Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Antropometrik Anak - PPTX (Repaired)
Încărcat de
lukinanda0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
31 vizualizări52 paginiAntropometrik Anak
Titlu original
Antropometrik Anak.pptx [Repaired]
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentAntropometrik Anak
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
31 vizualizări52 paginiAntropometrik Anak - PPTX (Repaired)
Încărcat de
lukinandaAntropometrik Anak
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 52
ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENT AND GROWTH
MONITORING IN NORMAL CHILDREN
Anthropometric Measurement
A part of well baby clinics
To detect growth faltering
To measure the prevalence of under nutrition
and over nutrition
To identify groups with increased nutritional
and health need.
Growth chart application
CDC Growth charts
WHO growth charts, 2005
Is my child growing well ?
Is my child growing well ?
Is my child short ?
What should be done to make my child
taller ?
Is children growth in different manner
If the parents are short, will all my
children became short ?
Evaluation of growth
Anthropometry: reliability
training
equipment
Plotting
Absolute height
Evaluation of growth
Height velocity
Measurement at 6 mos interval
Deceleration / crossing centiles age 3-12 yrs: indicates
pathologic until proven otherwise
Normal velocity indicates normal growth
Weight / height relationship
W/H ratio: suggestive endocrine causes
W/H ratio: suggestive systemic disease
Growth Phase
Infants
Deceleration
50% during 1
st
year
25% of 1
st
year growth
during 2
nd
year
Childhood
Constant 5-7 cm / year
Puberty
Acceleration
Deceleration
Halt
Interaction between GH and
sex steroids
Growth monitoring
Effective growth monitoring needs
Precise measurement
Accurate plotting on a chart
Correct interpretation
Plan of investigation
School entry measurement best
opportunity to detect growth disorder
Periodic assessment of child growth
Maintain or improve growth and health
Growth monitoring should not be a stand alone
activity, but part of broader community based
programme to improve primary health care,
education and sanitation.
Growth monitoring
NORMAL GROWTH :
When weight and height/length track along similar
percentiles or growth channels
Canadian Pediatric Society, Dietitians of Canada and Health Canada. Nutritional for healthy
infants, Minister of Public Works and Government Services, 1998
Hal-hal yang perlu dipantau dalam
pertumbuhan seorang anak
2 tahun pertama kehidupan:
Tinggi badan (TB/U), Berat badan (BB/U), BB/PB,
body mass index (BMI/U), dan lingkar kepala
(LK/U)
Usia 2-10 tahun:
TB/U, BB/U, dan BMI/U
Usia > 10 tahun:
Hal-hal diatas (2-10 th)
Penilaian perkembangan status pubertas anak
McGraw-Hill Copyright 2002
Measuring Body Weight
Electronic digital scales, calibrated
in metric units are recommended.
Chair scales are available for those
who are not capable of standing.
Weight Measurement
Weight Measurement
Measuring Growth in Length and
Stature
Recumbent length is measured from birth until a
child is able to stand
Measured from the vertex (highest point on skull) to the
soles of the feet
Length Measurement
Height Measurement
Measuring height
Measuring height is subject to error as a
result of
poor technique,
variations between instruments and observers,
diurnal variation
plotting mistakes
Single height measurement
Will identify only stature
Very short/tall child
Will not identify process of growth
Children growing slowly (CHD)
Turner syndrome
Acquired disorder : hypothyroidism, coeliac disease
Children growth crossing centiles
How many times height should be
measured ?
Consensus
Routinely up to 2 years
0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24 mos
Every 6 month up to 6 years
Every year up to 18 years
Additional parameter for
evaluation of growth
Target height
Boy = Fh+(Mh+13)
2
Girl= (Fh-13)+Mh
2
Mid parental height
Genetic height potential
Prediction of final height
5 Directory of Growth
1. Catch-up growth
2. Normal growth
3. Growth faltering
4. Flat growth
5. Loss of growth
Algorithm of Growth Monitoring
Weighing
Plotting
Make curve
Interpretatio
n
Increase
Not Increase
Identification of the problem
Solution
Evaluation
Not Increase
Catch-up Growth
Normal Growth
Growth Faltering
Flat Growth
Loss of Growth
Increase
Indices derived from growth
measurement
Constructed from two or more raw
anthropometric measurement and are simple
numerical ratio
Weight / Height
2
(BMI)
W for A : H for A : W for H
Essential part of the interpretation of
anthropometric measurement
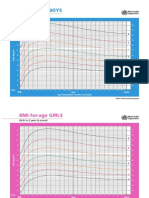
CDC GROWTH CHARTS
CDC Growth Charts
Based on American population 1977
White
Hispanic
Black
Asian
First growth charts without BMI charts,
then in 2002 BMI is included
WHO growth charts
Based on 18 cities in the world
First part 2005
Only for 1 5 years boys and girls
Nutricia workshop, 16 sept 2006 Malang
IMT WHO dan CDC
Nutritional
Status
IMT WHO
2006
(0-5 th)
IMT WHO 2007
(5-19 th)
IMT CDC
2000
(2-20 th)
Obesitas > +3 > +2 SD > P 95
Overweight +2 SD s/d +3
SD
> +1 SD P 85 p 95
Normal -2 SD s/d +2
SD
-2 SD s/d +2 SD P 3 - < p 85
Rekomendasi Klasifikasi Status Gizi
Status Gizi BB/TB
(% median)
BB/TB
WHO 2006
IMT CDC
2000
Obesitas > +3 > P 95
Overweight > +2 SD hingga +3 SD > P 85 P 95
Normal >90% -2SD hingga +2 SD
Gizi Kurang 70-90% -2 SD hingga -3 SD
Gizi buruk < 70% < - 3SD
Indikator Pertumbuhan
Z-score TB/PB menurut
usia
BB menurut
usia
BB/PB atau BB/TB BMI menurut usia
>3
>2
>1
0 (median)
Di bawah
-1
Di bawah
-2
Di bawah
-3
Pendek
(stunted)
Sangat pendek
(severely
stunted)
BB kurang
(underweight)
BB sangat
kurang
(severely
underweight)
Sangat gemuk
(obese)
Gemuk
(overweight)
Kemungkinan
risiko overweight
Kurus (wasted)
Sangat Kurus
(severely wasted)
Sangat gemuk
(obese)
Gemuk
(overweight)
Kemungkinan
risiko overweight
Kurus (wasted)
Sangat Kurus
(severely wasted)
Interpretasi Indikator Pertumbuhan WHO
Child Growth Standards
2014 03 01
2013 02 01
1 01 usia kronologis
01
Usia 1 th / 12 bln
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Growth MonitoringDocument77 paginiGrowth MonitoringPriti KhemkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 - Assessment of Growth and It's Abnormality, Dr.S.yudha Patria, Sp.a (K) ., PH.D (2021)Document58 paginiLecture 2 - Assessment of Growth and It's Abnormality, Dr.S.yudha Patria, Sp.a (K) ., PH.D (2021)Dzaki Prakoso RamadhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth: Increase in The Physical Size of The Body As Whole or Any of Its PartsDocument4 paginiGrowth: Increase in The Physical Size of The Body As Whole or Any of Its PartsAleenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identifying Poor Growth in Infants and ToddlersDocument15 paginiIdentifying Poor Growth in Infants and Toddlersriena456Încă nu există evaluări
- Pertemuan 5Document38 paginiPertemuan 5arÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Growth. Growth Disorders UpdateDocument57 paginiChild Growth. Growth Disorders UpdateShahpoor Ahmad ShirzadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth Charts For Children With Down Syndrome CanDocument12 paginiGrowth Charts For Children With Down Syndrome CanAfiqah So JasmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth Chart Differences WHO vs CDCDocument9 paginiGrowth Chart Differences WHO vs CDCkhoangmuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sharing Nutrition StatusDocument17 paginiSharing Nutrition StatusfirdakusumaputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Approach To Children and Adolescents With Short Stature - UpToDateDocument30 paginiDiagnostic Approach To Children and Adolescents With Short Stature - UpToDateadityoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth MonitoringDocument36 paginiGrowth MonitoringAugustus CaesarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CDC Growth Charts 2000: Centers For Disease Control and PreventionDocument47 paginiCDC Growth Charts 2000: Centers For Disease Control and PreventionJuita Auglina PasaribuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Growth and It's Abnormality - Hypothyroidism, Short Stature, EtcDocument56 paginiAssessment of Growth and It's Abnormality - Hypothyroidism, Short Stature, EtcKeya SakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth Monitoring 1Document56 paginiGrowth Monitoring 1hafeesadetunji01Încă nu există evaluări
- Experiment-7 Plotting and Interpretation of Growth CurveDocument8 paginiExperiment-7 Plotting and Interpretation of Growth Curvekanishka upadhyayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Approach To Children and Adolescents With Short Stature - UpToDateDocument27 paginiDiagnostic Approach To Children and Adolescents With Short Stature - UpToDateDiego Tzompa AcostaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CDC Growth Charts 2000: Centers For Disease Control and PreventionDocument47 paginiCDC Growth Charts 2000: Centers For Disease Control and PreventionZhwan AnwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Growth & DevelopmentDocument57 paginiLecture Growth & Developmentatharvasood2004Încă nu există evaluări
- Normal Growth Patterns in Infants and Prepubertal ChildrenDocument15 paginiNormal Growth Patterns in Infants and Prepubertal Childrenedu2029Încă nu există evaluări
- Anthropometric Measurements, Plotting and InterpretationDocument31 paginiAnthropometric Measurements, Plotting and Interpretationokwadha simionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter1 UnlockedDocument14 paginiChapter1 UnlockedLe HuyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutritional Status of Pre-School Children From Low Income FamiliesDocument11 paginiNutritional Status of Pre-School Children From Low Income FamiliesFiraz R AkbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penilaian Antropometri Remaja & DewasaDocument130 paginiPenilaian Antropometri Remaja & DewasaFathimah UswahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obesitas Pada Anak: DR - Sri S.Nasar, Spa (K)Document27 paginiObesitas Pada Anak: DR - Sri S.Nasar, Spa (K)Andrie WigunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition AssessmentDocument47 paginiNutrition AssessmentMohamed F. Nada100% (6)
- ObesityDocument35 paginiObesitysohilaw210Încă nu există evaluări
- Child Development GuideDocument3 paginiChild Development GuideAbu Bakarr SesayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prevent L-1Document31 paginiPrevent L-1Sara SalemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth MonitoringDocument34 paginiGrowth MonitoringSamana DuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth & Development Assessment: Desti HandayaniDocument49 paginiGrowth & Development Assessment: Desti HandayaniReffa Rizkyani IrawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Growth AND Puberty: Aditiawati Division of Pediatric Endocrinology Dept of Child Health FK Unsri-RSMHDocument77 paginiPhysical Growth AND Puberty: Aditiawati Division of Pediatric Endocrinology Dept of Child Health FK Unsri-RSMHAudrey Ira YunitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessing Nutrition Through Growth Measurement and StandardsDocument8 paginiAssessing Nutrition Through Growth Measurement and StandardsRavikumar ChodavarapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weight Status Category Percentile Range Underweight Normal or Healthy Weight 5th Percentile To Less Than The 85th Percentile Overweight ObeseDocument3 paginiWeight Status Category Percentile Range Underweight Normal or Healthy Weight 5th Percentile To Less Than The 85th Percentile Overweight Obese7ATUTORIALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obesity Prevention and Education For School Nurses Community Health NursingDocument66 paginiObesity Prevention and Education For School Nurses Community Health NursingGabrielaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obesity Presentation-640Document12 paginiObesity Presentation-640api-284092317Încă nu există evaluări
- Weight For Length 2015Document8 paginiWeight For Length 2015Apple BalaisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Failure To Thrive: Nutrition and Metabolic Disease Division Department of Pediatrics University of Sumatera UtaraDocument29 paginiFailure To Thrive: Nutrition and Metabolic Disease Division Department of Pediatrics University of Sumatera Utarasantayohana0% (1)
- Short Stature PDFDocument17 paginiShort Stature PDFNiranjan Hegde100% (1)
- Nutritional Disorders in Filipino ChildrenDocument9 paginiNutritional Disorders in Filipino ChildrenJill Sanchez-SadiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition: Nutrition Assessment Includes Taking AnthropometricDocument9 paginiDefinition: Nutrition Assessment Includes Taking AnthropometricannieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measure Nutrition with AnthropometryDocument84 paginiMeasure Nutrition with AnthropometryjwhssanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Childhood: EndingDocument68 paginiChildhood: EndingGiorgi KordzayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRF Lecture 1Document90 paginiHRF Lecture 1api-260145786100% (1)
- 2014 A Health Professionals Guide To Using The ChartsDocument14 pagini2014 A Health Professionals Guide To Using The ChartsCaity YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition Assessment and Classification: Helenita Arlene Mendones - MorosDocument26 paginiNutrition Assessment and Classification: Helenita Arlene Mendones - MorosAubrey MitraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Approach To Children and Adolescents With Short Stature - UpToDateDocument25 paginiDiagnostic Approach To Children and Adolescents With Short Stature - UpToDatePreetyFaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Failure To ThriveDocument68 paginiFailure To ThriveRachel SepthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aquifer Case - Summary - FamilyMedicine23 - 5-YeDocument9 paginiAquifer Case - Summary - FamilyMedicine23 - 5-YeHyunsoo EllisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth Assessment and Monitoring During Childhood: CommentaryDocument7 paginiGrowth Assessment and Monitoring During Childhood: CommentaryFajar SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GROWTH MONITORI-WPS OfficeDocument12 paginiGROWTH MONITORI-WPS OfficeFaith IriemiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth MonitoringDocument44 paginiGrowth MonitoringPrakash C Raavudi100% (1)
- Z-Scores - WHO Growth ChartsDocument9 paginiZ-Scores - WHO Growth ChartsShamaine Anne SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essential guide to anthropometry for child nutritionDocument2 paginiEssential guide to anthropometry for child nutritionChristian DaivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chart Fact Sheet A4 4ppDocument4 paginiChart Fact Sheet A4 4ppWijaya Kusuma BagusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obesity in Children OverviewDocument9 paginiObesity in Children OverviewthadikkaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Updates/Refresher For BHWS' Rules and Functions:: Inayangan Health Center Calinan DistrictDocument26 paginiUpdates/Refresher For BHWS' Rules and Functions:: Inayangan Health Center Calinan Districtbryan john barbosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Four: - Assessments of CommunityDocument37 paginiChapter Four: - Assessments of CommunityAbdurohaman BelayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric Nutrition Care: Skills Lab Block 24Document60 paginiPediatric Nutrition Care: Skills Lab Block 24Julius AnzarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Childhood Obesity: Causes and Consequences, Prevention and Management.De la EverandChildhood Obesity: Causes and Consequences, Prevention and Management.Încă nu există evaluări
- Epilepsy Guideline ST Epilepticus Children N Adult 2016Document14 paginiEpilepsy Guideline ST Epilepticus Children N Adult 2016Desi ChiloupChaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DapusDocument1 paginăDapuslukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document2 pagini1lukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burn InjuryDocument17 paginiBurn InjurylukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plain RadiographyDocument2 paginiPlain RadiographylukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burn InjuryDocument17 paginiBurn InjurylukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patofisiologi Morbus HansenDocument2 paginiPatofisiologi Morbus HansenlukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal THTDocument8 paginiJurnal THTwandajunitasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ika Febty Dyah Chiptarini - FkikDocument148 paginiIka Febty Dyah Chiptarini - FkikYuhadi EffendiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bull NeckDocument1 paginăBull NecklukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lembar Vii ABSTRACTDocument1 paginăLembar Vii ABSTRACTlukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jadwal ProgressDocument1 paginăJadwal ProgresslukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Morning Report: Departement of Surgery Saturday, 27 January 2018Document2 paginiMorning Report: Departement of Surgery Saturday, 27 January 2018lukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lapsus SyringomyeliaDocument5 paginiLapsus SyringomyelialukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Morning Report - 26 Sept 2017Document24 paginiMorning Report - 26 Sept 2017lukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IKM 1.3 Dr. Dian Yuliarta Lestari, SP PADocument1 paginăIKM 1.3 Dr. Dian Yuliarta Lestari, SP PAlukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Br. J. Anaesth. 2009 Walfish I47 56Document10 paginiBr. J. Anaesth. 2009 Walfish I47 56lukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PaymentDocument1 paginăPaymentlukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myasthenia GravisDocument11 paginiMyasthenia GravislukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CaecilianDocument3 paginiCaecilianlukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grafik CDCDocument10 paginiGrafik CDCArief Budi LesmanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lameshow Statistik PDFDocument247 paginiLameshow Statistik PDFqel_harizah100% (1)
- Zoids LegacyDocument302 paginiZoids LegacylukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Anatomy: Dr. Thontowi Djauhari NS, Mkes Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Muhammadiyah MalangDocument32 paginiGeneral Anatomy: Dr. Thontowi Djauhari NS, Mkes Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Muhammadiyah MalanglukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slide 5ljifblIWGHFlouhgOHF Oh C Woiht OHC OWIUHLAUHVNKLARHLAOUAO6Document1 paginăSlide 5ljifblIWGHFlouhgOHF Oh C Woiht OHC OWIUHLAUHVNKLARHLAOUAO6lukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PsoriasisDocument27 paginiPsoriasisMala PotterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Giardia duodenalis Life Cycle and StagesDocument55 paginiGiardia duodenalis Life Cycle and StageslukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ujian Tengah Blok 1Document11 paginiUjian Tengah Blok 1lukinandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ukulele Chord Chart - 1 PDFDocument4 paginiUkulele Chord Chart - 1 PDFkimin_3Încă nu există evaluări
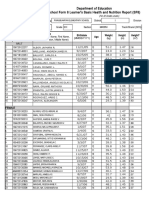
- School Form 8 SF8 Learner Basic Health and Nutrition ReportDocument4 paginiSchool Form 8 SF8 Learner Basic Health and Nutrition Reportbeatrice kate m. lattao0% (1)
- Grow Taller at Any AgeDocument78 paginiGrow Taller at Any AgeRITZ SANDYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Implications of A Novel Biomarker of Growth: DescriptionDocument3 paginiClinical Implications of A Novel Biomarker of Growth: Descriptionjunaid mÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turner Syndrome Pathogenesis ExplainedDocument7 paginiTurner Syndrome Pathogenesis ExplainedBayu SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methods in Human Growth ResearchDocument414 paginiMethods in Human Growth ResearchSvarta BergetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual of Pediatric NutritionDocument598 paginiManual of Pediatric NutritionjuniarsihsrkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Students Nutritional Status Template 1Document4 paginiStudents Nutritional Status Template 1Jeffreynald Arante FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consolidated Nutritional StatusDocument3 paginiConsolidated Nutritional StatusRalph Fael LucasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nam Mahima PDFDocument278 paginiNam Mahima PDFkanchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Short Stature: Problem-Based LearningDocument16 paginiShort Stature: Problem-Based LearningAhmed MostafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19 Clinical - Assessment - of - Nutritional - StatusDocument9 pagini19 Clinical - Assessment - of - Nutritional - StatusSamuel Kyei-BoatengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Owth & DevelopmentDocument9 paginiOwth & DevelopmentShalehudin SchurrleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength and Conditioning For Young Athletes Science and Application 2nbsped 0815361831 9780815361831 - CompressDocument256 paginiStrength and Conditioning For Young Athletes Science and Application 2nbsped 0815361831 9780815361831 - Compresscherbiti75% (4)
- Height Gain ExercisesDocument89 paginiHeight Gain Exercisesapi-3729180100% (16)
- DSE Biology - Structured Questions on Human GrowthDocument6 paginiDSE Biology - Structured Questions on Human GrowthEmily LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Mass Index Percentiles For Boys and Girls From 5-17 YearsDocument1 paginăBody Mass Index Percentiles For Boys and Girls From 5-17 YearsadadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human HeightDocument15 paginiHuman Heightsanbin007Încă nu există evaluări
- Ortho SwapnaDocument50 paginiOrtho SwapnaSwapnagandha R KateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnosis, Genetics, and Therapy of Short Stature in Children: A Growth Hormone Research Society International PerspectiveDocument14 paginiDiagnosis, Genetics, and Therapy of Short Stature in Children: A Growth Hormone Research Society International PerspectiveRima KhairunnisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hand Size Predicts HeightDocument4 paginiHand Size Predicts HeightjustneedmusicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stature Estimation From RX Sternum Length in A Contemporary Spanish PopulationDocument8 paginiStature Estimation From RX Sternum Length in A Contemporary Spanish PopulationDenys PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Giant's HouseDocument8 paginiThe Giant's HouseMarwa SamirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutritional Status of Babag StudentsDocument94 paginiNutritional Status of Babag StudentsClarice Faye NoynayÎncă nu există evaluări
- MasterTrack FT Installation GuideDocument12 paginiMasterTrack FT Installation GuidetoddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quest A Key To Ug Paediatrics PDFDocument192 paginiQuest A Key To Ug Paediatrics PDFSpice Reader100% (6)
- Sargent1921 PDFDocument8 paginiSargent1921 PDFfran jimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Giants by Glenn KimballDocument20 paginiGiants by Glenn KimballBrian Ngenoh100% (1)
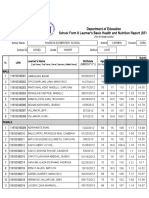
- SF 8 Learner Health ReportDocument4 paginiSF 8 Learner Health ReportLornaNirzaEnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Facial Growth and Facial OrthopedicsDocument211 paginiFacial Growth and Facial OrthopedicsMCU Ortho100% (2)
- 7 Anthropometry and Workplace DesignDocument22 pagini7 Anthropometry and Workplace DesignDeshanBenhurÎncă nu există evaluări