Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
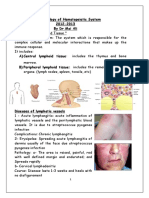
Pathology of Lymph Nodes: Norman Levy, MD
Încărcat de
Adi ParamarthaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pathology of Lymph Nodes: Norman Levy, MD
Încărcat de
Adi ParamarthaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pathology of Lymph Nodes
Norman Levy, MD
Big Picture
As with other organs, lymph nodes, and more globally, the
immune system, can be the site of infectious, immune and
neoplastic disease, the latter either primary or metastatic
The clinical manifestations of diseases of the lymph nodes
are:
Local enlargement, tender on nontender, +/_
Compression of adjacent structures +/_
Release of cytokines producing "systemic" symptoms
of fever, weight loss and night sweats
Infectious organisms can stimulate the same acute, chronic
or granulomatous reactions in the draining lymph nodes as
they characteristically stimulate at other sites
Big Picture 2
Several types of immune stimuli can cause "reactive"
enlargement of the entire lymph node, or selective
expansion of cortical, paracortical or medullary regions
Metastatic tumors spread to the lymph nodes primarily via
lymphatic drainage from adjacent solid organs
Primary neoplasms of the lymph nodes are all malignant
They are divided into malignant non-Hodgkin's
lymphomas (NHL), and Hodgkin lymphoma
Big Picture 3
NHL's are more common, and can be simply divided into
indolent, or slow growing types, and aggressive types
Malignant lymphomas represent clonal malignancies in
which mutational events have caused the majority of
progeny cells to freeze at a single stage of normal
lymphocyte differentiation
Lymphomas frozen at a stage associated with high
replication --> aggressive lymphomas;
Lymphomas frozen at stages associated with
recirculation or final function --> indolent lymphomas
Big Picture 4
The diagnosis of malignant lymphomas is based on the
microscopic recognition of the dominant cytologic cell
type, supplemented by immunologic and molecular
techniques
The treatment and prognosis of lymphomas are based on
The dominant cell type (and it's inherent biologic
behavior),
The extent of spread (Stage)
The underlying health of the patient
All of the previous statements are complicated by the fact
that indolent lymphomas can further mutate and transform
to aggressive types
Big Picture 5
Hodgkin lymphoma is a less common nodal disease
whose diagnosis is based on the detection of a
characteristic cell, the Reed Sternberg cell, in the
appropriate histologic setting
There are several (five) histologic subtypes, but prognosis
is based primarily on extent of disease
Hodgkin lymphoma is a more curable disease than non-
Hodgkin lymphomas
Now watch me confuse this relatively straightforward
information with the details.
Overview of the lymphoid
immune system
Lymphocytes evolve from pluripotent stem cells --> two
major functional cell types:
B lymphocytes, comprising the humoral immune -->
production of antibodies
T lymphocytes, comprising the cellular immune
system, -->
Direct killing of foreign or intracellularly infected
cells, cytotoxic T cells
Fine control of the immune response through the
secretion of cytokines, helper and suppressor T
cells.
Anatomical organization
The anatomic organization of the lymphoid immune system
divided into two major functional regions:
The primary immune organs, sites of initial maturation -->
immune competent cells:
B cells- bone marrow
T cells- thymus
The secondary immune organs, sites of antigen driven
replication and differentiation into committed effector cells
Lymph nodes
Spleen
Mucosal Associated Lymphoid System (MALT)- lymphoid
cells lining the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts
Everywhere else
The lymph nodes, in their totality, represent the largest secondary
organ, and the major site of lymphoid pathology
Lymph node anatomy
To recognize
lymph node
pathology,
one has to
be familiar
with normal
lymph node
anatomy
and cytology
Lymph node histology
Lymph node variation
Lymph node histology
is dynamic: follicles
In the absence of
immune stimulation,
primary follicles
In the presence of
immune stimulation,
secondary follicles or
germinal centers
Lymphocyte homing
After initial maturation in the primary
immune organs, "virgin" B and T
lymphocytes --> peripheral blood -->
home to specific sites within the lymph
node (and the other secondary
organs),
The sites of B cell homing include:
The primary and secondary
follicles of cortex-the sites of
antigen presentation
proliferation and
differentiation in response to
same
The medullary cords -->plasma
cells aggregate--> release their
immunoglobulins into the efferent
lymph
The site of T cell homing is the
paracortex
The separation of B and T lymphocytes
not absolute,
Both cell types present throughout
lymph node, necessary for coordinated
lymphoid immune response.
Lymphocyte recirculation
Normal lymphocytes recirculate, passing from blood -->
lymph nodes --> efferent lymphatics
Allows constant surveillance for the presence of the
antigen for which the lymphocyte has a unique and
specific receptor on it's surface.
If antigen not present, lymphocytes leave the node and
recirculate
Virgin lymphocytes have a finite lifespan, numbered in
weeks, unless they come in contact with antigen
Cytology of the lymph node
The normal or reactive lymph node is thus a dynamic organ
Composed of
Transient B and T lymphocytes
Antigen processing and presenting cells
Replicating B and T lymphocytes (in response to antigen)
Persistent and transient final effector cells
Macrophages
Some of these functional subgroups are cytologically unique,
others cytologically indistinguishable
The ultimate microscopic impression, with practice, is one of
cytologic heterogeneity, and histologic organization
Cell types I
Small lymphocytes
Small round dark blue dots. Round
nucleus, clumped chromatin, small or
absent nucleolus.
The dullest looking cells hiding the
greatest level of functional
heterogeneity.
Can be T or B cell, virgin
(unexposed to antigen) or
differentiated effector/memory cell.
Most likely lineage, B or T,
guessed by location within the
node, but lineage and state of
differentiation must be confirmed
by immunologic/molecular
techniques
Locations:
B cells- primary follicles,
mantle zone of secondary
follicles, medullary cords
T cells- paracortex, minor
population within germinal
center.
Kinetically, clumped
chromatin tells us that the cell is
not proliferating- not activated
to enter the cell cycle and
replicate
Cell types 2:Follicular (germinal)
center cells
Replicating and post-replicating B cells
Noncleaved cells, small and large
Replicating populations-
expanding antigen responsive
cells.
Round nuclei but larger than
resting small lymphocyte
Open or vesicular chromatin
Recognizable nucleoli.
Nucleus clear -->genetic
material unwound for
replication.
Size, large or small compared
nucleus of macrophage.
Small cleaved cells-
Nonreplicating population
Post mitotic memory or plasma
cell precursors
Clumped chromatin
Irregular folded and cleaved
nuclear profiles
Reactive germinal center
MZ
LZ
DZ
Cytology of lymph node 3
Immunoblasts
Replicating large cells found
outside the germinal centers.
May be of B or T cell type
Have nuclear characteristics of
replicating lymphocytes-
Vesicular chromatin
Nucleoli
Accessory cells
Antigen processing cells
Interdigitating reticulin cells- T cell
paracortex
Dendritic reticulin cells- B cell germinal
centers
Process and present antigen to B and T
lymphocytes
Invisible in normal lymph node
Macrophages (histiocytes)-
Phagoctytic cells of lymph node
Tingible body macrophages of germinal
centers
Medullary and subcapsular sinus
macrophages-
Abundant pale cytoplasm
Oval nucleus, single small nucleolus
Pathology of lymph nodes 1
Infections
Reactive hyperplasias
Sarcoidosis
Metastatic tumors
Malignant lymphomas
Non-Hodgkins lymphoma-NHL
Hodgkins lymphoma
Pathology of lymph nodes 2
Infections
Bacterial
Acute inflammation, abscess formation
Granulomatous, caseous and noncaseous
Diagnosis by culture, serologies, and/or special stains
Reactive hyperplasias
Exaggerations of normal histology.
Expansion of all regions or selective expansion
Some types characteristic of certain diseases, but most not
Follicular hyperplasia- increase in number and size of germinal centers,
spread into paracortex, medullary areas
Collagen vascular diseases
Systemic toxoplasmosis
Syphillis
Interfollicular hyperplasia- paracortex
Skin diseases
Viral infections
Drug reactions
Sinus histiocytosis- expansion of the medullary sinus histiocytes-
Adjacent cancer
Infections
Malignant lymphomas
(Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas-NHLs)
Malignancies of the lymphoid system which primarily
manifest themselves outside the bone marrow, at the sites
of normal lymphoid homing
Lymph nodes
Spleen
M.A.L.T.
Anywhere
(Lymphomas outside lymph nodes and spleen are
referred to as extranodal lymphomas)
Approximately 40, 000 cases per year, 20,000 deaths
Clinical presentation
Enlarging mass(es), typically painless, at sites of nodal tissue
Compression, infiltration of hollow organs
Pain, obstruction, perforation
Interference with normal organ function-
Solid organ infiltration- kidneys, liver, bone marrow
Systemic symptoms
Fever
Night sweats
Weight loss
If marrow infiltrated, can have leukemic component
NHL 2
Composed of cells that have lost the ability to pursue the full
range of lymphoid differentiation, and are frozen at a single
stage of the normal maturation/differentiation sequence
Recapitulate the biology and immunophenotype of normal cell
counterpart
Several cytologically and immunologically recognizable stages
of normal lymphoid maturation --> several subtypes of
lymphoma
Clonal malignancies, derived from a single cell that has
undergone a malignant transformation, mutation
Best initially conceptualized as two major clinical types
Indolent lymphomas
Aggressive lymphomas
NHL 3 Indolent lymphomas
Lymphomas frozen at stages not normally replicating, but
may be circulating
Diseases of slow accumulation, due to defective apoptosis
Often widespread at diagnosis
Prolonged natural history, median survivals >5 years
Will usually respond to chemo- or radiation therapy
Will usually relapse, but respond to same or alternative tx
Currently incurable unless
Localized disease or
Marrow ablation with some type of stem cell transplant
Classification of indolent lymphomas- later
Aggressive lymphomas
Lymphomas frozen at stages characterized by replication and
accelerated growth
Diseases of defective cell cycle control
More often localized at presentation than indolent lymphomas
More often extranodal
Shorter natural history; median survival </= 2 years
Require more aggressive therapy to achieve "clinical
remission"- disappearance of all detectable disease
Despite short natural history, curable disease in some with
aggressive therapy
Approximately 30-40% of adults
50-80% children
All childhood lymphomas of this type
Classification of lymphomas
Subtyping or classification within the two groupings necessary,
because different subtypes have
Distinct clinical presentations
Can require different therapy
Have differing prognoses, reflecting different mechanisms of
molecular pathogenesis.
Unfortunately, rarely unanimous acceptance of any one
classification scheme.
Intermittent upgrading of classification, with new terminology,
reflecting new information and classifier bias
Classification often lags behind advances in immunology, research
pathology
Final result:
Difficult area to teach
Difficult to remember
Job security for me
WorkingFormulation for
Clinical Usage
From 1982-1994, the classification used
in the United States
Based on:
The observed clinical history of
1200 patients classified according to
the terminology to right
Microsopic examination alone,
utilizing
Loss of normal nodal
architecture
The dominant cytologic cell
type observed under the
microscope
Presence or absence of
"follicularity" - mimicking of
normal lymphoid follicle
formation
Low grade
ML, small lymphocytic
ML, follicular small cleaved cell
ML, follicular, mixed small and large
cell
Intermediate grade:
ML, follicular, large cell
ML, diffuse, small cleaved cell
ML, diffuse, mixed small and large cell
ML, diffuse, large cell
High grade
ML, immunoblastic
ML, lymphoblastic
ML, small non-cleaved cell (Burkitt's vs
non-Burkitt's)
Miscellaneous (mycosis fungoides,
true histiocytic, etc.)
Working Formulation
Divided into three "grades" of lymphoma- low, intermediate and
high. As stated above,
Low grade = indolent
Intermediate and high = aggressive
Limitations
Purely morphologic classification mixed T and B cell
lymphomas together
Lumped distinct subtypes of B cell lymphomas together
Obscured the biologic, clinical and therapeutic differences
Distorted interpretation of clinical trials
R.E.A.L./W.H.O. Classification
WF replaced in 1994 by the Revised European American Lymphoma
(REAL) classification, now being modified by the World Health
Organization (WHO)
REAL/WHO is a "disease oriented rather than purely morphology
oriented classification, based on:
Cell lineage: B v T v NK v Histiocytic
Stage of maturation of the presumed normal counterpart.
Includes immunologic and molecular criteria in addition to purely
morphologic criteria of WF
Each disease entity may have differing grades of aggressiveness
Greatly expanded the list of entities; includes leukemias of
lymphoid origin
Made teaching to medical students (and in fact all physicians) even
more difficult than WF
REAL contained a number of provisional entities which have been
clarified in the upcoming W.H.O. revision.
B-Cell Neoplasms T/NK-Cell Neoplasms Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Precursor B-cell lymphoblastic
leukemia/lymphoma
Precursor T cell lymphoblastic
leukemia/lymphoma
Lymphocyte predominance,
nodular
Peripheral B-cell neoplasms Peripheral T-cell and NK-cell
neoplasms
Classical HL
B-cell CLL/SLL Predominantly
leukemic/disseminated
Lymphocyte rich classical HL
B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia Nodular sclerosis
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma T-cell large granular lymphocytic
(LGL) leukemia
Mi xed cellularity
Mantle cell lymphoma NK cell leukemia Lymphocyte depletion
Follicular lymphoma Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma Unclassifiable classical HL
Extranodal marginal zone B-
cell lymphoma, MALT type (+/-
monocytoid B cells)
Predominantly nodal
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell
lymphoma
Nodal marginal zone B-cell
lymphoma (+/-monocytoid B
cells)
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma
unspecified
Splenic marginal zone B-cell
lymphoma (+/-villous
lymphocytes)
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma,
T/null-cell
Predominantly extranodal
Hairy cell leukemia Mycosis fungoides
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma Sezary syndrome
Burkitt lymphoma Primary cutaneous (CD30+ T-cell
lymphoproliferative disorders)
Plasma cell myeloma Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-
cell lymphoma
Plasmacytoma NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal and
nasal-type
Enteropathy-type intestinal T-cell
lymphoma
Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma
g/d (gamma/delta)
a /b (alpha/beta )
REAL/WHO classification-
backbone
B cell neoplasms
Precursor B cells-related to acute leukemia
Peripheral B cell lymphomas- the majority of B
cell lymphomas
T cell and Natural Killer cell neoplasms
Precursor T cells
Peripheral T cell and NK neoplasms
Hodgkins lymphoma
Frequency of lymphomas
Indolent versus aggressive
Indolent
Small lymphocytic
lymphoma/CLL
Follicular lymphoma, Grades
1/2
Extranodal Marginal zone
lymphoma of MALT type
Nodal marginal zone
lymphoma
Splenic marginal zone
lymphoma
Hairy cell leukemia
Lymphoplasmacytic
lymphoma
Plasma cell myeloma
Plasmacytoma
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma
Cutaneous CD30+ anaplastic
large cell lymphoma
Aggressive
Prolymphocytic
leukemia
Large B cell lymphoma
Burkitt lymphoma
Mantle cell lymphoma
Anaplastic large cell
lymphoma
All peripheral T cell
lymphomas
Divides B and T
B cell neoplasms- Precursor B
Precursor B cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
Frozen at lymphoblast cell stage of antigen
independent B cell differentiation- normally restricted
to bone marrow
Usually present as acute leukemia +/- lymph node
involvement
Can initially present as node or skin disease, with later
progression to bone marrow
Treated as acute leukemia
80% cure rate in children
20-30% in adults because of "bad" cytogenetics:
frequent presence of Philadelphia chromosome
t(9;22)
Peripheral B-cell lymphomas
Lymphomas frozen at various stages of antigen dependent B cell maturation and
differentiation
Peripheral B-cell neoplasms
Frozen at various stages of antigen dependent B cell maturation and
differentiation
Small lymphocytic/CLL- the virgin B cell fresh from the marrow
Prolymphocytic leukemia- a more clinically aggressive variant of above
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma- the primary immune response
Mantle cell lymphoma- the mantle region surrounding the follicle
Follicular lymphoma- the follicle- grades 1-3
Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma- cells at the periphery of the follicle in
extranodal sites of lymphoid tissue- Mucosal Associated Lymphoid tissue-
such as G.I. tract
Nodal marginal zone lymphoma
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma- immunologically distinct
Hairy cell leukemia- pre-plasma cell
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma- this breaks the ideal of specific cell stage
but all represent lymphomas with high replication rate
Burkitt lymphoma- very aggressive
Plasma cell myeloma- diffuse bone marrow proliferation of plasma cells
Plasmacytoma- solitary focus of monoclonal plasma cells, with variable
risk of progression to myeloma, depending on site
Example Indolent Lymphoma:
Follicular lymphoma Grade I
Clinical
Most common type of indolent lymphoma in
US; second most common type lymphoma
overall
Disease of adults >40 (median age 59)
Usually widely disseminated at diagnosis,
incl. bone marrow
Will respond to gentle chemotherapy but
will relapse
Incurable short of bone marrow
transplant unless rare limited disease
Overall 5 yr survival 72%
Over time, additional mutations -->
progression (transformation) to large cell
lymphoma --> aggressive clinical course
Although Gr.1 is most common presentation,
some patients present with predominance of
large cells within follicles -->more aggressive
clinical course
Pathogenesis:
Due to t(14;18)(q32, q21)
Upregulates expression of an anti-
apoptotic protein Bcl2
Immortalizes lymphoma cells
Follicular lymphoma Grade I
Pathology/diagnosis
Benign equivalent: small cleaved cell
of germinal center
Clumped chromatin and infrequent
nucleolus like small lymphocyte
Irregular nuclear profile, with nuclear
folds or "cleavages"
Retain follicular structure, but
monotonous accumulation of single
cell type
Characteristic immunophenotype:
Positive:Monoclonal light chain,
CD19, CD10, Bcl2
Negative: CD5, Cyclin D1/Bcl1
Can also detect translocation by
cytogenetics and/or polymerase chain
reaction
Table X: Indolent B cell lymphomas
Follicular
Lymphoma
(Grade I)
Marginal zone
Lymphoma
Small lymphocytic
lymphoma/CLL
Frequency (%
all lymphomas
22% 8 7
Age of onset
median
59 61 65
Stage at
Presentation
Stage III/I V
Disseminated
Stage I Stage IV
Response to
Therapy
Good to most
treatments,
but incurable
short of
transplant
Frequently
curable
Similar to
Follicular
lymphoma
5 yr survival 72% 74% 51%
Predominant site
presentation
Nodal Extranodal Marrow/nodal
Pattern of nodal
Infiltration
Follicular Diffuse Diffuse
Benign cell
Equivalent
Germinal
center
small cleaved
cell
Marginal zone
Lymphocyte
Virgin B cell
Dominant cell
type
Small cleaved
cell in most
cases, but can
be large cell
Mix of small
lymphocytes,
plasma cells
Small
lymphocytes
with round
nucleus
Immunopheno
-type
Positive: CD19
CD10, Bcl2+
Negative: CD5-
Positive:
CD19, Bcl2
Negative:
CD10, CD5
Positive:
CD19, CD5
CD23
Negative:
CD10
Molecular
Pathogenesis
t(14;18)
Bcl2/JH
t(11;18),
Trisomy 3
Trisomy 12
Examples: aggressive B cell lymphoma-
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Clinical
Most common lymphoma- 30% NHL
Disease of adults and children, but median age 64
Limited versus widespread disease ~1:1
Presents with rapidly enlarging masses
Approximately 40% curable with aggressive chemotherapy/
stem cell transplant
Partially predictable by International Prognostic Index
(later)
Pathogenesis
Not as clearly defined as previous examples- several
cytogenetic abnormalities associated with large cell
lymphoma, but no defining one
Diffuse Large B cell lymphoma
Pathology
Benign equivalent- large replicating B
cells of germinal center and
paracortex
Diffuse infiltration of lymph node
Often necrosis; increased mitotic rate
Cytology: Oval or cleaved nucleus with
vesicular chromatin and 1-3 nucleolus
Nucleus larger than that of reactive
macrophage
Several cytologic subtypes initially felt
to have differing clinical behavior.
Yielded division into intermediate
versus high grade types- now not felt
valid or significant without
immunologic/molecular evidence
Immunophenotype characterized by
monoclonal light chain, CD19
expression,with variable expression of
other B cell associated antigens
Burkitt's lymphoma
Clinical
3% lymphomas
Disease of adults and children-
median age 31
Initially recognized in Africa by
Thomas Burkitt
Association with Epstein Barr
virus infection
Localization in jaw
In US, usually presents in ileocecal
region of children
1/3 of all childhood lymphomas
Earlier eras, very aggressive and
rapidly fatal
Now, ~70-80% children curable
40% of adults
Pathogenesis:
t(8;14), producing upregulation of
myc oncogene, a cell cycle
regulation gene
Burkitt's lymphoma
Pathology
Benign equivalent is replicating small
noncleaved cell of germinal center:
Diffuse infiltration of lymph node
Very high mitotic rate, lot of
ineffective proliferation;
Attracts macrophages to
phagocytize> starry sky pattern at
low power
Cytology: round nucleus, smaller
than that of reactive macrophage
Vesicular chromatin and 2-5 nucleoli
Immunophenotype:
Positive: Monoclonal light chain,
CD19, CD10
Negative: CD5
Mantle cell lymphoma
Clinical
6% lymphomas
Disease of adults (median
age 63)
Usually widely disseminated
Poor response to all
attempted therapies,
? curable with transplant
5yr survival 27%
Pathogenesis
Due to t(11;14)
Upregulates Bcl1 (cyclin
D1), a cell cycle regulator
Mantle cell lymphoma
Pathology/Diagnosis
Benign equivalent is lymphocyte of
inner mantle zone
Cytology similar to cleaved cell, but
nuclear irregularities not as
prominent
Nodal infiltration diffuse, vaguely
nodular or "mantle zone" around
residual benign follicles
Large cell progression infrequent
Immunophenotype:
Positive: monoclonal light
chain, CD19, CD5, Bcl1 (and
Bcl2)
Negative CD10, CD23
Follicular lymphoma
Bcl2
CyclinD1
Mantle cell lymphoma
Table X: Indolent B cell lymphomas
Follicular
Lymphoma
(Grade I)
Marginal zone
Lymphoma
Small lymphocytic
lymphoma/CLL
Mantle cell
Lymphoma
Frequency (%
all lymphomas
22% 8 7 6
Age of onset
median
59 61 65 63
Stage at
Presentation
Stage III/I V
Disseminated
Stage I Stage IV Stage III/IV
Response to
Therapy
Good to most
treatments,
but incurable
short of
transplant
Frequently
curable
Similar to
Follicular
lymphoma
Poor response to
all therapies
to date
5 yr survival 72% 74% 51% 27%
Predominant site
presentation
Nodal Extranodal Marrow/nodal Nodal
Pattern of nodal
Infiltration
Follicular Diffuse Diffuse Diffuse,
nodular
or
mantle zone
Benign cell
Equivalent
Germinal
center
small cleaved
cell
Marginal zone
Lymphocyte
Virgin B cell Mantle cell
Dominant cell
type
Small cleaved
cell in most
cases, but can
be large cell
Mix of small
lymphocytes,
plasma cells
Small
lymphocytes
with round
nucleus
Small cell
with irregular
nucleus,
similar to
cleaved
Immunopheno
-type
Positive: CD19
CD10, Bcl2+
Negative: CD5-
Positive:
CD19, Bcl2
Negative:
CD10, CD5
Positive:
CD19, CD5
CD23
Negative:
CD10
Positive:
CD19, CD5,
Bcl2
Negative:
CD10
Molecular
Pathogenesis
t(14;18)
Bcl2/JH
Trisomy 3 Trisomy 12 t(11;14)
Bcl1/JH
T cell lymphomas-Precursor T
Clinical
Disease of teenagers; boys>girls
Can present as acute leukemia or mediastinal mass+/- marrow
involvement
Aggressive lymphoma/leukemia, but curable: ~70% with
appropriate multiagent chemotherapy
Pathogenesis
No single gene culprit, but frequently involve translocation of
(onco)genes to site of T cell receptor genes, --> upregulation of
proteins
T cell lymphomas-Precursor T
Pathology
Benign equivalent
immature T cells of
thymus
Histology: Diffuse
infiltration of
thymus/adjacent lymph
nodes
Cytology: Blast cells
of intermediate size with
oval to convoluted
nuclear profiles, fine
chromatin and 0-1
nucleolus
Again need immunology
to distinguish from pre-B
Peripheral T cell lymphomas
Predominantly
leukemic/disseminated
T-cell prolymphocytic
leukemia
T-cell large granular
lymphocytic (LGL) leukemia
NK cell leukemia
Adult T-cell
leukemia/lymphoma
Predominantly nodal
Angioimmunoblastic T-cell
lymphoma
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma
unspecified
Anaplastic large cell
lymphoma, T/null-cell
Predominantly extranodal
Mycosis fungoides
Sezary syndrome
Primary cutaneous CD30+ T-
cell lymphoproliferative
disorders
Subcutaneous panniculitis-
like T-cell lymphoma
NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal
and nasal-type
Enteropathy-type intestinal T-
cell lymphoma
Hepatosplenic T-cell
lymphoma
Key points regarding T cell
lymphomas
Clinical
Represent 20% all lymphomas
More often extranodal than B
Can involve skin, midline facial
area, liver
Very characteristic clinical
presentations
Most diseases bad: high stage,
and poorer response to therapy
than B cell lymphomas of all
grades
Pathogenesis:
Characteristic cytogenetic findings
associated with several types
Anaplastic large cell
lymphoma- t(2;5): ALK1 gene
Hepatosplenic T cell
lymphoma- Isochromosome 7
Pathology
Cytologic features not as predictive of
behavior as B cell lymphomas
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma
--> better prognosis than most
indolent B cell lymphomas- 77% 5
year survival
Mycosis fungoides, indolent
cutaneous lymphoma, incurable, but
with long clinical course
Immunophenotypic studies frequently
demonstrate
Loss of normal T cell associated
antigens
Antigens associated with Natural
Killer cell function
Immunology absolutely necessary to
recognize
Ancillary diagnostic studies
Use of immunologic/molecular techniques
Malignant lymphomas reproduce the immunobiology of their
benign counterparts
This reproduction may be aberrant, and hence distinguishable
from normal
Expression, normal and aberrant can be used to:
Determine lineage, B versus T versus NK
Detect clonality
Suspect malignancy- loss or aberrant expression of
expected antigens
Recognize characteristic patterns of antigenic expression
associated with certain subtypes of lymphoma
Normal lymphoid maturation
Requires two major activities
The production of a unique
antigenic receptor on it's
surface
The expression of several
surface proteins necessary for
antigen recognition, cell
activation, cell-cell
communication.
Antigen receptors are
generated through the process
of "genetic rearrangement"- the
random selection and
juxtaposition of discontinuous
genetic segments encoding the
antigen receptor genes
B cells
Immunoglobulin receptor
composed of two heavy
and two light chains
Select specific heavy
chain antigen
recognition sequence
Select only one of two
light chains, kappa or
lambda
T cells
Select one of two
heterodimeric receptors
Alpha/Beta
heterodimer T cell
receptor
Gamma/Delta
heterodimer T cell
receptor
Normal lymphoid maturation
Requires two major activities
The production of a unique antigenic receptor on it's surface
The expression of several surface proteins necessary for antigen
recognition, cell activation, cell-cell communication.
Antigen receptors are generated through the process of "genetic
rearrangement"- the random selection and then juxtaposition of
discontinuous genetic segments encoding the antigen receptor genes
B cells
Immunoglobulin receptor composed of two heavy chains and
two light chains
Select specific heavy chain gene sequences
Select only one of two light chains, kappa or lambda
T cells
Select one of two heterodimeric receptors
Alpha/Beta heterodimer T cell receptor
Gamma/Delta heterodimer T cell receptor
Antigen receptor selection- B cell
Surface antigen production
Immune cells require numerous surface molecules for
effective immune response, cell-cell communication and
regulation
Classified into B cell associated, T cell associated, activation
associated, cytokine receptors
Expression occurs in an orderly sequence in lymphoid
maturation
Antibodies to these molecules cataloged thru the CD -
clusters of differentiation - numerical system
Initially developed to characterize monoclonal antibodies
detecting proteins whose function was unknown .
Now up to CD166. You'll only be tested on 1-130 though
(- a joke for you paranoid types.)
B cell antigen expression
T cell antigen expression
Immunologic Techniques
Flow cytometry-automated
fluorescent microscopy
Immunohistochemistry- in situ
immunologic detection
through the use of enzyme
substrate color deposition
Both utilize monoclonal
antibodies to detect clonality
and unique antigenic patterns
Immunologic Techniques
Flow cytometry-automated fluorescent microscopy
Immunohistochemistry- in situ detection through the use of
enzyme substrate color deposition
Examples
B cell small lymphocytic lymphoma-
Monoclonal light chain, CD19, CD20, CD5, CD23
positive, CD10 negative
B cell follicular lymphoma-
Monoclonal light chain, CD19, CD20, CD10
positive, CD5 negative
Molecular techniques
Detection of antigen receptor clonality
Detection of unique cytogenetic
rearrangements/translocations
Examples
Clonal gene rearrangement by Southern blot
Bcl2/JH rearrangement by polymerase chain
reaction
Clinical presentation
Enlarging mass(es), typically painless, at sites of nodal
tissue
Obstruction, ulceration of hollow organs- pain, perforation
Interference with normal organ function-
Solid organ infiltration- kidneys, liver, bone marrow
Systemic symptoms
Fever
Night sweats
Weight loss
If marrow infiltrated, can have leukemic component
Clinical staging of lymphomas
Defines extent of disease; determines therapy and prognosis
Based on physical, radiologic examination, bone marrow biopsy and
aspiration
Ann Arbor Staging system
B symptoms- fever, weight loss > 10% body weight, night sweats
Staging table
Prognosis
International prognostic index
Aggressive lymphomas
Cytogenetics
Oncogenes
International Prognostic Index 1
Clinical features
identifying prognostic
subsets of diffuse
large cell lymphoma
Identified through
retrospective
statistical analysis of
large set patients
Assigned 1 point for
each bad feature
Survival curves
Therapy I Indolent lymphomas
Seminar cases will also discuss
Limited stage (5-10% cases)
Radiation therapy
Can be curative
Disseminated indolent/low grade lymphomas (90%)
No therapy
Low morbidity limited chemotherapy
Older patients
No expectation of cure
Most will respond totally or partially, with
months to years of disease free survival,
but will relapse
Many will respond to additional rounds of
similar or alternative regimens
Pts will die of disease, or interceding
disease of elderly
Death from disease due to
Immune suppression- infections
Progression to aggressive lymphoma
"Bone marrow transplant"-
Effort at cure
Reserved for younger patients <60
High dose chemotherapy and
allogeneic transplantation
High dose chemotherapy and
autologous peripheral stem cell
collection/reinfusion
Increased morbidity
Therapy II- Aggressive
lymphoma
Limited disease localized disease treated with irradiation
plus limited cycles multiagent chemotherapy
More extensive disease with more cycles multiagent (>/= 4
drugs) chemotherapy
Complete remission rates 60-80%
30-40% cured
Newer therapies and their roles still being established
Bone marrow transplantation
Allogeneic
Autologous
Immunotherapy
Hodgkin's lymphoma
Less common than NHL; ~
10,000 cases per year
Age incidence bimodal, with one
peak in late adolescence, young
adulthood, second peak
beginning in sixth decade
Bimodal curve shifts to
younger ages in poorer
countries
Unlike NHL, HL diagnosed by
the presence of a minor cellular
component, the Reed-
Sternberg cell, found in the
appropriate microscopic cellular
background
Hodgkin's lymphoma
classification
Rye Classification REAL/WHO Classification
Lymphocyte predominant-5% Lymphocyte predominance,
nodular
Nodular sclerosis-70%
Mixed cellularity-20% Classical HL
Lymphocyte depleted-5% Lymphocyte rich classical HL
Nodular sclerosis
Mixed cellularity
Lymphocyte depletion
Unclassifiable classical HL
Hodgkin's Histologic subtypes
Are characteristic patterns of
involvement, and characteristic
variants of Reed Sternberg cell
associated with different subtypes
Nodular sclerosing HL
Most common type Hodgkin's
lymphoma in US/Europe
Usually presents in the anterior
mediastinum and neck of young
adult females
Characterized by fibrotic capsule
and bands subdividing tissue and
Lacunar variant Reed Sternberg
cell
Histologic
subtypes 2
Lymphocyte predominant
Usually presents with limited disease in the
neck of young adults
Associated with L and H (lymphocytic and
histiocytic) or "popcorn cell" variant RS cell
Mixed cellularity
More extensive disease
Older patients than NS and LP
More R-S cells, eosinophils, plasma cells
Mononuclear variant R-S cells
Inherently more aggressive disease
Lymphocyte depleted
Often presents in retroperitoneum, older
patients
Accompanied by loss lymphocytes,
sclerosis and pleomorphic RS cell variants
Also more aggressive disease
Ancillary studies
Ancillary immunologic studies assist the dx of Hodgkins' lymphoma
Distinguish HL from
Immunoblast reactions
Unusual variants of NHL
CD15 and CD30 antigens in golgi and on cell membrane of R-S cells
most useful
Patterns of spread
Hodgkin's lymphoma spreads contiguously via
lymphatics
Staging as in NHL- may or may not include
laparotomy/splenectomy
Therapy
Limited stage, low bulk disease treated with
radiation therapy
Higher stage, B symptoms (IIB-IV) treated with
multi-agent chemotherapy+/- radiation therapy
Complications of therapy
Radiation effects to lungs, heart, bone marrow
Sterility
Splenectomy associated sepsis
Therapy associated second malignancies
Prognosis
Hodgkin's lymphoma is a curable malignancy
Overall cure rate approximately 80%
With modern therapy, prognosis based more on
staging, bulk of disease, than morphologic subtype
Not true in earlier era, where prognosis decreased
with number of lymphocytes; lymph depleted HL
had a terrible prognosis
Pathobiology
The etiology of HL is still unknown
The lineage of the R-S cell was also obscure until recently
The mixed cellular infiltrate, unusual large cells, clustered familial
cases, and early evidence of immune dysfunction suggest an infectious
etiology+/- an inherited predisposition
In approximately 30% of cases, Epstein Barr virus found within the RS
cells
Molecular studies, utilizing single cell dissection and PCR based
sequencing of the antigen receptor genes indicate that the R-S cell in
the majority of cases is an altered B cell.
Thus HL is a type of B cell lymphoma, but with a very different
biology from the other types of B cell lymphoma
Still deserves a separate category in the classification system
Molecular information
The molecular abnormalities within the different types of
R-S variants effect the expression of lineage associated antigens
L and H cells of lymphocyte predominant HL express B cell
antigens, and are clonal proliferations of this cell type
RS cells of other types may express T cell, B cell and macrophage
associated antigens, but usually fail to express antigen receptors
At the molecular level, show B cell gene rearrangements with out of
frame mutations or.
Mutations in transcription/translation systems so no antigen receptor
proteins transported to surface
The End!
Additional figures
Reed Sternberg cells
Large cells
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cells of The Immune SystemDocument38 paginiCells of The Immune SystemprabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells Tissues and Organs of The Immune System ClassDocument57 paginiCells Tissues and Organs of The Immune System ClassKoushali Banerjee100% (2)
- Lymphoid NeoplasmsDocument52 paginiLymphoid NeoplasmsAmalia Riska GÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisDe la EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphatic SystemDocument22 paginiLymphatic SystemdrynwhylÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells of The Immune SystemDocument28 paginiCells of The Immune SystemWei Zhu100% (3)
- Chapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFDocument61 paginiChapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFanaraudhatulÎncă nu există evaluări
- RA & SLE Kuliah Blok 2014 EditDocument75 paginiRA & SLE Kuliah Blok 2014 EditAdi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbiology Exam 1 ReviewDocument39 paginiMicrobiology Exam 1 ReviewanthonymirabellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Lymphatic System and ImmunityDocument140 paginiThe Lymphatic System and ImmunityAditya Bayukusuma100% (1)
- WBC Lymph Node SpleenDocument12 paginiWBC Lymph Node Spleendr brijesh TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma (Report)Document50 paginiNon-Hodgkins Lymphoma (Report)Dayledaniel SorvetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Anatomy) Chapter 12 - Lymphatic SystemDocument71 pagini(Anatomy) Chapter 12 - Lymphatic SystemJezreel Mian A. LacsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Stroke WritingDocument9 paginiPost Stroke WritingAdi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphatic SystemDocument13 paginiLymphatic SystemBasant karn100% (6)
- Soojeedes Human Anatomy and Physiology PDFDocument119 paginiSoojeedes Human Anatomy and Physiology PDFmaxamed Buule IsaaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphoma (Ean's) - 2Document29 paginiLymphoma (Ean's) - 2eanfital11Încă nu există evaluări
- 2020 Diagnosiscodefrequencies AsDocument710 pagini2020 Diagnosiscodefrequencies AsM del100% (1)
- Pathology of Hematopoietic System 2012-2013 by DR - Mai AliDocument17 paginiPathology of Hematopoietic System 2012-2013 by DR - Mai AliMuhammad Hilman Abu BakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Hodgkin'S Lymphoma: Oliveros Francis!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Document48 paginiNon-Hodgkin'S Lymphoma: Oliveros Francis!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!francis00090Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic and Clinical Immunology PDFDocument86 paginiBasic and Clinical Immunology PDFAbbass El-Outa100% (1)
- Limfoma Maligna FinalDocument50 paginiLimfoma Maligna FinalAulia Ayu PuspitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diseases and Tumors of Lymphoid SystemDocument97 paginiDiseases and Tumors of Lymphoid SystemamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphoma: Pro - Dr.Ahmed EisaDocument45 paginiLymphoma: Pro - Dr.Ahmed EisaOmar Mohammed100% (1)
- LymphomaDocument53 paginiLymphomaRobert ChristevenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kuliah LymphadenopathyDocument78 paginiKuliah LymphadenopathyaisyaahnpÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1pathology Limfnode UnimalDocument85 pagini1pathology Limfnode UnimalJefry SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology of Lymph Nodes: Norman Levy, MDDocument92 paginiPathology of Lymph Nodes: Norman Levy, MDDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 15-Mature-Lymphoid-Neoplasms-SCDocument65 paginiWeek 15-Mature-Lymphoid-Neoplasms-SCKyle CollladoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A7Document4 paginiA7Saman SadeghiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patho - 4th Asessment - Lymphoproliferative Disorders I - 31 Jan 2007Document24 paginiPatho - 4th Asessment - Lymphoproliferative Disorders I - 31 Jan 2007api-3703352100% (1)
- Blockxiv Neoplasms Lymphoid 2006Document54 paginiBlockxiv Neoplasms Lymphoid 2006Ryo RyozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hem QuizDocument38 paginiHem QuizRaneem AljuhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Haematology 16 The Lymphoid SystemDocument33 paginiHaematology 16 The Lymphoid SystemAkbar AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic and Clinical ImmunologyDocument86 paginiBasic and Clinical ImmunologyWael AlkhatibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic ImmuneDocument38 paginiBasic ImmuneAseel BabikerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leucocytes (White Blood Cells) : NeutrophilsDocument9 paginiLeucocytes (White Blood Cells) : NeutrophilsKhant Si ThuÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Microbiology and Immunology Competency-MI1.8: Prof Pradyot PrakashDocument40 paginiGeneral Microbiology and Immunology Competency-MI1.8: Prof Pradyot PrakashKotha Chaitanya AbhiramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells of Immune SystemDocument16 paginiCells of Immune SystemKrishnanand NagarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hodgkin's LymphomaDocument33 paginiHodgkin's LymphomaAnsu MaliyakalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphoreticular FinalDocument42 paginiLymphoreticular FinalNafis Fuad SheikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDocument26 paginiCells and Organs of The Immune SystemMithila BanikÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.cells of Immune System Notes PowerpointDocument34 pagini2.cells of Immune System Notes Powerpointt4ths999Încă nu există evaluări
- LHYMPHOMADocument24 paginiLHYMPHOMACryptic LadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Cells of The Immune SystemDocument42 pagini2 Cells of The Immune SystemRayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leukocytes White Blood CellsDocument64 paginiLeukocytes White Blood CellsNevin BhunjunÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 WBCsDocument31 pagini2 WBCsDanz ShÎncă nu există evaluări
- PATHO LEC WBC Lymph Nodes Spleen Thymus Part1 CompressedDocument84 paginiPATHO LEC WBC Lymph Nodes Spleen Thymus Part1 CompressedAngelo HinonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathomorphology of Immune System. Reactions and Mech Anisms of HypersensitivityDocument72 paginiPathomorphology of Immune System. Reactions and Mech Anisms of HypersensitivityEdi Kerina SembiringÎncă nu există evaluări
- White Blood Cells (WBCS)Document31 paginiWhite Blood Cells (WBCS)T NÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concepts in ImmunologyDocument56 paginiBasic Concepts in ImmunologyDedy SambahtraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Neoplastic WBC DisordersDocument17 paginiNon Neoplastic WBC Disordersdr100% (1)
- Genevieve Crane - Approach To Lymph Node-Path Cast Lymph Node Pathology Eve CraneDocument75 paginiGenevieve Crane - Approach To Lymph Node-Path Cast Lymph Node Pathology Eve CraneJose SirittÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology - Cells and Anatomy of The Immune SystemDocument9 paginiBiology - Cells and Anatomy of The Immune SystemFelix LupulescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benign Disoders of WBCsDocument40 paginiBenign Disoders of WBCsaliabumrfghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bahan Kuliah Id-1-2020Document63 paginiBahan Kuliah Id-1-2020Andi SaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphoid OrganDocument23 paginiLymphoid OrganSwetha RameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malignant Lymphomas: DR Nilukshi PereraDocument48 paginiMalignant Lymphomas: DR Nilukshi PereraThaveeshaLindsayWhiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leukocytes (WBCS) : Drsallama Hamid Consultant Lecturer DoctorDocument5 paginiLeukocytes (WBCS) : Drsallama Hamid Consultant Lecturer DoctorAhmed Ali AssafÎncă nu există evaluări
- White Blood Cell (Leucocyte)Document77 paginiWhite Blood Cell (Leucocyte)Dr.Gomathi sivakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- LNs HNDocument190 paginiLNs HNNinna Isabel VictorioÎncă nu există evaluări
- White Blood CellDocument21 paginiWhite Blood CellAnonymous 0C4OZmRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphadenopathy LymphomaDocument72 paginiLymphadenopathy LymphomaKelly YeowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1 - Intro and Overview of The Immune ResponseDocument67 paginiTopic 1 - Intro and Overview of The Immune ResponseAmber ChenÎncă nu există evaluări
- WBC Disorders Modified Aug 2021Document154 paginiWBC Disorders Modified Aug 2021PALATTAO, AUBRIE L. BSMT2-8Încă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 1 ImmunologyDocument82 paginiUNIT 1 ImmunologySivarama KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guia de Estudios PCFDocument7 paginiGuia de Estudios PCFOmar AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09-22!11!2 (Revised, Abbreviated) Cells of The Immune System (Chaplin)Document12 pagini09-22!11!2 (Revised, Abbreviated) Cells of The Immune System (Chaplin)Sheelendra Mangal BhattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malnutrition: A Secular Challenge To Child Nutrition: Review ArticleDocument13 paginiMalnutrition: A Secular Challenge To Child Nutrition: Review ArticleAdi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. Immunohematology: I. Basic PrinciplesDocument15 paginiA. Immunohematology: I. Basic PrinciplesAdi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clickers: What Are They? How Can I Use Them?: Educational Technologies CenterDocument21 paginiClickers: What Are They? How Can I Use Them?: Educational Technologies CenterAdi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prescription WritingDocument23 paginiPrescription WritingAdi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Condom Use Promotes Regression of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Clearance of Human Papillomavirus: A Randomized Clinical TrialDocument6 paginiCondom Use Promotes Regression of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Clearance of Human Papillomavirus: A Randomized Clinical TrialAdi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Based Learning and Textbook Chapter Review Session February 1, 2008Document2 paginiCase Based Learning and Textbook Chapter Review Session February 1, 2008Adi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Development and It'S Microscopic StructureDocument19 paginiBone Development and It'S Microscopic StructureAdi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 FullDocument3 pagini15 FullAdi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spirituality of Saluang Sirompak Music in Taeh Baruah Community, Minangkabau Nil IkhwanDocument6 paginiSpirituality of Saluang Sirompak Music in Taeh Baruah Community, Minangkabau Nil IkhwanAdi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Health Symposium: Community Based Primary Health Care, Empowerment and EquityDocument16 paginiGlobal Health Symposium: Community Based Primary Health Care, Empowerment and EquityAdi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Guide Med Profesionalism (SMTR II) 17 Maret 2014Document37 paginiStudy Guide Med Profesionalism (SMTR II) 17 Maret 2014Adi ParamarthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marieb ch20Document12 paginiMarieb ch20Intan KarmilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of The AxillarDocument43 paginiAnatomy of The AxillarJustine NyangaresiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tamil Nadu Class 12 - Bio-Zoology-Zoology - English Medium - Possible 5 Mark Questions With Answer.Document34 paginiTamil Nadu Class 12 - Bio-Zoology-Zoology - English Medium - Possible 5 Mark Questions With Answer.revamanian57% (7)
- Chapter 14 - Lymph and ImmunityDocument13 paginiChapter 14 - Lymph and Immunityapi-220531452Încă nu există evaluări
- Genevieve Crane - Approach To Lymph Node-Path Cast Lymph Node Pathology Eve CraneDocument75 paginiGenevieve Crane - Approach To Lymph Node-Path Cast Lymph Node Pathology Eve CraneJose SirittÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essay On AnthraxDocument6 paginiEssay On AnthraxAssignment GirlÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnatDocument45 paginiAnatRinxas VerinxtÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 Usmle Review Lecture Histology and Cell Biology I Rhys BrooksDocument25 pagini2015 Usmle Review Lecture Histology and Cell Biology I Rhys BrooksRushi ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIIMS Pharmacology May 2017 - 180517151700Document16 paginiAIIMS Pharmacology May 2017 - 180517151700SelvaArockiamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphocyte TraffickingDocument8 paginiLymphocyte TraffickingAbhishek KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Feather Follicle Cyst in ChickensDocument4 paginiFeather Follicle Cyst in ChickensShah NawazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Holstein B Cell Lecture 11-13-14Document47 paginiHolstein B Cell Lecture 11-13-14Alex DennisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neoplasia 1Document14 paginiNeoplasia 1Omar MaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7. Elements of Host Protective Responses - ClinicalKeyDocument12 paginiChapter 7. Elements of Host Protective Responses - ClinicalKeyد. محمد سند راشد الحصينيÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anaphysio of BreastDocument3 paginiAnaphysio of BreastVictor BiñasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 10 The Lymphatic System: ZOO 115 Animal Histology Laboratory Exercises 1Document4 paginiExercise 10 The Lymphatic System: ZOO 115 Animal Histology Laboratory Exercises 1Christi Lorraine LayogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 50 Assessment of Immune FunctionDocument12 paginiChapter 50 Assessment of Immune FunctionChan SorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thyroid & Lymph NodesDocument44 paginiThyroid & Lymph NodesSarah CornerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rewiew Study of VadamargDocument10 paginiRewiew Study of Vadamargkonic singh chauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Vessel and Lymphatic Lab OutputDocument12 paginiBlood Vessel and Lymphatic Lab OutputDayledaniel SorvetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- THE Lymphatic System & Body DefensesDocument39 paginiTHE Lymphatic System & Body DefensesSaiful AmriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lymphatic CaseDocument6 paginiLymphatic CaseGlenn Arjay BataraoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 20 Lymphatic SystemDocument48 paginiChapter 20 Lymphatic SystemRahmah Intan Aprilia100% (1)
- Chapter 29 Lymphatic System PDFDocument24 paginiChapter 29 Lymphatic System PDFMACON824Încă nu există evaluări