Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
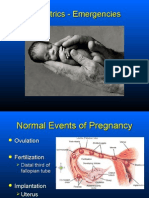
Pregnancy Complications and Labor Management
Încărcat de
Don Oliveros ÜTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pregnancy Complications and Labor Management
Încărcat de
Don Oliveros ÜDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Complications of
Pregnancy
Placenta Previa
Usually
presents with
painless
bleeding.
Never attempt
vaginal exam.
Treat for shock.
Transport
immediately
treatment is
delivery by
c-section.
Abruptio Placentae
Signs and
symptoms vary.
Classified as
partial, severe, or
complete.
Life-threatening.
Treat for shock,
fluid
resuscitation.
Transport left
lateral recumbent
position.
Labor
Stage One
(Dilation)
Stage Two
(Expulsion)
Stage
Three
(Placental
Stage)
Management of a Patient
in Labor
Transport the patient in labor unless
delivery is imminent.
Maternal urge to push or the
presence of crowning indicates
imminent delivery.
Delivery at the scene or in the
ambulance will be necessary.
Apgar Scoring
Abnormal Delivery
Situations
Breech Presentation
The buttocks or both feet present
first.
If the infant starts to breath with
its face pressed against the
vaginal wall, form a V and push
the vaginal wall away from
infants face. Continue during
transport.
Prolapsed Cord
The umbilical cord precedes the fetal
presenting part.
Elevate the hips, administer oxygen, and
keep warm.
If the umbilical cord is seen in the vagina,
insert two gloved fingers to raise the
fetus off the cord. Do not push cord
back.
Wrap cord in sterile moist towel.
Transport immediately; do not attempt
delivery.
Limb Presentation
With limb presentation, place
the mother in kneechest
position, administer oxygen,
and transport immediately.
Do not attempt delivery.
Other Abnormal
Presentations
Whenever an abnormal presentation or
position of the fetus makes normal
delivery impossible, reassure the
mother.
Administer oxygen.
Transport immediately.
Do not attempt field delivery in these
circumstances.
Other Delivery
Complications
Multiple Births
Follow normal guidelines, but
have additional personnel and
equipment.
In twin births, labor starts earlier
and babies are smaller.
Prevent hypothermia.
Cephalopelvic
Disproportion
Infants head is too big to pass through
pelvis easily.
Causes include oversized fetus,
hydrocephalus, conjoined twins, or fetal
tumors.
If not recognized, can cause uterine rupture.
Usually requires cesarean section.
Give oxygen to mother and start IV.
Rapid transport .
Precipitous Delivery
Occurs in less than 3 hours of
labor.
Usually in patients in grand
multipara, fetal trauma, tearing of
cord, or maternal lacerations.
Be ready for rapid delivery , and
attempt to control the head.
Keep the baby warm.
Shoulder Dystocia
Infants shoulders are larger than
its head.
Turtle sign.
Do not pull on the infants head.
If baby does not deliver, transport
the patient immediately.
Meconium Staining
Fetus passes feces into the
amniotic fluid.
If meconium is thick, suction the
hypopharynx and trachea using
an endotracheal tube until all
meconium has been cleared from
the airway.
Maternal Complications
of Labor and Delivery
Postpartum Hemorrhage
Defined as a loss of more than
500 cc of blood following delivery.
Establish two large-bore IVs of
normal saline.
Treat for shock as necessary.
Follow protocols if applying
antishock trousers.
Uterine Rupture
Tearing, or rupture, of the uterus.
Patient complains of severe abdominal
pain and will often be in shock.
Abdomen is often tender and rigid.
Fetal heart tones are absent.
Treat for shock.
Give high-flow oxygen and start two
large-bore IVs of normal saline.
Transport patient rapidly.
Uterine Inversion
Uterus turns inside out after delivery
and extends through the cervix.
Blood loss ranges from 800 to 1,800
cc.
Begin fluid resuscitation.
Make one attempt to replace the
uterus. If this fails, cover the uterus
with towels moistened with saline and
transport immediately.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- O&G Protocol and ProcedureDocument9 paginiO&G Protocol and ProcedureMas Zuraidah100% (1)
- Obstetric Emergencies 1Document38 paginiObstetric Emergencies 1bmukiri62Încă nu există evaluări
- Cesarean Birth (Breech Presentation)Document5 paginiCesarean Birth (Breech Presentation)Dave Noel AytinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intrapartal ComplicationsDocument5 paginiIntrapartal ComplicationsJeremiah JustoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prolonged Labor Complications and Fetal MalpositionsDocument9 paginiProlonged Labor Complications and Fetal Malpositionslarissedeleon100% (1)
- Umbilical Cord ProlapseDocument26 paginiUmbilical Cord Prolapsesulekhaanoob100% (2)
- Labor Process and Nursing Care GuideDocument9 paginiLabor Process and Nursing Care GuideMary Florence VelardeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intrapartal Complications Obstetric EmergenciesDocument9 paginiIntrapartal Complications Obstetric EmergenciesMay Princes Torregosa AbucejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Obstetric Emergencies During PregnancyDocument22 paginiManagement of Obstetric Emergencies During PregnancyGeorge NakojaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Woman Who Develops Complications During Labor and BirthDocument55 paginiThe Woman Who Develops Complications During Labor and BirthVincent Maralit MaterialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Life-Threatening Uterine Inversion Complication of ChildbirthDocument5 paginiLife-Threatening Uterine Inversion Complication of ChildbirthJemin KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCPreportDocument4 paginiMCPreportlovelylalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handouts OBSTETRICS EMERGENCYDocument9 paginiHandouts OBSTETRICS EMERGENCYAshish GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abnormal Delivery Types and ManagementDocument12 paginiAbnormal Delivery Types and ManagementBadrul MunirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstetrics and Gynecological EmergenciesDocument59 paginiObstetrics and Gynecological Emergenciesputri azzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Partograph - Used When The Mother Is About 4 CM Cervical Dilatation - The Updated Usage of It According To TheDocument5 paginiPartograph - Used When The Mother Is About 4 CM Cervical Dilatation - The Updated Usage of It According To TheGenierose YantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breech Delivery PDFDocument72 paginiBreech Delivery PDFEldrinAbquinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Management For LTCS For Non-Reassure Fetal StatutsDocument3 paginiCase Management For LTCS For Non-Reassure Fetal StatutsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hesi Hints MaternityDocument4 paginiHesi Hints MaternityThomas Stewart91% (11)
- Postpartal ComplicationsDocument7 paginiPostpartal ComplicationsCeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transverse and Unstable LieDocument31 paginiTransverse and Unstable LieRose Ann GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malpresentation and Malposition - BreechDocument21 paginiMalpresentation and Malposition - BreechNishaThakuri100% (1)
- INTRAPARTUM COMPLICATIONSDocument10 paginiINTRAPARTUM COMPLICATIONSkeinwayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems With The PowersDocument5 paginiProblems With The PowersAlexander Ruiz Queddeng100% (1)
- Fetal MalpresentationDocument83 paginiFetal MalpresentationArianJubaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstracteded LabourDocument4 paginiObstracteded LabourNishaThakuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregnancy: Types of Delivery: What Is An Assisted Delivery?Document4 paginiPregnancy: Types of Delivery: What Is An Assisted Delivery?Siafei RabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The PartogramDocument6 paginiThe PartogramCamille AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care for High-Risk Labor and DeliveryDocument170 paginiNursing Care for High-Risk Labor and DeliveryLongyapon Sheena Stephanie100% (2)
- OB Stages of Labor and Care in The Stages of Labor With VideoDocument45 paginiOB Stages of Labor and Care in The Stages of Labor With VideodsmagallanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uterine AtonyDocument3 paginiUterine AtonyArsheina Paradji100% (1)
- Precipitate and Difficult DeliveriesDocument15 paginiPrecipitate and Difficult DeliveriesDanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obgyn SL2Document21 paginiObgyn SL2mustafe omarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active Management of Normal LabourDocument16 paginiActive Management of Normal LabourjincyneeleshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal Labour& Abnormal LabourDocument23 paginiNormal Labour& Abnormal LabourThetnaungsoe100% (1)
- Complications During Labor and BirthDocument4 paginiComplications During Labor and BirthAudree Bustamante100% (2)
- MCN ObDocument7 paginiMCN ObJoshua SaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nur 146 (Rle)Document138 paginiNur 146 (Rle)Antoinette PeleñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Third stage labor complications guideDocument29 paginiThird stage labor complications guideAsogaa MeteranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1a. Obstetric Emergencies Koros E.KDocument225 pagini1a. Obstetric Emergencies Koros E.KSalman KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Umbilical Cord ProlapseDocument6 paginiUmbilical Cord ProlapseJules Cantal100% (3)
- Placenta Previa and Abruptio Placentae Nursing CareDocument12 paginiPlacenta Previa and Abruptio Placentae Nursing CareAyen Fajardo-HernalÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Contracture in Any of These Can Result in CPDDocument7 paginiA Contracture in Any of These Can Result in CPDMika SamsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Stage of LaborDocument2 paginiFirst Stage of LaborngetcholetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ob 2.25.07Document65 paginiOb 2.25.07Yudi Siswanto100% (1)
- Eech & Abnormal PresentationsDocument14 paginiEech & Abnormal Presentationsasri khazaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prepared by Marjorie Galicia Romano Clinical InstructorDocument106 paginiPrepared by Marjorie Galicia Romano Clinical InstructorMarjorie Galicia Romano-AndalisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complications during labor and deliveryDocument16 paginiComplications during labor and deliveryEden NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Operative ObstetricsDocument32 pagini12 Operative ObstetricsRana VandanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complication During Labor DeliveryDocument68 paginiComplication During Labor DeliveryEllie ELLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shaafi Medical College Obstetrics GuideDocument39 paginiShaafi Medical College Obstetrics Guidemustafe omarÎncă nu există evaluări
- MalpresentationDocument19 paginiMalpresentationHanelie B. AldeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Cord ProlapseDocument16 paginiUnit 1 Cord ProlapseHendrik MuremiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complication During Labor DeliveryDocument68 paginiComplication During Labor DeliveryJhennie Rose PalaganasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstetrical EmergenciesDocument61 paginiObstetrical EmergenciesKavya S Mohan100% (2)
- Emergencies ObsDocument7 paginiEmergencies ObsAshish GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMPLICATIONS OF LABOR AND DELIVERYDocument19 paginiCOMPLICATIONS OF LABOR AND DELIVERYkrizele ann santosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5 - Obsteric Emergencies-1Document103 paginiLecture 5 - Obsteric Emergencies-1Priscilla Sarah PayneÎncă nu există evaluări
- It's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookDe la EverandIt's Not Just a Heavy Period; The Miscarriage HandbookEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- Advice To Wives On The Management Of Themselves, During The Periods Of Pregnancy, Labour And SucklingDe la EverandAdvice To Wives On The Management Of Themselves, During The Periods Of Pregnancy, Labour And SucklingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coal Flow RateDocument2 paginiCoal Flow RateDon Oliveros ÜÎncă nu există evaluări
- MagnifierDocument9 paginiMagnifierDon Oliveros ÜÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Tuberculosis ProgramDocument37 paginiNational Tuberculosis ProgramDon Oliveros ÜÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ring BusDocument11 paginiRing BusDon Oliveros ÜÎncă nu există evaluări
- OB/GYN For EMS ProvidersDocument94 paginiOB/GYN For EMS ProvidersPaulhotvw67100% (6)
- English 54 ReportDocument3 paginiEnglish 54 ReportDon Oliveros ÜÎncă nu există evaluări
- High-Risk Pregnancy Factors & CareDocument19 paginiHigh-Risk Pregnancy Factors & CareRoger Jr PumarenÎncă nu există evaluări
- TWINKL Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 paginiTWINKL Knowledge OrganiserDearbhla HubbardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Konsep Asuhan Prakonsepsi: Ferina, BD., M.KebDocument20 paginiKonsep Asuhan Prakonsepsi: Ferina, BD., M.KebRuni LestariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar Penyakit Icd-X: No Kode ICD 10 DeskripsiDocument14 paginiDaftar Penyakit Icd-X: No Kode ICD 10 DeskripsiFiitria Wuulaan DariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art de OxitocinaDocument5 paginiArt de OxitocinaGuillermo David Polit HurtadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture15 - (161) Hormone in ReproductionDocument12 paginiLecture15 - (161) Hormone in ReproductionMujeres Virglius PabliusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge, Attitude and Practise Regarding Emergency Contraceptive PillsDocument6 paginiKnowledge, Attitude and Practise Regarding Emergency Contraceptive PillsEditor IJTSRDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conduct of LaborDocument8 paginiConduct of LaborChristine Evan HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Puerperal InfectionsDocument61 paginiManaging Puerperal InfectionsTadesse MuhammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture On Sexual AbnormalitiesDocument33 paginiLecture On Sexual AbnormalitiesRenz L. Salumbre80% (5)
- Preterm Charts Combined BoysDocument1 paginăPreterm Charts Combined BoysEnny AndrianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The DSM Diagnostic Criteria For Fetishism: Archives of Sexual Behavior October 2009Document7 paginiThe DSM Diagnostic Criteria For Fetishism: Archives of Sexual Behavior October 2009Nunung MirawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 12 Family PlanningDocument147 paginiUnit 12 Family PlanningBikash KandelÎncă nu există evaluări
- TTA Classic Chart (C)Document1 paginăTTA Classic Chart (C)madeleinegermaineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstetrical Procedures Forceps Delivery Cesarean SectionDocument3 paginiObstetrical Procedures Forceps Delivery Cesarean SectionRosnalia HariyantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Sexual Dysfunction-1Document7 paginiFemale Sexual Dysfunction-1Risky SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MRCOG Short Answer Questions September 2013Document1 paginăMRCOG Short Answer Questions September 2013Dr.Marva YusafzaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 5 2nd Quarter ExamDocument3 paginiScience 5 2nd Quarter ExamLouie Ric FiscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orgasm After OrgasmDocument46 paginiOrgasm After Orgasmonzpr032550% (2)
- Unihorn Pyometra in A BitchDocument5 paginiUnihorn Pyometra in A BitchIndian Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Divinity 4Document322 paginiDivinity 4Kj BabyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Youngest Birth Mothers Records ListDocument26 paginiYoungest Birth Mothers Records Listrainfall17Încă nu există evaluări
- Rape-Investigation-Part 1Document25 paginiRape-Investigation-Part 1kemerutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar Pustaka: Nitrition. Maryland: An Aspen PublicationDocument17 paginiDaftar Pustaka: Nitrition. Maryland: An Aspen PublicationrestartÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ayurvedic Management of Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding A Case StudyDocument3 paginiAyurvedic Management of Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding A Case StudyTarun PandianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step 3 - Inform All Pregnant Women of The Benefits and Management of Breastfeeding. CULTURE VariesDocument14 paginiStep 3 - Inform All Pregnant Women of The Benefits and Management of Breastfeeding. CULTURE VariesJudith DurensÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total and Acute Uterine Inversion After Delivery: A Case ReportDocument5 paginiTotal and Acute Uterine Inversion After Delivery: A Case ReportMuhammad AzkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nle MCN Road To SuccessDocument59 paginiNle MCN Road To SuccessKaye PatanindagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2012 Longer Penis OrgasmsDocument10 pagini2012 Longer Penis OrgasmsLucano Alvares100% (1)
- 1970 - Zuger Vs Money-A Critical Review of The Evidence From HermaphroditismDocument20 pagini1970 - Zuger Vs Money-A Critical Review of The Evidence From HermaphroditismRafael FredaÎncă nu există evaluări