Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Sense Organs - Gustatory - Untad 2012
Încărcat de
donordarah93Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Sense Organs - Gustatory - Untad 2012
Încărcat de
donordarah93Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
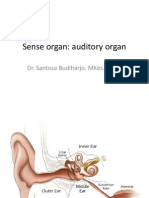
Sense organ: gustatory organ
(clinical oriented)
dr. Santosa Budiharjo, MKes., PA(K)
Lingua
Lingua berpangkal pada
dasar mulut bagian
occipital
Terdiri otot, dilapisi
tunica mucosa
Dibedakan: apex,
dorsum, radix
Sulcus terminalis,
foramen cecum, 1/3
posterior, 2/3 anterior
Mukosa: papilla
lingualis: circumvalata,
fungiformis, foliata,
filliformis, lenticularis
Otot extrinsik
(longitudinal sup-or &
inf-or, transversus,
verticalis)& ekstrinsik
(palatoglossus,
hyoglossus,
styloglossus,
genioglossus, innervasi:
n. hypoglossus, kecuali
m. palatoglossus))
Papilla linguales
Papillae foliate berbentuk lembaran daun terdapat
di bagian posterior mendekati margo lingualis.
Papillae Conicae atau papillae filiformis berbentuk
conus bila lebih besar dan
Papilla filiform : papilla kecil, menyerupai jari
dijumpai pada dataran anterior dorsum linguae.
Papilla fungiformes berbentuk cendawan terdapat
pada apex dan sisi lateral lingua.
Papilla lenticularis terdapat di dorsal sulcus
terminalis.
Distribution and Innervation of Taste Buds Taste buds are located on different types of taste
papillae found on the tongue, palate, pharynx, and larynx.
Types of taste papillae include fungiform and foliate papillae on the anterior and lateral
aspects of the tongue and circumvallate papillae on the base of the tongue
The latter may contain several hundred taste buds.
The tongue in humans may have several thousand taste buds.
The sensitivity of different regions of the tongue for different taste qualities varies only
slightly because taste buds responding to each type of flavor are widely distributed.
The taste buds are innervated by three cranial nerves.
The chorda tympani branch of the facial nerve (CN VII) supplies taste buds on the anterior
two thirds of the tongue, and the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) supplies taste buds on the
posterior third of the tongue . The vagus nerve (CN X) supplies a few taste buds in the larynx
and upper esophagus.
n. facialis
Paralysis of the facial nerve causes face drop.
This is more marked with a lower motor neurone
(LMN) lesion than an upper motor neurone (UMN)
lesion.
The best way to differentiate between the two is to
test the muscles of the forehead.
They have bilateral innervation at the upper motor
neurone level and so, in a UMN lesion such as a
pseudobulbar palsy, they are spared.
An LMN lesion such as Bell's palsy will involve the
forehead.
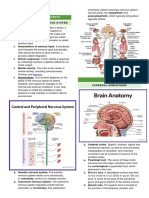
Homunculus sensoric
Innervasi motorik
photos of Hypoglossal Nerve Palsy affecting the left side of the
tongue
finer control is demonstrated by
the ability to say "la" and "ta"
tongue movements to command -
from side to side etc the side of
the tongue
that is palsied deviates towards
the side of the lesion
n.hypoglossus
The Hypoglossal Nerve supplies
motor fibres to all of the muscles of
the tongue (ie
there is no sensory function) except
the Palatoglossus muscle, which is
innervated
by the Vagus Nerve (Cranial Nerve 10
/ CN X) or according to some
classifications, by fibres from the
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (Cranial
Nerve 9 / CN
IX) that "hitchhike" within the Vagus.
Weakness of the tongue manifests
itself as a slurring of speech & by
wasting of
the side of the tongue which has the
palsy.
The patient complains that their
tongue feels "thick", "heavy" or
"clumsy. Lingual
sounds (i.e., l's, t's, d's, n's, r's etc) are
slurred and this is obvious in
conversation
even before direct examination.
UMN vs LMN
If the tongue deviates to
one side when protruded,
this suggests a hypoglossal
nerve lesion.
If it is an LMN lesion, the
protruded tongue will
deviate towards the side of
the lesion.
With an upper motor
neurone (UMN) lesion, the
tongue will deviate away
from the side of the lesion.
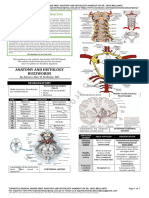
Tractus corticobulbar
menyilang di linea
mediana
Nukleus N. XII khusus
m. genioglossus
mendapat dari UMN
kontralateral
(hemisferium lain
pihak), dan n XII kiri
menginervasi otot kiri
(ipsilateral)
Dysgeusia is the medical term for an altered,
distorted or reduced ability to taste.
Egeusia = can not able to taste
Specific types of taste disorders include
hypogeusia
Glositis: geographic, migratory, median rhomboid,
labiopalatognathoschiziz
sialolithiasis
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Neurological AssessmentDocument13 paginiNeurological AssessmentLorenz Jude CańeteÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- ENT Hodder Arnold PDFDocument176 paginiENT Hodder Arnold PDFAkbar LimpoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Neurology ModuleDocument46 pagini6 Neurology ModuleCoffee MorningsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 5Document8 paginiExercise 5KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bells PalsyDocument33 paginiBells PalsyBea AbordoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autonomic Nervous System PharmacologyDocument7 paginiAutonomic Nervous System Pharmacologydonordarah93Încă nu există evaluări
- AllDocument54 paginiAlladham bani younesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ll6mn Temporal Bone CT and MRI Anatomy A Guide To 3D Volumetric AcquisitionsDocument220 paginiLl6mn Temporal Bone CT and MRI Anatomy A Guide To 3D Volumetric AcquisitionsPJ Sandhu100% (1)
- Cummings 6th Ed TitlesDocument8 paginiCummings 6th Ed TitlesBurhan QureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sense Organ - Auditory - Untad 2012Document53 paginiSense Organ - Auditory - Untad 2012donordarah93Încă nu există evaluări
- Current Concepts in The Management of Helicobacter PyloriDocument11 paginiCurrent Concepts in The Management of Helicobacter Pyloridonordarah93Încă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Trial Healing of NSAIDDocument11 paginiClinical Trial Healing of NSAIDdonordarah93Încă nu există evaluări
- Evolve Resources For Illustrated Anatomy of The Head and Neck 5th Edition Fehrenbach Test BankDocument17 paginiEvolve Resources For Illustrated Anatomy of The Head and Neck 5th Edition Fehrenbach Test Bankjoshuabowmanymctpnejsw100% (29)
- 1 - Cranial Nerve 5, 6,7Document44 pagini1 - Cranial Nerve 5, 6,7ewijayapalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Otolaryngology Board ReviewDocument417 paginiOtolaryngology Board Reviewmohamed shamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cranial NervesDocument7 paginiCranial NerveshamnahrjunaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnatomyDocument286 paginiAnatomyAbbyramy NÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Petrous FaceDocument15 paginiAnatomy of Petrous FaceKelompok F8 CoasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of Facial NerveDocument11 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of Facial NerveMohammed RahmathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thefacialandintermediusnerves PDFDocument23 paginiThefacialandintermediusnerves PDFzed-medÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved Passed Paper FCPS Part-2 DaleepDocument20 paginiSolved Passed Paper FCPS Part-2 DaleepUmair AwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Facial PalsyDocument37 paginiFacial PalsyamshaydeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cranial Nerve ExamDocument19 paginiCranial Nerve ExamVivian MaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 28 Temporal Bone (Done)Document7 pagini28 Temporal Bone (Done)Ayah HyasatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Anatomy Ang Histology Buzzwords Oct 2023 Jamaiyah H. Serad - Hadji OsopDocument7 pagini2 - Anatomy Ang Histology Buzzwords Oct 2023 Jamaiyah H. Serad - Hadji OsopmikzhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oropharynx PPT VigneshDocument39 paginiOropharynx PPT VigneshsakthimuruganaravindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy PDFDocument13 paginiTrigeminal Nerve Anatomy PDFvinaykishore0% (1)
- Anatomy - Head and NeckDocument18 paginiAnatomy - Head and NeckPrudhvirani ChidipothuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurologic Examination: Cranial NervesDocument68 paginiNeurologic Examination: Cranial Nerves2013SecBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organon Visuum: Tri Indah Winarni, MD, PHD Anatomy Dept. Faculty of Medicine Diponegoro UniversityDocument46 paginiOrganon Visuum: Tri Indah Winarni, MD, PHD Anatomy Dept. Faculty of Medicine Diponegoro UniversityLailatuz ZakiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 9 Cra NervesDocument3 paginiLec 9 Cra NervesDewi Wahyuni SupangatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duplication of The External Auditory Canal Two CasDocument5 paginiDuplication of The External Auditory Canal Two CasIvana SupitÎncă nu există evaluări
- FAQs 3Document198 paginiFAQs 3Rajan GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgery For The Dry Eye Scientific PDFDocument343 paginiSurgery For The Dry Eye Scientific PDFbudi100% (1)