Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Overview of The 80x86 Family
Încărcat de
TarekHemdan0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
23 vizualizări16 paginiThe document provides an overview of the 80x86 family of microprocessors from 1978 to 2001. It discusses the benefits of assembly language over high-level languages, including speed, space efficiency, and capability. It also covers binary numbers, registers, segments and offsets in memory addressing. The 80x86 family introduced segmentation to allow addressing over 1 megabyte of memory using 16-bit registers.
Descriere originală:
Lecture 1
Titlu original
Lecture 1
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe document provides an overview of the 80x86 family of microprocessors from 1978 to 2001. It discusses the benefits of assembly language over high-level languages, including speed, space efficiency, and capability. It also covers binary numbers, registers, segments and offsets in memory addressing. The 80x86 family introduced segmentation to allow addressing over 1 megabyte of memory using 16-bit registers.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
23 vizualizări16 paginiOverview of The 80x86 Family
Încărcat de
TarekHemdanThe document provides an overview of the 80x86 family of microprocessors from 1978 to 2001. It discusses the benefits of assembly language over high-level languages, including speed, space efficiency, and capability. It also covers binary numbers, registers, segments and offsets in memory addressing. The 80x86 family introduced segmentation to allow addressing over 1 megabyte of memory using 16-bit registers.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 16
Overview of the 80x86 Family
1978 8086 (AM: 1 M)
1982 80286 (AM: 16M, VM: 1G)
1985 80386 (AM: 4G, VM: 64T; 32-bits)
1989 80486 (as above; faster)
1993 Pentium (as above; more powerful)
2001 Itanium (64-bits)
Why Assembly Language
Speed
assembly language programs much faster
(potentially) 5 to 10 times faster
Space
assembly language programs often the smallest
space considerations not ignorable - even today
Why Assembly Language
Capability
you can do things that are difficult or impossible in
HLLs
e.g. I/O devices
Knowledge
write better programs, even in HLLs
understand how things really happen
Binary Numbers
1 bit (0 or 1)
1 nibble: (four binary digits or bits)
min: 0000 (0h) max: 1111 (0Fh/15)
1 byte: (8 bits/2 nibbles)
min: 00000000 (0h) max: 11111111 (0FFh/255)
1 word: (16 bits)
min: 0000 0000 0000 0000 (0h)
max: 1111 1111 1111 1111 (0FFFFh/65,536)
register size
Registers
place in the CPU where a number is stored and
manipulated
3 sizes
8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit
4 types
general purpose
segment
index
stack
General Purpose Registers
16-bit/32-bit registers, located on-chip
all arithmetic and location operations occur in regs
(E)AX - accumulator register
(E)BX - base register
(E)CX - count register
(E)DX - data register
Others: IP, Flags
faster than memory (on-chip)
Index Register
also called pointer registers
mainly used for string instructions
SI - source index
DI - destination index
IP - instruction pointer
also: ESI and EDI
BX can also be used to index strings
IP cant be manipulated
Stack Register
BP - base pointer
SP - stack pointer
Register
Summary
Segments and Offsets
powerful memory management mechanism
break programs into modules
provide a way to easily implement OO programs
two processes can share data
BUT
many people think its terrible
Why?
Segments and Offsets
Segments and Offsets
8086 max addressable memory: 1M
couldnt use memory beyond 1M
only 16-bit regs => only address 64K
segmentation: 64K->1M (> 64K effort, > 256K lot of effort)
80286 max addressable memory: 16M
Fixed with 80386 but ...
MS-Dos still uses 1976 segmentation!
Linux, Unix, Windows 9x Windows NT OK
Segments and Offsets
Linear addressing
linear array of bytes
single address/index selects a particular byte
Segment addressing
segments of bytes
segment value and offset selects a particular byte
segment value and offset should be independent of one
another
offset size limits the max size of a segment
Segments and Offsets
allows programs to have local variables
(also implemented via protected mode 80286)
8086/80286
segment and offset components 16-bit constants
max segment is 64K
80386/later
16-bit or 32-bit components
4GB segments, 32-bit offsets
Segments and Offsets
segmented address = logical address
actual linear address = physical address
Segments and Offsets
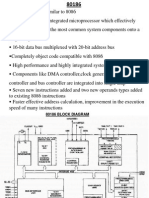
8086, 8088, 80186, 80188
Segment to Physical Address Mapping
Segment Offset
Segments and Offsets
Segment registers
CS - Code
DS - Data
ES - Extended
SS - Stack
386+
FS, GS
Offset registers
BX
DI
SI
BP
SP
IP
386+
any general reg can be used as
offset reg
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- CH02Document53 paginiCH02GemechuBGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course NotesDocument147 paginiCourse Noteszihad bin islamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 32 - Bit Microprocessor-Intel 80386Document71 pagini32 - Bit Microprocessor-Intel 80386Ibtisam Anwar KhattakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microprocessor and Assembly Language: LECTURE-3-THE 80X86 MicroprocessorDocument47 paginiMicroprocessor and Assembly Language: LECTURE-3-THE 80X86 MicroprocessorIqraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intel IA32 (80x86) Microprocessors: Dr. Doug L. Hoffman Computer Science 330 Spring 2002Document28 paginiIntel IA32 (80x86) Microprocessors: Dr. Doug L. Hoffman Computer Science 330 Spring 2002amdevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 2-Intel x86 Processor Architecture and EvolutionDocument37 paginiLec 2-Intel x86 Processor Architecture and EvolutionIsaac SindigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture: Assignment: 80X86 FamilyDocument17 paginiComputer Architecture: Assignment: 80X86 FamilyAnjan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mpi Unit 1Document22 paginiMpi Unit 1sree ramyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organization of The IBM Personal Computer: Chapter-3Document41 paginiOrganization of The IBM Personal Computer: Chapter-3plabon kumar sahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16-bit Microprocessors TransitionDocument145 pagini16-bit Microprocessors TransitionAASTHA KIETÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8086introductionDocument175 pagini8086introductionSasanka Sekhar SahuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week2-The 8086 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument48 paginiWeek2-The 8086 Microprocessor ArchitectureJerone CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-I: - 80386 IntroductionDocument74 paginiUnit-I: - 80386 IntroductionOmkar MarkadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intel 8086 Microprocessor Architecture GuideDocument9 paginiIntel 8086 Microprocessor Architecture Guidedz15dzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architecture of 80386Document42 paginiArchitecture of 80386santosh.parsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MPMC (Unit 02) Part 01Document101 paginiMPMC (Unit 02) Part 01bovas.biju2021Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1-MicroprocessorsDocument110 paginiUnit 1-MicroprocessorsRaj DesaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 80286 Microprocessor Supports Multitasking in Protected ModeDocument50 pagini80286 Microprocessor Supports Multitasking in Protected ModeLim Yee FattÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8086 16-bit Microprocessor HistoryDocument20 pagini8086 16-bit Microprocessor HistorySanjaykumar GowreÎncă nu există evaluări
- YMCA - BC - MP (Wk2)Document67 paginiYMCA - BC - MP (Wk2)harshiiitj9070Încă nu există evaluări
- 80386 FEATURESDocument39 pagini80386 FEATURESSorabh ChhabraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 NotesDocument12 paginiUnit 1 NotesShreyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Complete Understanding of Microprocessors and Intro To ARMDocument56 paginiThe Complete Understanding of Microprocessors and Intro To ARMasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- SEC1601Document231 paginiSEC1601Chetan GaurkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FEATURES OF 80386:: 2) Address 4GB of Memory 2) 16 MB ofDocument39 paginiFEATURES OF 80386:: 2) Address 4GB of Memory 2) 16 MB ofJ VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture4 - CISCArchitecture (Nibs-PC's Conflicted Copy 2016-07-27)Document32 paginiLecture4 - CISCArchitecture (Nibs-PC's Conflicted Copy 2016-07-27)Mitrasish MukherjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture#2 Fut Microprocessor PDFDocument81 paginiLecture#2 Fut Microprocessor PDFAhmedGamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architecture of 80386Document39 paginiArchitecture of 80386Jaimon JacobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1Document48 paginiUnit 120IF207 Gayatri PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Intel 8086 Processor: Laying the Foundation for Modern x86 ArchitectureDocument14 paginiThe Intel 8086 Processor: Laying the Foundation for Modern x86 ArchitectureKim S KevohÎncă nu există evaluări
- WINSEM2023-24_BECE204L_TH_VL2023240505482_2024-03-26_Reference-Material-IDocument34 paginiWINSEM2023-24_BECE204L_TH_VL2023240505482_2024-03-26_Reference-Material-Iprathampalgandhi10Încă nu există evaluări
- ArchDocument17 paginiArchpriyaam37Încă nu există evaluări
- 8086 MICROPROCESSOR OVERVIEWDocument89 pagini8086 MICROPROCESSOR OVERVIEWkhisham20005389Încă nu există evaluări
- The 8086 Architecture: CS227 Western Washington UniversityDocument17 paginiThe 8086 Architecture: CS227 Western Washington UniversitySaranya PriyankaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The MICROPROCESSORS 8088/8086Document67 paginiIntroduction To The MICROPROCESSORS 8088/8086Melek MeleGim MeleGim100% (1)
- Tms320c64x ArchitectureDocument29 paginiTms320c64x ArchitectureMuru GanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microprocessor 80386Document40 paginiMicroprocessor 80386eshwar_worldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture: The Pentium ProcessorDocument43 paginiComputer Architecture: The Pentium ProcessorHussain JehlÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8086 Third Term TopicsDocument46 pagini8086 Third Term TopicsgandharvsikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- RegistersDocument3 paginiRegisterslokssaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to MicroprocessorsDocument33 paginiIntroduction to MicroprocessorsZaid Ali AlsurmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microprocessor Lecture2Document6 paginiMicroprocessor Lecture2CS420100% (12)
- Unit 3 MicroprocessorDocument155 paginiUnit 3 MicroprocessorHUISCIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap - 2 MPDocument53 paginiChap - 2 MPBeky KitawmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mic ProjectDocument15 paginiMic Projectsudarshan sonawaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- M4 Notes 1Document4 paginiM4 Notes 1pvyshnav371Încă nu există evaluări
- Real-Mode Memory AddressingDocument20 paginiReal-Mode Memory AddressingJas LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Intel 80x86: Thorne: Section 1.4-1.6, 2.2.4, Section 3.4 (Irvine, Edition IV: Section 2.2)Document25 paginiThe Intel 80x86: Thorne: Section 1.4-1.6, 2.2.4, Section 3.4 (Irvine, Edition IV: Section 2.2)Mohamed EnnajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8086 MICROPROCESSOR REGISTERS AND ADDRESSINGDocument89 pagini8086 MICROPROCESSOR REGISTERS AND ADDRESSINGBharathi MolletiÎncă nu există evaluări
- IBM PCDocument41 paginiIBM PCanishadandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MPMC Unit 1Document75 paginiMPMC Unit 1Bhure VedikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP Unit 1 OneshotDocument8 paginiMP Unit 1 Oneshotlococo2836Încă nu există evaluări
- MP - Lec 02 - The Microprocessor and Its ArchitectureDocument40 paginiMP - Lec 02 - The Microprocessor and Its ArchitectureuabdulgwadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assembly LanguageDocument18 paginiAssembly LanguageKurt Ira PobreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Organization of A PC: MemoryDocument33 paginiInternal Organization of A PC: MemoryPrasath SanthanamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microprocessor NotesDocument85 paginiMicroprocessor NotesJasmine KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architecture of 80386 MicroproDocument39 paginiArchitecture of 80386 MicroproDeepthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Konsep Dasar MikrokomputerDocument50 paginiKonsep Dasar Mikrokomputersekar mÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationDe la EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3De la EverandMega Drive Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #3Încă nu există evaluări
- B-07 Matrix 1Document10 paginiB-07 Matrix 1TarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orange Machine LearningDocument8 paginiOrange Machine LearningTarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example 2Document11 paginiExample 2TarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Graphics OpenGL Lecture NotesDocument44 paginiComputer Graphics OpenGL Lecture NotesAdnan OmanovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructions of 80x86Document41 paginiInstructions of 80x86Shrikant Suman Jaydeorao PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- OpenGl 1.CppDocument1 paginăOpenGl 1.CppTarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viewing and TransformationDocument28 paginiViewing and TransformationTarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glut CPPDocument59 paginiGlut CPPSuryanto YehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review 1 Opengl IDocument46 paginiReview 1 Opengl ITarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Op EnglDocument6 paginiOp EnglPrince KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolutionary Computation PerlDocument28 paginiEvolutionary Computation PerlReed Jones0% (1)
- Contour and Texture Analysis For Image SegmentationDocument21 paginiContour and Texture Analysis For Image SegmentationTarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microsoft Excel Basics Useful Tips For BeginnersDocument20 paginiMicrosoft Excel Basics Useful Tips For BeginnersB MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detmer Ch2Document49 paginiDetmer Ch2TarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructions of 80x86Document41 paginiInstructions of 80x86Shrikant Suman Jaydeorao PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Computer BasicsDocument188 paginiIntroduction To Computer BasicsJan Jamison ZuluetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detmer Ch6 PPDocument32 paginiDetmer Ch6 PPTarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReviewDocument30 paginiReviewTarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Windows 7 Beginners PDFDocument43 paginiWindows 7 Beginners PDFTarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excel 10 BasicsDocument22 paginiExcel 10 Basicsapi-269534646Încă nu există evaluări
- Getting Started With Windows7Document24 paginiGetting Started With Windows7TarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Al2ed Chapter7Document43 paginiAl2ed Chapter7TarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Getting Started With Windows7Document24 paginiGetting Started With Windows7TarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Letter To Minia University Business Skills0001Document1 paginăLetter To Minia University Business Skills0001TarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microsoft Tips and TricksDocument95 paginiMicrosoft Tips and TricksTarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntroductionDocument11 paginiIntroductionTarekHemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Computer BasicsDocument188 paginiIntroduction To Computer BasicsJan Jamison ZuluetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 65 Shelby SurvivorDocument19 pagini65 Shelby Survivorasdfa asdfasdfdsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tecumseh Model Ov358ea 206904f Parts ListDocument5 paginiTecumseh Model Ov358ea 206904f Parts Listcamdog1010% (1)
- HCIA-Data Center V1.5 Exam OutlineDocument3 paginiHCIA-Data Center V1.5 Exam OutlineBenjaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2way2sat Idirect InstallationDocument15 pagini2way2sat Idirect InstallationDaniel Piette100% (1)
- Von Neumann Computer ArchitectureDocument4 paginiVon Neumann Computer Architectureecoboss100% (6)
- Software TestingDocument61 paginiSoftware Testingmalik143iÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Origins of MS-DOSDocument12 paginiThe Origins of MS-DOSNilay Tryambak KaradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DX DiagDocument10 paginiDX Diaghenrik_nordstrom94Încă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of ElectronicsDocument2 paginiFundamentals of ElectronicsatulzendeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Keytek Ce Master System UsersDocument108 paginiKeytek Ce Master System UsersSteven J BaynesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18.314 Practice Final ExamDocument4 pagini18.314 Practice Final ExamLionel CarlosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wily Intro Scope FaqDocument3 paginiWily Intro Scope Faqramprasad_ks75% (4)
- Computer AssignmentDocument7 paginiComputer Assignmentaroosh16Încă nu există evaluări
- Microprocessor Question BankDocument3 paginiMicroprocessor Question BankDORAIRAJ ADARSH Y UEC19132Încă nu există evaluări
- Pcs Command ReferenceDocument4 paginiPcs Command Referencegyan1Încă nu există evaluări
- DxDiag CESARDISEÑODocument10 paginiDxDiag CESARDISEÑOCesar Villalta CuetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- High and Low Level LanguagesDocument5 paginiHigh and Low Level LanguagesAhmed HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be301 02 PDFDocument56 paginiBe301 02 PDFNikita SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdul Hakeem SAP FICO Consultant Mobile No: +91 9533330964Document4 paginiAbdul Hakeem SAP FICO Consultant Mobile No: +91 9533330964dharmendra undavalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marine Electrical Systems ExplainedDocument8 paginiMarine Electrical Systems Explainedsunil1237Încă nu există evaluări
- Metode de Dezvoltare SoftwareDocument33 paginiMetode de Dezvoltare Softwaresilviu20aÎncă nu există evaluări
- TM 11-5805-262-34P - Switchboard - SB-22 - 1978 PDFDocument40 paginiTM 11-5805-262-34P - Switchboard - SB-22 - 1978 PDFWurzel1946Încă nu există evaluări
- Intel EssayDocument39 paginiIntel EssayBudila MariusÎncă nu există evaluări
- ConfigPro 5 Software GuideDocument99 paginiConfigPro 5 Software Guiderommel76100% (1)
- HPUX Add RAID-5 external disk enclosure SA20 to Itanium rx2600Document5 paginiHPUX Add RAID-5 external disk enclosure SA20 to Itanium rx2600iqbal_sabetowal7547Încă nu există evaluări
- Solar Powered Light Duty Flexible Drilling MechanismDocument4 paginiSolar Powered Light Duty Flexible Drilling MechanismOmkar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Manual: Genmitsu CNC Router 3018-ProverDocument50 paginiUser Manual: Genmitsu CNC Router 3018-Proverfrancois xavier chize100% (1)
- OEM/Dealer Manual: Lcs Itb LC-50Document80 paginiOEM/Dealer Manual: Lcs Itb LC-50Jaffer HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phoenix BIOS Post Codes - BIOS CentralDocument9 paginiPhoenix BIOS Post Codes - BIOS CentralLito HulipasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switch: Data SheetDocument29 paginiCisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switch: Data SheetHamed AhmadnejadÎncă nu există evaluări