Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Drainage
Încărcat de
alagarhema0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
159 vizualizări25 paginidrianage
Titlu original
Drainage.ppt
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentdrianage
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
159 vizualizări25 paginiDrainage
Încărcat de
alagarhemadrianage
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 25
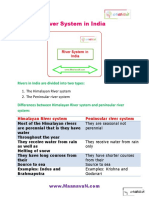
the river system of an area.
The Himalayan river system
They are Perennial. They have
water throughout the year.
They receive their water form
rain as well as melted snow for
the mountains.
The major rivers the Indus, the
Brahmaputra and Ganga.
The rivers are long and have
large volume of water.
They cover a large land area.
They perform intensive
erosional activity form
meanders, ox-bow lake, and
delta.
The Peninsular river system.
They are seasonal and their
flow is dependent on
rainfall.
Some of the rivers such as
Narmada and Tapi originate
in the Central highlands and
westward but most for
eastwards and drain into the
Bay of Bengal
They are short, and cover a
comparatively short
distance.
They are seasonal rivers as
they are drained by rains
A river along with
its tributaries is
known as river
system
The Indus flows through Baltistan and Gilgit and emerges
from the mountains at Attock .
The Indus has a length of 2900 km which makes it one of
the longest rivers
Over a third of the Indus basin is located in India in the
states of Jammu and Kashmir , Himachal Pradesh ,and
Punjab and the rest in Pakistan
THE COURSE OF THE
RIVER
It rises in Tibet east of Mansarovar lake.
It flows eastwards parallel to the Himalayas.
On reaching the Namcha Barwa it takes a U
turn and enters India in ARUNACHAL
PRADESH through a gorge. Here it called
Dihang. It is joined by the Dibang , the Lohit
,and many other tributaries to form the
Brahmaputra in Assam
In Tibet it carries a smaller volume of water
and silt as it is a cold and a dry area.
I t passed the entire of Assam and form
riverine islands
Every year during the rainy season , the river
overflows its banks , causing widespread
devastsation due to floods in Assam and
Bangladesh . Unlike other north Indian rivers
the Brahmaputra is marked by huge deposit of
silt on its bed causing the river bed to rise . The
river also shifts its channel frequently
The Course Of The
River Ganga
The headwaters of the Ganga,
called the Bhagirathi is fed by the
Gangotri Glacier and joined the
Alaknanda at Devpryag in
uttarkhand.
At Haridwar the Ganga emerges
from the mountains on the the
plains.
The Ganga is joined by many
tributaries from Himalayas a few
of them being major rivers such as
the Yamuna, the Ghaghara the
Gandak and Kosi
The river Yamuna rises
from the Yamunotri
Glacier in the Himalayas
. It flows parallel to the
Ganga and as a right
bank tributary meets
ganga at Allahabad .
The Ghagra, the Gandak
, and the Kosi rise in the
Nepal Himalaya .The
main tributaries from
the peninsular uplands
are the chambal,the
betwa and the son .
These rise from semi
arid areas, have short
courses and do not carry
much water in them
The ganga flows eastwards
till Farakka in west bengal .
This is the northern most
point of the ganga delta . The
length of ganga is over
2500km , Ambala is located
on the water divide between
the Indus and the ganga river
systems .
The plains from Ambala to
the Sunderban stretch over
nearly 1800km
The Narmada rises in the
Amarkantak hill in
Madhya Pradesh.It flows
towards west in a rift
valley formed due to
faulting .
The Marble rocks near
Jabalpur; the river flows
through a deep gorge.
The Dhuadhar falls are
great attractions in the
Narmada Basin
The narmada basin covers
parts of madhya pradesh
and gujarat
It is known as the Dakshin ganga because of its
length and the area it covers.
It is the largest PENINSULAR river.
It rises in the slopes of the Western Ghats in the
Nasik district and drains into the Bay of Bengal.
It drainage basin covers parts of Maharashtra
Madhya Pradesh, Orissa and Andhra Pradesh.
It tributaries are Purna, the Waedha, pranhita, the
Manjra, the Waiganga and Penganga
Its length is about 1500km
It drains into the Bay of Bengal . Its drainage basin
is also the largest among the peninsular rivers .
It rises near
Mahabeleshwar and
flows for about 1400 km
and reaches the Bay of
Bengal.
The Drainge basin is
shared by Maharashtra,
Karnataka and Andhra
Pradesh.
The tungabhadra , the
koyana ,the ghatprabha
, the musi, tribut and
the bhima are some of
its tributaries
The Tapi rises in the Satpura
ranges in the Betul districts of
Madhya Pradesh.
It flows in a rift valley parallel
to river Narmada.
Basin covers parts of madhya
pradesh ,gujarat, and
maharashtra.
The main west flowing rivers
are sabarmati, mahi,
bharatpuzha and periyar.
The Mahanadi rises in
the highlands of
Chattisgarh. It flows
through Orissa to reach
the bay of Bengal. the
length of the river is 860
km . Its drainage basin is
shared by Maharashtra,
Chattisgarh, Jharkhand
and Orissa
The Kaveri rises in the
Brahmagiri range of the
western ghats and it reaches
the Bay of Bengal in south
of Cuddalore , in Tamil
nadu . Total length of the
river is 760 km .Its main
Tributaries are Amravati,
Bhavani, Hemavati, and
Kabini . Its basin drains
parts of karnataka, kearla
and tamil nadu
Frsh water
lakes
Salt water
lakes
Manmade
lakes
Types of lakes
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Gore Mountain Range MapDocument3 paginiGore Mountain Range MapMichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 SocSc DrainageDocument6 pagini9 SocSc DrainageAjay AnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rivers of India PDFDocument6 paginiRivers of India PDFAbhishek VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drainage: Peninsular Rivers. The Himalayan RiversDocument4 paginiDrainage: Peninsular Rivers. The Himalayan RiverssimsamsmartÎncă nu există evaluări
- Here, It Is Called The Dihang and It Is Joined by The Dibang, The Lohit, and Many Other. Tributaries To Form The Brahmaputra in AssamDocument2 paginiHere, It Is Called The Dihang and It Is Joined by The Dibang, The Lohit, and Many Other. Tributaries To Form The Brahmaputra in AssamMohamed Ishak DeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rivers of IndiaDocument15 paginiRivers of IndiaABHIDEV J KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 9Document4 paginiGrade 9lovika malhotraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maxfort School, Dwarka: Recognised Senior Secondary School Affiliated To CBSEDocument18 paginiMaxfort School, Dwarka: Recognised Senior Secondary School Affiliated To CBSELasya ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- GangesDocument2 paginiGangesKaushal SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2607 Topper 21 101 1 23 7334 Drainage Up201807191143 1531980807 6187Document6 pagini2607 Topper 21 101 1 23 7334 Drainage Up201807191143 1531980807 6187Deepa MundadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drainage Class 9 Chapter 3Document8 paginiDrainage Class 9 Chapter 3abhishekkrbxroutlookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drainage - RiversDocument8 paginiDrainage - Riversgreen falafelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drainage System in IndiaDocument4 paginiDrainage System in IndiaJosya CLS2RÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRAINAGE CLASS 9TH GeographyDocument21 paginiDRAINAGE CLASS 9TH GeographyShipra agrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRAINAGEDocument60 paginiDRAINAGEsy96024902Încă nu există evaluări
- Drainage: India: Delhi Public School Ruby Park, Kolkata Class Ix SESSION 2022-23 Geography: Study MaterialDocument5 paginiDrainage: India: Delhi Public School Ruby Park, Kolkata Class Ix SESSION 2022-23 Geography: Study MaterialOishi GoswamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drainage Part - 2: ContentDocument12 paginiDrainage Part - 2: ContentNihalÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRAINAGEDocument4 paginiDRAINAGERitvik GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- DrainageDocument34 paginiDrainageAthar ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combined Geo NoteDocument34 paginiCombined Geo NotealienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drainage NotesDocument6 paginiDrainage NotesAdithya VinodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ganga River SystemDocument3 paginiGanga River SystemMayank BhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian River SystemDocument3 paginiIndian River SystemAshish PratapÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPT - RiversOfIndiaPart2PPTDocument64 paginiPPT - RiversOfIndiaPart2PPTAshish Dwivedi AshishÎncă nu există evaluări
- World Major Rivers, Mountains, Passes, Lakes, Seas, Bays, StraitsDocument31 paginiWorld Major Rivers, Mountains, Passes, Lakes, Seas, Bays, Straitssainihimani27augÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Major Indian River Systems Geography Notes For UPSCDocument4 paginiList of Major Indian River Systems Geography Notes For UPSCHarsha HarshuÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRAINAGEDocument26 paginiDRAINAGESarvagya ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SeasonsDocument17 paginiSeasonsVirag ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name:-Ishwin Gupta ROLL NO: - 07 CLASS:-09Document16 paginiName:-Ishwin Gupta ROLL NO: - 07 CLASS:-09JsmBhanotÎncă nu există evaluări
- The River Systems of India Can Be Classified Into Four GroupsDocument14 paginiThe River Systems of India Can Be Classified Into Four Groupsem297Încă nu există evaluări
- A Brief Summary of IndiaDocument91 paginiA Brief Summary of IndiaumeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Drainage System - 3480724Document10 paginiIndian Drainage System - 3480724PO, ITDA BhadrachalamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rivers of India Part 2 CRUXDocument18 paginiRivers of India Part 2 CRUXaditya.kml.007Încă nu există evaluări
- Rivers of IndiaDocument15 paginiRivers of IndiavishasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian River SystemDocument14 paginiIndian River Systemroja sapavatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alfi AzizDocument19 paginiAlfi Azizsafamanz001 safaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geography Chapter 3 DrainageDocument22 paginiGeography Chapter 3 Drainage41 Shaivya ManaktalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drainage-Chapter - 3-GeographyDocument6 paginiDrainage-Chapter - 3-GeographyAryaman ParidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rivers Notes 15Document7 paginiRivers Notes 15pankaj.mishra.20995Încă nu există evaluări
- Ganga River SystemDocument17 paginiGanga River Systemjerilynmary jÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geography 42Document20 paginiGeography 42pramaniknitai99Încă nu există evaluări
- Drainage System of IndiaDocument12 paginiDrainage System of IndiaNagesh Kshirsagar NKÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 GeographyDocument14 pagini11 Geographygolichamolu6Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 3 Geography Class 9thDocument10 paginiChapter - 3 Geography Class 9thDevendra Singh100% (1)
- Rivers in IndiaDocument10 paginiRivers in IndiasatishsankhlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aboutthe River GangaDocument3 paginiAboutthe River Gangarushikesh panditÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geo Hy NotesDocument8 paginiGeo Hy NotesRidhima KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Notes Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 - DrainageDocument4 paginiCBSE Notes Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 - DrainageHarish Lunge100% (1)
- Class 9 Geography Gist of The Lesson Taught: Chapter 3 DrainageDocument7 paginiClass 9 Geography Gist of The Lesson Taught: Chapter 3 DrainageMadhusudan BanerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course: Bhagirathi River GangotriDocument3 paginiCourse: Bhagirathi River GangotriBlessen ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian River SystemDocument34 paginiIndian River Systemboranihar34Încă nu există evaluări
- Ganga River System Upsc Notes 81Document4 paginiGanga River System Upsc Notes 81Ganesh BishtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drainage System of IndiaDocument16 paginiDrainage System of IndiaAju 99Gaming100% (1)
- Stratigraphy of IndiaDocument48 paginiStratigraphy of Indiavenkatakrishna chalapaathi100% (12)
- CH - 3 DrainageDocument3 paginiCH - 3 DrainageVeena VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GEOGRAPHYDocument59 paginiGEOGRAPHYKumar Debabrata Patra100% (1)
- River System in IndiaDocument6 paginiRiver System in IndiashivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drainage Patterns and Drainage Systems of IndiaDocument6 paginiDrainage Patterns and Drainage Systems of Indiaharshm4018Încă nu există evaluări
- Drainage NotesDocument3 paginiDrainage NotesKhushi DalalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harvesting RainwaterDocument17 paginiHarvesting RainwateralagarhemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HelloDocument1 paginăHelloalagarhemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cloud ComputingDocument14 paginiCloud ComputingalagarhemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harvesting RainwaterDocument17 paginiHarvesting RainwateralagarhemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HelloDocument1 paginăHelloalagarhemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HelloDocument1 paginăHelloalagarhemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HelloDocument1 paginăHelloalagarhemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WRD Cswo Sesc Manual Unit1 - 556402 - 7Document18 paginiWRD Cswo Sesc Manual Unit1 - 556402 - 7Sean CrossÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Geoteknik (Perancangan Keairan) (Recovered)Document14 paginiData Geoteknik (Perancangan Keairan) (Recovered)Wingky PratamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes - USST 7 Geography of South AsiaDocument2 paginiNotes - USST 7 Geography of South AsiaAyesha Syed0% (1)
- Schumm 1979Document32 paginiSchumm 1979Jacob LuttrellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Natural ResourcesDocument58 paginiTypes of Natural ResourcesPrakriti Sahitya Manch100% (1)
- Cornwall Coastal Management Issue CompletedDocument9 paginiCornwall Coastal Management Issue CompletedHeart BukkabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kosi Bridge ReportDocument19 paginiKosi Bridge ReportManojPatneÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABE 424 - LWCE - Module3 - Lessons3-5 - 2023Document31 paginiABE 424 - LWCE - Module3 - Lessons3-5 - 2023Daniel Nicole HenobiagonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthen Channel DesignDocument84 paginiEarthen Channel DesignAbrar AfzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drilled Shaft 2Document126 paginiDrilled Shaft 2andradeinsuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sequence Stratigraphy of Coastal Alluvial Plain Westphalian B Coal Measures in Northumberland and The Southern North SeaDocument30 paginiSequence Stratigraphy of Coastal Alluvial Plain Westphalian B Coal Measures in Northumberland and The Southern North SeaJohann WolfÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015.31463.gazetteer of The Hazara District 1907 TextDocument458 pagini2015.31463.gazetteer of The Hazara District 1907 TextMustar OulakhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrology ReportDocument60 paginiHydrology ReportpanikarickyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soils of India - Map PracticeDocument42 paginiSoils of India - Map PracticeAbhaygyan SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal - FERALDO SANDRIO - 17080024 - D3 2017Document14 paginiJurnal - FERALDO SANDRIO - 17080024 - D3 2017FeraldoSandrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rehabilation TSL CanalDocument9 paginiRehabilation TSL CanalJahanzebÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Chocolate HillsDocument1 paginăWhat Is Chocolate HillsEla AmarilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iloilo Geohazard Report 372012 1Document162 paginiIloilo Geohazard Report 372012 1rolandoriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Country Codes ListDocument5 paginiCountry Codes ListDartfrog ImiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stability of Natural Deposits During Earthquakes: La Stabilitydesdepots Naturelslorsdestremblements DeterreDocument56 paginiStability of Natural Deposits During Earthquakes: La Stabilitydesdepots Naturelslorsdestremblements Deterrejoake spasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scour Protection at Bridge PiersDocument10 paginiScour Protection at Bridge PiersAlexDeLacRuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of Hydrology: Research PapersDocument11 paginiJournal of Hydrology: Research PapersMichael Elvis QuispeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gams - Notion and Forms of Contact KarstDocument14 paginiGams - Notion and Forms of Contact KarstCaegeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Features of IndiaDocument2 paginiPhysical Features of IndiaHANSIKA REDDYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 7 Sub Social Science Geography Chapter Life in The DesertDocument4 paginiClass 7 Sub Social Science Geography Chapter Life in The DesertSonu VishwakarmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geology and GeomorphologyDocument9 paginiGeology and GeomorphologyPawan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ang Tangway o Peninsula Ay Isang Makitid at Mahabang Anyong Lupa Na Nakaungos Sa Dagat o Iba Pang Bahaging TubigDocument1 paginăAng Tangway o Peninsula Ay Isang Makitid at Mahabang Anyong Lupa Na Nakaungos Sa Dagat o Iba Pang Bahaging Tubigpidot101100% (4)
- Fess 206Document8 paginiFess 206Vinayak ThaparÎncă nu există evaluări
- BplanschsyllDocument34 paginiBplanschsyllJdohndlfjbdÎncă nu există evaluări