Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
DRAINS
Încărcat de
Agus SugihartoDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
DRAINS
Încărcat de
Agus SugihartoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
PROCESS
DRAINS
EXP-PR-PR120a-EN
Rev. 0
2
Process Drains
In this course you will learn:
The functions of drains
How drains work
Different types of drains
Drains and the process
Operating parameters
Operating drains
3
Process Drains
The functions of drains
The function of drainage
systems is to collect the
occasional liquid purges
from the production units.
4
Process Drains
How drains work
Closed drains
The closed drain system is balanced on the LP flare network
The hydrocarbons from the tank are collected by a pump operating under
ON/OFF level control and are sent into the oil line
The pump lift lines are fitted with high pressure safeties linked to the
Process Safety System (PSS).
The closed drain tank is equipped with a very low LSLL level safety
linked to the PSS and with a very high LSHH level safety linked to the
Emergency Shutdown System (ESD).
5
Process Drains
How drains work
Open drains
The open drain system is in balance with the atmosphere
The open drain tank is equipped with a baffle
The drains manifold feeds the tanks by means of a plunger tube
The mixed water / hydrocarbon phase accumulates in the lower part and
the hydrocarbons that are lighter than water are carried over to the
second part of the receptacle by flowing over the separator baffle.
These hydrocarbons are collected by a pump operating under ON/OFF
level control and returned to the closed drain tank
The water phase is sent to the waste tube
Another decantation process takes place in this waste tube and the
hydrocarbons floating on the top are returned to the open drain tank
6
Process Drains
Different types of drains
The closed drain
Closed drains are made up of a network of manifolds and sub-manifolds
that collect:
Oily bleed-off from processes, such as liquids from flare drums
Liquids from the degassing drum skimmer
Hydrocarbons from the oily discharge outlet of the hydrocyclones
Hydrocarbons from the sump tank
The hydrocarbon phase recovered from the open drain
The vessels are linked to the collectors by lines fitted with valves to
prevent the hydrocarbons fromp coming into contact with the air.
The different collectors are linked to the closed drain drum by a main
manifold.
7
Process Drains
Different types of drains
Open drains or sump tanks
Open drains are made up of a network of manifolds and sub-manifolds
that collect the installation's various oily water purges
The vessels are not directly linked to collectors and bleed off occurs
through lines fitted with valves that open into funnels installed on the
manifolds
The collectors are connected to a drum by a main manifold, as for closed
drains
A discharge tube linked to the drain drum discharges the decanted water
to the sea, on an offshore installation, or to water treatment on an
onshore installation
8
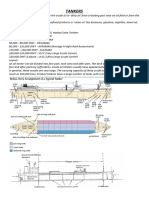
Process Drains
Different types of drains
Valve set-up for open and
closed drains
9
Process Drains
Drains and the process
Location and criticality
Drain systems have a high criticality: it is the last barrier preventing liquid
hydrocarbons from being sent to the environment
It is prohibited to connect the closed-drains networks with the open-drain
networks
10
Process Drains
Operating parameters
Closed drains
A very low LSLL level detected in the closed drain tank leads to shutting
down the hydrocarbon collection pumps and closing the SDV safety
valves at the pump suctions in order to protect the latter
A very high LSHH detected in this tank triggers a General Production
Shut Down
Open drains
A very low LSLL level detected in the open drain tank leads to shutting
down the hydrocarbon phase collection pumps towards the open drain
and closing the safety valve at the pump lifts
11
Process Drains
Operating drains
Start-up
Before start-up, it is imperative to carry out an inertance of the closed drain
system. This inertance can be done with either nitrogen, with an inert gas, or with
water from which all traces of liquid hydrocarbons (in emulsion) have been
removed
Normal operation
Carry out a weekly test of booster pumps
Check that the open drains are not obstructed
On an offshore installation, check the colour of the waste water to the sea (lack of
iridescence indicating a hydrocarbon leak)
Shut-down
The drainage system is shut-down after the installations are shut down.
Before maintenance operations of any nature whatsoever are carried out, it is
imperative to inert the closed drain system
This is done by means of a nitrogen sweep after having purged all the liquid
hydrocarbons
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Statistics for Process Control Engineers: A Practical ApproachDe la EverandStatistics for Process Control Engineers: A Practical ApproachÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operating ManualDocument102 paginiOperating ManualLulu ChaniagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled YIYUIGUDocument44 paginiUntitled YIYUIGUShwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXP-PR-RT030-EN-R0 - 1 - Intro HC PDFDocument48 paginiEXP-PR-RT030-EN-R0 - 1 - Intro HC PDFbali100% (2)
- EXP-PR-EQ080-R1-EN SeparatorsDocument119 paginiEXP-PR-EQ080-R1-EN SeparatorshediÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXP-PR-UT040-EN-R0 - Slides Fresh WaterDocument48 paginiEXP-PR-UT040-EN-R0 - Slides Fresh Waterfasert sarytghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sulfur RecoveryDocument13 paginiSulfur RecoveryLarbi HammounÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Safety System (Relief and Blowdown System) : Psvs and Mechanical Systems Flare Gathering Network Flares and VentsDocument36 paginiProcess Safety System (Relief and Blowdown System) : Psvs and Mechanical Systems Flare Gathering Network Flares and Ventsandi dipayadnyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXP-PR-UT030-EN-R0 - 1 - Instrument AirDocument45 paginiEXP-PR-UT030-EN-R0 - 1 - Instrument AirAnonymous aIuHKoKZj100% (1)
- PROCESS DepressurisationDocument38 paginiPROCESS DepressurisationMuhammad Feri IrawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heaters & FurnaceDocument86 paginiHeaters & FurnaceArintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp PR Eq040 en r0 - 1 PipingDocument62 paginiExp PR Eq040 en r0 - 1 Pipingbali50% (2)
- ColumnsDocument90 paginiColumnsArintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methods of Ethane Liquid Recovery From Natural GasDocument35 paginiMethods of Ethane Liquid Recovery From Natural GasJeff Formica100% (1)
- EXP-PR-EQ130-R0-EN Support CoursDocument65 paginiEXP-PR-EQ130-R0-EN Support Courshedi100% (1)
- Introduction World Oil GasDocument160 paginiIntroduction World Oil Gasbali100% (3)
- High Integrity Pressure Protection System (HIPPS)Document6 paginiHigh Integrity Pressure Protection System (HIPPS)Ridho Saputro HutomoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Offsites and UtilitiesDocument70 paginiOffsites and Utilitiesankitalalwani100% (1)
- Exp PR Pr070 en r0 - 1 SeparationDocument150 paginiExp PR Pr070 en r0 - 1 SeparationAmin Hammemi100% (3)
- EXP-PR-EQ070-EN Slides PumpsDocument103 paginiEXP-PR-EQ070-EN Slides PumpsStive Ozimba Ebomi100% (4)
- EXP-PR-UT040-EN-R0 - 1 - Fresh WaterDocument79 paginiEXP-PR-UT040-EN-R0 - 1 - Fresh Waterfasert sarytghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upstream Process Engineering Course: 3. Environment ManagementDocument19 paginiUpstream Process Engineering Course: 3. Environment ManagementMohamed SelimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Des AlterDocument96 paginiDes AlterArintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emergency Shutdown (ESD) System PhilosophyDocument1 paginăEmergency Shutdown (ESD) System PhilosophyTimothy Leonard100% (1)
- 14 Gas Dehydration PDFDocument47 pagini14 Gas Dehydration PDFNic RicÎncă nu există evaluări
- SymbolS VALVULAS-GuideDocument6 paginiSymbolS VALVULAS-GuideEnrique DguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natural Gas FractionationDocument28 paginiNatural Gas Fractionationmohamed100% (1)
- Hydraulic & Pneumatic EquipmentDocument183 paginiHydraulic & Pneumatic EquipmentArintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shell Gasification TechnologyDocument30 paginiShell Gasification TechnologychatuusumitavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sour Gas ProcessingDocument5 paginiSour Gas ProcessingihllhmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valves and ActuatorsDocument129 paginiValves and Actuatorsmhmd100% (1)
- Mechanical Course - Process Gas DehydrationDocument3 paginiMechanical Course - Process Gas DehydrationmahdicmmÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXP PR EQ180 en R0 - 1 Reduction UnitsDocument24 paginiEXP PR EQ180 en R0 - 1 Reduction UnitsbaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXP-PR-EQ070-R0-EN Support CoursDocument182 paginiEXP-PR-EQ070-R0-EN Support CourshediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genesis Twister Study PDFDocument34 paginiGenesis Twister Study PDFMarco Antonio Lara CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cascade ControlDocument10 paginiCascade ControlManoj RajagopalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic ChemistrDocument48 paginiBasic ChemistrJuwaini FahmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 Steam GenerationDocument30 paginiUnit 3 Steam GenerationkhalimnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flare SystemDocument29 paginiFlare SystemLuis EnriqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instrumentation AccessoriesDocument115 paginiInstrumentation AccessoriesRonilson SenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp MN Sm090 en r0 SealsDocument60 paginiExp MN Sm090 en r0 SealsbaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flaresim PDFDocument448 paginiFlaresim PDFAnonymous exuebXBKXX71% (7)
- 5 Process ControlDocument79 pagini5 Process ControlGurunath EpiliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intrument Air ConsumptionDocument4 paginiIntrument Air ConsumptionyogacruiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp PR Di010 en r0 - 1 DiagramsDocument67 paginiExp PR Di010 en r0 - 1 Diagramsbali100% (3)
- Filtration and Separation in RefineriesDocument30 paginiFiltration and Separation in RefineriesprogerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total GasDocument58 paginiTotal GasTuấn Anh NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 - HX PresentationDRAFT 3Document14 pagini4 - HX PresentationDRAFT 3Islam SolimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Electric Systems Technology Manual Service and Instrument Air SystemsDocument13 paginiGeneral Electric Systems Technology Manual Service and Instrument Air SystemsNavern MoodleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relief and Blowdown SystemDocument43 paginiRelief and Blowdown SystemMohamed Sayed Abdo83% (6)
- Over Pressure Cases For Pressure Relief Valve SizingDocument2 paginiOver Pressure Cases For Pressure Relief Valve SizinginstrengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Depressuring in Aspen Hysys®: Revised: Nov 27, 2012Document6 paginiDepressuring in Aspen Hysys®: Revised: Nov 27, 2012udokasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.19 Process Isolation System Design Philosophy PDFDocument6 pagini6.19 Process Isolation System Design Philosophy PDFdamanpb3633Încă nu există evaluări
- ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINES Boiler Systems Rev1.3web PDFDocument29 paginiENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINES Boiler Systems Rev1.3web PDFMohsen KadivarÎncă nu există evaluări
- E1.0 - Crude Stab - Foaming PDFDocument32 paginiE1.0 - Crude Stab - Foaming PDFRégis Ongollo100% (2)
- Gas Dehydration PDFDocument67 paginiGas Dehydration PDFMahathir Che Ap100% (2)
- 08 DehydrationDocument71 pagini08 DehydrationjollyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vacuum Leakage TestDocument11 paginiVacuum Leakage Testsambhu100% (1)
- Vacuum Sewage SystemsDocument1 paginăVacuum Sewage SystemsDenberg CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oil Tanker Cargo WorkDocument12 paginiOil Tanker Cargo WorkAshutosh Singh100% (4)
- Pressure Data Analysis Using Derivative Type Curve For Multilayered Gas ReservoirDocument27 paginiPressure Data Analysis Using Derivative Type Curve For Multilayered Gas ReservoirArif pmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steam Oil Iom 2000 0401 - Rev 122311 PDFDocument76 paginiSteam Oil Iom 2000 0401 - Rev 122311 PDFedgardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SA - Separation System - Operating Instructions - 2002Document30 paginiSA - Separation System - Operating Instructions - 2002Centrifugal SeparatorÎncă nu există evaluări
- 30HX 14PDDocument56 pagini30HX 14PDDaniel TaveiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Donaldson Ready Recokner 2018Document6 paginiDonaldson Ready Recokner 2018Hemant PanpaliyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Studies On The Operation of Loop-Seal in Circulating Fluidized Bed Boilers, P. BasuDocument9 paginiStudies On The Operation of Loop-Seal in Circulating Fluidized Bed Boilers, P. BasuyukselenturkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1140523021191Document110 pagini1140523021191Irimia Matei Alex100% (3)
- Natural Gas ProcessingDocument384 paginiNatural Gas ProcessingMichael AntipuestoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8-8-3 Water Filling Machine Project Proposal: Quoted By: Nina Chan Email: Tel/Whatsapp: +86 13402094268Document11 pagini8-8-3 Water Filling Machine Project Proposal: Quoted By: Nina Chan Email: Tel/Whatsapp: +86 13402094268Huong NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- EN 73 (V3) Manual Code 01 94 00 115Document133 paginiEN 73 (V3) Manual Code 01 94 00 115Taufan Justvands0% (1)
- Apd Catalog PDFDocument28 paginiApd Catalog PDFsoo RenÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPI SeparatorDocument77 paginiCPI SeparatorVidyasen100% (1)
- Interview Questions For Engineers-1512639929Document11 paginiInterview Questions For Engineers-1512639929Andrii100% (1)
- Ahu Low Res PDFDocument52 paginiAhu Low Res PDFmo farawelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best Blackpowder2013Document24 paginiBest Blackpowder2013sohail1985Încă nu există evaluări
- Systematic Lessons Learned Analysis ForDocument100 paginiSystematic Lessons Learned Analysis ForPranpath NarupantawartÎncă nu există evaluări
- Copland Outdoor UnitsDocument18 paginiCopland Outdoor UnitsatiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ar166 208 260Document82 paginiAr166 208 260michaelxiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- WEMCO Depurator MBLDocument6 paginiWEMCO Depurator MBLallen_renzi0% (1)
- Start Up Slug Catcher and Train 1Document43 paginiStart Up Slug Catcher and Train 1Larbi HammounÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACT 20 500 Manual 2012Document68 paginiACT 20 500 Manual 2012UbanAirlanggaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19 - Storvik - Subsea SeparationDocument19 pagini19 - Storvik - Subsea SeparationMarco Andrés Guevara LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Important Points To Note For Maintenance of Emergency Generators On ShipDocument13 pagini8 Important Points To Note For Maintenance of Emergency Generators On ShipstamatisÎncă nu există evaluări
- NM Methane Advisory Panel Draft Technical ReportDocument301 paginiNM Methane Advisory Panel Draft Technical ReportNM Transparency InitiativeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide For Visatron Oil Mist Detector Users - V 1.2.3 PDFDocument64 paginiA Guide For Visatron Oil Mist Detector Users - V 1.2.3 PDFGENNIEL SABA100% (4)
- Biogas Safety RulesDocument48 paginiBiogas Safety RulesanuvdevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compressor 1 (WORD)Document11 paginiCompressor 1 (WORD)azizi_ghazaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nuclear Engineering and TechnologyDocument8 paginiNuclear Engineering and TechnologyBharat MahajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 4Document43 paginiChap 4adrien_ducaillouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Woosung LOVD 36Document52 paginiWoosung LOVD 36sayeem bikashÎncă nu există evaluări