbs with two objects.
Send sth to sb/ send sb sth
Explain
Show
Give
Bring
Ex: He sent us a postcard.
or: He sent a postcard to us.
We were sent a postcard.
A postcard was sent to us.
Ex: He sent us a postcard.
or: He sent a postcard to us.
He sent it to us.
He sent Kim a postcard.
Never say: - He sent us it.
Passive with prepositions: Do not drop
the preposition when using passive
voice.
They filled the tank with gas.
The tank was filled with gas.
What was the tank filled with?
OR: With what the tank filled? (formal)
They brought up the boy so well.
The boy was brought up so well.
COMPOUND SENTENCES
Compound sentences
Ex: Pat is abroad right now, but she can contact her
office regularly.
Ex: Pat is abroad right now; however, she can contact
her office regularly.
Ex: Pat is abroad right now. However, she can contact
her office regularly.
Ex: Noah has finished all his homework, so he can go
out with his friends now.
Ex: Noah has finished all his homework; therefore, he
can go out with his friends now.
Ex: Noah has finished all his homework. Therefore, he
can go out with his friends now.
Ex: Dave turned off all the lights in the room, and
then went out.
Ex: Dave turned off all the lights in the room. After
that, he went out.
Complex sentences
Ex: Although Pat is abroad right now, she can
contact her office regularly.
Ex: Since/ Because Noah has finished all his
homework, he can go out with his friends now.
Ex: After Dave turned off all the lights in the room.
He went out.
Coordinating
Conjunctions
(Conjunctive adverbs)
1. moreover; furthermore
2. Besides
3. In fact
4. In other words
5. In that case
6. Otherwise; if not
7. On the other hand; in
contrast
8. However; nevertheless
Subordinating
Conjunctions
1. In addition to the fact
that
2. N/a
3. N/a
4. N/a
5. If; provided that; as long
as
6. Unless
7. Whereas; while
8. Although; even though;
even if;
9. (cause)
10. Therefore; as a
result; thus;
consequently; so
11. previously;
12. Until then
13. After that;
afterwards; then
14. Since then
15. For this reason
9. because, since, as,
due to the fact that
10. So
11. before
12. until
13. After
14. since
15. So that; in order that
A compound sentence contains two
independent clauses joined by a
coordinator. The coordinators are as
follows: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.
Ex: I tried to speak Spanish, and my friend
tried to speak English.
A complex sentence consists of one
independent clause, and one or more
dependent clauses. The clauses are
connected through either a subordinate
conjunction or a relative pronoun.
Ex: As long as it isn't cold (Dependent
clause) , it doesn't matter if it rains
(Independent clause) .
Ex: The house which Abraham Lincoln was
born in is still standing.
ADJECTIVE CLAUSES
Defining adjective clauses
Ex: Have you ever spoken to the people who live
next door? (not yet identified) (subject)
Have you ever spoken to the people that live
next door? (subject)
Ex: I dont know the man whom/ who/ that/
(not yet identified) (Object)
Jane is talking to.
The relative pronouns as the subject:
Ex: The trees WHICH/THAT at one time lined this
road have all been cut down.
Ex: Do you like the car that/ which is in
(not yet identified) (subject)
Johns garage?
The relative pronouns as the object:
Ex: Can I borrow the CD WHICH/ THAT/ you
bought?
Ex: Theres a program on tonight which/ that/
(not yet identified) (Object)
you might like.
Non-defining Relative clauses
Ex: This is Mr. Rogers, who is our new
(definite) (subject)
manager.
BUT we cannot use THAT. It is INCORRECT.
This is Mr. Rogers, THAT is our new
(definite) (subject)
manager.
We cannot use THAT in non-defining Relative
clauses.
Ex: This is Mr. Rogers, whom Jane
(definite) (object)
is going to marry.
But we cannot use WHO.It is INCORRECT.
This is Mr. Rogers, who Jane is going
(definite) (object)
to marry.
We cannot use THAT or WHO
or OMIT whom in non-defining Relative clauses.
Ex: Janes house, WHICH is in District 8,
has a garden.
BUT we cannot use THAT in non-defining
clauses.
You cannot leave out who, which, that when: it
is the subject of the verb in the relative clause
and in non-defining relative clauses
DEFINING CLAUSES
Person Thing Place Time Reason
Subject Who/ that Which/that
Object Who/whom/that/ Which/that / Where When Why
possession Whose Whose
NON-DEFINING CLAUSES
Person Thing
Subject Who Which
Object Whom Which
possession Whose Whose
WHOSE = of sth
Ex: Ive just talked to the man. His house
looks over the river.
Ive just talked to the man WHOSE house
looks over the river.
Ex: Look at that man. His son is a pop singer.
Look at that man WHOSE SON is a pop
singer.
WHERE = preposition (in/ at/ on/ etc.)+ Noun of
place
Ex: This is the place. I was born there/ in that
place.
This is the place WHERE I was born
This is the place IN WHICH I was born.
Ex: - I dislike the hotel. We are going to stay at that
hotel.
I dislike the hotel where we are going to stay.
I dislike the hotel at which we are going to stay.
NOTES
Noun of place = WHICH
Ex: They are going to move to Ottawa. It is
the capital of Canada.
They are going to move to Ottawa, which is
the capital of Canada.
Ex: He works for a spy network, about which
I know nothing.
OR: He works for a spy network (which) I
know nothing about.
Ex: The people with whom he worked
have all been arrested. (Formal)
OR: The people (who) he worked with have
all been arrested. (Informal)
We often use THAT instead of who or which
when the antecedents are the following
phrases:
All, every(thing), some(thing), any(thing),
no(thing), little, few, much, only, and after
superlative structures
Ex: The only thing THAT matters is to find our way
home.
Ex: Its the best film THAT has ever been made.
NOUN CLAUSES
A Noun Clause often begins with:
that (That-clause), who, which, how, etc.
Ex: HER STORY WAS NOT TRUE
(Subj.) V
Ex: - What he was saying was not true.
Ex: - Im not sure where he is from.
Ex: - Do you know what he is doing?
Ex: - That he is not here now worries all
of us.
A noun clause can be the subject, object,
complement.
AS THE SUBJECT:
Ex: WHAT the little boy has done
recently is really worrying.
Ex: THAT Jane received the scholarship
satisfied her parents.
As the object of a verb:
Ex: - Joe asserted that he hadnt been
there on Tuesday night.
Ex: - She never tells me where Joan lives.
Ex: Mary is not responsible for what Billy
did.
As a complement:
Ex: Billys mistake was that he refused to
take lessons.
Ex: Everybody is sad that Billy drowned.
ADVERB CLAUSES
Adv clauses of time:
as, when, as soon as, before, after, now that, since,
while, etc.
Ex: When I came, they were discussing the
meeting.
Adv clauses of manner:
as if, as though, etc.
Ex: She made us work hard as if we had been her
slaves.
Adv clauses of condition:
unless, if, even if, whether or not, provided that, etc.
Ex: I wont tell you that secret unless you
promise not to tell it to anyone.
Adv clauses of cause and effect:
because, since, so that, in order that, etc.
Ex: He put on more warm clothes since it was
so cold outside.
Adv clauses of concession:
although, while, though, even though, whereas, etc.
Ex: Although its raining heavily, theyre still
working in the rain.
Adv clauses of comparison:
more than, as as, etc.
Ex: Hes worked much harder than I have.
REPORTED SPEECH
Reported speech
A. Statements
Ex: Harry said, Im leaving for China tomorrow.
Harry said to me that he was leaving for China
the next day.
B. Yes-No questions
Ex: Ted asked, Will you come tomorrow, Tom?
Ted asked Tom IF/ WHETHER Tom (he) would
come tomorrow.
Ex: Bill asked, Laura, are you free now?
Bill asked Laura IF/ WHETHER she was free at
that moment.
C. Wh-questions
Ex: Jack asked, Lilly, where are you going?
Jack asked Lilly where she was going?
EX: Tom asked, What did you do yesterday?
Tom asked me what I had done the day before.
D. An imperative.
Ex: Jim said, Go out!
Jim told me to go out
Jim shouted at me to go out.
D. An offer/ request
Ex: Jane asked, Tim, can you help me move this
table?
Jane wanted Tim to help her move that table.
Jane asked Tim if he could help her move that
table.
Ex: Ted asked, Would you please come back at
10a.m.?
Ted wanted me to come there at 10a.m.
Ted asked me if I would come there at 10 a.m.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Construction Project Documentation: Discussions on Building WorksDocument120 paginiConstruction Project Documentation: Discussions on Building WorksCuong Nguyen Tien100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- TCVN 5760-1993 HT Chua Chay Yeu Cau KT - LD - Su DungDocument5 paginiTCVN 5760-1993 HT Chua Chay Yeu Cau KT - LD - Su DungSuSi AothunthoitrangÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- COÄNG HOØA XAÕ HOÄI CHUÛ NGHÓA VIEÄT NAMDocument6 paginiCOÄNG HOØA XAÕ HOÄI CHUÛ NGHÓA VIEÄT NAMBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- Doko - VN 154419 Tong Hop Text Tieng Anh On Thi Cong ChucDocument45 paginiDoko - VN 154419 Tong Hop Text Tieng Anh On Thi Cong ChucBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- TCVN 9361 2012 Cong Tac Nen Mong - Thi Cong Nghiem ThuDocument67 paginiTCVN 9361 2012 Cong Tac Nen Mong - Thi Cong Nghiem ThuBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Bia 1Document1 paginăBia 1Batisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- TCVN 9360 2012Document61 paginiTCVN 9360 2012Batisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- TCVN 6073 2005 - Unprotected PDFDocument17 paginiTCVN 6073 2005 - Unprotected PDFBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Tieu Chuan Coc EpDocument41 paginiTieu Chuan Coc EpMinhBáÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- Quy Hoach Do Thi 1Document71 paginiQuy Hoach Do Thi 1Batisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dien Able TechDocument22 paginiDien Able TechBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gia Giao Thau - Phung R0Document7 paginiGia Giao Thau - Phung R0Batisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Precast, Prestressed Concrete BridgesDocument24 paginiPrecast, Prestressed Concrete BridgesTeodora PopovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- IHMC Literature Review On Concept MappingDocument108 paginiIHMC Literature Review On Concept MappingBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- JL 06 March April 5Document12 paginiJL 06 March April 5Batisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- PCI Bridge Design Manual Appendix A Notation GuideDocument20 paginiPCI Bridge Design Manual Appendix A Notation GuideBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- JL 06 March April 3Document12 paginiJL 06 March April 3Batisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- AASHTO BEAMS Standard DimentionsDocument16 paginiAASHTO BEAMS Standard Dimentionsjedidestroyer100% (1)
- Behavior of Prestressed Concrete Box-Beam Bridges Using CFRP TendonsDocument16 paginiBehavior of Prestressed Concrete Box-Beam Bridges Using CFRP TendonsBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- JL 06 March April 1Document12 paginiJL 06 March April 1Batisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- A Field Trial For Soft Clay Consolidation Using Electric Vertical DrainsDocument19 paginiA Field Trial For Soft Clay Consolidation Using Electric Vertical DrainsBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- 1000 Cautracnghiem TrietDocument161 pagini1000 Cautracnghiem TrietDuy TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing: SENTENCE TRANSFORMATION: Choose The Correct AnswerDocument25 paginiWriting: SENTENCE TRANSFORMATION: Choose The Correct AnswerBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
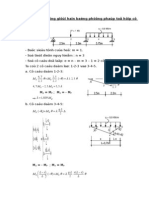
- L X L XL .X: 4. Tìm Taûi Roïng Giôùi Haïn Baèng Phöông Phaùp Toå Hôïp Cô CaáuDocument2 paginiL X L XL .X: 4. Tìm Taûi Roïng Giôùi Haïn Baèng Phöông Phaùp Toå Hôïp Cô CaáuBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Writing: SENTENCE TRANSFORMATION: Choose The Correct AnswerDocument25 paginiWriting: SENTENCE TRANSFORMATION: Choose The Correct AnswerBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strut Tie Model - STMDocument10 paginiStrut Tie Model - STMshish0iitrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dich Tieng AnhDocument10 paginiDich Tieng AnhBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing: SENTENCE TRANSFORMATION: Choose The Correct AnswerDocument25 paginiWriting: SENTENCE TRANSFORMATION: Choose The Correct AnswerBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Grammar ReviewsDocument52 paginiGrammar ReviewsBatisxuta MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Headache in ChildrenDocument34 paginiHeadache in Childrensai saiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Health Effects of ObesityDocument7 paginiMental Health Effects of ObesityMohd FaizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Physiotherapy Rehabilitation On Volkmann Ischemic Contracture-A Case StudyDocument2 paginiEffect of Physiotherapy Rehabilitation On Volkmann Ischemic Contracture-A Case StudyIntan HaddadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuberculosis in Pregnancy Effects Risks TreatmentDocument36 paginiTuberculosis in Pregnancy Effects Risks TreatmentOfel Santillan100% (1)
- Understanding Typhoid Fever: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument41 paginiUnderstanding Typhoid Fever: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentMeldiana88% (8)
- Drug StudyDocument3 paginiDrug StudyKorina FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metabolic Acidosis: Irish Grace A. Dayao Dra. RamosDocument14 paginiMetabolic Acidosis: Irish Grace A. Dayao Dra. RamosBing DayaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gouty Arthritis Case PresentationDocument75 paginiGouty Arthritis Case PresentationVan Talawec100% (2)
- Lepra 2022Document4 paginiLepra 2022Ketut ArtawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Women's Heart HealthDocument3 paginiWomen's Heart HealthMatt ThielkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Diarrhea and Malabsorption SyndromesDocument152 paginiChronic Diarrhea and Malabsorption SyndromesAndrei DumitruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Preoperative Testing and Medication ManagementDocument27 paginiPreoperative Testing and Medication ManagementWidya JelitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical AbbreviationDocument13 paginiMedical AbbreviationRaf Luis100% (1)
- Esophagus: DrzaiterDocument37 paginiEsophagus: DrzaiterdrynwhylÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 1: Cholecystolithiasis Answers To Guide QuestionsDocument2 paginiCase 1: Cholecystolithiasis Answers To Guide QuestionsSharmaine IboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes and Characteristics of Onset of Weakness in ExtremitiesDocument2 paginiCauses and Characteristics of Onset of Weakness in ExtremitiesYulyani PratiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Positive Language Guide - 0Document22 paginiPositive Language Guide - 0Xristos BeretisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Herbal PlantsDocument14 paginiHerbal Plantsapi-3739910100% (2)
- Indoor Air PollutionDocument24 paginiIndoor Air PollutionMohamed SalemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tracheomalacia 131030001629 Phpapp01Document52 paginiTracheomalacia 131030001629 Phpapp01SaaraAlleyahAlAnaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- GOLD 2011 Guideline SummaryDocument25 paginiGOLD 2011 Guideline SummaryebramnainggolanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Using Guava Leaves As An Alternative Medicine For DiarrheaDocument32 paginiAssessment of Using Guava Leaves As An Alternative Medicine For DiarrheaKamela AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding the Mind-Body Link in Chronic IllnessDocument3 paginiUnderstanding the Mind-Body Link in Chronic IllnessJitendra SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of HydrocephalusDocument4 paginiManagement of HydrocephalusShine CharityÎncă nu există evaluări
- PediatricsDocument21 paginiPediatricsJo Anne75% (8)
- G.R. No. 196102 November 26, 2014 Government Service Insurance System, Petitioner, AURELIA Y. CALUMPIANO, RespondentDocument4 paginiG.R. No. 196102 November 26, 2014 Government Service Insurance System, Petitioner, AURELIA Y. CALUMPIANO, RespondentMarra RicaldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capsicum Frustascens Cayenne Pepper Decoction As An Alternative Killer For CockroachesDocument4 paginiCapsicum Frustascens Cayenne Pepper Decoction As An Alternative Killer For CockroachesRhitzelynn Ann BarredoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument11 paginiAbruptio PlacentaAlynna ValbuenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs Used in The Management of Pain: Non Opioid AnalgesicsDocument6 paginiDrugs Used in The Management of Pain: Non Opioid Analgesicstesfamichael mengistuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Local anesthetic bupivacaine nursing considerationsDocument2 paginiLocal anesthetic bupivacaine nursing considerationsPutuÎncă nu există evaluări