Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Operations Management: Topic 9 - Quality Management (TQM)
Încărcat de
faz143Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Operations Management: Topic 9 - Quality Management (TQM)
Încărcat de
faz143Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 1
Operations
Management
Topic 9 -
Quality Management
(TQM)
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 2
Quality Management
Objectives
be able to understand modern
concepts of quality and dimensions
of quality
be able to discuss employee
involvement and J IT in Total Quality
Management
be able to describe basic quality tools
Introduction to ISO
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 3
QUALITY is the ability of a
product or service to consistently
meet or exceed customer
expectations.
What Does the Term QUALITY
means?
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 4
Traditional vs. Modern Concept of
Quality Control
Traditional Modern
One person, small
group
Include everyone from raw
material, productivity,
design, process, top
management
Find mistakes after
completion, at the end
of line
Find where the mistakes
might occur, before
completion
No specific methods,
based on experience
Use statistical; control
charts to monitor
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 5
Dimension of Quality
Performance main characteristics
Special Features extra characteristics
Conformance how well corresponds to
expectation
Reliability consistency of performance without
breakdown
Durability useful life time
Safety safe to use as directed
Aesthetics nice to look at
Service After Sale handling of complaints, help
lines and checking customer satisfaction
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 6
Consequences of Poor Quality
Reputation & image will suffer
Pay special attention to potential liability
due to injury, damage or even death
Rework have to be done, slow the process
to accommodate rework, high scraps
Increase cost of rework, scrap, repair &
replacement, legal expenses
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 7
Responsibility for Quality
Top management
Design
Procurement
Production/operations
Quality assurance
Packaging and shipping
Marketing and sales
Customer service
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 8
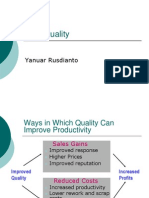
Cost of Quality
Internal Cost
Failure cost: results from production of defective
parts before delivery (rework, scrap, downtime)
Appraisal cost: evaluating products (lab testing,
inspector)
Prevention cost: reducing potential for defective
(training, awareness program)
External cost
occur after delivery (liabilities, warranty, sued by
customer)
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 9
Quality Certification
ISO 9000
Set of international standards on quality management
and quality assurance, critical to international
business
ISO 14000
A set of international standards for assessing a
companys environmental performance
Must go through process documenting procedures
Then onsite visit to verify, award certificate & series of
audits
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 10
Total Quality Management
New attitude towards quality using Three Philosophies
Continuous improvement KAIZEN
Involvement of everyone in the organization
Customer satisfaction
Expands the traditional view of quality beyond looking
only at the quality of the final product or service but to
look at quality of every aspect of the process
Not only on product, but also services e.g. banking,
hospital
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 11
Elements of TQM
Utilizes education & training everyone
Encourages empowerment of the employees in
the work place, team approach
Promote understanding & fulfilling the needs of
customers
Define quality in term of customer requirement
Use statistical reasoning with data to solve
problems & to improve
View quality improvement as never ending
quest to improve the process
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 12
Employee Involvement
In every step of production process,
involve directly with the system
Everyone must be responsible on their
work
Build communication network,
employees with supervisor (open
minded, supportive)
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 13
Relationship between TQM and
Just-In-Time
J IT emphasizes continuous improvement
& enforces problem solving since design
to production stage; deliver just as
needed
Target less inventory, less scrap, rework,
reduce cost
Limits potential sources of error, give
early warning, produce in small batches
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 14
TQM Lead to Lower Production
Cost
Emphasize the quality from supplier &
distributor
Reduce prevention cost ( less potential
for defective parts from employees)
Reduce cost of inspection
Reduce cost of rework, replacement
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 15
Obstacles to Implementing TQM
Lack of:
Company-wide definition of quality
Strategic plan for change
Customer focus
Real employee empowerment
Emphasis on short-term financial results
Time to devote to quality initiatives
Leadership
View of quality as a quick fix
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 16
The PDSA
Cycle
Plan
Do
Study
Act
PDCA
Check
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 17
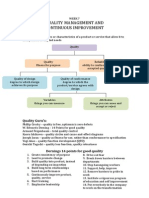
The Process Improvement Cycle
Implement the
Improved process
Select a
process
Study/document
Seek ways to
Improve it
Design an
Improved process
Evaluate
Document
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 18
Basic Quality Tools
There are a number of tools that
can be used for problem solving
and process improvement
Tools aid in data collection and
interpretation, and provide the
basis for decision making
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 19
Basic Quality Tools
1. Flowcharts
2. Check sheets
3. Histograms
4. Pareto Charts
5. Scatter diagrams
6. Control charts
7. Cause-and-effect diagrams
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 20
FLOWCHART
Drive in
check price
self serve?
to pump
shut off
engine
walk to pay
station
yes
no
check card
transmit approved?
turn on
pump
yes
no
back
to car
pump
gas
walk to
booth
wait
employee
totals
charges
check
accuracy
prepare
receipt
sign
copy
copy to
file
copy to
wallet
return to car
on the road
again
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 21
/
/
/ / /// /
// ///
// ////
///
//
/
Hour
Defect 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
A
B
C
/
/
//
/
(a) Check Sheet: An organized method of
recording data
Figure 6.6
CHECK SHEETS
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 22
Histogram
(f) Histogram: A distribution showing the
frequency of occurrences of a variable
Figure 6.6
Distribution
Repair time (minutes)
F
r
e
q
u
e
n
c
y
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 23
PARETO ANALYSIS
80% of the
problems
may be
attributed to
20% of the
causes.
Smeared
print
N
u
m
b
e
r
o
f
d
e
f
e
c
t
s
Off
center
Missing
label
Loose Other
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 24
Scatter Diagram
(b) Scatter Diagram: A graph of the value
of one variable vs. another variable
Absenteeism
P
r
o
d
u
c
t
i
v
i
t
y
Figure 6.6
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 25
CONTROL CHART
970
980
990
1000
1010
1020
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
UCL
LCL
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 26
CAUSE-AND-EFFECT DIAGRAM
Effect
Materials Methods
Equipment People
Environment
Cause
Cause
Cause
Cause
Cause
Cause
Cause
Cause
Cause
Cause
Cause
Cause
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 27
Benchmarking Process
Identify a critical process that needs
improving
Identify an organization that excels in
this process
Contact that organization
Analyze the data
Improve the critical process
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 28
Lets Recap!
What are the dimensions of quality?
Whose responsible for quality?
Name some of the basic quality tools.
What are the consequences of poor
quality?
Which quality certificate involve with
environmental performance?
10/15/2014 NY - KJP 585 2009 29
Summary
Understand the Concept of Total
Quality Management
Significant Impact of Total Quality
Management in Modern Manufacturing
Next class, we will have some
calculations in Statistical Quality
Control
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Process Improvement Simplified: A How-to-Book for Success in any OrganizationDe la EverandProcess Improvement Simplified: A How-to-Book for Success in any OrganizationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost of Quality PDFDocument33 paginiCost of Quality PDFAlvin DimasacatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsDocument35 paginiTotal Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key Elementsronski17Încă nu există evaluări
- Cost of Quality PDFDocument29 paginiCost of Quality PDFSenthil KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improving Service Quality and ProductivityDocument23 paginiImproving Service Quality and ProductivityUtsav MahendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality: Presented By: Mohd Saiful Izwaan Bin Saadon Lecturer (Quality Engineering Dept.)Document40 paginiQuality: Presented By: Mohd Saiful Izwaan Bin Saadon Lecturer (Quality Engineering Dept.)Khairul ZaimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost of QualityDocument27 paginiCost of QualityAkshitha BasavarajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment and Reduction of Cost of Quality at Elgi Sauer Compressors LimitedDocument49 paginiAssessment and Reduction of Cost of Quality at Elgi Sauer Compressors LimitedVasanth KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHP 19 - Quality, Time and The Theory of Constraints (Complete) (With Answers)Document59 paginiCHP 19 - Quality, Time and The Theory of Constraints (Complete) (With Answers)kenchong7150% (1)
- Unit 4 Total Quality Management-Rev-01-2019Document23 paginiUnit 4 Total Quality Management-Rev-01-2019Vinayak VinayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Management and Continuous ImprovementDocument6 paginiQuality Management and Continuous ImprovementautumntaitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost of Quality As A Driver For Continuous Improvement - Case Study - Company XDocument8 paginiCost of Quality As A Driver For Continuous Improvement - Case Study - Company XAbdur Rahman UsamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution Manual, Managerial Accounting Hansen Mowen 8th Editions - CH 15Document46 paginiSolution Manual, Managerial Accounting Hansen Mowen 8th Editions - CH 15jasperkennedy089% (18)
- Value ChainDocument6 paginiValue ChainSyed NazrulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Quality: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument16 paginiManagement of Quality: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinhenryagyemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACE Silver 2015 PresentationDocument20 paginiACE Silver 2015 PresentationY BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality CostDocument21 paginiQuality Costankitd7777Încă nu există evaluări
- Quality ManagementDocument26 paginiQuality ManagementNur AisyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost of QualityDocument27 paginiCost of Qualitykashifbutty2kÎncă nu există evaluări
- TS16949 TrainingDocument40 paginiTS16949 TrainingP K Senthil KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation Management Chapter 12Document70 paginiOperation Management Chapter 12Ahmad Izzat HamzahÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASD CV Jan 21Document4 paginiASD CV Jan 21Anil DesaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost of QualityDocument41 paginiCost of QualityJayesh Vishnuswami100% (2)
- Kra 210114 RDocument157 paginiKra 210114 RVikas Kashyap100% (1)
- Cost of Quality, Group-6Document21 paginiCost of Quality, Group-6AarushiÎncă nu există evaluări
- OM M9 TQM HandoutDocument64 paginiOM M9 TQM HandoutChandan SainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cost of QualityDocument41 paginiThe Cost of QualityKundan Kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Five Quality Management and Control 5.1. Overview of Total Quality Management and Quality SpecificationDocument7 paginiChapter Five Quality Management and Control 5.1. Overview of Total Quality Management and Quality SpecificationGebrekiros ArayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Performance MeasuresDocument20 pagini5 Performance MeasuresBrennan Roi DuagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Six SigmaDocument35 paginiSix SigmaSantosh Iim LucknowÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Sigma InternetDocument35 pagini6 Sigma InternetPratibha SainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch11 Cost of QualityDocument13 paginiCh11 Cost of QualityAmeliaErfaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benifits of ISO Certification by BVQIDocument9 paginiBenifits of ISO Certification by BVQIMubeen AhsanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SM IiiDocument11 paginiSM IiiAnonymous lZ0hmpoFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Management: Topic 1: Basic Concepts in Operation ManagementDocument33 paginiIndustrial Management: Topic 1: Basic Concepts in Operation Managementfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic of Quality, SPC, Process CapabilityDocument110 paginiBasic of Quality, SPC, Process CapabilityminionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost of Quality Section ADocument46 paginiCost of Quality Section APranav ShandilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 6331Document4 paginiAssignment 1 6331ALIKNFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bme 9 and 10Document16 paginiBme 9 and 10Unnecessary BuyingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro Quality - TQMDocument62 paginiIntro Quality - TQMAgung GuskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoqDocument7 paginiCoqbharathimanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continuous Process Improvement Deming's 14 Points: Total Quality ManagementDocument63 paginiContinuous Process Improvement Deming's 14 Points: Total Quality ManagementVilmarie Baez MelendezÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO 9001-2008 AwarenessDocument44 paginiISO 9001-2008 AwarenesssamksampathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viswanathan: QA/Operational ExcellenceDocument4 paginiViswanathan: QA/Operational ExcellenceumeshjmangroliyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- World Class Quality ManagementDocument28 paginiWorld Class Quality ManagementSelva Ganapathy88% (8)
- Case Study 3 Software Industry IT Six Sigma ProjectDocument14 paginiCase Study 3 Software Industry IT Six Sigma Projectvikrambakshi67Încă nu există evaluări
- Apqp REV01Document152 paginiApqp REV01venkat59cÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost of Quality-PresentationDocument78 paginiCost of Quality-PresentationSweeetMimi100% (2)
- TQM Course ContentDocument22 paginiTQM Course ContentCriseldo CalinawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work Content of Production Team LeaderDocument18 paginiWork Content of Production Team LeaderSivakumar VedachalamÎncă nu există evaluări
- TQM 2&16 Mark With AnswerDocument25 paginiTQM 2&16 Mark With AnswerJaga Deesh100% (1)
- Advanced Quality AuditingDocument34 paginiAdvanced Quality AuditingNando EriawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q-A Sigma Green BeltDocument32 paginiQ-A Sigma Green BeltchrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality: A. Quality: A Management PhilosophyDocument12 paginiQuality: A. Quality: A Management PhilosophyBehbehlynnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coq - Assessing Quality CostsDocument44 paginiCoq - Assessing Quality CostsRazidah SagapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lean Tactics for Architects, Engineers, and IPD ContractorsDe la EverandLean Tactics for Architects, Engineers, and IPD ContractorsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Solving: The 5-Why’s: Unlocking the Power of Quality Assurance for Success in BusinessDe la EverandProblem Solving: The 5-Why’s: Unlocking the Power of Quality Assurance for Success in BusinessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Validating Chromatographic Methods: A Practical GuideDe la EverandValidating Chromatographic Methods: A Practical GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Modeling for Injection Molding: Simulation, Optimization, and ControlDe la EverandComputer Modeling for Injection Molding: Simulation, Optimization, and ControlHuamin ZhouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computers and Chemical Engineering: K.H. Chan, E.J. Dozal-Mejorada, X. Cheng, R. Kephart, B.E. YdstieDocument13 paginiComputers and Chemical Engineering: K.H. Chan, E.J. Dozal-Mejorada, X. Cheng, R. Kephart, B.E. Ydstiefaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Study of Boiler Maintenance For Enhanced Reliability of System A ReviewDocument8 paginiStudy of Boiler Maintenance For Enhanced Reliability of System A Reviewfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Planning of Operation & Maintenance Using Risk and Reliability Based MethodsDocument8 paginiPlanning of Operation & Maintenance Using Risk and Reliability Based Methodsfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- MVAC Testing & Commissioning Procedure - 2007Document245 paginiMVAC Testing & Commissioning Procedure - 2007spencersiu100% (6)
- Draft For Public Comment SPAN TS 21827 Part 1 2013Document45 paginiDraft For Public Comment SPAN TS 21827 Part 1 2013Jazlan90Încă nu există evaluări
- An Evaluation System of The Setting Up of Predictive Maintenance ProgrammesDocument19 paginiAn Evaluation System of The Setting Up of Predictive Maintenance Programmesfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Management: Topic 1: Basic Concepts in Operation ManagementDocument33 paginiIndustrial Management: Topic 1: Basic Concepts in Operation Managementfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Topic 8 - Project ManagementDocument62 paginiTopic 8 - Project Managementfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Operations Management: Topic 9 - Quality Management (TQM)Document29 paginiOperations Management: Topic 9 - Quality Management (TQM)faz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Operations Management: Topic 9 - Quality Management (TQM)Document29 paginiOperations Management: Topic 9 - Quality Management (TQM)faz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Topic 8 - Project ManagementDocument62 paginiTopic 8 - Project Managementfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Topic 7B-Short Term SchedulingDocument22 paginiTopic 7B-Short Term Schedulingfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Operations Management: Topic 7A - Production Planning and Control (Aggregate Planning)Document51 paginiOperations Management: Topic 7A - Production Planning and Control (Aggregate Planning)faz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Topic 3 - Plant LocationDocument35 paginiTopic 3 - Plant Locationfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Topic 2 - ForecastingDocument49 paginiTopic 2 - Forecastingfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Operations Management: Topic 3 - Plant LayoutDocument79 paginiOperations Management: Topic 3 - Plant Layoutfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Topic 5a - Procurement and Inventory ControlDocument54 paginiTopic 5a - Procurement and Inventory Controlfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1 - Introduction To OMDocument31 paginiTopic 1 - Introduction To OMfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Topic 3 - Plant LocationDocument35 paginiTopic 3 - Plant Locationfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1 - Introduction To OMDocument31 paginiTopic 1 - Introduction To OMfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- Topic 2 - ForecastingDocument49 paginiTopic 2 - Forecastingfaz143Încă nu există evaluări
- "Next Friend" and "Guardian Ad Litem" - Difference BetweenDocument1 pagină"Next Friend" and "Guardian Ad Litem" - Difference BetweenTeh Hong Xhe100% (2)
- Guideline On Smacna Through Penetration Fire StoppingDocument48 paginiGuideline On Smacna Through Penetration Fire Stoppingwguindy70Încă nu există evaluări
- Exercises - Fluid MechanicsDocument3 paginiExercises - Fluid MechanicsgemnikkicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review - Practical Accounting 1Document2 paginiReview - Practical Accounting 1Kath LeynesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Money Tree International Finance Corp. Checklist of Standard Loan RequirementsDocument2 paginiMoney Tree International Finance Corp. Checklist of Standard Loan RequirementsAgape LabuntogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Libro Resumenes 2012Document735 paginiLibro Resumenes 2012fdobonat613100% (2)
- Far Eastern University - Manila Income Taxation TAX1101 Fringe Benefit TaxDocument10 paginiFar Eastern University - Manila Income Taxation TAX1101 Fringe Benefit TaxRyan Christian BalanquitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Data: PD2310 ApplicationsDocument1 paginăElectrical Data: PD2310 ApplicationsKSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uas MR1Document2 paginiUas MR1IvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Employment Offer: 1. Employer InformationDocument2 paginiEmployment Offer: 1. Employer InformationnavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Potato Storage and Processing Potato Storage and Processing: Lighting SolutionDocument4 paginiPotato Storage and Processing Potato Storage and Processing: Lighting SolutionSinisa SustavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Standard (First Revision) : Method of Chemical Analysis of Hydraulic CementDocument44 paginiIndian Standard (First Revision) : Method of Chemical Analysis of Hydraulic CementArijit dasguptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report On Analysis of TSF Water Samples Using Cyanide PhotometerDocument4 paginiReport On Analysis of TSF Water Samples Using Cyanide PhotometerEleazar DequiñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- India Wine ReportDocument19 paginiIndia Wine ReportRajat KatiyarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care of Clients With Problems in OxygenationDocument5 paginiCare of Clients With Problems in OxygenationSkyla FiestaÎncă nu există evaluări
- K EtaDocument14 paginiK EtaJosue Teni BeltetonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installing Touareg R5 CamshaftDocument1 paginăInstalling Touareg R5 CamshaftSarunas JurciukonisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Pharmacology For AnesthetistDocument162 paginiComparative Pharmacology For AnesthetistGayatri PalacherlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- United States v. Victor Vallin-Jauregui, 4th Cir. (2013)Document4 paginiUnited States v. Victor Vallin-Jauregui, 4th Cir. (2013)Scribd Government DocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6Document2 pagini6Min Hsuan HsianÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Kuliah Liver CirrhosisDocument55 pagini6 Kuliah Liver CirrhosisAnonymous vUEDx8100% (1)
- Border Collie Training GuidelinesDocument12 paginiBorder Collie Training GuidelinespsmanasseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reaction Paper-RprDocument6 paginiReaction Paper-Rprapi-543457981Încă nu există evaluări
- Food Processing NC II - SAGDocument4 paginiFood Processing NC II - SAGNylmazdahr Sañeud DammahomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blueprint Huynh My Ky Duyen 2022 McDonald'sDocument2 paginiBlueprint Huynh My Ky Duyen 2022 McDonald'sHuỳnh Mỹ Kỳ DuyênÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of 100 New English Words and MeaningsDocument5 paginiList of 100 New English Words and MeaningsNenad AngelovskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q1. (A) The Diagram Shows A Microphone Being Used To Detect The Output From ADocument10 paginiQ1. (A) The Diagram Shows A Microphone Being Used To Detect The Output From ASivmi MalishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inverter 1 KW ManualDocument44 paginiInverter 1 KW ManualLeonardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DyslexiaDocument19 paginiDyslexiaKeren HapkhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Sajjad Hussain Sumrra Isomerism (CHEM-305) Inorganic Chemistry-IIDocument48 paginiDr. Sajjad Hussain Sumrra Isomerism (CHEM-305) Inorganic Chemistry-IITanya DilshadÎncă nu există evaluări