Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
BT1 - Siteworks
Încărcat de
Melannie ArgenteraDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
BT1 - Siteworks
Încărcat de
Melannie ArgenteraDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Part 1
Material of Construction
1.1 Acronyms:
AASHTO American Association of State Highway and
Transportation Officials
ANSI American National Standards Institute
ASTM American Society of Testing Materials
DPWH Department of Public Works and Highways
USCS Unified Soil Classification System
A. Siteworks
A. 1. Earthworks
1.2 Standard Tests
AASHTO Classifies inorganic soils for suitability as sub
grade materials in terms of good drainage and bearing
capacity
A. Siteworks
A. 1. Earthworks
Defines particle sizes as:
a. Boulders above 75mm
b. Gravel 75mm to No. 10 Sieve
c. Coarse Sand No. 10 to No. 40 Sieve
d. Fine Sand No. 40 to No. 200 Sieve
e. Silt Clay Particles passing no. 200 Sieve
1.2 Standard Tests
ATTERBERG LIMITS tests performed on soils passing the no. 40
sieve (Fine Sand)
a. Liquid Limit (LL) moisture content at which a soil changes
from liquid state to the plastic state.
b. Plastic Limit (PL) the water content at which a silt clay
material will just begin to crumble when rolled into a tread.
c. Plasticity Index (PI) defined as the liquid limit minus the
plastic limit .
A. Siteworks
A. 1. Earthworks
1.3 Fill Materials
a. Fill Materials
- Soil, crushed stone, and sand used to raise and
existing grade, or as a man-made deposit, generally
used under spread footings, pavers, or concrete slabs
on grade.
A. Siteworks
A. 1. Earthworks
1.3 Fill Materials
b. Granular Fill or Filters
A. Siteworks
A. 1. Earthworks
1.3 Fill Materials
c. Borrow Fill
A. Siteworks
A. 1. Earthworks
Soil materials
suitable as fill
or subgrade.
1.3 Fill Materials
d. Base Course Materials
A. Siteworks
A. 1. Earthworks
Eskumbro - Earthfill
Tagalog time:
1.4 Riprap (Rock Lining)
A. Siteworks
A. 1. Earthworks
A constructed
layer or facing a
stone, placed to
prevent erosion,
scourging or
sloughing of a
structure or
embankment.
1.5 Gabion Systems
A. Siteworks
A. 1. Earthworks
Wire-enclosed
riprap consisting
of mats or baskets
fabricated from
the wire mesh,
filled with small
riprap and
anchored to a
slope.
1.6 Geosynthetic
A. Siteworks
A. 1. Earthworks
Construction materials consisting of synthetic components
made for use with or within earth materials.
Earth materials plus synthetics
Geotextiles
Geomembranes
Geocomposites
Geo-membrane
A. Siteworks
A. 1. Earthworks
Are for silt fence
applications. They
serve the purpose of
filtering runoff, the
mechanism by which
they function is
different than
subsurface drainage
or erosion control
application.
Geo-composites
A. Siteworks
A. 1. Earthworks
Usually sheet or
edge drains
consisting of a
prefabricated core
to which a
geotextile is
bonded.
Two types:
1. Physical barriers
2. Chemical Barrier
A. Siteworks
A. 2. Termite Proofing
3.1 Subgrade and Base Course Materials
A. Siteworks
A. 3. Roads and Parking
3.2 Surface Paving Materials
a. Hot Mix Asphalt or Asphaltic
Concrete
- a dark brown to black
cementite's material, solid or
semi-solid, composed of bitumen
which occur in nature but are
obtained artificially in petroleum
and which when mixed with
graded aggregates is used as
paving material by placing,
shaping and compacting while
hot over a prepared base.
A. Siteworks
A. 3. Roads and Parking
3.2 Surface Paving Materials
b. Cold Mix Asphalt or
Asphaltic Concrete
- prepared with
relatively light and slow
curing asphalt, placed over a
surface without heat, hardens
to a state that is less firm and
durable than hot mix.
A. Siteworks
A. 3. Roads and Parking
3.2 Surface Paving Materials
c. Asphalt Macadam
- formed by grading
and compacting layers of
crushed stone or gravel, then
binding the top layer with
asphalt to stabilize the stone
provided a smoother surface
and seal against water
penetration.
A. Siteworks
A. 3. Roads and Parking
3.2 Surface Paving Materials
d. Asphalt Overlay
- when one or more
courses or layers of asphalt
levelling course made of an
asphalt and aggregate
mixture of variable thickness
to correct the contour of
existing surface, are placed
on existing pavement.
A. Siteworks
A. 3. Roads and Parking
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Understanding the Building Construction Process: Simply ExplainedDe la EverandUnderstanding the Building Construction Process: Simply ExplainedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sitework: Building Technology 1: Div 02Document48 paginiSitework: Building Technology 1: Div 02arki_37826160Încă nu există evaluări
- Building Science Notes 2021 2022Document23 paginiBuilding Science Notes 2021 2022Aminu QaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building TechnologyDocument3 paginiBuilding TechnologyClaro III TabuzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building ScienceDocument25 paginiBuilding ScienceHuiyiChangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Tech 1 (Div 03 Concrete) ReviewerDocument4 paginiBuilding Tech 1 (Div 03 Concrete) ReviewerKristin Josette RempilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Site Planning ProcessDocument53 paginiSite Planning ProcessKenet EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Layers of A Floor - Anatomy, and Parts (Illustrated)Document8 paginiLayers of A Floor - Anatomy, and Parts (Illustrated)Melaine A. FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Building DrawingsDocument42 paginiChapter 2 - Building DrawingsSölömön KinfeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESTIMATE SWIMMING POOL (Version 1zDocument7 paginiESTIMATE SWIMMING POOL (Version 1zcoffee addict 73Încă nu există evaluări
- History Materials Building ConstructionDocument530 paginiHistory Materials Building ConstructionMarvin Siron100% (1)
- Proprac ReportDocument201 paginiProprac ReportJames Jr BalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 Masonry ConstructionMethodsDocument78 pagini14 Masonry ConstructionMethodsMaverick LastimosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 37 Sustainable Construction and Building MaterialsDocument9 pagini37 Sustainable Construction and Building Materials薇神Încă nu există evaluări
- Aluminium Doors - Doors - GharExpertDocument3 paginiAluminium Doors - Doors - GharExpertdishkuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation Systems.Document9 paginiFoundation Systems.PRECIOUS AMY TITIWAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete ConstructionDocument155 paginiConcrete ConstructionBaoNguyen100% (1)
- Construction Supervisors GuideDocument85 paginiConstruction Supervisors GuideJBMRMMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine LEA Syllabus for ArchitectsDocument8 paginiPhilippine LEA Syllabus for ArchitectsMaryknoll DauzÎncă nu există evaluări
- StaircaseDocument28 paginiStaircasepemo ezungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finishing MaterialsDocument60 paginiFinishing Materialsmalatek yowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Saver Standards For Architectural Design Data - 860Document1 paginăTime Saver Standards For Architectural Design Data - 860Ajir Still HereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sustainable Construction SolutionsDocument71 paginiSustainable Construction SolutionsArunashish MazumdarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developing Architectural Services for Young FamiliesDocument8 paginiDeveloping Architectural Services for Young FamiliesJay Jay Pasiliao0% (1)
- SSPDocument53 paginiSSPAlbert NamoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Flooring Materials GuideDocument66 paginiTypes of Flooring Materials GuideDesalegn EndebuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory of Structures - Floor SystemsDocument31 paginiTheory of Structures - Floor SystemsLawrence Babatunde OgunsanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greeen MaterialsDocument5 paginiGreeen MaterialsRohit kumsrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimationpart 1Document42 paginiEstimationpart 1Çhårū KêshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Design + Construction 9 (2017) PDFDocument84 paginiBuilding Design + Construction 9 (2017) PDFMauricio MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Minimizing Materials Wastage in ConstructionDocument22 paginiMinimizing Materials Wastage in Constructionneeraj8162Încă nu există evaluări
- Wall FinishDocument12 paginiWall FinishAidi Amar0% (1)
- Estimation and CostingDocument22 paginiEstimation and CostingAvinash KowtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architecture SymbolDocument2 paginiArchitecture SymbolMin Costillas ZamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Staircase Design and Load DistributionDocument9 paginiStaircase Design and Load DistributionRuzengulalebih ZEta's-ListikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plastics and Their Use in ConstructionDocument46 paginiPlastics and Their Use in ConstructionEzhil ThalapathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wall FinishesDocument75 paginiWall FinishesBriliana Nur AzizahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Grilling Materials: Submitted by - DigangganaDocument18 paginiTypes of Grilling Materials: Submitted by - DigangganaDiganggana BharadwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthquake Resistant Construction DetailingDocument33 paginiEarthquake Resistant Construction DetailingsamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Technology and Materials I PDFDocument4 paginiBuilding Technology and Materials I PDFShubhankar JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCOPE of Works For A Building ConstructionDocument5 paginiSCOPE of Works For A Building ConstructionlemersonlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Floor Finishes Types and MaterialsDocument25 paginiFloor Finishes Types and MaterialsLalit NagleÎncă nu există evaluări
- AISC Engineering Journal Classic Papers on Concrete Floor PondingDocument4 paginiAISC Engineering Journal Classic Papers on Concrete Floor PondingKrish DoodnauthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alternative Building MaterialsDocument18 paginiAlternative Building MaterialsShiela Louisianne AbañoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Building Material: Topic: PlasticDocument19 paginiAdvanced Building Material: Topic: PlasticSneha SahniÎncă nu există evaluări
- On WALL FINISHES Usually Used in India.... As Class SeminarDocument30 paginiOn WALL FINISHES Usually Used in India.... As Class SeminarNida Qadir89% (18)
- Roof CoveringDocument26 paginiRoof CoveringNaresh SankuruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architectural AbbreviationsDocument15 paginiArchitectural AbbreviationsMohamed AjeemusshaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wall FinishesDocument21 paginiWall FinisheslavekushÎncă nu există evaluări
- CX Aggregates Brochure FINAL LowRes PDFDocument4 paginiCX Aggregates Brochure FINAL LowRes PDFRafael Obusan100% (1)
- Building Technology 5: (Assignment No. 5)Document4 paginiBuilding Technology 5: (Assignment No. 5)Daryl AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction Materials Properties and ApplicationsDocument9 paginiConstruction Materials Properties and ApplicationsEverson Murungweni0% (1)
- Finishes To ConcreteDocument19 paginiFinishes To Concretenikhita0412Încă nu există evaluări
- Division 4 MasonryDocument39 paginiDivision 4 MasonryLynette CabantingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction SpecsDocument17 paginiConstruction SpecsBryan Sacramento De LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Technology Reviewer Concrete Summarized PDF FreeDocument5 paginiBuilding Technology Reviewer Concrete Summarized PDF FreeMc Ronniel CortezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disadvantages of WPC BoardDocument32 paginiDisadvantages of WPC BoardvidhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BT1 - SiteworksDocument21 paginiBT1 - SiteworksEdrian Dups DupraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refresher Notes 2011Document70 paginiRefresher Notes 2011M KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Tech. Module 2. Site Constructiion, ConcreteDocument10 paginiBuilding Tech. Module 2. Site Constructiion, ConcretePrincessdy CocadizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waste WaterDocument24 paginiWaste WaterMelannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- DENR Recognized Environmental Laboratorie1asofDec2012Document11 paginiDENR Recognized Environmental Laboratorie1asofDec2012Melannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sources of Water On Concrete StrengthDocument5 paginiSources of Water On Concrete StrengthAmadu FarrowÎncă nu există evaluări
- DENR Recognized Environmental Laboratorie1asofDec2012Document11 paginiDENR Recognized Environmental Laboratorie1asofDec2012Melannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm c150 2007Document10 paginiAstm c150 2007Gabriela RockaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Saline Water on Concrete Compressive StrengthDocument3 paginiEffect of Saline Water on Concrete Compressive StrengthMelannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document8 paginiChapter 1Melannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- HydrologyDocument38 paginiHydrologyMelannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulics EngineeringDocument35 paginiHydraulics EngineeringsagarsagarjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Steel BeamsDocument25 paginiDesign of Steel Beamsronaldnyirenda2230Încă nu există evaluări
- RCC 06Document29 paginiRCC 06Engr SwapanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Road Design Standards Criteria for Urban, Rural & ExpresswayDocument4 paginiRoad Design Standards Criteria for Urban, Rural & ExpresswayMelannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application LetterDocument2 paginiApplication LetterMelannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE370 LabManual 2010Document37 paginiCE370 LabManual 2010parichay03Încă nu există evaluări
- Green BuildingDocument72 paginiGreen BuildingMelannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pascal's LawDocument1 paginăPascal's LawMelannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- How to Obtain Tax Exemption for Educational Imports in 7 DaysDocument2 paginiHow to Obtain Tax Exemption for Educational Imports in 7 DaysMelannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer Quiz 3 - POLICIESDocument2 paginiReviewer Quiz 3 - POLICIESMelannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Injury and Accident RecordsDocument44 paginiInjury and Accident RecordsMelannie Argentera100% (1)
- Report of Death (EC Form BPN-105)Document1 paginăReport of Death (EC Form BPN-105)Melannie Argentera57% (7)
- Experiment 2.5Document5 paginiExperiment 2.5Melannie ArgenteraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master of Professional EngineeringDocument1 paginăMaster of Professional EngineeringEduardo Jose Tovar CamachoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choice Code: 627819110 Course Name: Civil Engineering (First Shift) Total Seats: 30 (CAP Seats: 30)Document12 paginiChoice Code: 627819110 Course Name: Civil Engineering (First Shift) Total Seats: 30 (CAP Seats: 30)Saurabh DeshmukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amie Lab ProjectguideDocument8 paginiAmie Lab ProjectguidekskumargieÎncă nu există evaluări
- APFC Relays Catalogue 2 1Document12 paginiAPFC Relays Catalogue 2 1Maulik PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- General KnowledgeDocument36 paginiGeneral Knowledgeamitkap00rÎncă nu există evaluări
- Space RoboticsDocument9 paginiSpace RoboticsRushikesh WareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Projected cash flow and accomplishments for construction contractDocument6 paginiProjected cash flow and accomplishments for construction contractswazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elastic Architecture: A B C D E F GDocument0 paginiElastic Architecture: A B C D E F GNandhitha RajarathnamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leak Test PDFDocument48 paginiLeak Test PDFdaniel oliveira100% (1)
- Master Aubs enDocument1.045 paginiMaster Aubs enZar MaghustÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simplified Assessment of Bending Moment Capacity For RCDocument11 paginiSimplified Assessment of Bending Moment Capacity For RCAbhishek KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Easily Mounted Floor System For Large Spans: Hoesch Additive Floor Technical InformationDocument16 paginiThe Easily Mounted Floor System For Large Spans: Hoesch Additive Floor Technical InformationIvan ŠpacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction Materials and TestingDocument24 paginiConstruction Materials and TestingJames NeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plinth & Slab Beam DetailsDocument1 paginăPlinth & Slab Beam Detailsnandu523Încă nu există evaluări
- Melbourne Business School Library Project Management BibliographyDocument8 paginiMelbourne Business School Library Project Management BibliographyAndre Joseph Fournier0% (1)
- Report Template I3 GIMDocument19 paginiReport Template I3 GIMPan ThonvuthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classified Advertising: TEL: 444 666 09 FAX: 444 188 11 PB NO. 533Document5 paginiClassified Advertising: TEL: 444 666 09 FAX: 444 188 11 PB NO. 533vsraj1999Încă nu există evaluări
- TSW and HFSW Project Level 3 Time Schedule Phase 1 & Phase 2Document4 paginiTSW and HFSW Project Level 3 Time Schedule Phase 1 & Phase 2Suraj PetkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- David R. Taylor (Resume)Document2 paginiDavid R. Taylor (Resume)sumnerdaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- P&ID-Essential Piping and Instrument DiagramDocument23 paginiP&ID-Essential Piping and Instrument DiagramAmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two Cell Box CulvertDocument12 paginiTwo Cell Box CulvertAhmad Arslan Rafique71% (7)
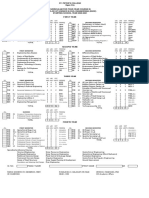
- St. Peter's College BSCE Curriculum 2020-2021Document1 paginăSt. Peter's College BSCE Curriculum 2020-2021Arafat BauntoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 010 Frank Pecafil Application Guide BRDocument22 pagini010 Frank Pecafil Application Guide BREduardo Gamarra PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- SGS IND Construction Material Inspection in India A4 EN 10 PDFDocument2 paginiSGS IND Construction Material Inspection in India A4 EN 10 PDFIndra MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- En Wikipedia Org Wiki Civil EngineeringDocument22 paginiEn Wikipedia Org Wiki Civil EngineeringSushanta Kumar RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLC Automation ProjectsDocument3 paginiPLC Automation Projectswhanumant100% (1)
- An Introduction To Electrical Machinery Safety Paul LaidlerDocument41 paginiAn Introduction To Electrical Machinery Safety Paul LaidlerSafetyjoe2100% (1)
- CourseInfo BookletDocument48 paginiCourseInfo BookletArindam MohantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEP Design StagesDocument12 paginiMEP Design Stageskadek supartaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UnknownDocument827 paginiUnknownExequiel Medina100% (1)