Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Automobile Engineering Unit Ii
Încărcat de
Ravindra_1202Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Automobile Engineering Unit Ii
Încărcat de
Ravindra_1202Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING
UNIT II
DRIVE TRAIN
Clutch
A Clutch is a device used to connect the
driving shaft to a driven shaft, so that the
driven shaft may be started or stopped at will,
without stopping the driving shaft.
A popularly known application of clutch is in
automotive vehicles where it is used to connect
the engine and the gear box. Here the clutch
enables to crank and start the engine
disengaging the transmission Disengage the
transmission and change the gear to alter the
torque on the wheels.
Classification of Clutches
1. Friction Clutch:
a. Cone Clutch :
b. Single Plate Clutch:
c. Multiplate Clutch:
i. Wet type ii .Dry type
2. Centrifugal Clutch
3. Diaphragm Spring Clutch
4. Positive Clutch
Single Plate Clutch
Single plate clutch is the one in which only
one friction plate is used to transmit torque
from the engine to the gearbox input shaft.
Used in most of the light vehicle nowadays.
In clutch, flywheel acts as a driving member,
whereas gearbox input shafts acts as driven
member.
Clutch unit consist of friction plate, pressure
plate, pressed steel cover and diaphragm
springs.
Single Plate Clutch
Single Plate Clutch
Single Plate Clutch
Construction
In single plate, the friction plate is held in
between flywheel and pressure plate.
Springs are used to provide clamping force on
the friction plate.
Gearbox input shaft is provided with internal
splines that engage directly to the splines of the
central hub of the pressure plate.
Friction facing is provided on both the sides of
friction plate to provide friction surfaces for
power transmission
Working
When engine rotates, the torque of the crank
shaft is transmitted to gear box input shaft
through flywheel, friction plate and the central
hub of pressure plate.
As the input shaft of gear box is directly
splined to the central hub, it also starts
rotating.
Thus, the engine torque is transmitted from
the engine flywheel to the gear box shaft
through friction plate and central hub of
pressure plate. This is the engaged position of
clutch to the engine.
Working
Similarly, when the clutch pedal is pressed,
the pressure plate is moved back against the
force of diaphragm spring, which makes
friction plate free between flywheel and
pressure plate, and torque of engine could
not be transmitted to the transmission shaft.
This is disengaging position of the clutch
from the engine.
ADVANTAGES
a. Gear shifting is easy.
b. More reliable
DISADVANTAGES
1. Springs has to be stiffer so required more
force to operate the clutch pedal
Figure
The diaphragm type clutch uses a diaphragm or
a conical spring instead of coil spring to produce
adequate pressure for engaging the clutch.
The clutch cover is secured to the engine
flywheel.
The pivot rings are held in the clutch cover.
The outer rim of the diaphragm spring is in
contact with the pressure plate.
In engaged position, the diaphragm spring keeps
the pressure plate in firm contact with the
flywheel.
To disengage the clutch, clutch pedal is pressed
which causes the linkage to move the throw out
bearing forward.
This causes the ring of the diaphragm spring
move backward, which is away from flywheel.
This happens because diaphragm spring is
pivoted.
Advantages:
a. Does not have release levers.
b. Less effort is required.
c. Compact in design.
Centrifugal Clutch
A centrifugal clutch is a clutch that uses
centrifugal force to connect two concentric
shafts, with the driving shaft nested inside the
driven shaft.
Construction & Working:
1. The centrifugal force is used to apply the
required pressure to keep the clutch in
engaged position .
2. As the speed increases , the weight flies there
by operating the bell crank lever which
presses the pressure plate.
This force is transmitted to the clutch disc by
means of spring.
The clutch disc containing friction lining is thus
pressed against the flywheel there by engaging
the clutch.
The spring serves to keep the clutch disengaged
at low speed. The stopper limits the amount of
centrifugal force.
USE :
Centrifugal clutches are often used in mopeds
, under bones, lawnmowers, go-karts,
chainsaws, and mini bikes .
Advantages:
Any kind of control mechanism is not
required.
It is cheaper than other clutches.
Prevents the internal combustion
engine from stalling when the output shaft is
slowed or stopped abruptly therefore
decreases the engine braking force.
dvantages:
Since it involves friction and slipping
between driver and driven parts there is loss
of power.
As it involves slipping, therefore it is not
desirable in cases where there is heavy load
or in high torque requirements.
Electromagnetic Clutch
The clutch has a conventional type of friction disc.
When battery current is supplied to the magnetic
coil , an electromagnet in the flywheel gets
energized.
Now the armature is pulled by the electromagnet
compressing the push off spring.
The pressure plate assembly moves towards the
flywheel makes the clutch plate contact in between
flywheel and pressure plate.
The electromagnetic clutch is best suited where
remote operation is desired since no linkages are
required to control its engagement
The fluid flywheel or hydraulic coupling is
normally used in automatic transmissions.
It consist of two members the driving and the
driven.
The driving member is attached to engine
flywheel and driven member to transmission
shaft.
The two members do not have any direct contact.
The shell is always filled with fluid of suitable
viscosity.
When the flywheel starts rotating the oil in the
impeller starts moving.
Due to the force of the rotation of the oil
impinges on the blades of turbine and causes it
to move. In this way the moving fluid
transmits the engine power is transmitted to
any components to which is turbine is
attached.
Theoretically the turbine speed becomes
almost equal to that of the pump only under
the best operating condition when the fluid
coupling efficiency is highest. But in actual the
turbine speed is less than that of pump. The
lag of turbine behind the pump is known as
slip.
For engine speed below about 500rpm percentage
of slip is 100 which means the clutch is
disengaged.
As the engine speed increases the percentage of
slip rapidly falls down to 10% beyond which the
slip decreases gradually to a small value of 2 %.
Advantages:
No wear on moving parts & Simple in design.
Car can stop in gear and moved on.
No maintenance required except oil level.
No adjustments to be made.
No skill required for operating.
Asbestos
Resin Silica
Cast Steel
Gear Box
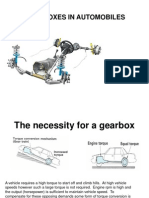
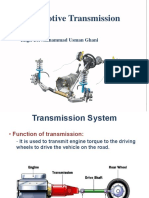
Gear box is an important part of automobiles.
It transmits power from engine shaft to the drive
wheels.
Necessity of Gear Box:
1. In order to enable the engine to run faster than
the road wheels as well as multiply the torque.
2. To overcome the resistances or forces opposing
the motion of vehicles.
3. Air resistance , Gradient resistance and Rolling
resistance i.e. total resistance should be
overcome by tractive force to run the vehicle.
Transmission or Gear Box
Functions:
1) To provide a means to vary the leverage
or torque ratio.
2) To provide a neutral position
3) To provide a means to back the car.
Necessity:
a)Variation of resistance to the vehicle motion at
various speeds.
b)Variation of tractive effort of the vehicle available
at various speeds.
Types of Gear Boxes
Sliding Mesh Gear Box
Constant Mesh Gear Box
Torque Converter
Automatic Transmission System
Epicyclic Gear Box
Sliding Mesh Gear Box
Neutral Position
Constant Mesh Gear Box
Neutral Position
Synchromesh Gear Box
Neutral Position
Working of Gear Box
Animation: Automobile
Engineering\videos\gear box.flv
Video: Automobile Engineering\videos\gear
box operation.flv
Torque Converter
Animation: The Principle Of Torque
converter 3D animation.flv
Automatic Transmission Torque Converter
Operation & Explanation System.Flv
Automatic Transmission
Animation: Automobile
Engineering\videos\6-Speed-Automatic-
Transmission-Lepelletier-Set.avi.flv
Automobile Engineering\videos\ZF 8-Speed
Automatic Transmission.flv
Automobile Engineering\videos\Toyota
U660E U760E 6-Speed Automatic
Transaxle Power flow.flv
Continuously Variable
Transmission
Animation:
Automobile Engineering\videos\AGCO's
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT)
Explained.flv
Automobile Engineering\videos\Nissan CVT
(Continuously Variable Transmission).flv
Epicyclic Transmission
Animation: Automobile
Engineering\videos\Epicycloidal Gear
Train.flv
Automobile Engineering\videos\Ravigneaux
compound planetary gear set.flv
Propeller Shaft
Propeller Shaft
Automobile Engineering\videos\Propeller
Shaft.flv
Differential and final Drive
Differential and final Drive
Automobile Engineering\videos\differential
motion (unlock).flv
Automobile Engineering\videos\How a
Differential Works and Types of
Differentials.flv
Automobile Engineering\videos\Inventor
Differentialgetriebe.flv
Automobile Engineering\videos\Mercedes
4Matic All Wheel Drive System
Explanation.flv
Automobile Engineering\videos\New BMW
Vision Concept Car Drive-train
animation.flv
Automobile Engineering\videos\How
Clutches Work.flv
THANK YOU
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Gearboxes in AutomobilesDocument95 paginiGearboxes in AutomobilesAravind LakhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automatic Transmission SystemDocument34 paginiAutomatic Transmission SystemGurpreet Singh AnttalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Pneumatic BrakesDocument14 paginiHydraulic Pneumatic Brakesabyzen100% (1)
- Starting SysytemDocument12 paginiStarting SysytemMathews P RejiÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-2-Starter Motor and DrivesDocument34 paginiUNIT-2-Starter Motor and DrivesChandan135100% (1)
- Ignition SystemsDocument10 paginiIgnition Systemselvergonzalez1Încă nu există evaluări
- Be Sem 8 Automobile Engineering NotesDocument75 paginiBe Sem 8 Automobile Engineering NotesVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (7)
- Suspension Control SystemsDocument39 paginiSuspension Control SystemsKRISHNAPRIYAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automatic Transmission SystemDocument25 paginiAutomatic Transmission SystemHemanth VallalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8.0 Brake by Wire Ja505Document16 pagini8.0 Brake by Wire Ja505Nareesh RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Vehicle Electronic Systems and Fault DiagnosisDocument20 paginiIntroduction To Vehicle Electronic Systems and Fault Diagnosisyogita patil100% (1)
- Steering SystemDocument15 paginiSteering SystemSatya NarayanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steering GeometryDocument23 paginiSteering GeometryChetanPrasadSevana100% (1)
- Modern Brake SystemDocument24 paginiModern Brake Systemfadhilah91Încă nu există evaluări
- Auto Transmission - NotesDocument34 paginiAuto Transmission - Notesvandanaharikumar100% (2)
- Brake by Wire SystemsDocument16 paginiBrake by Wire Systemsdevhx86% (7)
- Body ConstructionDocument3 paginiBody ConstructionVaibhav Vithoba Naik100% (3)
- Steering System AEDocument46 paginiSteering System AEShubham GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automotive Steering SystemsDocument36 paginiAutomotive Steering SystemsDineshBirdi67% (3)
- Ch-10-Steering and Front AxleDocument45 paginiCh-10-Steering and Front Axlekeval patel100% (2)
- Automotive Transmission: Clutch and Gear BoxDocument28 paginiAutomotive Transmission: Clutch and Gear BoxMohan100% (1)
- Super Magnet Braking System1Document23 paginiSuper Magnet Braking System1Srini Vasan P P100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Drum Brake SystemDocument1 paginăChapter 4 Drum Brake Systemvijendra1125Încă nu există evaluări
- Automobile Engineering - UNIT 3:transmission SystemDocument19 paginiAutomobile Engineering - UNIT 3:transmission SystemSirajAyesha100% (1)
- Charging System - Test: Previous ScreenDocument15 paginiCharging System - Test: Previous ScreenWalterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dual Clutch TransmissionDocument22 paginiDual Clutch Transmissionsaifz201283% (12)
- Automatic Transmission ReportDocument15 paginiAutomatic Transmission ReportDinesh ChahalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Double Wishbone Suspension System ComponentsDocument26 paginiAnalysis of Double Wishbone Suspension System Componentsauhut100% (1)
- Regenerative Braking SystemDocument15 paginiRegenerative Braking SystemVinay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Suspention SystemDocument25 paginiSuspention SystemraviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Bank: AT6502 Automotive Electrical & ElectronicsDocument7 paginiQuestion Bank: AT6502 Automotive Electrical & ElectronicsLovely BhuvaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar Report On Disc Brake: Submitted byDocument34 paginiSeminar Report On Disc Brake: Submitted bySouraj PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- BRAKESDocument46 paginiBRAKESDianna MadejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automotive Brake SystemDocument39 paginiAutomotive Brake Systemjubaer ahmed50% (4)
- Final Drive and DifferentialDocument9 paginiFinal Drive and DifferentialVasantha SeelanÎncă nu există evaluări
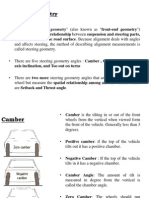
- Castor Camber KingpinDocument7 paginiCastor Camber KingpinahamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrolastic SuspensionDocument16 paginiHydrolastic Suspensionpulkitymcaust_112907Încă nu există evaluări
- 5 Classification of Brakes 160217042825Document39 pagini5 Classification of Brakes 160217042825manipsg100% (1)
- ClutchDocument24 paginiClutchJayson B. Cadelina100% (1)
- ClutchesDocument22 paginiClutchesravi100% (1)
- Abs TCS EbdDocument15 paginiAbs TCS EbdNB Huy100% (1)
- Power Units and TransmissionDocument42 paginiPower Units and TransmissionAmarjeet RaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Power SteeringDocument6 paginiHydraulic Power SteeringMohamad Nadzri YahayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuel Injection SystemDocument24 paginiFuel Injection SystemDevendra Pratap SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automatic Transmission System SeminarDocument14 paginiAutomatic Transmission System SeminarAnonymous 2YgIckU0Încă nu există evaluări
- Chasis Frame and BodyDocument53 paginiChasis Frame and BodyGeorgy Kurien100% (1)
- Ignition SystemDocument11 paginiIgnition SystemSatyajitSahooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multistage and Poly Stage ConverterDocument22 paginiMultistage and Poly Stage ConverterkirthikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ignition SystemDocument5 paginiIgnition SystemPankaj GauravÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exhaust Gas RecirculationDocument12 paginiExhaust Gas RecirculationPriyank GabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combined Ignition and Fuel Control System, Petrol EnginesDocument16 paginiCombined Ignition and Fuel Control System, Petrol EnginesNandakumar BasavarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ignition System UploadDocument39 paginiIgnition System UploadmehrakindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2Document96 paginiUnit 2David GaddalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6.1 Transmission System ClutchDocument33 paginiChapter 6.1 Transmission System ClutchdoomraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5 - Transmission SystemDocument41 paginiLecture 5 - Transmission SystemengineeringdesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automotive Transmission: Presented byDocument48 paginiAutomotive Transmission: Presented bySumit SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transmission SystemDocument85 paginiTransmission SystempavanmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automotive Transmission: Be Skilled Be SmartDocument55 paginiAutomotive Transmission: Be Skilled Be SmartgvnagamaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automotive Transmission SystemDocument65 paginiAutomotive Transmission SystemEngr Usman GhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Auto 5sem ATEDocument97 paginiAuto 5sem ATEShyam PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Performance Measurement Sys PDFDocument44 paginiSupply Chain Performance Measurement Sys PDFRavindra_1202Încă nu există evaluări
- UNIT I General Aspects of Energy ManagementDocument54 paginiUNIT I General Aspects of Energy ManagementRavindra_1202Încă nu există evaluări
- 50 AEDG Grocery Stores TABLES - Climate Zone 5Document5 pagini50 AEDG Grocery Stores TABLES - Climate Zone 5Ravindra_1202Încă nu există evaluări
- Applied Thermodynamics and Engineering Fifth Edition by T.D Eastop and A. McconkeyDocument593 paginiApplied Thermodynamics and Engineering Fifth Edition by T.D Eastop and A. McconkeyEgonPittoors100% (2)
- Unit V Cooling SystemDocument20 paginiUnit V Cooling SystemRavindra_1202Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 paginiWhat Is Mechanical EngineeringRavindra_1202Încă nu există evaluări
- Skills Needed For Mechanical EngineerDocument2 paginiSkills Needed For Mechanical EngineerRavindra_1202Încă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulic Power and ControlDocument12 paginiHydraulic Power and ControlRavindra_1202Încă nu există evaluări
- Job Activities For Mechanical EngineerDocument3 paginiJob Activities For Mechanical EngineerRavindra_1202Încă nu există evaluări
- Job Duties and Tasks of Mechanical EngineerDocument3 paginiJob Duties and Tasks of Mechanical EngineerRavindra_1202100% (1)
- Unit - IV Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument26 paginiUnit - IV Hydraulics and PneumaticsRavindra_1202Încă nu există evaluări
- Tridium Europe DatasheetDocument2 paginiTridium Europe DatasheetHoàngTrầnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comsigua HBIDocument0 paginiComsigua HBIproxywarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3949-Article Text-8633-1-10-20180712Document10 pagini3949-Article Text-8633-1-10-20180712Volodymyr TarnavskyyÎncă nu există evaluări
- If You Restyou RustDocument4 paginiIf You Restyou Rusttssuru9182Încă nu există evaluări
- Certification Roadmap 11-30-16Document1 paginăCertification Roadmap 11-30-16Cristian Gavilanes MontoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entrepreneurial BehaviourDocument16 paginiEntrepreneurial Behaviournonalyn tomboconÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loading and Hauling Dump Truck: DumperDocument2 paginiLoading and Hauling Dump Truck: DumperRJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cloudworx Pdms UsDocument2 paginiCloudworx Pdms Usguru4lifegmailcomÎncă nu există evaluări
- FMDS0102Document69 paginiFMDS0102hhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19 - 22187 - Pritchard RD (1969)Document36 pagini19 - 22187 - Pritchard RD (1969)Isaias MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teacher Empowerment As An Important Component of Job Satisfaction A Comparative Study of Teachers Perspectives in Al Farwaniya District KuwaitDocument24 paginiTeacher Empowerment As An Important Component of Job Satisfaction A Comparative Study of Teachers Perspectives in Al Farwaniya District KuwaitAtique RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renaissance QuestionsDocument3 paginiRenaissance QuestionsHezel Escora NavalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prestressed Concrete ProblemDocument9 paginiPrestressed Concrete ProblemPrantik Adhar SamantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BUCA IMSEF 2021 Jury Evaluation ScheduleDocument7 paginiBUCA IMSEF 2021 Jury Evaluation SchedulePaulina Arti WilujengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigation: Present By:Shivam Ranabhat Project Title: Esport Players Recruit SystemDocument18 paginiInvestigation: Present By:Shivam Ranabhat Project Title: Esport Players Recruit Systemjames chhetriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure Exterior LightingDocument49 paginiBrochure Exterior Lightingmurali_227Încă nu există evaluări
- May 2021 Examination Diet School of Mathematics & Statistics ID5059Document6 paginiMay 2021 Examination Diet School of Mathematics & Statistics ID5059Tev WallaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Translated Copy of Jurnal B.inggris 41117110162 Aditya NurfajriDocument16 paginiTranslated Copy of Jurnal B.inggris 41117110162 Aditya Nurfajriaditya estimatorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Michael S. Lewis-Beck-Data Analysis - An Introduction, Issue 103-SAGE (1995)Document119 paginiMichael S. Lewis-Beck-Data Analysis - An Introduction, Issue 103-SAGE (1995)ArletPR100% (1)
- Cutting Aws C5.3 2000 R2011Document33 paginiCutting Aws C5.3 2000 R2011Serkan AkşanlıÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prescriptions For Closing The Seven Service Quality GapsDocument1 paginăPrescriptions For Closing The Seven Service Quality GapsReema NegiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESQLDocument2 paginiESQLajay110125_kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question 1: As Shown in Figure 1. A 6-Pole, Long-Shunt Lap-Wound CompoundDocument4 paginiQuestion 1: As Shown in Figure 1. A 6-Pole, Long-Shunt Lap-Wound Compoundالموعظة الحسنه chanelÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Trade SyllabusDocument3 paginiInternational Trade SyllabusDialee Flor Dael BaladjayÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Research Paper On DormitoriesDocument5 paginiA Research Paper On DormitoriesNicholas Ivy EscaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wbuhs PG ThesisDocument7 paginiWbuhs PG Thesisgbx272pg100% (2)
- Dynamic Analysis of Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drives Based On Simulink and Finite Element ModelDocument5 paginiDynamic Analysis of Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drives Based On Simulink and Finite Element ModelenmnabilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interplater 85/125P HDX: Setting New Processing Standards For High-End UsersDocument2 paginiInterplater 85/125P HDX: Setting New Processing Standards For High-End Usershackko24Încă nu există evaluări
- Mini Riset Bahasa Inggris BisnisDocument10 paginiMini Riset Bahasa Inggris BisnissyahsabilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Absolute Containers Brochure 2019 2 27 PDFDocument19 paginiAbsolute Containers Brochure 2019 2 27 PDFEduardo SolanoÎncă nu există evaluări