Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Asjldjlasdjsjdksdjskljdklasdlsa
Încărcat de
Vikas RockTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Asjldjlasdjsjdksdjskljdklasdlsa
Încărcat de
Vikas RockDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
COMMUNICATION SWITCHING
TECHNIQUES
PRESENTED
BY:-
CHAND
KATARIA
M.B.A-I
INTRODUCTION
A network consist of large number of
computer and various other intermediate
devices. All these devices and computer
need to be connected so as to transfer data
from one computer other in the network.
In order to provide one to one
communication between the computers, one
possible way is to make point to point
connection between the
Each pair of devices i.e every computer in the
network is having a link with every other
computer. However, this method requires lot
of wiring and will increase the cost.
DEFINATION
Another technique that can determine how
connections are made between the devices
and how data movement is handle is
switching.
A switched network consists of series of
interlinked nodes called switches . Switches
are hardware and software devices that are
capable of creating temporary connections
Between two or more devices linked to the
switch.
TYPES OF SWITCHING
Circuit switching
Packet switching
Message switching
Switching
Circuit
switching
Packet
switching
Message
switching
CIRCUIT SWITCHING
In circuit switching the routing decisions is made
when path is up across the network. After the
link has been set between the sender and
receiver, the information is forwarded
continuously over the link.
The dedicated Path established between the
sender and the receiver is maintained for entire
duration of conversation.
This link or path is released only when data
transmission between sender and receiver is
over.
Data transferred between the two stations
are not packetized.
There is no addressing involved in data
transferred.
The telephone systems circuit switching is
used.
CIRCUIT SWITCHING
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
ADVANTAGES
The dedicated path established between
sender and receiver provides a guaranted
data rate.
Once the circuit is established, data is
transmitted without any delay as there is no
waiting time at each switch.
The method is suitable for long continuous
transmission.
DISADVANTAGES
As the connection is dedicated it cannot be
used to transmit any other data even if the
channel is free.
As resources are allocated for the entire
duration of connection, these are not
available to other connection.
PACKET SWITCHING
In packet switching, message is broken up
into packets of fixed or variables size.
Each packets includes a header that
contains source address, destination address
and other control information.
The size of a packet depends upon the type
of network and protocol used.
In packet switching no resources are
allocated
PACKET SWITCHING
A
B
C
D
1
2
3
3 2
4
1
4
4
4 3 2 1
4 3 2 1
ADVANTAGES
As the routing is done on the packet basis,
the intermediate nodes do not have to wait
for the entire message, hence the
transmission is very fast.
The network allowing many devices to
communicate through the same network
channel.
DISADVANTAGES
Packets may be lost on their route, so
sequence numbers are required to identify
missing packets.
Switching nodes for packet switching require
large amount of RAM to handle large
quantities of packets.
MESSAGE SWITCHING
A message switching is a logical unit of
information and can be of any length.
In message switching, if a station wishes to
send a message to another station, it first
adds the destination address to the
message.
No direct link is established from sender to
receiver.
Each message is treated as an independent
unit.
ADVANTAGES
No physical connection is required between
the source and destination.
It reduces the traffic congestion on network
because of stored and forward facility.
DISADVANTAGE
No physical connection is required between
the source and destination.
It provides efficient traffic management.
It support the message length of unlimited
size.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Elasticity of Demand Class JLD LSK LDK Ask DK Asd As DK Las Dkas KLD As DK Ask Ldkals KDL SKL Dkal SK LDDocument24 paginiElasticity of Demand Class JLD LSK LDK Ask DK Asd As DK Las Dkas KLD As DK Ask Ldkals KDL SKL Dkal SK LDVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demand and Supply Analysis-1 SdsakldjlasjldjlasldlasjldjklasdjasljdljasldjlaskldasljdlasjlklDocument30 paginiDemand and Supply Analysis-1 SdsakldjlasjldjlasldlasjldjklasdjasljdljasldjlaskldasljdlasjlklVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- M21_nethistory jjlldjlas;ldas;ldl;asldas;ld;ls;lda;lskd;laskd;lksl;dklksd;lkas;lkd;las;ldklas;kelaks;lekas;ldlks;alkd;laskl;dk;laskd;la;ldk;akd;ask;ldk;laskd;laks;kd;laskd;lks;ld;laskd;las;ldas;lkdkas;ldkas;lkdsak;dka;ld;alkd;lak;dla;kd;alask;dk;akd;lskd;askd;las;ldkas;lkd;lak;dlkasd;lkas;ldkas;lkd;lask;ldas;kd;lask;dlkas;ldas;ldk;lkd;lsd;lask;dlaks;lkd;lkd;lask;dka;lkd;ald;l;ldk;aslkd;aslk;dlka;ld;aslkds;lakd;lask;dl;dsa;lkd;laskd;lask;dlkas;ldkas;lkd;lk;Document10 paginiM21_nethistory jjlldjlas;ldas;ldl;asldas;ld;ls;lda;lskd;laskd;lksl;dklksd;lkas;lkd;las;ldklas;kelaks;lekas;ldlks;alkd;laskl;dk;laskd;la;ldk;akd;ask;ldk;laskd;laks;kd;laskd;lks;ld;laskd;las;ldas;lkdkas;ldkas;lkdsak;dka;ld;alkd;lak;dla;kd;alask;dk;akd;lskd;askd;las;ldkas;lkd;lak;dlkasd;lkas;ldkas;lkd;lask;ldas;kd;lask;dlkas;ldas;ldk;lkd;lsd;lask;dlaks;lkd;lkd;lask;dka;lkd;ald;l;ldk;aslkd;aslk;dlka;ld;aslkds;lakd;lask;dl;dsa;lkd;laskd;lask;dlkas;ldkas;lkd;lk;Vikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPM - Planning of Vinit RaidfdsfsdfdsdfdsfdsfDocument11 paginiPPM - Planning of Vinit RaidfdsfsdfdsdfdsfdsfVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dka LK LSKD LSK LDKDocument10 paginiDka LK LSKD LSK LDKVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cash Flow StatementDocument10 paginiCash Flow StatementVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pricing Methods HHHJHJGHJGHJGHJGHJGHJHJGHJGHJGHJGHJGHJGHJDocument8 paginiPricing Methods HHHJHJGHJGHJGHJGHJGHJHJGHJGHJGHJGHJGHJGHJVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- OB Leadership GFDSFDSLFKL DSLFK Llfkds LKFLKDSL KFL DKF LDK Lfklds KLFDSJFLDKLFKLDKFKFKF Lkds LKFL DK LFK LLDocument8 paginiOB Leadership GFDSFDSLFKL DSLFK Llfkds LKFLKDSL KFL DKF LDK Lfklds KLFDSJFLDKLFKLDKFKFKF Lkds LKFL DK LFK LLVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Languages: Presented By: Kimmy Arora M.B.A-IDocument15 paginiComputer Languages: Presented By: Kimmy Arora M.B.A-IVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human in Retaili KsdklasjkldakskdasjdkllasdlasklkldkaskdlsaklldkaskljdklklkDocument31 paginiHuman in Retaili KsdklasjkldakskdasjdkllasdlasklkldkaskdlsaklldkaskljdklklkVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Languages: Presented By: Kimmy Arora M.B.A-IDocument15 paginiComputer Languages: Presented By: Kimmy Arora M.B.A-IVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Merchandise Management: Buying and Handling The Merchandise MixDocument87 paginiMerchandise Management: Buying and Handling The Merchandise MixVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- V KJHHKJKJJKHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJJKHKKKJKJHKJHKKJHJKHKJKJHKJHKJJKJKHKHKKJJKHKKHKHJKHKHKJHKJHJHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJDocument12 paginiV KJHHKJKJJKHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJJKHKKKJKJHKJHKKJHJKHKJKJHKJHKJJKJKHKHKKJJKHKKHKHJKHKHKJHKJHJHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Output DevicesDocument16 paginiOutput DevicesVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- RewardshhkllklklkkjljkljkljkljkljljDocument1 paginăRewardshhkllklklkkjljkljkljkljkljljVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cash Flow StatementDocument10 paginiCash Flow StatementVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- SHRISTIDocument18 paginiSHRISTIVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- V KJHHKJKJJKHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJJKHKKKJKJHKJHKKJHJKHKJKJHKJHKJJKJKHKHKKJJKHKKHKHJKHKHKJHKJHJHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJDocument12 paginiV KJHHKJKJJKHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJJKHKKKJKJHKJHKKJHJKHKJKJHKJHKJJKJKHKHKKJJKHKKHKHJKHKHKJHKJHJHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Networks ,llsldlasldk;lask;lds;lad;las;ldkl;askd;las;ldk;laskd;lklas;kdlaskldklaskdlkasl;dlakldklaskdlkasldklaskldkaslkd;laskldkas;lkd;laskd;lkaslkdlaskldk;laskdas;lkd;lsakldkasl;d;laskld;kas;lkd;lask;dkas;kd;lask;dlask;l fgkdgsjkgkldfklgdklflgkdfkljgdfklgkljdfklgjkldfklgjkldfjklgjdfkljgkljdfkgjdfjkgjkldfjglfkjgldfjgkljlkgjdfkljgkljdfkljgkldfjklgjdflkjgkldfljglkdfjglkdfjklgjdfkljgdljgkldfjgkldfjgkldjfklgjdfkljgkldfjkjgkljkDocument14 paginiComputer Networks ,llsldlasldk;lask;lds;lad;las;ldkl;askd;las;ldk;laskd;lklas;kdlaskldklaskdlkasl;dlakldklaskdlkasldklaskldkaslkd;laskldkas;lkd;laskd;lkaslkdlaskldk;laskdas;lkd;lsakldkasl;d;laskld;kas;lkd;lask;dkas;kd;lask;dlask;l fgkdgsjkgkldfklgdklflgkdfkljgdfklgkljdfklgjkldfklgjkldfjklgjdfkljgkljdfkgjdfjkgjkldfjglfkjgldfjgkljlkgjdfkljgkljdfkljgkldfjklgjdflkjgkldfljglkdfjglkdfjklgjdfkljgdljgkldfjgkldfjgkldjfklgjdfkljgkldfjkjgkljkVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human in Retaili KsdklasjkldakskdasjdkllasdlasklkldkaskdlsaklldkaskljdklklkDocument31 paginiHuman in Retaili KsdklasjkldakskdasjdkllasdlasklkldkaskdlsaklldkaskljdklklkVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daimlerchryslermerger-120117024935-Phpapp02 K Kdlkas LD Laslkdlsldk Lasklkas Lkdlskldklas D Lsa LDK LLDocument15 paginiDaimlerchryslermerger-120117024935-Phpapp02 K Kdlkas LD Laslkdlsldk Lasklkas Lkdlskldklas D Lsa LDK LLVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Merchandise Management: Buying and Handling The Merchandise MixDocument87 paginiMerchandise Management: Buying and Handling The Merchandise MixVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presented by Nitesh SabharwalDocument6 paginiPresented by Nitesh SabharwalVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Diagram of ComputerkjkkkkjkljlkjkDocument10 paginiBlock Diagram of ComputerkjkkkkjkljlkjkVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- 25 Lessons Jack Wesdaskdaskdk Asld As DL Asl 'Dlad La Lda SL DL' Asl' Dlasldasl DL Asl DL LCH Ten3 Minicourse2Document21 pagini25 Lessons Jack Wesdaskdaskdk Asld As DL Asl 'Dlad La Lda SL DL' Asl' Dlasldasl DL Asl DL LCH Ten3 Minicourse2Vikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aeb41-Week4 KKJKJKJLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLDocument41 paginiAeb41-Week4 KKJKJKJLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growing Prominance of Credit and Debit CardsDocument10 paginiGrowing Prominance of Credit and Debit CardsVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aeb41-Week4 KKJKJKJLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLDocument41 paginiAeb41-Week4 KKJKJKJLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value, Norm, Chara& Affec On Consum BehaviouDocument30 paginiValue, Norm, Chara& Affec On Consum BehaviouVikas RockÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
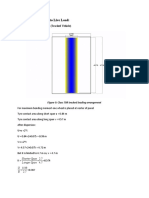
- Bending Moment Due To Live Load:: A) IRC Class 70R Load (Tracked Vehicle)Document9 paginiBending Moment Due To Live Load:: A) IRC Class 70R Load (Tracked Vehicle)Tashi TamangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data-Mining-Lab-Manual Cs 703bDocument41 paginiData-Mining-Lab-Manual Cs 703bAmit Kumar SahuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ericsson Training PDFDocument118 paginiEricsson Training PDFNuwan100% (1)
- Chapter 26Document17 paginiChapter 26api-317344426100% (1)
- Structural Beam Deflection CalculationDocument36 paginiStructural Beam Deflection CalculationjaamartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Praepagen HY - CleanersDocument16 paginiPraepagen HY - CleanersCARMEN LINARESÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICAO Flight PlanDocument4 paginiICAO Flight Planrmpilot2012Încă nu există evaluări
- WPS For Structure Mild Steel Fillet WeldDocument2 paginiWPS For Structure Mild Steel Fillet WeldHarkesh Rajput76% (17)
- Xtralis VESDA ASPIRE2: ASPIRE2 - Air Sampling Smoke Detection Made EasyDocument2 paginiXtralis VESDA ASPIRE2: ASPIRE2 - Air Sampling Smoke Detection Made Easy17souravÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glencoe Mcgraw Hill Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Answer KeyDocument8 paginiGlencoe Mcgraw Hill Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Answer Keybodinetuzas2100% (1)
- Esteem 11 Brochure (24032023)Document9 paginiEsteem 11 Brochure (24032023)TeaMeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Solutions Week 10Document3 paginiTutorial Solutions Week 10Jaden EuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bentley RM Bridge Advanced Detalii Module AditionaleDocument4 paginiBentley RM Bridge Advanced Detalii Module AditionalephanoanhgtvtÎncă nu există evaluări
- FP35 Hearing Aid Analyzer TrainingDocument85 paginiFP35 Hearing Aid Analyzer TrainingPamela Tamara Fernández EscobarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understand WorkFlow in DetailDocument118 paginiUnderstand WorkFlow in DetailSaquib MahmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- PY0101 - Python For Data Science, AI, & Development Cheat SheetDocument2 paginiPY0101 - Python For Data Science, AI, & Development Cheat SheetManju KiranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Python For GISDocument3 paginiWhy Python For GISalebeley21Încă nu există evaluări
- AOAC Official Methods of Analysis for Phosphorus in FertilizersDocument2 paginiAOAC Official Methods of Analysis for Phosphorus in FertilizersDjaloel KhairÎncă nu există evaluări
- SBC Code 301Document350 paginiSBC Code 301Marwan Mokhadder100% (6)
- 0610 m22 Ms 52 PDFDocument7 pagini0610 m22 Ms 52 PDFsolihinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CXC Elec Paper 1sDocument60 paginiCXC Elec Paper 1sapi-255989257100% (1)
- Basics of Robotics KTUDocument6 paginiBasics of Robotics KTUBoni SamuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- TechRef ShuntDocument32 paginiTechRef ShuntAlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sweater Consumption CostingDocument2 paginiSweater Consumption Costingapi-214283679Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes Schwarzschild GeometryDocument27 paginiLecture Notes Schwarzschild Geometryga.simplicio2Încă nu există evaluări
- Small Wind Turbine For Grid-Connected and Stand-Alone OperationDocument4 paginiSmall Wind Turbine For Grid-Connected and Stand-Alone OperationPranav PiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tangents and Normal: IIT JEE (Main) ExaminationDocument18 paginiTangents and Normal: IIT JEE (Main) ExaminationHanuman VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper Test Critical ThinkingDocument10 paginiPaper Test Critical Thinkingandrea217Încă nu există evaluări
- Technical Data Sheet 3#5 Copper Clad Steel Wire: ITEM CODE - 600305Document2 paginiTechnical Data Sheet 3#5 Copper Clad Steel Wire: ITEM CODE - 600305Victor DoyoganÎncă nu există evaluări