Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Motion
Încărcat de
Harsh ChaddaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Motion
Încărcat de
Harsh ChaddaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
NAME DEEPANSHU BAJAJ
CLASS 9
th
A
ROLL NO. -14
TOPIC
MOTI ON
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I WHOLE HEARTEDLY THANK MY
COMPUTER TEACHER
MRS.J ASJ EET FOR GI VI NG SUCH A
KNOWLEDGEFUL PROJ ECT.I TOOK
HELP OF I NTERNET,DI FFERENT
BOOKS AND MY PARENTS.
A body is said to be in motion when its position
changes continuously with respect to a stationary
object taken as reference point .
Uniform Motion
A body is said to be in
uniform motion when it
travels equal distances in
equal intervals of time.
Non-Uniform
Motion
A body is said to be in
non-uniform motion
when it travels unequal
distance in equal
intervals of time.
Distance
time graph
in uniform
motion
The distance - time
graph is for uniform
motion in a straight
line.
For example , a car
running at a constant
speed say ,10 metres
per second, will cover a
distance of 10 metres ,
every sec every second,
so its motion will be so
uniform.
graph in
non
uniform
motion
The distance
time graph for a
body having non
uniform motion
is a curved line.
The motion of a
free falling body
is an example of
non uniform
motion.
Speed is the distance travelled by it per unit
time .the SI Unit of speed is meter per
second square .Speed is of two types-
UNIFORM and NON UNIFORM.
UNIFORM SPEED-IF a body covers equal
distances in equal intervals of times.
Non uniform speed-if a body covers unequal
distances in equal intervals of time.
Simple harmonic motion (e.g. pendulum).
Linear motion motion which follows a straight linear path, and
whose displacement is exactly the same as its trajectory.
Reciprocating (i.e. vibration)
Brownian Motion (i.e. the random movement of particles)
Circular motion (e.g. the orbits of planets)
Rotary motion a motion about a fixed point ex. the wheel of a
bicycle
Curvilinear Motion It is defined as the motion along a curved
path that may be planar or in three dimensions.
uniform motion
THERE ARE THREE EQUATIONS
OF MOTION WHICH HELPS US IN
CALCULATING PROBLEMS
RELATED TO MOTION. THESE
ARE
1V=U+AT
2S=UT+A*T*T/2
3V*V-U*U=2AS
Description of Motion in One Dimension
Motion is described in terms of displacement (x), time (t), velocity (v),
andacceleration (a). Velocity is the rate of change of displacement
and the acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. The average
velocity and average acceleration are defined by the relationships
THE END
THANK YOU
I HOPE YOU LI KED
THE
PRESENTATI ON.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Descriptors of MotionDocument30 paginiDescriptors of MotionCamilleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greek Views On MotionDocument26 paginiGreek Views On MotionElvira Sta. MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plates BoundariesDocument13 paginiPlates BoundariesMarife GuadalupeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Balanced and Unbalanced ForcesDocument31 paginiBalanced and Unbalanced ForcesInah MasubayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Describing Motion (Grade 7)Document18 paginiDescribing Motion (Grade 7)Genelyn Borja100% (1)
- Origin of The UniverseDocument45 paginiOrigin of The UniverseSheena Jane Tioc100% (1)
- Plate BoundariesDocument55 paginiPlate BoundariesnoliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mountain Building PowerpointDocument26 paginiMountain Building Powerpointjoie gucci100% (3)
- Earth and Its SubsystemDocument18 paginiEarth and Its SubsystemFabelina Bunoan MaricarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Origin of The Universe PPT Earth and Life ScienceDocument33 paginiOrigin of The Universe PPT Earth and Life ScienceCarlos TuazonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Law of Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagini1st Law of Motion WorksheetMelanie TrinidadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Land and Sea Breezes Monsoon Cold and Warm Fronts ItczDocument40 paginiLand and Sea Breezes Monsoon Cold and Warm Fronts ItczJeric ValdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distance Vs DisplacementDocument13 paginiDistance Vs DisplacementDominador Masirag100% (1)
- Science 8 Learning Enrichment Module (REVISED)Document53 paginiScience 8 Learning Enrichment Module (REVISED)Ken Mitchell MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 2 Universe and Solar SystemDocument44 paginiLesson 2 Universe and Solar SystemJelson Castro IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Force and Motion PowerPointDocument13 paginiForce and Motion PowerPointMark Cliffton BadlonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of The AtomDocument114 paginiStructure of The AtomRaja Ina100% (1)
- Layers of The AtmosphereDocument19 paginiLayers of The AtmosphereDeevie R. DecioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theories: N The Origin of TheDocument30 paginiTheories: N The Origin of TheKyan PanganibanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Work Energy and PowerDocument15 pagini4 Work Energy and PowerReyzel Anne FaylognaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GravitationDocument14 paginiGravitationpradyumna bhideÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP PS 48 Ma. Elizabeth S. AraraoDocument4 paginiDLP PS 48 Ma. Elizabeth S. AraraoJose Benavente100% (1)
- CellsDocument18 paginiCellsapi-272901382Încă nu există evaluări
- Processes and Landforms Along Plate BoundariesDocument47 paginiProcesses and Landforms Along Plate BoundariesMille GrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do Now:: What Is Motion? Describe The Motion of An ObjectDocument22 paginiDo Now:: What Is Motion? Describe The Motion of An ObjectJoan Melendres100% (1)
- Balanced and Unbalanced Forces and Net Force Notes PowerpointDocument27 paginiBalanced and Unbalanced Forces and Net Force Notes PowerpointJeiril Divino100% (1)
- States (Phases) of Matter: Science 6Document14 paginiStates (Phases) of Matter: Science 6Zahid MahmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors That Affect ClimateDocument31 paginiFactors That Affect ClimateRitchelle PerochoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Costellation ActivityDocument4 paginiCostellation ActivityFranz Dominic Laus100% (1)
- Elements and CompoundsDocument8 paginiElements and CompoundsJerry De Leon TaayÎncă nu există evaluări
- AtomDocument4 paginiAtomanjaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1-The Formation of The UniverseDocument41 paginiLesson 1-The Formation of The UniverseRaymond EscuzarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Momentum and Impulse WorksheetDocument1 paginăMomentum and Impulse WorksheetCurtis CollinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Branches of Science PPTDocument19 paginiThe Branches of Science PPTRonielyn CasullaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laws of MotionDocument17 paginiLaws of MotionGraceyxie GrasyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument4 paginiChapter 1 Matter in Our SurroundingsManash SinghaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4thQ Week1 PPT DigestiveDocument49 pagini4thQ Week1 PPT DigestiveGeronimo SantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth & Life Science (Las 1-2)Document4 paginiEarth & Life Science (Las 1-2)Jhev LeopandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument21 paginiNewton's Laws of MotionharlequinlhaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laws of MotionDocument18 paginiLaws of MotionJhen BonÎncă nu există evaluări
- EARTH SCIENCE. Lesson 1 - Universe & Solar SystemDocument65 paginiEARTH SCIENCE. Lesson 1 - Universe & Solar SystemJeydibi MharjomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Particulate Nature of MatterDocument12 paginiParticulate Nature of Matterpaul enrileÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Science 7 Week 1-2Document4 paginiEnvironmental Science 7 Week 1-2cathlyn ranarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument46 paginiThe Particulate Nature of MatterDinara Dzhakishova100% (1)
- Locating Places q4 Module 1Document21 paginiLocating Places q4 Module 1Sweetie Wilgee Rose ViñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coastal Processes and HazardDocument25 paginiCoastal Processes and HazardJonard Flores100% (1)
- WavesDocument48 paginiWavesJun Perez0% (1)
- The Invisible World Through The Lens of ADocument12 paginiThe Invisible World Through The Lens of AChristine DamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion in Two DimensionDocument34 paginiMotion in Two DimensionMarArizalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure PowerpointDocument13 paginiAtomic Structure PowerpointMary TaklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Locating Places On EarthDocument59 paginiLocating Places On EarthRasay Michelle BalbidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan in Science 7Document10 paginiLesson Plan in Science 7Maricel AlcoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.introduction of Earth ScienceDocument34 pagini1.introduction of Earth ScienceIvanReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continental Drift PowerPointDocument17 paginiContinental Drift PowerPointNatasha Liliane LootÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument26 paginiMatter in Our SurroundingsULTRA BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3-Evolution, Species Interactions, and Biological CommunitiesDocument5 paginiChapter 3-Evolution, Species Interactions, and Biological CommunitiesKiana HolmesÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Causes SeasonsDocument15 paginiWhat Causes SeasonsSteve GraffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kenetic and Potential Energy PowerpointDocument27 paginiKenetic and Potential Energy Powerpointbarcelot tortogoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion and Rest: Made by Sarthak KumarDocument18 paginiMotion and Rest: Made by Sarthak KumarAnonymous AQPr7tkSBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion Combine For Sankalp TeleDocument81 paginiMotion Combine For Sankalp TeleDivyansh RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 1 Read PDFDocument14 paginiTest 1 Read PDFHarsh ChaddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 1 ReadDocument12 paginiTest 1 ReadHarsh ChaddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 1 Read PDFDocument14 paginiTest 1 Read PDFHarsh ChaddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Window AccessoriesDocument9 paginiWindow AccessoriesHarsh ChaddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Book 5 Test ADocument2 paginiBook 5 Test AHarsh ChaddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 1 ReadDocument14 paginiTest 1 ReadHarsh ChaddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RS Monthly Stock and Sales ReportDocument14 paginiRS Monthly Stock and Sales ReportHarsh ChaddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Aid Pocket GuideDocument24 paginiFirst Aid Pocket GuideHarsh Chadda67% (3)
- 005 - Fuel Design Requirements - Al ManzerDocument26 pagini005 - Fuel Design Requirements - Al ManzerGeorge CălinÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCM-Manual 0507Document32 paginiPCM-Manual 0507PamellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDS - GulfSea Synth Compressor Oil 46 68Document2 paginiPDS - GulfSea Synth Compressor Oil 46 68Md.Obydur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zes Lmg500 Datasheet eDocument12 paginiZes Lmg500 Datasheet eJuan Carlos Añazco PazosÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME460 Exam No. 2: NameDocument1 paginăME460 Exam No. 2: NameSayyadh Rahamath BabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meter L&TDocument12 paginiMeter L&TnenusakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ms6001b Operation DescriptionDocument53 paginiMs6001b Operation Descriptionprasad503486% (7)
- Form Rumusan Makalah Seminar InternasionalDocument3 paginiForm Rumusan Makalah Seminar InternasionalMiedson miedsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building The Foundation - : On Scene Commander Development ProgramDocument4 paginiBuilding The Foundation - : On Scene Commander Development ProgramSaran rasayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIL-H-5440G Hydraulic Systems, AircraftDocument49 paginiMIL-H-5440G Hydraulic Systems, AircraftRonny Valero Montoya0% (1)
- Kirlosker Pump Selection Models PDFDocument36 paginiKirlosker Pump Selection Models PDFgarimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH8251-Material Science QN Bank ValliammaiDocument10 paginiPH8251-Material Science QN Bank ValliammaiThaya GanapathyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alternative Propulsion For Automobiles by Cornel StanDocument348 paginiAlternative Propulsion For Automobiles by Cornel StanThuận Vũ Đình100% (1)
- The Future of The Automobile Industry in India - McKinseyDocument13 paginiThe Future of The Automobile Industry in India - McKinseyDhiraj KhotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Keitai LED Catalogue 2011-2012Document85 paginiKeitai LED Catalogue 2011-2012Adam McConnellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer Cooling MethodsDocument4 paginiTransformer Cooling MethodsZappa VaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Shett Do Atenuador VaristorDocument13 paginiData Shett Do Atenuador VaristorTiagohowpy RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machine - 2 Lab ManualDocument50 paginiElectrical Machine - 2 Lab ManualMohit ChetiwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oisd 142Document170 paginiOisd 142poojaupes100% (2)
- Influence MN S Properties Cast IronDocument14 paginiInfluence MN S Properties Cast Ironvivek1312Încă nu există evaluări
- Weld Quality PDFDocument31 paginiWeld Quality PDFNaceur TurkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 36-775 Control of Plant Construction Repair and Maintenance Welding Activities (Rev 1)Document22 pagini36-775 Control of Plant Construction Repair and Maintenance Welding Activities (Rev 1)Vinoth Rajendra100% (1)
- CP132 SN 2162BR2036Document120 paginiCP132 SN 2162BR2036Ovh MaquinariasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task 1Document6 paginiTask 1ashkar aliÎncă nu există evaluări
- JPR 54079 DailmerAG EquityResearch Report 1303Document35 paginiJPR 54079 DailmerAG EquityResearch Report 1303André Fonseca100% (1)
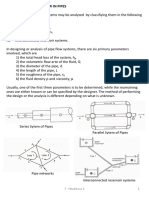
- ME303 7 Head Loss 2 BranchedDocument39 paginiME303 7 Head Loss 2 BranchedtoshugoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LC1044 LRP14 3PH QRG 0823Document2 paginiLC1044 LRP14 3PH QRG 0823FlakooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automatic Drainage Cleaning Machine Run Through Solar PowerDocument8 paginiAutomatic Drainage Cleaning Machine Run Through Solar Powervikalpsharma96Încă nu există evaluări
- Acb Terasaki ManualDocument114 paginiAcb Terasaki ManualTuấn TrầnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resolver Vs EncoderDocument7 paginiResolver Vs EncoderAmirtha swamy.nÎncă nu există evaluări