Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Business Studies: Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
Încărcat de
Venkatramana K0%(2)0% au considerat acest document util (2 voturi)
225 vizualizări43 paginiThis document provides information about Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL), a large public sector undertaking in India. It discusses BHEL's establishment in 1956 and growth into a major player in India's power, industry, transportation and other core sectors. Some key points covered include BHEL's workforce of over 43,500 employees, manufacturing facilities across India, role in generating 73% of India's power, exports to over 60 countries, and corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Descriere originală:
Capital Budgeting in BHEL
Titlu original
Capital Budgeting in BHEL
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThis document provides information about Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL), a large public sector undertaking in India. It discusses BHEL's establishment in 1956 and growth into a major player in India's power, industry, transportation and other core sectors. Some key points covered include BHEL's workforce of over 43,500 employees, manufacturing facilities across India, role in generating 73% of India's power, exports to over 60 countries, and corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0%(2)0% au considerat acest document util (2 voturi)
225 vizualizări43 paginiBusiness Studies: Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
Încărcat de
Venkatramana KThis document provides information about Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL), a large public sector undertaking in India. It discusses BHEL's establishment in 1956 and growth into a major player in India's power, industry, transportation and other core sectors. Some key points covered include BHEL's workforce of over 43,500 employees, manufacturing facilities across India, role in generating 73% of India's power, exports to over 60 countries, and corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 43
BUSINESS STUDI ES
BHARAT HEAVY ELECTRICALS LIMITED
Brightening LivesPowering
Progress
The customer is centric to all activities in a
business organisation.The real challenge is all
about marshalling the resources in pursuit of
customer excellence.
--Ashok K. Puri,Chairman and Managing Director,BHEL
Birth of an Industrial Giant
The power equipment industry was established in
India with the setting up of the first plant of BHEL
at Bhopal in 1956(under Heavy Electricals India
Limited-HEIL).
Today,BHEL is the only Navratna company in
the engineering sector.
Spread of Operations
With 180 products under 30
major product groups,BHEL
caters to the core sectors of
Indian economy-
Power,
Industry,
Transportation,
Transmission,
Oil and Gas,
Renewable Energy etc.
Employment Opportunities
BHEL has a workforce of nearly 43,500 employees at 14
manufacturing divisions,eight service centres and four
power sector regional centres,besides over 100 project
sites spread all over India and abroad.
All the major units\divisions have been upgraded to the
latest ISO-9001:2000 version quality standard
certification.BHEL has also secured ISO-14001
certification for environmental management systems and
OHSAS-18001 certification for occupational health and
safety management systems.
In service of the Nation
BHEL sets generate 73% of the
total power in the country while
accounting for 65% of Indias
total installed generating capacity
of 1,23,668 MV(as on
Dec.31,2013).That translates into
nearly three out of every four
homes in India being lit up with
power generated by BHEL sets!
Harnessing Solar Energy
Leaps of Success
Over 70% of the locomotives on Indian
Railways(the second largest railway network in the
world) are powered by BHEL built traction
electrics.
Technologies have been developed and
commercialised for exploiting non-conventional
sources of energy.These include wind electric
generators,solar photovoltaic(PV) cells and
modules,solar lanterns, solar heating systems etc.
WORK IN PROGRESS
GLOBAL REACH
BHEL is one of the largest exporters of
engineering products and services from India.Over
the years,BHEL has established its reference in
over 60 countries-from United States in the west to
New Zealand the other side of the world.
PEOPLE IN THE FOREFRONT
So far 52 BHEL
employees have won 40
Prime Ministers Shram
Awards for their
outstanding achievements
leading to higher
productivity,improved
quality and foreign
exchange savings.
A Responsible Corporate citizen
As part of its Corporate Social
Responsibility BHEL has adopted
56 villages in the vicinity of its
manufacturing plants throughout
the country.The company has also
joined the United NationsGlobal
Compact,a partnership between
the UN,the business
community,international labour
and NGOs..
A Growing Industrial Unit at
Bangalore
Significant Landmarks (Part-I)
1956 - First manufacturing plant of BHEL set-up at
Bhopal under Heavy Electricals(India)Limited
1969 - BHELs entry into Indias Power Sector with
supply and installation of a 30 Megawatt Steam Turbine
Generating set at Basin Bridge in Tamil Nadu
1970 - BHEL supplied and commissioned first hydro set
(33 MV rating) at Obra Hydro Power Station in U.P
Significant Land marks (Part-II)
1971 - Bags first export
order for boilers for
Tuanku Jafar Thermal
Power Station,Malaysia
1976 - BHEL received the
first overseas turnkey
contract for 2*120 MV
Tripoli West Thermal
Power Station in Libya.
Significant Landmarks (Part-III)
1980 - Commissions first 120 MV unit at Tripoli
West Power Station of Electricity Corp.,Libya
1984 - Commissions Indias first 500 MV Steam
Turbine Generator set at Trombay Thermal Power
Station of Tata Power Company
1989 - The first BHEL manufactured 25kV AC
locomotive for hauling passengers and goods trains
was supplied to Indian Railways
Significant Landmarks (Part-IV)
1993 - Sets up Gas
Turbine based
Power
Project(2*Frame 6)
at Connaught Bridge
Power Station in
Malaysia in a record
time of six months
Capital Budgeting
Techniques
Project Evaluation and Selection
Potential Difficulties
Capital Rationing
Project Monitoring
Post-Completion Audit
Project Evaluation:
Alternative Methods
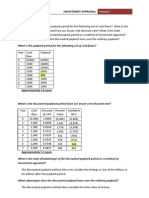
Payback Period (PBP)
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Net Present Value (NPV)
Profitability Index (PI)
Payback Period (PBP)
PBP is the period of time required for
the cumulative expected cash flows
from an investment project to equal the
initial cash outflow.
0 1 2 3 4 5
-40 K 10 K 12 K 15 K 10 K 7 K
PBP Strengths
and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Easy to use and
understand
Can be used as a
measure of
liquidity
Easier to forecast ST
than LT flows
Weaknesses:
Does not account
for TVM
Does not consider
cash flows beyond
the PBP
Cutoff period is
subjective
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
IRR is the discount rate that equates the present
value of the future net cash flows from an
investment project with the projects initial
cash outflow.
CF
1
CF
2
CF
n
(1+IRR)
1
(1+IRR)
2
(1+IRR)
n
+ . . . + +
ICO =
IRR Acceptance Criterion
No! The firm will receive 11.57% for each
dollar invested in this project at a cost of
13%. [ IRR < Hurdle Rate ]
The management of Basket Wonders has
determined that the hurdle rate is 13% for
projects of this type.
Should this project be accepted?
IRR Strengths
and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Accounts for
TVM
Considers all
cash flows
Less
subjectivity
Weaknesses:
Assumes all cash
flows reinvested at
the IRR
Difficulties with
project rankings and
Multiple IRRs
Net Present Value (NPV)
NPV is the present value of an
investment projects net cash flows
minus the projects initial cash
outflow.
CF
1
CF
2
CF
n
(1+k)
1
(1+k)
2
(1+k)
n
+ . . . + + - ICO
NPV =
NPV Acceptance Criterion
No! The NPV is negative. This means that the
project is reducing shareholder wealth. [Reject
as NPV < 0 ]
The management of Basket Wonders has
determined that the required rate is 13%
for projects of this type.
Should this project be accepted?
NPV Strengths
and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Cash flows
assumed to be
reinvested at the
hurdle rate.
Accounts for TVM.
Considers all
cash flows.
Weaknesses:
May not include
managerial
options embedded
in the project. See
Chapter 14.
Profitability Index (PI)
PI is the ratio of the present value of a
projects future net cash flows to the
projects initial cash outflow.
CF
1
CF
2
CF
n
(1+k)
1
(1+k)
2
(1+k)
n
+ . . . + + ICO PI =
PI = 1 + [ NPV / ICO ]
<< OR >>
Method
#2:
Method
#1:
PI Strengths
and Weaknesses
Strengths:
Same as NPV
Allows
comparison of
different scale
projects
Weaknesses:
Same as NPV
Provides only
relative profitability
Potential Ranking
Problems
DATA ANALYSIS & CONCLUSION
Projects evaluated
Project 1 project 2 project 3 project 4 project 5
Cost of investment 5125 10250 4125 8125 1920
PBDT Year1 Year2 Year3 Year4 Year5 Year6 Year7 Year8 Year9 Year10 Total
Project1 1020 1520 1520 1620 1720 1520 1650 1520 1210 1310 14610
Project2 3060 4560 4560 4860 5160 4560 4950 4560 3630 3930 43830
Project3 306 456 456 486 516 456 495 456 363 393 4383
Project4 1122 1672 1672 1782 1892 1672 1815 1672 1331 1441 16071
Project5 91.8 136.8 136.8 145.8 154.8 137 148.5 136.8 108.9 117.9 1314.9
*In Lakhs
Depreciation as per the profit and loss account 15% SLM
Depreciation as per the income tax act 1
st
year 2
nd
year onward
35% 15%Wdv
Tax Rate 33%
Present value factor 13%
NPV, IRR, PI, ROI
Project 1
(Estimate budget RS 5125 Lacks)
Years
PBDT
-Dep &
Tax
PBT
-Tax 33%
PAT
+Depr
CFAT
CCFAT
1 1020 1794 -774 -255 -519 1794 1276 1276
2 1520 500 1020 337 683 500 1183 2459
3 1520 425 1095 361 734 425 1159 3618
4 1620 361 1259 415 844 361 1205 4823
5 1720 307 1413 466 947 307 1254 6077
6 1520 261 1259 415 844 261 1105 7182
7 1650 222 1428 471 957 222 1179 8361
8 1520 188 1332 439 893 188 1081 9442
9 1210 160 1050 346 704 160 864 10306
10 1310 136 1174 387 787 136 923 11229
Total 14610 4354 10256 3382 6874 4354 11229
Years CFAT CCFAT PV@13% Total PV PV@20% Total pv
1 1276 1276 0.885 1129 0.833 1061
2 1183 2458 0.783 926 0.694 821
3 1159 3618 0.693 803 0.579 671
4 1205 4823 0.613 739 0.482 581
5 1254 6077 0.543 681 0.402 504
6 1105 7182 0.480 530 0.335 370
7 1179 8361 0.425 501 0.279 329
8 1081 9442 0.376 406 0.233 252
9 864 10306 0.333 288 0.194 168
10 923 11229 0.295 272 0.162 150
Total 6275 4907
Present value cash inflow = 6275
Present value cash outflow=5125
PRESENT VALUE METHOD
Net present value = cash inflow-cash outflow
= 6275 - 5125
NPV @ 13% = 1150
PROFITABILITY INDEX
P.I = Total present value of cash inflow/ Total Investment
= 6275/5125
= 1.22 Times
INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (IRR)
Inflows at lower rate-investment
IRR= Lower rate + ---------------------------------------- * (HR-LR)
Inflows at lower rate-Inflow at higher rate
6275-5125
= 13 + ---------------- *(20-13)
6275- 4097
= 13 + 5.88
=19%
PAY BACK PERIOD METHOD
Investment - CCFAT
Based period + --------------------------------
Next CFAT
5125 4823
= 4 + ------------------
1254
= 4 + 0.2 = 4.2 years
Return of Investment on cash inflow basis (or) book profit
Average cash inflow
ROI= ---------------------------- * 100
Average Investment
Average cash inflow=11229/10 = 1122.9
Average Investment = 5125/2 = 2563
=1123/2563 *100
= 43.8% (OR) 44%
Project 2
(Estimate budget RS 10250 Lacks)
Years
PBDT
Less
depreciatio
n as per
income tax
PBT
Less Tax
33%
PAT
ADD
Deprec
iation
CFAT
CCFAT
1 3060 3588 -528 -174 -354 3588 3234 3234
2 4560 999 3561 1175 2386 999 3385 6619
3 4560 849 3711 1224 2486 850 3336 9955
4 4860 722 4138 1366 2772 722 3494 13449
5 5160 614 4546 1501 3046 613 3659 17108
6 4560 522 4038 1333 2706 521 3227 20335
7 4950 443 4507 1487 3019 444 3463 23798
8 4560 377 4183 1380 2803 377 3180 26978
9 3630 320 3310 1092 2218 320 2538 29516
10 3930 272 3658 1207 2451 272 2723 32239
Total 43830 8706 35124 11590 23534 8706 32239
Years CFAT CCFAT PV@13% Total PV PV@20% Total pv
1 3234 3234 0.885 2862 0.833 2694
2 3385 6619 0.783 2651 0.694 2349
3 3336 9955 0.693 2311 0.579 1932
4 3494 13449 0.613 2143 0.482 1684
5 3659 17108 0.543 1986 0.401 1471
6 3227 20335 0.480 1550 0.335 1081
7 3463 23798 0.425 1472 0.279 966
8 3180 26978 0.376 1196 0.232 741
9 2538 29516 0.333 845 0.194 492
10 2723 32239 0.295 802 0.162 441
Total 17818 13851
Present value cash inflow = 17818
Present value cash outflow= 10250
PRESENT VALUE METHOD
Net present value= cash inflow-cash outflow
= 17818 - 10250
NPV @ 13% = 7268
PROFITABILITY INDEX
P.I = Total present value of cash inflow/ Total Investment
= 17818/10250
= 1.73 Times
INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (IRR)
Inflows at lower rate-investment
IRR= Lower rate + ---------------------------------------- * (HR-LR)
Inflows at lower rate-Inflow at higher rate
17818 - 10250
= 13 + ------------------ *(20-13)
17818 - 13851
= 26.3%
PAY BACK PERIOD METHOD
Investment - CCFAT
Based period + ---------------------------
Next CFAT
10250 9955
=3 + ------------------
3494
=3 + 0.08 = 3.08 years
Return of Investment on cash inflow basis (or) book profit
Average cash inflow
ROI= ---------------------------- * 100
Average Investment
Average cash inflow=32239/10 = 3223.9
Average Investment = 10250/2 = 5125
=3224/5125 *100
= 63%
Project 3
(Estimate budget RS 4125 Lacks)
Years
PBDT
Less
depreciation
as per income
tax
PBT
Less
Tax
33%
PAT
ADD
Depreciatio
n
CFAT
CCFAT
1 306 1444 -1138 -376 -762 1444 682 682
2 456 402 54 18 36 402 438 1120
3 456 342 114 38 76 342 418 1538
4 486 291 195 64 131 291 422 1960
5 516 247 269 89 180 247 427 2387
6 456 210 246 81 165 210 375 2762
7 495 178 317 105 212 178 390 3152
8 456 152 304 100 204 152 356 3508
9 363 129 234 77 157 129 286 3794
10 393 110 284 94 190 109 299 4093
Total 4383 3505 879 289 589 3504 4093
Years CFAT CCFAT PV@13% Total PV PV@20% Total pv
1 682 682 0.885 604 0.833 568
2 438 1120 0.783 343 0.694 304
3 418 1538 0.693 290 0.579 242
4 422 1960 0.613 259 0.482 203
5 427 2387 0.543 232 0.402 172
6 375 2762 0.480 180 0.335 126
7 390 3152 0.425 166 0.279 109
8 356 3508 0.376 134 0.233 83
9 286 3794 0.333 95 0.194 55
10 299 4093 0.295 88 0.162 48
Total 2391 1910
Present value cash inflow = 2391
Present value cash outflow= 4125
PRESENT VALUE METHOD
Net present value= cash inflow-cash outflow
= 2391 - 4125
NPV @ 13% = -1734
PROFITABILITY INDEX
P.I = Total present value of cash inflow/ Total Investment
= 2391/4125
= 0.58 Times
INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (IRR)
Inflows at lower rate-investment
IRR= Lower rate + ---------------------------------------- * (HR-LR)
Inflows at lower rate-Inflow at higher rate
As a sum of pre discounted cash inflow is less then cost of investment there cant be IRR
(or) IRR < o
PAY BACK PERIOD METHOD
Investment - CCFAT
Based period + ---------------------------
Next CFAT
Total investment has not been realized by the cash inflow. So there is no payback period.
Return of Investment on cash inflow basis (or) book profit
Average cash inflow
ROI= ---------------------------- * 100
Average Investment
Average cash inflow=4094/10 = 409.4
Average Investment = 4125/2 = 2062.5
= 19.8% (OR) 20%
Project 4
(Estimate budget RS 8125 Lacks)
Years
PBDT
Less
depreciation
as per
income tax
PBT
Less
Tax
33%
PAT
ADD
Depreciati
on
CFAT
CCFAT
1 1122 2844 -1722 -568 -1154 2844 1690 1690
2 1672 792 880 290 590 792 1382 3072
3 1672 673 999 330 669 673 1342 4414
4 1782 572 1210 399 811 572 1383 5797
5 1892 487 1405 464 941 487 1428 7225
6 1672 341 1331 439 892 341 1233 8458
7 1815 289 1526 504 1022 289 311 9769
8 1672 246 1426 471 955 246 1201 10970
9 1331 209 1122 350 752 209 961 11931
10 1441 178 1263 417 846 178 1024 12955
Total 16071 9440 12955
Years CFAT CCFAT PV@13% Total PV PV@20% Total pv
1 1690 1690 0.885 1496 0.833 1408
2 1382 3072 0.783 1082 0.694 959
3 1342 4414 0.693 930 0.579 777
4 1383 5797 0.613 848 0.482 667
5 1428 7225 0.543 775 0.402 574
6 1233 8458 0.480 592 0.335 413
7 1311 9769 0.425 557 0.279 336
8 201 10970 0.376 452 0.233 280
9 961 11931 0.333 320 0.194 186
10 1024 12955 0.295 302 0.162 166
Total 12955 77354 5766
Present value cash inflow = 7354
Present value cash outflow= 8125
PRESENT VALUE METHOD
Net present value= cash inflow-cash outflow
= 7354 - 8125
NPV @ 13% = -771
PROFITABILITY INDEX
P.I = Total present value of cash inflow/ Total Investment
= 7354/8125
= 0.9 Times
INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (IRR)
Inflows at lower rate-investment
IRR= Lower rate + ---------------------------------------- * (HR-LR)
Inflows at lower rate-Inflow at higher rate
7354 - 8125
= 13 + ------------------ *(20-13)
7354 - 5766
= 13 + (-3.39)
= 9.6%
PAY BACK PERIOD METHOD
Investment - CCFAT
Based period + ---------------------------
Next CFAT
8125 7225
= 5 + ------------------
1233
= 5 + 0.7
= 5 .7 years
Return of Investment on cash inflow basis (or) book profit
Average cash inflow
ROI= ---------------------------- * 100
Average Investment
Average cash inflow=12955/10 = 1296
Average Investment = 8125/2 = 4062.5
=1296/4063 *100
= 32%
Project 5
(Estimate budget RS 1920 Lacks)
Years
PBDT
Less
depreciatio
n as per
income tax
PBT
Less
Tax
33%
PAT
ADD
Deprecia
tion
CFAT
CCFAT
1 91.8 672 -580.2 -191.5 -388.7 672 283.3 283.3
2 136.8 187 -50.2 -16.6 -33.6 187 153.4 436.7
3 136.8 159 -22.2 -7.3 -14.9 159 144.1 580.8
4 145.8 135 10.8 3.6 7.2 135 142.2 723
5 154.8 115 39.8 13.1 26.7 115 141.7 864.7
6 136.8 98 38.8 12.8 26.0 98 124.0 988.7
7 148.8 83 65.5 21.6 43.9 83 126.9 1115.6
8 136.8 71 65.8 21.7 44.1 71 115.1 1230.7
9 108.9 60 48.9 16.1 32.8 60 92.8 1323.5
10 117.9 51 66.9 22.1 44.8 51 95.8 1419.3
Total 1314.9 1631 -316.1 -104.4 -211.7 1631 1419.3
Years CFAT CCFAT PV@13% Total PV PV@10% Total pv
1 283.3 283.3 0.88496 251 0.90909 257
2 153.4 436.7 0.78315 120 0.82654 127
3 144.1 580.8 0.69305 100 0.75131 108
4 142.2 723 0.61332 87 0.68301 97
5 141.7 864.7 0.54276 77 0.62092 88
6 124.0 988.7 0.48032 60 0.56447 70
7 126.9 1115.6 0.42506 54 0.51361 65
8 115.1 1230.7 0.37616 43 0.46651 54
9 92.8 1323.5 0.33288 31 0.42410 39
10 95.8 1419.3 0.29459 28 0.35009 37
Total 1419.3 851 942
Present value cash inflow = 851
Present value cash outflow= 1920
PRESENT VALUE METHOD
Net present value= cash inflow-cash outflow
= 851 - 1920
NPV @ 13% = -1069
PROFITABILITY INDEX
P.I = Total present value of cash inflow/ Total Investment
= 851/1920
= 0.44 Times
INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN (IRR)
Inflows at lower rate-investment
IRR= Lower rate + ---------------------------------------- * (HR-LR)
Inflows at lower rate-Inflow at higher rate
As a sum of pre discounted cash inflow is less then cost of investment there cant be IRR
(or) IRR < o
PAY BACK PERIOD METHOD
Investment - CCFAT
Based period + ---------------------------
Next CFAT
Total investment has not been realized by the cash inflow. So there is no pay back period.
Return of Investment on cash inflow basis (or) book profit
Average cash inflow
ROI= ---------------------------- * 100
Average Investment
Average cash inflow=1419.3/10 = 141.93
Average Investment = 1920/2 = 960
=141.93/960 *100
= 14.78% (OR) 15%
FINDINGS AND CONCLUSIONS
The study concerned with the capital budgeting with reference to BHEL. The data is
collected, organized, analyzed and interpreted. BHEL has a good organization culture,
excellent working environment and a very precious asset that is highly dedicate, herd-
working, well qualified efficient and knowledgeable workforce.
The following findings are obtained from the analysis of data.
The first project i.e. generate is the unequal cash flows for 10 years. The initial
investment is RS 5125 lacks.
1. The discounted PBP is 4.2 years. The investment will recover in 4 years
and 2 months.
2. NPV and IRR are positive for the proposal. Then the required rate of
return 19%.
3. The profitability index is 1.22 times > 1
4. The return of investment is 44 percentages.
The second project i.e. generate is the unequal cash flows for 10 years. The initial
investment is RS 10250 lacks.
1. The discounted PBP is 3.1 years. The investment will recover in 3 years
and 1 months.
2. NPV and IRR are positive for the proposal. Then the required rate of
return 26.35%.
3. The profitability index is 1.73 times
4. The return of investment is 63 percentages
CONCLUSION
BHEL is the leading Organization in India, and is one among the Navaratna. BHEL
maintains the standard, quality of services and the brand image through its
uncompromising customer service. It has separate finance department which is
entrusted with the task of carrying out its various roles efficiently. The business of
BHEL is carried on in a very scientific manner. The procedure followed in the capital
budgeting of the proposal is in the scientific manner. The Organization also does the
sensitivity analysis so that in case of any contingency the organization will not have
loss. Overall, the financial performance of the organization is very well as it is having a
continuous growth.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Assignment - Group 6 - Case Analysis (Investment Analysis and Lockheed Tristar)Document6 paginiAssignment - Group 6 - Case Analysis (Investment Analysis and Lockheed Tristar)Rajat Gupta100% (4)
- Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual For MST SWGRDocument105 paginiInstallation, Operation and Maintenance Manual For MST SWGRAkicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Plan Led LightingDocument115 paginiBusiness Plan Led LightingAARON HUNDLEYÎncă nu există evaluări
- In Partial Fulfillment For The Award of The Degree Of: "Capital Budgeting"Document108 paginiIn Partial Fulfillment For The Award of The Degree Of: "Capital Budgeting"amitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research and Thesis On Earthing System in LV NetworksDocument87 paginiResearch and Thesis On Earthing System in LV NetworksEngr Gulfam80% (5)
- Chapter 17 Electric Fields PDFDocument43 paginiChapter 17 Electric Fields PDFPathmanathan NadesonÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Elec) Generator Excitation SystemDocument51 pagini(Elec) Generator Excitation SystemThanh Son100% (1)
- Solar Power Generation PlantDocument37 paginiSolar Power Generation Plantshani27100% (8)
- Module 1-WESM FundamentalsDocument39 paginiModule 1-WESM FundamentalsbertovalenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-Ii Project Evaluation: 16 MarksDocument13 paginiUnit-Ii Project Evaluation: 16 MarksVidhya100% (1)
- Engineering MCQs ThermodynamicsDocument16 paginiEngineering MCQs ThermodynamicsTinku Mittal83% (6)
- Improving Energy Efficiency and Reducing Emissions through Intelligent Railway Station BuildingsDe la EverandImproving Energy Efficiency and Reducing Emissions through Intelligent Railway Station BuildingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project FinanceDocument18 paginiProject FinanceJay RanvirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Finance: Valuing Unlevered ProjectsDocument41 paginiProject Finance: Valuing Unlevered ProjectsKelsey GaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MarketingDocument40 paginiMarketingnprash123Încă nu există evaluări
- Project Report On: Larsen & Toubro Limited (L&T)Document31 paginiProject Report On: Larsen & Toubro Limited (L&T)rohitghulepatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Appraisal of Water Treatment FacilityDocument20 paginiFinancial Appraisal of Water Treatment FacilitySarthakAryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChandanDocument28 paginiChandanSakshi GoelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investment Decision QuestionsDocument44 paginiInvestment Decision QuestionsAkash JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 36 - Battery Eliminator by Rakesh KumarDocument15 pagini36 - Battery Eliminator by Rakesh KumarAbdu SamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- New & Renewable Energy: Presentation byDocument30 paginiNew & Renewable Energy: Presentation byDebasmita PandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HMM 409 Project Management Unit - 2Document46 paginiHMM 409 Project Management Unit - 2Shivam SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Report On The Neogi Chemical CompanyDocument7 paginiProject Report On The Neogi Chemical Companyabhisheknagpal27Încă nu există evaluări
- "Working Capital": A Project Report On GNFCDocument13 pagini"Working Capital": A Project Report On GNFCEr Priti SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- InternshipDocument17 paginiInternshipHimanshu Sekhar GuruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apex Industries Business Plan SummaryDocument25 paginiApex Industries Business Plan Summarybhavesh_mankani7373Încă nu există evaluări
- BITS Pilani Distance Learning Project Appraisal ExamDocument3 paginiBITS Pilani Distance Learning Project Appraisal Examrajpd28Încă nu există evaluări
- TI India - PPT - Oct 12Document60 paginiTI India - PPT - Oct 12vishmittÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task1: Comparison of Two Competing Investment Projects in Private and Public SectorDocument5 paginiTask1: Comparison of Two Competing Investment Projects in Private and Public SectorYogirajsinh GohilÎncă nu există evaluări
- RAPDRP Part-B implementation and impact in MPPKVVCL IndoreDocument20 paginiRAPDRP Part-B implementation and impact in MPPKVVCL IndoreArvind YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 - Adv Issues in Cap BudgetingDocument17 pagini01 - Adv Issues in Cap BudgetingMudit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Task No.1: Course Title Course CodeDocument9 paginiAssignment Task No.1: Course Title Course CodeKunchala SwathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Second Power System Development (Loan 1121-MLD (SF) )Document40 paginiSecond Power System Development (Loan 1121-MLD (SF) )Independent Evaluation at Asian Development BankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Source: Funding ProposalDocument29 paginiProject Source: Funding Proposalheena23Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No. 1Document8 paginiAssignment No. 1Babar AdeebÎncă nu există evaluări
- PAT TrainingDocument40 paginiPAT TrainingLokesh ChourasiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Other Supporting Docs NeededDocument33 paginiOther Supporting Docs NeededMark Ivan JagodillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Petronet Corporate Presentation June 2011Document34 paginiPetronet Corporate Presentation June 2011veeruduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sadbhav Engineering: Performance HighlightsDocument13 paginiSadbhav Engineering: Performance HighlightsAngel BrokingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company Name: Shivalik Bimetal Controls LTDDocument4 paginiCompany Name: Shivalik Bimetal Controls LTDSandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final BUSINESS PLAN FOR CONNS LIMITEDDocument66 paginiFinal BUSINESS PLAN FOR CONNS LIMITEDOwunari Adaye-Orugbani100% (1)
- Main Project Capital Budgeting MbaDocument110 paginiMain Project Capital Budgeting Mbasushain koulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13Document34 paginiChapter 13Aryan JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capital BudgetingDocument48 paginiCapital BudgetingVIVEK JAISWAL100% (1)
- FM ProjectDocument10 paginiFM ProjectriyapantÎncă nu există evaluări
- SelectionDocument8 paginiSelectionpradeep_mi2014Încă nu există evaluări
- EFM - Capital Budgeting Techniques Ctnd. - Lec 12-MSESPM2019Document60 paginiEFM - Capital Budgeting Techniques Ctnd. - Lec 12-MSESPM2019Raut SumeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sadbhav Engg, 1Q FY 2014Document13 paginiSadbhav Engg, 1Q FY 2014Angel BrokingÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Global Air Conditioning and Engineering Services CompanyDocument50 paginiA Global Air Conditioning and Engineering Services Companyraj_mrecj6511Încă nu există evaluări
- Analyst Meet 2013Document44 paginiAnalyst Meet 2013anon_481361080Încă nu există evaluări
- Slides of NPV, Free Cash Flow, Sensitivity Analysis Project DecisionsDocument57 paginiSlides of NPV, Free Cash Flow, Sensitivity Analysis Project DecisionsSebastian GorhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wijaya Karya: Facing HeadwindsDocument5 paginiWijaya Karya: Facing HeadwindsDediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Main Project Capital Budgeting MbaDocument110 paginiMain Project Capital Budgeting MbaRaviKiran AvulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capital Budgeting Illustrative NumericalsDocument6 paginiCapital Budgeting Illustrative NumericalsPriyanka Dargad100% (1)
- DPR For Ahmedabad Pharma Machinery ClusterDocument32 paginiDPR For Ahmedabad Pharma Machinery ClusterGaurav VaghelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 - Capital Budgeting - 3A - Questions 2022-23Document10 paginiModule 3 - Capital Budgeting - 3A - Questions 2022-23Manya GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capital BudgetingDocument26 paginiCapital BudgetingGowryshankar SumatharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nagarjuna Construction (NAGCON) : Rising Debt Level To Restrict Earnings GrowthDocument6 paginiNagarjuna Construction (NAGCON) : Rising Debt Level To Restrict Earnings GrowthEquity DynamicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Management Tutorial 2 AnswersDocument6 paginiFinancial Management Tutorial 2 AnswersDelfPDF100% (2)
- LeadacidbatteryDocument20 paginiLeadacidbatteryanilÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Capital Budgeting and Cost of CapitalDocument50 paginiInternational Capital Budgeting and Cost of CapitalGaurav Kumar100% (2)
- IVRCL Infrastructure: Performance HighlightsDocument12 paginiIVRCL Infrastructure: Performance HighlightsAngel BrokingÎncă nu există evaluări
- New In-Principle Approval Format Bank of BarodaDocument13 paginiNew In-Principle Approval Format Bank of BarodaPriyanka VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LNT AnalysisDocument7 paginiLNT AnalysisGagan KarwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The CDMDocument20 paginiThe CDMapi-3700769Încă nu există evaluări
- Acf302: Corporate Finance: Capital Budgeting and Valuation With Leverage - Part IDocument43 paginiAcf302: Corporate Finance: Capital Budgeting and Valuation With Leverage - Part IXue Meng LuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre AssessmentDocument9 paginiPre AssessmentVenkatramana KÎncă nu există evaluări
- HR Recruiter Jobs in Bengaluru for TTK ServicesDocument3 paginiHR Recruiter Jobs in Bengaluru for TTK ServicesVenkatramana KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kittu PublicationDocument3 paginiKittu PublicationVenkatramana KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Commission On The Promotion of Business Jets Interim Report: June 2011Document17 paginiCommission On The Promotion of Business Jets Interim Report: June 2011Venkatramana KÎncă nu există evaluări
- APSPDCLDocument1 paginăAPSPDCLVenkatramana KÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSD JD Oct 13thDocument2 paginiMSD JD Oct 13thVenkatramana KÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSD JD Oct 13thDocument2 paginiMSD JD Oct 13thVenkatramana KÎncă nu există evaluări
- S.No: HR Tele Callers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8Document1 paginăS.No: HR Tele Callers 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8Venkatramana KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Receipt 888912985265Document1 paginăReceipt 888912985265Venkatramana KÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.5 Electric MotorsDocument64 pagini1.5 Electric MotorsLeojhun PalisocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Your Electricity BillDocument8 paginiYour Electricity BillE EeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Gigih Udi Atmo - Overview of Electric Vehicles Development in APECDocument23 paginiDr. Gigih Udi Atmo - Overview of Electric Vehicles Development in APECArfie IkhsanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Siemens Substation Pi enDocument8 paginiSiemens Substation Pi enSbase ventilacionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Electromagnetic Engine, No Fuel ConsumptionDocument11 paginiDesign of Electromagnetic Engine, No Fuel ConsumptionKaran SaharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jndal Power ResumeDocument2 paginiJndal Power ResumeRahul Kumar YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 Model 3 LR: Nominal Full Pack (KWH) - Predicted Range (KM) vs. Driven DistanceDocument5 pagini2021 Model 3 LR: Nominal Full Pack (KWH) - Predicted Range (KM) vs. Driven DistanceYosi SoltÎncă nu există evaluări
- Productbrochurev52 UKDocument6 paginiProductbrochurev52 UKjavier8970Încă nu există evaluări
- Part-3 Electric DrivesDocument46 paginiPart-3 Electric Drivesankushff7872Încă nu există evaluări
- 30 Steps For Correct Sequence For Starting Steam Turbine - AskpowerplantDocument10 pagini30 Steps For Correct Sequence For Starting Steam Turbine - Askpowerplantlara noorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Office of The Building OfficialDocument2 paginiOffice of The Building OfficialJanico Lanz BernalÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Potential of Earth-Air Heat Ex Changers For Low Energy Cooling of BuildingsDocument2 paginiThe Potential of Earth-Air Heat Ex Changers For Low Energy Cooling of BuildingsCristi IonescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 2 General InformaionsDocument6 paginiChapter - 2 General InformaionsJahangir AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lampiran 8. Cost BlastingDocument1 paginăLampiran 8. Cost BlastingSundek HariyadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ifyil Katalog Eng 2017Document17 paginiIfyil Katalog Eng 2017DanSailaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Variable Speed DC Compressors and Condensing UnitsDocument16 paginiVariable Speed DC Compressors and Condensing UnitsFEF777Încă nu există evaluări
- 2008 Shell Eco Marathon Americas ResultsDocument2 pagini2008 Shell Eco Marathon Americas Resultsncwilde43Încă nu există evaluări
- Hipot Test VT Reading Sample For GisDocument1 paginăHipot Test VT Reading Sample For GisNOWFALÎncă nu există evaluări
- UBI BrochureDocument2 paginiUBI BrochureDEEPAKÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAF-WEEKLY ASSESSMENT 8-Advantages and Disadvantages of Series and Parallel ConnectionDocument2 paginiMAF-WEEKLY ASSESSMENT 8-Advantages and Disadvantages of Series and Parallel ConnectionMarissa FontanilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 10Document6 paginiUnit 10Hà Thu NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indoor Surge Arresters-Model - SPFDocument3 paginiIndoor Surge Arresters-Model - SPFSOUMENÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9A10705 Power Plant InstrumentationDocument4 pagini9A10705 Power Plant InstrumentationsivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classified Paper 4 (2021)Document406 paginiClassified Paper 4 (2021)Sir AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări