Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 09 Slides
Încărcat de
Darryl Wallace0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
18 vizualizări14 paginistrategic management
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentstrategic management
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
18 vizualizări14 paginiChapter 09 Slides
Încărcat de
Darryl Wallacestrategic management
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 14
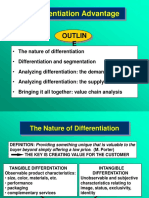
Differentiation Advantage
The nature of differentiation
Differentiation and segmentation
Analyzing differentiation: the demand side
Analyzing differentiation: the supply side
Bringing it all together: value chain analysis
OUTLIN
E
The Nature of Differentiation
TOTAL CUSTOMER RESPONSIVENESS
differentiation not just about the product, it embraces the whole relationship
between the supplier and the customer.
INTANGIBLE DIFFERENTATION
Unobservable and subjective
characteristics relating to image,
status, exclusively, identity
TANGIBLE DIFFERENTATION
Observable product characteristics
size, color, materials, etc.
performance
packaging
complementary services
DEFINITION: Providing something unique that is valuable to the
buyer beyond simply offering a low price. (M. Porter)
THE KEY IS CREATING VALUE FOR THE CUSTOMER
Differentiation and Segmentation
DIFFERENTIATION: is concerned with how a firm competes within
a market.
SEGMENTATION: is concerned with where a firm competes
within a market.
Does differentiation imply segmentation?
Not necessarily, depends upon the differentiation strategy:
BROAD SCOPE DIFFERENTIATION: Appealing to what is in common
between different customers
(McDonalds hamburgers, Honda cars,
Sears)
FOCUSED DIFFERENTIATION: Appealing to what distinguishes
different customer groups (BMW, Doc
Marten footwear)
Differentiation vs. Cost Leadership as a Basis for
Sustained Competitive Advantage
Highest returns to shareholders among the Fortune 200, 1990-2000
Av. annual return (%) Av. annual return (%)
Cisco Systems 73.4 Microsoft 35.4
Oracle 65.1 Safeway 35.2
Solectron 61.7 Freddy Mac 34.8
Dell Computer 56.9 Washington Mutual 34.4
Best Buy 51.3 J.P. Morgan Chase 33.3
Applied Materials 49.8 Pfizer 32.1
Sun Microsystems 45.2 Lowes 31.6
Merrill Lynch 41.1 Enron 31.3
CitiGroup 40.8 Walgreen 30.7
Intel 38.2 Wells Fargo 30.1
Goldman Sachs 38.2 Cigna 30.0
General Dynamics 38.1 Cardinal Health 29.6
Texas Instruments 36.3 Tech Data 29.4
UnitedHealth Group 35.7 Houshold International 29.4
QUESTION: Which is the primary basis for competitive advantage
in the above companies: cost or differentiation?
Differentiation and the Product Life Cycle
New packages of hardware
and software introduced
SYSTEM
Augmentation:
repackaging of
hardware and
software
PRODUCTS
& SERVICES
Decommoditization
COMMODIT
Y
PRODUCTS
& SERVICES
Commoditization
Desystematization
: some packages
unbundled
Analyzing the Demand Side
Techniques for analyzing product attributes and
positioning:
Multidimensional Scaling
Conjoint Analysis
Hedonic Price Analysis
Differentiation in Pain Relievers:
Multidimensional Scaling of
Competing Products in the U.S.
High
Low
Low High
EFFECTIVENESS
GENTLENESS
Tylenol
Bufferin
Excedrin
Bayer
Anacin
Private
label
aspirin
Identifying Differentiation Potential:
The Demand Side
THE PRODUCT
THE
CUSTOMER
What needs
does it satisfy?
By what
criteria do
they choose?
What
motivates
them?
What are key
attributes?
Relate patterns of
customer
preferences to
product
attributes
What price
premiums do
product attributes
command?
What are
demographic,
sociological,
psychological
correlates of
customer behavior?
FORMULATE
DIFFERENTIATION
STRATEGY
Select product
positioning in
relation to product
attributes
Select target
customer group
Ensure customer /
product
compatibility
Evaluate costs
and benefits of
differentiation
SYSTEM PRODUCT
SERVICE COMMODITY
SUPPORT
(SOFTWARE)
Differentiated Undifferentiated
Differentiated
MERCHANDISE
(HARDWARE)
Undifferentiated
Differentiation of Hardware and Software
Consistency of Differentiation
Strategy: Product Integrity
Key to successful differentiation is consistency of all
aspects of the firms relationship with its customers.
Product Integrity: the total balance of product features
Internal integrity: consistency between
function and structure
External integrity:fit between the product
and the customers
objectives, values, lifestyle
etc..
Producers strategies
High quality Low quality
High 7 10
Consumers price 7 -5
strategies
Low -5 3
price 10 3
Note: In each cell, the lower left number is the payoff
to the consumer and the upper right number is
the payoff to the producer.
The problem of experience goods : quality can only be
ascertained after purchase. Hence: Prisoners Dilemma:-
Equilibrium reached with consumer paying a low price for a low quality item.
If producer can signal quality--- both consumer and producer can move to
preferred position: high quality product carrying a high price
Problem of Quality in Experience Goods:
A Prisoners Dilemma
The Impact of Quality on Profitability
Low 25% 60% High
Relative market share
R
e
l
a
t
i
v
e
p
r
o
d
u
c
t
q
u
a
l
i
t
y
L
o
w
3
3
%
6
7
%
H
i
g
h
R
e
l
a
t
i
v
e
p
r
o
d
u
c
t
q
u
a
l
i
t
y
L
o
w
3
3
%
6
7
%
H
i
g
h
R
e
l
a
t
i
v
e
p
r
o
d
u
c
t
q
u
a
l
i
t
y
L
o
w
3
3
%
6
7
%
H
i
g
h
Low 25% 60% High
Relative market share
Low 25% 60% High
Relative market share
ROI (%) Relative Price Relative Direct Cost
Conclusion: Increases in quality add more to price then they do to cost.
19 28 38 107 107 108 104 103 101
14 20 28 103 104 104 104 102 100
7 16 23 101 101 102 104 102 100
Using the Value Chain to Identify
Differentiation Potential on the Supply Side
FIRM INFRASTRUCTURE
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT
INBOUND OPERATIONS OUTBOUND MARKETING SERVICE
LOGISTICS LOGISTICS & SALES
MIS that supports
fast response
capabilities
Training to support
customer service
excellence
Unique product features.
Fast new product
development
Quality of
components &
materials
Defect free
products.
Wide variety
Fast delivery.
Efficient order
processing
Building brand
reputation
Customer technical
support. Consumer
credit. Availability of
spares
Identifying Differentiation Opportunities through
Linking the Value Chains of the Firm and its
Customers: Can Manufacture
1. Distinctive can design can assist canners marketing activities.
2. High manufacturing tolerances can avoid breakdowns in customers canning lines.
3. Frequent, reliable delivery can permit canner to adopt JIT can supply.
4. Efficient order processing system can reduce customers ordering costs.
5. Competent technical support can increase canners efficiency of plant utilization.
S
u
p
p
l
i
e
s
o
f
s
t
e
e
l
&
a
l
u
m
i
n
u
m
S
e
r
v
i
c
e
&
t
e
c
h
n
i
c
a
l
s
u
p
p
o
r
t
S
a
l
e
s
D
i
s
t
r
i
b
u
t
i
o
n
I
n
v
e
n
t
o
r
y
h
o
l
d
i
n
g
M
a
n
u
f
a
c
t
u
r
i
n
g
D
e
s
i
g
n
E
n
g
i
n
e
e
r
i
n
g
I
n
v
e
n
t
o
r
y
h
o
l
d
i
n
g
P
u
r
c
h
a
s
i
n
g
D
i
s
t
r
i
b
u
t
i
o
n
M
a
r
k
e
t
i
n
g
C
a
n
n
i
n
g
P
r
o
c
e
s
s
i
n
g
I
n
v
e
n
t
o
r
y
h
o
l
d
i
n
g
P
u
r
c
h
a
s
i
n
g
CANNER CAN MAKER
1
2
4
5
3
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Seven Essentials of Supplier Quality Management A Concise Guide: A systematic approach in managing supplier towards delivering zero-defect material consistentlyDe la EverandSeven Essentials of Supplier Quality Management A Concise Guide: A systematic approach in managing supplier towards delivering zero-defect material consistentlyEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Differentiation AdvantageDocument6 paginiDifferentiation AdvantageVisioneering ETCEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 09 SlidesDocument14 paginiChapter 09 SlidesAkanksha SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NPD Chapter Thirteen 2023Document44 paginiNPD Chapter Thirteen 2023Ola MikatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to SPCDocument20 paginiIntroduction to SPCComputer Maintainance Hardware and softwareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session - 15 To 17Document66 paginiSession - 15 To 17suvodip.senÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHP 3Document51 paginiCHP 3tanvi virmaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1Document66 paginiLecture 1Samriddhi SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competitive AdvantageDocument38 paginiCompetitive AdvantageTade FaweyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Cheat SheetDocument2 paginiMarketing Cheat SheetAbhishek Anand100% (2)
- Industrial and Competitive AnalysisDocument20 paginiIndustrial and Competitive AnalysisPranav PahwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competitive Strategies NewDocument35 paginiCompetitive Strategies NewMohammed RafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business-Level Strategy Lecture SlidesDocument57 paginiBusiness-Level Strategy Lecture SlidesBirungi TinishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Market Segmentation, Targeting, and PositioningDocument22 paginiMarket Segmentation, Targeting, and PositioningravishankerpandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- M1 Product & Product Related StrategiesDocument106 paginiM1 Product & Product Related Strategiesdhrjmjn100% (1)
- Value ChainDocument7 paginiValue ChainNadun IshankaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10-Lesson 10 - Developing and Managing Pricing Strategies and Marketing ChannelsDocument33 pagini10-Lesson 10 - Developing and Managing Pricing Strategies and Marketing ChannelssurangauorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slides Business Level StrategyDocument24 paginiSlides Business Level StrategyThảo PhạmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competition in Manufacturing StrategyDocument16 paginiCompetition in Manufacturing StrategyAAYUSH ANANDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industry Competitive Forces and AnalysisDocument35 paginiIndustry Competitive Forces and AnalysisJunaly PanagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operations and Supply Strategy FrameworkDocument32 paginiOperations and Supply Strategy FrameworkAngelinaGuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PriceDocument47 paginiPriceChaitanya KulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To MKT Week 10Document58 paginiIntro To MKT Week 10imamibrahim726Încă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Concepts Explained in 40 CharactersDocument32 paginiMarketing Concepts Explained in 40 CharactersKristina SisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pricing, Pharmaceutical MarketingDocument7 paginiPricing, Pharmaceutical MarketingShamim Ahmed Piyal 183-29-1340Încă nu există evaluări
- Pricing Meaning, Objectives, Factors & PoliciesDocument56 paginiPricing Meaning, Objectives, Factors & Policiespankajdeshwal@gmail.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Software License and Maintenance Pricing Principles - Best Practices and Case StudiesDocument35 paginiSoftware License and Maintenance Pricing Principles - Best Practices and Case StudiesChandra Ardilla PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definitions: Quality TermsDocument25 paginiDefinitions: Quality TermsPankaj KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Quality?Document19 paginiWhat Is Quality?patricia navasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Testing The Trade-Offs By: Sanjit Kumar Sahoo (Um14376)Document12 paginiTesting The Trade-Offs By: Sanjit Kumar Sahoo (Um14376)Sahoo SKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study - 2 Global Supplier SelectionDocument5 paginiCase Study - 2 Global Supplier SelectionNancy suriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost Driven Approach (Process Approach)Document19 paginiCost Driven Approach (Process Approach)Boateng SilvestaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013 CH 7 The Sources and Dimensions of Competitive AdvantageDocument18 pagini2013 CH 7 The Sources and Dimensions of Competitive AdvantageHelen MoyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- wk1 Strategy-NewDocument34 paginiwk1 Strategy-NewAnu DÎncă nu există evaluări
- A16E - BNT Group - Chapter 7 - MKT ManagementDocument50 paginiA16E - BNT Group - Chapter 7 - MKT ManagementTâm Nguyễn Ngọc ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Otal Uality AnagementDocument143 paginiOtal Uality AnagementJohn Rex PanestanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Metrics: Prof. Rashmi JainDocument51 paginiMarketing Metrics: Prof. Rashmi JainAaditya BhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Management Course OutlineDocument135 paginiQuality Management Course OutlineMisgana ShewangizawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Importance of marketing strategyDocument11 paginiImportance of marketing strategyhvactrg1Încă nu există evaluări
- LOB - Product DesignDocument50 paginiLOB - Product DesignahyaniluthfianasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Strategy: Topic 2 Industry and Competitive AnalysisDocument38 paginiBusiness Strategy: Topic 2 Industry and Competitive AnalysisKiet NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jaiib PPT Downloaded From Iibf PDFDocument42 paginiJaiib PPT Downloaded From Iibf PDFnani NaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document42 paginiChapter 1Bernard VillalobosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 06: No Name IdDocument41 paginiGroup 06: No Name IdBD Fox TubeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing: T.Bhaskar Faculty, SIMS College, PUTTURDocument42 paginiMarketing: T.Bhaskar Faculty, SIMS College, PUTTURbhaskartapalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building and Defending Competitive Advantages - Lesson 5Document6 paginiBuilding and Defending Competitive Advantages - Lesson 5api-3738338100% (1)
- Session 18 - Pricing in B2BDocument27 paginiSession 18 - Pricing in B2BRutwik PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pricing: Suman Lahiri Ximb 01 August 2019Document16 paginiPricing: Suman Lahiri Ximb 01 August 2019Sawan Kumar AcharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functions of RetailingDocument24 paginiFunctions of Retailingsurabhi01197500% (1)
- Module 3 Generic StrategiesDocument23 paginiModule 3 Generic Strategiesamit thakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 New Product DevelopmentDocument28 paginiUnit 2 New Product DevelopmentsarkctÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concepts Of: Quality ManagementDocument37 paginiBasic Concepts Of: Quality ManagementAndy ChongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 11Document28 paginiLesson 11Tirusameer YarlagaddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 5 - Product and Brand StrategyDocument30 paginiSession 5 - Product and Brand StrategyMadhav VakhariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- External and Customer Analysis InsightsDocument51 paginiExternal and Customer Analysis InsightsSatish Kumar KarnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JAIIB/DB&F-Principles & Practices of Banking - Module D-Support Services - Marketing of Banking Services - Ms - Neha GuptaDocument42 paginiJAIIB/DB&F-Principles & Practices of Banking - Module D-Support Services - Marketing of Banking Services - Ms - Neha GuptanehaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Situation AnalysisDocument22 paginiSituation AnalysisVikas NarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Ekonomi Labuhan BatuDocument10 paginiSekolah Tinggi Ilmu Ekonomi Labuhan Batuyuno eperitingÎncă nu există evaluări
- James Personal Study Guide - PDF RoomDocument88 paginiJames Personal Study Guide - PDF RoomDarryl WallaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal Study Guide - PDF RoomDocument41 paginiPersonal Study Guide - PDF RoomDarryl WallaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Complete Guide To Volume Price Analysi - A. CoullingDocument242 paginiA Complete Guide To Volume Price Analysi - A. CoullingGiundat Giun Dat97% (129)
- (Media Business and Innovation) Artur Lugmayr, Cinzia Dal Zotto (Eds.)-Media Convergence Handbook - Vol. 1_ Journalism, Broadcasting, And Social Media Aspects of Convergence-Springer-Verlag Berlin HeiDocument430 pagini(Media Business and Innovation) Artur Lugmayr, Cinzia Dal Zotto (Eds.)-Media Convergence Handbook - Vol. 1_ Journalism, Broadcasting, And Social Media Aspects of Convergence-Springer-Verlag Berlin HeiCîrstea AndreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 59.business Intelligence and Analytics PDFDocument317 pagini59.business Intelligence and Analytics PDFWilliam Archila100% (2)
- (BCPI, CLI, Warren J. Sonne) Criminal InvestigatioDocument186 pagini(BCPI, CLI, Warren J. Sonne) Criminal InvestigatioSP Samuel Crespo100% (1)
- Persodevmanual PDFDocument1 paginăPersodevmanual PDFSyedaffanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acsm Personal Trainer Exam Study GuideDocument18 paginiAcsm Personal Trainer Exam Study GuideHong Ye100% (1)
- Explore The Bible Personal Study Guide - King James Version - PDF RoomDocument20 paginiExplore The Bible Personal Study Guide - King James Version - PDF RoomDarryl WallaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trading in The Shadow of The Smart Money BookDocument192 paginiTrading in The Shadow of The Smart Money BookSalvo Nona85% (46)
- 0902 Trading The Line PDFDocument45 pagini0902 Trading The Line PDFRara Laki Laki100% (2)
- The Small Business Owner's Manual - Everything You Need To Know To Start Up and Run Your Business PDFDocument312 paginiThe Small Business Owner's Manual - Everything You Need To Know To Start Up and Run Your Business PDFkonserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coffee Can Investing - The Low Risk Road To Stupendous WealthDocument364 paginiCoffee Can Investing - The Low Risk Road To Stupendous WealthKristen Ravali100% (38)
- Investigative Journalism Manual (PDFDrive)Document121 paginiInvestigative Journalism Manual (PDFDrive)Darryl Wallace100% (2)
- TenThingsYouMustKnow KHMTRAVELDocument15 paginiTenThingsYouMustKnow KHMTRAVELDarryl WallaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cloud Computing Framework for Apparel Supply ChainsDocument12 paginiCloud Computing Framework for Apparel Supply ChainsDarryl WallaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selecting A Travel Management Company: Business Travel Buyer'S HandbookDocument6 paginiSelecting A Travel Management Company: Business Travel Buyer'S HandbookDarryl WallaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ada 596948Document214 paginiAda 596948Hajji Assamo PadilÎncă nu există evaluări
- FCM Redefining Corporate Travel Management 2019Document68 paginiFCM Redefining Corporate Travel Management 2019Darryl WallaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- DK Eyewitness Travel Guide - Barcelona & Catalonia (PDFDrive) PDFDocument210 paginiDK Eyewitness Travel Guide - Barcelona & Catalonia (PDFDrive) PDFDarryl Wallace100% (1)
- Unlocking The Guitar Fretboard - An Intervallic Approach Towards M PDFDocument169 paginiUnlocking The Guitar Fretboard - An Intervallic Approach Towards M PDFANMOL100% (2)
- Travel Agent - Outside Sales Support Netqork - Official Member HandbookDocument128 paginiTravel Agent - Outside Sales Support Netqork - Official Member HandbookDarryl Wallace100% (1)
- Erin Kennedy Executive ResumeDocument3 paginiErin Kennedy Executive ResumeDarryl WallaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Everything You Need To Know About Becoming A: Successful Inteletravel AdvisorDocument8 paginiEverything You Need To Know About Becoming A: Successful Inteletravel AdvisorDarryl WallaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lead Guitar 6 Lesson GuideDocument37 paginiLead Guitar 6 Lesson GuideCarlos FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume PrepareDocument28 paginiResume PreparekaparaveniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eden WT500, WT600, WT800 - SchematicDocument307 paginiEden WT500, WT600, WT800 - SchematicDarkbass BowieÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Did House Bands Become A Filipino Export - The New York TimesDocument11 paginiHow Did House Bands Become A Filipino Export - The New York TimesDarryl WallaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrician Guide Test PrepDocument6 paginiElectrician Guide Test PrepDarryl Wallace33% (3)
- Exam PrepDocument57 paginiExam PrepMoh Slam100% (2)
- Auditors Report PDFDocument39 paginiAuditors Report PDFMia Laurice Rubio - MarquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 Problems On VAT (PRTC) PDFDocument17 pagini1.1 Problems On VAT (PRTC) PDFmarco poloÎncă nu există evaluări
- BBA Course Curriculum UGC Approved America Bangladesh UniversityDocument3 paginiBBA Course Curriculum UGC Approved America Bangladesh UniversityKiron KamruzzamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yamaha Corporation (13035676)Document13 paginiYamaha Corporation (13035676)NguyenZumÎncă nu există evaluări
- ParcorDocument12 paginiParcoreys shop100% (1)
- ISWKi - Transport Fees Reconciliation 21062017Document20 paginiISWKi - Transport Fees Reconciliation 21062017dprosenjitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Horizon Trial: Dawn Phillips Witness StatementDocument4 paginiHorizon Trial: Dawn Phillips Witness StatementNick WallisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smart BetaDocument24 paginiSmart BetaAbhishek GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designing BrandsDocument154 paginiDesigning BrandsDora Luz Contreras100% (1)
- Timex NA-33 Flix Manual - W-09 M814 FlixDocument1 paginăTimex NA-33 Flix Manual - W-09 M814 FlixNavi SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINAL KRA of Finance HeadDocument3 paginiFINAL KRA of Finance HeadRuchita AngreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kodak's failure to understand changing photo habitsDocument13 paginiKodak's failure to understand changing photo habitsenna_sys100% (1)
- BG Group strategy update document summaryDocument63 paginiBG Group strategy update document summarygv360Încă nu există evaluări
- HULDocument15 paginiHULGaurav NavaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hindustan Zinc Limited - Tanisha 08351Document4 paginiHindustan Zinc Limited - Tanisha 08351Tanisha KalraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Real Estate Agent Email ListDocument16 paginiReal Estate Agent Email ListJince JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Cost Basis CalculatorDocument2 pagini3 - Cost Basis Calculatorsumit6singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capital Adequacy and Liquidity Risk AnalysisDocument18 paginiCapital Adequacy and Liquidity Risk AnalysisTural100% (1)
- Accounting Principles: Amity Business SchoolDocument11 paginiAccounting Principles: Amity Business SchoolSaloni AggarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case of Air BlueDocument10 paginiCase of Air Blueshah_zain89Încă nu există evaluări
- Walmart - History & Profile: Early Years (1945 - 1969)Document4 paginiWalmart - History & Profile: Early Years (1945 - 1969)vinivasu06Încă nu există evaluări
- Rainbow PUSH Coalition Press Release 3.16.14Document4 paginiRainbow PUSH Coalition Press Release 3.16.14Kendra Y. HillÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMPLETE LIST OF TEACHING MATERIALSDocument17 paginiCOMPLETE LIST OF TEACHING MATERIALSunicornmfkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labor Recruitment RulesDocument10 paginiLabor Recruitment RulesRuby ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Right of Pre-Emption ExplainedDocument19 paginiRight of Pre-Emption ExplainedRitesh KumaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amendments To Revised AFRS For SSEsDocument6 paginiAmendments To Revised AFRS For SSEsZubair Ziaullah BaigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Office Space ProposalDocument7 paginiOffice Space ProposalRishebhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organizatio Nal Structure and Design - Ford MotorsDocument15 paginiOrganizatio Nal Structure and Design - Ford MotorsmopsalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goped LTD v. Amazon - Com - Complaint PDFDocument11 paginiGoped LTD v. Amazon - Com - Complaint PDFMark JaffeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NON Stock Corporations Stock CorporationsDocument7 paginiNON Stock Corporations Stock CorporationsJay Vhee OohÎncă nu există evaluări