Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Characteristics of IC 555
Încărcat de
ISHAN CHAUDHARYDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Characteristics of IC 555
Încărcat de
ISHAN CHAUDHARYDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Submitted by:-
Pallavi Choudhary
Roll No:-11538
Characteristics of IC 555
What is IC 555
The 555 timer IC is an integrated circuit (chip)
used in a variety of timer, pulse generation, and
oscillator applications. The 555 can be used to
provide time delays, as an oscillator, and as a flip-
flop element. Derivatives provide up to four timing
circuits in one package.
Introduced in 1971 by Signetics, the 555 is still in
widespread use due to its ease of use, low price,
and stability. It is now made by many companies
in the original bipolar and also in low-power
CMOS types. As of 2003, it was estimated that 1
billion units are manufactured every year.
Image of IC 555 AND its Working
The IC was designed in 1971 by Hans
Camenzind under contract to Signetics,
which was later acquired by Philips
(now NXP).
Depending on the manufacturer, the
standard 555 package includes 25
transistors, 2 diodes and 15 resistors
on a silicon chip installed in an 8-pin
mini dual-in-line package (DIP-8).
[2]
Variants available include the 556 (a
14-pin DIP combining two 555s on one
chip), and the two 558 & 559s (both a
16-pin DIP combining four slightly
modified 555s with DIS & THR
connected internally, and TR is falling
edge sensitive instead of level
sensitive).
The NE555 parts were commercial
temperature range, 0 C to +70 C, and
the SE555 part number designated the
military temperature range, 55 C to
+125 C.
IC 555 PIN OUT
IC 555
MODES
Monostable mode: In this mode, the 555 functions as a
"one-shot" pulse generator. Applications include timers,
missing pulse detection, bouncefree switches, touch
switches, frequency divider, capacitance measurement,
pulse-width modulation (PWM) and so on.
Astable (free-running) mode: The 555 can operate as an
oscillator. Uses include LED and lamp flashers, pulse
generation, logic clocks, tone generation, security alarms,
pulse position modulation and so on. The 555 can be used
as a simple ADC, converting an analog value to a pulse
length. E.g. selecting a thermistor as timing resistor allows
the use of the 555 in a temperature sensor: the period of
the output pulse is determined by the temperature. The
use of a microprocessor based circuit can then convert the
pulse period to temperature, linearize it and even provide
calibration means.
Bistable mode or Schmitt trigger: The 555 can operate as
a flip-flop, if the DIS pin is not connected and no capacitor
is used. Uses include bounce-free latched switches.
IC 555 MODES
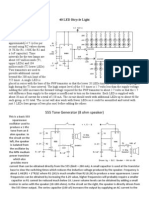
IC 555 as MONOSTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR
In the monostable mode, the 555 timer acts as a
"one-shot" pulse generator. The pulse begins
when the 555 timer receives a signal at the trigger
input that falls below a third of the voltage supply.
The width of the output pulse is determined by the
time constant of an RC network, which consists of
a capacitor (C) and a resistor (R). The output
pulse ends when the voltage on the capacitor
equals 2/3 of the supply voltage. The output pulse
width can be lengthened or shortened to the need
of the specific application by adjusting the values
of R and C.
The output pulse width of time t, which is the time
it takes to charge C to 2/3 of the supply voltage, is
given by
t=RCln(3)1.1RC where t is in seconds, R is in
ohms (resistance) and C is in farads(capacitance).
While using the timer IC in monostable mode, the
main disadvantage is that the time span between
any two triggering pulses must be greater than the
RC time constant
IC 555 as MONOSTABLE
MULTIVIBRATOR
t=RCln(3)1.1RC where t is in seconds, R is in
ohms (resistance) and C is in
farads(capacitance).
Experimental Value = 943.2us
Theoretical Value = 1.1*80*0.0022uf
= 193.6us
IC 555 as
ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR
In astable mode, the 555 timer puts
out a continuous stream of rectangular
pulses having a specified frequency.
Resistor R
1
is connected between V
CC
and the discharge pin (pin 7) and
another resistor (R
2
) is connected
between the discharge pin (pin 7), and
the trigger (pin 2) and threshold (pin 6)
pins that share a common node.
Hence the capacitor is charged
through R
1
and R
2
, and discharged
only through R
2
, since pin 7 has low
impedance to ground during output
low intervals of the cycle, therefore
discharging the capacitor.
IC 555 as
ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR
F = 1.45
(R+2R3) C1
Experimental Value = 3.01khz
Theoretical Value = 1.45__________
(0.562*10^-3+2*100kohm) 0.0022*10^-6
= 2.87khz(approx.)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 555 Timer Ic: Project ReportDocument10 pagini555 Timer Ic: Project ReportHarshada HalarnkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- STM32F303 PDFDocument133 paginiSTM32F303 PDFLuis SenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 555 Applications NoteDocument19 pagini555 Applications NoteIsaac Herrera100% (1)
- Retro Pan 320Document1 paginăRetro Pan 320YusufÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Cross-Processing" Color Negative Films in Process E-6Document1 pagină"Cross-Processing" Color Negative Films in Process E-6周明蕾Încă nu există evaluări
- Infrared Sensor Based Power SaverDocument7 paginiInfrared Sensor Based Power SaverShirishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wet Plate Emporium: Joseph J. McallisterDocument26 paginiWet Plate Emporium: Joseph J. McallisteranimaparadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 555 Full PWM CircuitDocument2 pagini555 Full PWM CircuitNash_HoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- FX 39Document1 paginăFX 39Massimo RapoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cool Summer Juices PDFDocument14 paginiCool Summer Juices PDFEmily JamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory of Oscilloscope: Introduction To CADDocument23 paginiTheory of Oscilloscope: Introduction To CADHifdzul Malik ZainalÎncă nu există evaluări
- STM32F Discovery BoardDocument42 paginiSTM32F Discovery BoardVehid TavakolÎncă nu există evaluări
- LZ ThesisDocument349 paginiLZ ThesiscalcurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequency Shift Keying FSK Modulator Using IC 555Document15 paginiFrequency Shift Keying FSK Modulator Using IC 555Sandoval FranklinÎncă nu există evaluări
- DELTA 100 Professional: Technical InformationDocument6 paginiDELTA 100 Professional: Technical Informationgiovanni.castelletti2004Încă nu există evaluări
- Rollei RPX 25 (Technical Datasheet) - Google TranslationDocument5 paginiRollei RPX 25 (Technical Datasheet) - Google Translationsalehina974Încă nu există evaluări
- Small Circuits of 555 I.CDocument6 paginiSmall Circuits of 555 I.Cبنیاد پرست100% (4)
- 8051 Microcontroller OSCILLATOR AND CLOCKDocument1 pagină8051 Microcontroller OSCILLATOR AND CLOCKsumitbahl50% (2)
- Clock3 Junior Assembly ManualDocument31 paginiClock3 Junior Assembly ManualTheHarbingerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fp4 Plus: Technical InformationDocument6 paginiFp4 Plus: Technical Informationgiovanni.castelletti2004Încă nu există evaluări
- Tone Generator Using Two 555 Timers - Electronics AreaDocument7 paginiTone Generator Using Two 555 Timers - Electronics AreaMharco ColipapaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ilford Pan F PlusDocument6 paginiIlford Pan F Plusmathun1Încă nu există evaluări
- Fomapan 200Document2 paginiFomapan 200Theo DelCampo100% (1)
- Avt 721Document4 paginiAvt 721Martins StarastsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 555 Timer CircuitDocument5 pagini555 Timer CircuitMack San MiguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Delta 3200 Ficha TecnicaDocument7 paginiDelta 3200 Ficha TecnicaFernando GiorgioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stacker Raspberry PiDocument5 paginiStacker Raspberry PiJederVieiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fomapan 100Document3 paginiFomapan 100hxbxrtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Projects Web MicroDocument30 paginiProjects Web MicroArdhika Dhennis Putra AnandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OscilloscopeDocument13 paginiOscilloscopeh_abhishek99Încă nu există evaluări
- GizDuino Users ManualDocument13 paginiGizDuino Users ManualreggieguapoÎncă nu există evaluări
- STM32F4 Advanced PeripheralsDocument26 paginiSTM32F4 Advanced PeripheralsMohamedAliFerjaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- PWM Fan 555 Driver W MosfetDocument3 paginiPWM Fan 555 Driver W Mosfetosbert6quimby100% (1)
- DPScope Build Your Own USBPC Based OscilloscopeDocument28 paginiDPScope Build Your Own USBPC Based Oscilloscopealidurrani50% (2)
- Designing A PC Oscilloscope Using FreeduinoDocument11 paginiDesigning A PC Oscilloscope Using FreeduinodiearzÎncă nu există evaluări
- AVR Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsDocument4 paginiAVR Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsMikoto RifkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- LED Cube 4x4x4Document6 paginiLED Cube 4x4x4Dusan Petrovic100% (1)
- Fomapan 100Document2 paginiFomapan 100alexandru_gheoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Testing The PIC Microcontroller 16F84ADocument4 paginiTesting The PIC Microcontroller 16F84AMatt Imri100% (2)
- Circuit Analysis With An OscilloscopeDocument4 paginiCircuit Analysis With An Oscilloscopegearhead1Încă nu există evaluări
- PIC 16F84A TutorialDocument58 paginiPIC 16F84A TutorialEduardo LaRaa100% (1)
- What Is A MicrocontrollerDocument3 paginiWhat Is A MicrocontrollerPotato BitsÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESP8266 Wi-Fi DatasheetDocument31 paginiESP8266 Wi-Fi DatasheetMert Solkıran100% (2)
- Exp 2 Resistors, Ohm's Law, Power Rating and I-V Caharacteristic (2012)Document10 paginiExp 2 Resistors, Ohm's Law, Power Rating and I-V Caharacteristic (2012)usmpowerlabÎncă nu există evaluări
- The 555 TimerDocument14 paginiThe 555 Timergurudatha265100% (4)
- 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument19 pagini8051 MicrocontrollerPrasath Rajendran100% (1)
- Kodak Professional Plus-X 125 Film / 125PX: Technical Data / Black-And-White FilmDocument10 paginiKodak Professional Plus-X 125 Film / 125PX: Technical Data / Black-And-White FilmGreg MartÎncă nu există evaluări
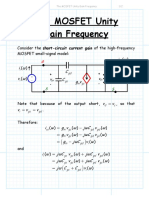
- The MOSFET Unity Gain FrequencyDocument2 paginiThe MOSFET Unity Gain Frequencyhariansyah0Încă nu există evaluări
- SiliconChipReview BitScope BS310Document4 paginiSiliconChipReview BitScope BS310FelipePerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- PIC Part5 InterruptsDocument53 paginiPIC Part5 InterruptsJean Profite100% (2)
- Snap Circuits SC-300Document3 paginiSnap Circuits SC-300grahambandleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Install Raspbian On RaspberryDocument26 paginiInstall Raspbian On RaspberryRiyadh Ar-Ridha YakubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osbahr Reversal FilmsDocument24 paginiOsbahr Reversal FilmsAndreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dual Trace OscilloscopeDocument8 paginiDual Trace OscilloscopeSudip MondalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vehicle Accident Prevention Using Eye Blink Sensor - SUSHANTDocument39 paginiVehicle Accident Prevention Using Eye Blink Sensor - SUSHANTMayugam InfotechÎncă nu există evaluări
- ILFORD SIMPLICITY Technical Data SheetDocument4 paginiILFORD SIMPLICITY Technical Data SheetParth ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 555 Oscillator ApplicationsDocument17 pagini555 Oscillator Applicationsgopir28Încă nu există evaluări
- 555 Timer ICDocument8 pagini555 Timer ICSaju NirankariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 555 Timer WikipediaDocument7 pagini555 Timer WikipediakalimbaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The 555 Timer?: Philips Components and Semiconductors AustraliaDocument15 paginiWhat Is The 555 Timer?: Philips Components and Semiconductors AustraliaLorena RabinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consolidation & Mergers in BankingDocument7 paginiConsolidation & Mergers in BankingISHAN CHAUDHARYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passport App Form V1.0Document6 paginiPassport App Form V1.0Ravi P RameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terms Associated With SportsDocument3 paginiTerms Associated With SportsISHAN CHAUDHARYÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMPLETE Project On NetworkingDocument128 paginiCOMPLETE Project On NetworkingISHAN CHAUDHARY100% (2)
- Ccna Project ReportDocument48 paginiCcna Project ReportISHAN CHAUDHARY89% (36)
- Work Order TemplateDocument2 paginiWork Order TemplateRed DragonÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fracture MechanicsDocument81 paginiOn Fracture MechanicsDEEPAK100% (1)
- D.E.I Technical College, Dayalbagh Agra 5 III Semester Electrical Engg. Electrical Circuits and Measurements Question Bank Unit 1Document5 paginiD.E.I Technical College, Dayalbagh Agra 5 III Semester Electrical Engg. Electrical Circuits and Measurements Question Bank Unit 1Pritam Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Bar Q Salaries Part 2Document5 paginiBar Q Salaries Part 2Brigette DomingoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20151201-Baltic Sea Regional SecurityDocument38 pagini20151201-Baltic Sea Regional SecurityKebede MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Details For Order #002 5434861 1225038: Not Yet ShippedDocument1 paginăDetails For Order #002 5434861 1225038: Not Yet ShippedSarai NateraÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAN MIGUEL CORPORATION, ANGEL G. ROA and MELINDA MACARAIG, vs. NATIONAL LABOR RELATIONS COMMISSION (Second Division), LABOR ARBITER EDUARDO J. CARPIO, ILAW AT BUKLOD NG MANGGAGAWA (IBM), ET ALDocument6 paginiSAN MIGUEL CORPORATION, ANGEL G. ROA and MELINDA MACARAIG, vs. NATIONAL LABOR RELATIONS COMMISSION (Second Division), LABOR ARBITER EDUARDO J. CARPIO, ILAW AT BUKLOD NG MANGGAGAWA (IBM), ET ALLaila Ismael SalisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form DVAT 27A: Intimation of Deposit of Government DuesDocument2 paginiForm DVAT 27A: Intimation of Deposit of Government DueshhhhhhhuuuuuyyuyyyyyÎncă nu există evaluări
- OPERATING MANUAL Micro Powder MillDocument51 paginiOPERATING MANUAL Micro Powder MillSher AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transport StrikeDocument9 paginiTransport StrikeYsrael Von ArcillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 6 - Dr. Cemre Erciyes PDFDocument24 paginiUNIT 6 - Dr. Cemre Erciyes PDFMaries San PedroÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Guide To Oauth and API SecurityDocument12 paginiHow To Guide To Oauth and API Securitysilviuleahu100% (1)
- Audi Navigation System Plus - MMI Operating ManualDocument100 paginiAudi Navigation System Plus - MMI Operating ManualchillipaneerÎncă nu există evaluări
- SecuritizationDocument46 paginiSecuritizationHitesh MoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safe and Gentle Ventilation For Little Patients Easy - Light - SmartDocument4 paginiSafe and Gentle Ventilation For Little Patients Easy - Light - SmartSteven BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Splunk Certification: Certification Exam Study GuideDocument18 paginiSplunk Certification: Certification Exam Study GuidesalemselvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trahar (2013) - Internationalization of The CurriculumDocument13 paginiTrahar (2013) - Internationalization of The CurriculumUriel TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Approved Journals For Promoting Purposes at The University of JordanDocument3 paginiList of Approved Journals For Promoting Purposes at The University of JordanZaid MarwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detroit ManualDocument435 paginiDetroit Manualvictorhernandezrega50% (2)
- Agenda 9Document46 paginiAgenda 9Bala Gangadhar TilakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caselet - LC: The Journey of The LCDocument5 paginiCaselet - LC: The Journey of The LCAbhi JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- IM0973567 Orlaco EMOS Photonview Configuration EN A01 MailDocument14 paginiIM0973567 Orlaco EMOS Photonview Configuration EN A01 Maildumass27Încă nu există evaluări
- LEBV4830Document371 paginiLEBV4830anton100% (1)
- 4 3 3LeaseLinesignedDocument42 pagini4 3 3LeaseLinesignedJagat Brahma PatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Navi Mumbai C.A. ListDocument48 paginiNavi Mumbai C.A. ListManish Shetty67% (9)
- Data Sheet: Permanent Magnet GeneratorDocument2 paginiData Sheet: Permanent Magnet Generatordiegoadjgt100% (1)
- Determination of Sales Force Size - 2Document2 paginiDetermination of Sales Force Size - 2Manish Kumar100% (3)
- Annex 1C - Ice Plant and Cold Storage Inspection ChecklistDocument9 paginiAnnex 1C - Ice Plant and Cold Storage Inspection ChecklistMaxmore Karumamupiyo100% (2)
- Java ProgramsDocument36 paginiJava ProgramsPrashanth MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- David-Huynh Indeed ResumeDocument3 paginiDavid-Huynh Indeed Resumeapi-546353822Încă nu există evaluări