Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Genetics
Încărcat de
JengagalokaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Genetics
Încărcat de
JengagalokaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Genetics and Heredity
Probability
Probability
The likelihood that a specific event will
occur
Probability = # of 1 times event occurs
number of possible outcomes
Example: What is the
probability that a tossed
coin will be heads?
or 50%
Probability
The First Law of Probability:
the results of the first trial
of a chance event do not
affect the results of later
trials of the same event.
In other words, no matter
how many times a flipped
coin lands on tails, every flip
still has a chance of tails.
Probability
Second Law of Probability: The
probability of two or more
independent events occurring
together is the product of their
separate probabilities.
What is the probability that a couple
will have four boys?
50% (1/2 probability each time)
x x x = 1/16
Inherited Traits
Your eye color
Your height
Your hair color and texture
Are these inherited traits?
Are these inherited traits?
Your personality
Your musical,
athletic, and
artistic abilities
Think about this.
My parents have brown eyes, why are
mine blue?
My brother is tall. Why am I short?
Why does my sister have blonde hair
while mine is brown?
Gregor Mendel
These are questions that Gregor
Mendel tried to answer..
Born in 1822 in Austria
1843 Studied
Theology
1846-Studied Science
at the University of
Vienna
Father of Genetics
Mendels studies led to:
Dominant (H)
Homozygous (HH or hh)
Genotype (HH, Hh or hh)
Purebred (HH or hh)
Recessive (h)
Heterozygous (Hh)
Phenotype (blonde,
brown, red)
Hybrid (Hh)
Concepts in Inheritance
Theory of Heredity
Inherited allele for
purple P
Inherited allele
for purple P
HOMOZYGOUS
purple flower PP
Theory of Heredity
Inherited allele for
purple flower (P)
Inherited allele for
pink flower (p)
HETEROZYGOUS
purple flower (Pp)
Theory of Heredity
Inherited for pink
flower (p)
Inherited for pink
flower (p)
HOMOZYGOUS pink
flower (pp)
PREDICTING HEREDITY
PUNNETT SQUARES
A Punnett square is a tool used to help
predict the probability of offspring of a
couple.
1. Decide the genes that could be passed
on to the offspring in the gametes from
each parent.
2. Cross the different gene/gamete
possibilities for each possible offspring
combination.
Monohybrid Cross
Monohybrid Cross: a cross that shows the
possible offspring for one trait
Aa x Aa
A: White fur
a: Brown fur
Parent Aa has what
gentotype?
Parent Aa can produce a
gamete with either an A
or with an a
Monohybrid Cross
Monohybrid Cross: a cross that shows the
possible offspring for one trait
Aa x Aa
A: White fur
a: Brown fur
Aa produces gamete A or a
A
a
A
a
Separate the two genes (as though they were
separating into different gametes) and place one
outside the first row on the left and the other under
it outside the second row.
Separate the other parent genes and place at the
top, one above each column.
Monohybrid Cross
Monohybrid Cross: a cross that shows the
possible offspring for one trait
Aa x Aa
A: White fur
a: Brown fur
A a
A
a
AA
Aa
Aa aa
Cross over the
genes to fill in the
boxes of the
square.
Genotypic Ratios
Genotypic Ratios compare the possible
genotypes (gene combinations in the offspring.
Genotypic ratio:
Number of offspring with homozygous dominant genes AA
Number of offspring with heterozygous/hybrid genes Aa
Number of offspring with homozygous recessive genes aa
A a
A
a
AA
Aa
Aa aa
Aa x Aa
A: White fur
a: Brown fur
Sometimes abbreviated as:
GR = #hom dom (AA) : #hyb (Aa) : hom rec (aa)
GR = 1 : 2 : 1
Phenotypic Ratios
Phenotypic Ratios compare the possible
phenotypes (appearance of the offspring); how
many show the dominant trait or recessive trait.
Phenotypic ratio:
Number of offspring showing the dominant trait (AA & Aa)
Number of offspring showing the recessive trait (aa)
A a
A
a
AA
Aa
Aa aa
Aa x Aa
A: White fur
a: Brown fur
Sometimes abbreviated as:
PR = #show dom (AA & Aa) : #show rec (aa)
PR = 3 : 1
Practice!
Cross a HOMOZYGOUS dominant female with a
HETEROZYGOUS male using the same trait.
A A
A
a
AA
AA
Aa Aa
What is the
genotypic ratio?
What is the
phenotypic ratio?
2:2 or 50%
4 white fur
Dihybrid Cross
Dihybrid Cross: shows the possible offspring
for two traits
This shows a
cross between
parents hybrid
for two traits:
BbRr x BbRr
Fur Color:
B: Black
b: White
Coat Texture:
R: Rough
r: Smooth
BbRr x BbRr
BR
bR
br
bR
Br
BR
br
Br
BBRR BbRR BbRr
BBRr BBrr BbRr Bbrr
BbRR BbRr bbRR bbRr
BbRr Bbrr bbRr bbrr
BBRr
BR
bR
br
bR
Br
BR
br
Br
BBRR BbRR BbRr
BBRr BBrr BbRr Bbrr
BbRR BbRr bbRR bbRr
BbRr Bbrr bbRr bbrr
BBRr
16
Dihybrid Crosses
Phenotypic Ratio: # dom/dom : # dom/rec : # rec/dom : # rec/rec
Phenotypic Ratio: 9:3:3:1
How many of the
offspring would have
a black, rough coat?
(#dom/dom)
How many would
have a black,
smooth coat?
(#dom/rec)
How many would
have a white, rough
coat? (#rec/dom)
How many would
have a white,
smooth coat?
(#rec/rec)
BR
bR
br
bR
Br
BR
br
Br
BBRR BbRR BbRr
BBRr BBrr BbRr Bbrr
BbRR BbRr bbRR bbRr
BbRr Bbrr bbRr bbrr
BBRr
16
1
Dihybrid Crosses
If mouse #1 were crossed with mouse #16, what
would their offspring look like?
#1 x #16
BBRR x bbrr
#6 x #10
BBrr x BbRr
#14 x #16
Bbrr x bbrr
Fur Color:
B: Black
b: White
Coat Texture:
R: Rough
r: Smooth
More Complex Patterns
of Heredity
Codominance
Multiple Alleles
Sex-Linked Traits
Codominance
C
R
C
R
C
W
C
W
C
R
C
W
Codominance: two dominant alleles are
expressed at the same time
Codominance
Sickle-Cell Anemia is
another codominant
trait.
N
A
N
A
N
S
N
A
N
S
N
A
N
S
N
A
N
A
N
A
N
A
N
A
N
A
=Normal RBC N
S
=Sickle Cell RBC
National Institute of Health,
http://www.cc.nih.gov/ccc/ccnews/nov99/
Photo attributed to Drs. Noguchi,
Rodgers, and Schechter of NIDDK.
Multiple Alleles
Multiple Alleles: traits with more than 2
alleles
Blood type has 3 alleles: A, B, O
A and B are codominant over O
O is recessive
Phenotype Genotype
Can Receive
From
Can Donate To
A I
A
I
A
, I
A
i A, O A, AB
B I
B
I
B
, I
B
i B, O B, AB
AB I
A
I
B
A, B, AB,O AB
O ii O A, B, AB, O
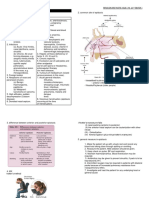
What are Sex-Linked Traits?
Traits that are located on one of the
sex chromosomes (XY or XX)
Hemophilia: Failure of
blood to clot
Muscular Dystrophy:
wasting away of
muscles
Alix and Nicholas II
Can I inherit a sex-linked disease?
Fathers (XY) can
only pass
disorders to
daughters (XX)
Mothers (XX) can
pass disorders to
both sons (XY) and
daughters (XX)
Most disorders are carried on
the X chromosome, so males
are more likely to inherit them.
How can I tell if I have a genetic disorder?
Karyotypes are a map of all 46 (23 pair)
of chromosomes.
Whats wrong with this Karyotype?
Is this a male or a female?
Whats wrong with this Karyotype?
Turners Syndrome
Whats wrong with this Karyotype?
Klinefelters Syndrome
Whats wrong with this Karyotype?
Down Syndrome
Pedigree Analysis
A pedigree shows inheritance of genetic
traits over several generations
male
female
Female
Carrier
Marriage
Offspring
Royal Hemophilia Pedigree
http://www.sciencecases.org/hemo/hemo.asp
Pedigree for Colorblindness
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Unit8 - GeneticsProblems - Assignment KeyDocument5 paginiUnit8 - GeneticsProblems - Assignment KeyJasmine KingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mendelian Genetics: Dominant & Recessive Review: Genotype: PP Genotype: PP Genotype: PPDocument36 paginiMendelian Genetics: Dominant & Recessive Review: Genotype: PP Genotype: PP Genotype: PPangela0% (1)
- Tiffany Shoham - UntitledDocument2 paginiTiffany Shoham - Untitledknoblock_michaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Practice Problems - Dihybrid - Answer KeyDocument6 paginiGenetics Practice Problems - Dihybrid - Answer KeyCris Obello31Încă nu există evaluări
- Brain TeasersDocument13 paginiBrain Teasersshan_batiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Ch04 Test Bank PDFDocument10 paginiGenetics Ch04 Test Bank PDFejanlindsay50% (2)
- Genetics Nonmendelian 150722002319 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument81 paginiGenetics Nonmendelian 150722002319 Lva1 App6891 PDFLeby Fastidio100% (1)
- JOHARI Window WorksheetDocument2 paginiJOHARI Window WorksheetAnonymous j9lsM2RBaIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Your Marathon Training PlanDocument16 paginiYour Marathon Training PlanAndrew Richard ThompsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Medelian - Genetics TunayDocument41 paginiNon-Medelian - Genetics TunayCHARMAINE ORUGAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics PowerpointDocument39 paginiGenetics PowerpointcamsdelacruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non MedelianDocument27 paginiNon MedelianmichelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non MedelianDocument29 paginiNon MedelianKlaudette Collin PaynorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geneticsprobs 1Document4 paginiGeneticsprobs 1Aesea GalidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACTIVITYGeneticspracticequestions 2Document6 paginiACTIVITYGeneticspracticequestions 2prem19999Încă nu există evaluări
- GeneticsDocument31 paginiGeneticsapi-267309851Încă nu există evaluări
- Genetics PowerpointDocument39 paginiGenetics PowerpointRizky EliandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deviation From Mendelian Genetic 1Document38 paginiDeviation From Mendelian Genetic 1Yuliandini Pangestika Wiyono100% (1)
- Genetic ProblemsDocument20 paginiGenetic Problemsatik0% (2)
- Cyto TalentoDocument6 paginiCyto TalentoJethro TalentoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incomplete Dominance and CodominanceDocument43 paginiIncomplete Dominance and Codominancecocosarang439Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab 02 Extra - Extentions To Mendelian GeneticsDocument6 paginiLab 02 Extra - Extentions To Mendelian Genetics13ucciÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Mendelian GeneticsDocument64 paginiNon Mendelian GeneticsDipanshi shahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10 - Unit 2 - Booklet - Genetics - 2 - SonDocument32 paginiGrade 10 - Unit 2 - Booklet - Genetics - 2 - SonBenanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Independent Assortment No Effect Father of GeneticsDocument22 paginiIndependent Assortment No Effect Father of GeneticshycherioneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology 2Document13 paginiBiology 2ZJC 2333Încă nu există evaluări
- Mendelian ProblemsDocument4 paginiMendelian Problemsprashant parmanu0% (1)
- 1-OG Genetics PowerpointDocument54 pagini1-OG Genetics PowerpointElizabeth DeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple AllelesDocument6 paginiMultiple AllelesMarvin AmparoÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Genetic ProblemsDocument8 paginiNew Genetic Problemsmzunl25476Încă nu există evaluări
- Other Forms of InheritanceDocument7 paginiOther Forms of InheritanceDaniel BerryÎncă nu există evaluări
- lAP Biology Genetics Problem Set: in Peas, Seeds May Be Round (R) or Wrinkled (R)Document4 paginilAP Biology Genetics Problem Set: in Peas, Seeds May Be Round (R) or Wrinkled (R)Mary Rose CatalbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Problem SetDocument6 paginiGenetics Problem SetKunvarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dihybrid and Pedigree AnalysisDocument25 paginiDihybrid and Pedigree Analysisengr beyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics 2nd Weeks, Monohybrid CrossesDocument25 paginiGenetics 2nd Weeks, Monohybrid CrossesAlam NuanzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO 1020 Unit 9Document25 paginiBIO 1020 Unit 9rbyq9Încă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Notes: Independent Assortment No Effect Father of GeneticsDocument22 paginiGenetics Notes: Independent Assortment No Effect Father of GeneticsTevfik DoğanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heridity, Inheritance and VariationDocument101 paginiHeridity, Inheritance and Variationdiana liberatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Practice Problems PDFDocument9 paginiGenetics Practice Problems PDFanaphade5Încă nu există evaluări
- 2016 Olympiad Training Genetics (Student)Document73 pagini2016 Olympiad Training Genetics (Student)dimpledblissÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Mendelian Inheritance2Document41 paginiNon-Mendelian Inheritance2Jeremy Christian MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HeredityDocument39 paginiHereditySamantha CunananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Mendelian GeneticsDocument25 paginiNon Mendelian GeneticsGeronimo Miano HitosisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5. B. Extensions of Mendelian GeneticsDocument25 paginiChapter 5. B. Extensions of Mendelian GeneticsXilca JamaimahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sex-Linked Inheritance & PedigreesDocument7 paginiSex-Linked Inheritance & PedigreesDaniel BerryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology - Genetics Review 2Document15 paginiBiology - Genetics Review 2lanichung100% (1)
- Practice Questions Extensions ofMendelianGeneticsAnswersDocument10 paginiPractice Questions Extensions ofMendelianGeneticsAnswersPouncingDeer1762Încă nu există evaluări
- ProplemsDocument6 paginiProplemselctoyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch. 11 Mendel F17 Ap BiologyDocument41 paginiCh. 11 Mendel F17 Ap BiologyEDITH NeslenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dominant and Recessive AllelesDocument3 paginiDominant and Recessive AllelesDanny Siloka100% (1)
- Genetics 2Document44 paginiGenetics 2Precious Miracle Lucas SacataniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classical Genetics Final Review Packet KeyDocument6 paginiClassical Genetics Final Review Packet KeyBecky KoshyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetics Can Be FunDocument9 paginiGenetics Can Be FunSir100% (1)
- Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument18 paginiNon-Mendelian GeneticsKristina CalejesanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 5 - Homework - Answer Key Due Feb. 23, 2013Document6 paginiWeek 5 - Homework - Answer Key Due Feb. 23, 2013Ricardo Afonso SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework #1Document4 paginiHomework #1dobbs07100% (1)
- Genetics PowerpointDocument22 paginiGenetics PowerpointAditya VaishnavÎncă nu există evaluări
- HeredityDocument45 paginiHeredityLevy GerpacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Homework: Abdulrahman Y. Al-Malki 3/1Document3 paginiBiology Homework: Abdulrahman Y. Al-Malki 3/1ebn-alramadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apgeneticsworksheet 1Document7 paginiApgeneticsworksheet 1Omar MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heredity: Inheritance and VariationDocument32 paginiHeredity: Inheritance and VariationLevy GerpacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 120-202 Lab Manual Spring 2012Document107 pagini120-202 Lab Manual Spring 2012evacelon100% (1)
- UNIT 3 Polymer and Fuel ChemistryDocument10 paginiUNIT 3 Polymer and Fuel Chemistryld6225166Încă nu există evaluări
- The Importance of Early Childhood InterventionDocument11 paginiThe Importance of Early Childhood Interventionsilverlining0814100% (3)
- Coiled Tubing Safety Impact Firing Head (HP) - by DynaDocument16 paginiCoiled Tubing Safety Impact Firing Head (HP) - by DynamahsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agriculture and FisheryDocument5 paginiAgriculture and FisheryJolliven JamiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing 7 BulletsDocument4 paginiMaternal and Child Health Nursing 7 BulletsHoneylie PatricioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Habits Across Generations: Before ReadingDocument3 paginiDigital Habits Across Generations: Before ReadingSharina RamallahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pentacon Six-02Document28 paginiPentacon Six-02Melissa Moreira TYÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-V300!1!6-L-GP General Purpose Potable Water Commercial Industrial Hi-Flo Series JuDocument2 paginiA-V300!1!6-L-GP General Purpose Potable Water Commercial Industrial Hi-Flo Series JuwillgendemannÎncă nu există evaluări
- PC110R 1 S N 2265000001 Up PDFDocument330 paginiPC110R 1 S N 2265000001 Up PDFLuis Gustavo Escobar MachadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 4 (Theories)Document15 paginiWeek 4 (Theories)Erica Velasco100% (1)
- Mental Health & TravelDocument18 paginiMental Health & TravelReyza HasnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final PR 2 CheckedDocument23 paginiFinal PR 2 CheckedCindy PalenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mrunal Handout 12 CSP20Document84 paginiMrunal Handout 12 CSP20SREEKANTHÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARS122 Engine Spare Part Catalogue PDFDocument134 paginiARS122 Engine Spare Part Catalogue PDFIrul Umam100% (1)
- Z0109MN Z9M TriacDocument6 paginiZ0109MN Z9M TriaciammiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compounds and Chemical FormulasDocument35 paginiCompounds and Chemical Formulasjolina OctaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tinh Toan Tang AP Cau Thang - CT Qui LongDocument20 paginiTinh Toan Tang AP Cau Thang - CT Qui Longntt_121987Încă nu există evaluări
- Sasol Polymers PP HNR100Document3 paginiSasol Polymers PP HNR100Albert FortunatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Big Elephants Are Useful Mnemonics & IdiomsDocument144 paginiBig Elephants Are Useful Mnemonics & IdiomsNachoAndrésLlorente100% (1)
- Tda12110h1 N300Document1 paginăTda12110h1 N300rolandseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diarrhoea in PediatricsDocument89 paginiDiarrhoea in PediatricsKimbek BuangkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nikki CV FormatedDocument2 paginiNikki CV FormatedSaif AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- HandbookDocument6 paginiHandbookAryan SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sialoree BotoxDocument5 paginiSialoree BotoxJocul DivinÎncă nu există evaluări
- All About Hemp Plant HempInc-eBookDocument17 paginiAll About Hemp Plant HempInc-eBookFelix MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information HumaLyzer Primus Setting Update and Extension enDocument3 paginiInformation HumaLyzer Primus Setting Update and Extension enluisoft88Încă nu există evaluări
- Sore Throat, Hoarseness and Otitis MediaDocument19 paginiSore Throat, Hoarseness and Otitis MediaainaÎncă nu există evaluări