Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Myers Briggstypeindicator1234
Încărcat de
arunsanskritiDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Myers Briggstypeindicator1234
Încărcat de
arunsanskritiDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
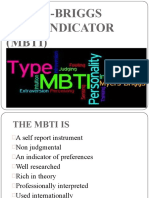
MYERS-BRIGGS TYPE
INDICATOR
(MBTI)
THE MBTI IS
A self report instrument
Non judgmental
An indicator of preferences
Well researched
Rich in theory
Professionally interpreted
Used internationally
A way to sort, not to measure
HISTORY OF MBTI
Based on Swiss psychologist Carl G Jungs
type theory (1920s)
Behaviour is individual and predictable
Developed by Katherine Briggs (mother)
and Isabel Myers (daughter) 1940s
The most widely used personality indicator
in the world
Approximately 1 to 3 million people are
administered by MBTI each year
THE MBTI DOES NOT MEASURE
IQ
Psychiatric disturbances
Emotions
Trauma
Stress
Learning
Normalcy
Maturity
Illness
Affluence
ASSUMPTIONS OF TYPE THEORY
Preferences are inborn
We use both poles at different times, but not
with equal confidence
All of the types are equally valuable
PREFERENCE SCALES
Extraversion -------------- Introversion
Sensing -------------- Intuition
Thinking -------------- Feeling
Judging -------------- Perception
Extravert :-action oriented
Introvert :-contemplative(Look at thoughtfully)
Sensing :-pragmatic(practical)
Intuition :-visionary(Instinctive knowledge)
Thinking :-logical
Feeling :-compassionate(Caring, Humane)
Judging :-planful(Evaluate)
Perceiving :-adaptable(To become aware of
through senses)
E-I DICHOTOMY
EXTRAVERSION INTROVERSION
Attention focused
outward: people, things,
action
Using trial and errors
with confidence
Relaxed and confident
Scanning the
environment for
stimulation
Seeks variety and action
Wants to be with others
Live it, then understand
it
Attention focused
inward: concepts,
ideas, feelings
Considering deeply
before acting
Reserved and
questioning
Probing inwardly for
stimulation
Seeks quiet for
concentration
Wants time to be alone
Understand it before,
live it
S-N DICHOTOMY
SENSING INTUITION
Perceiving with the 5
senses
Reliance on experience
and actual data
Practical
In touch with physical
realities
Attending to the present
moment
Live life as it is
Prefer using learned skills
Pay attention to details
Make few factual errors
Perceiving with memory
and association (6
th
sense)
Seeing patterns and
meanings
Innovation
Seeing possibilities
Future achivement
Projecting possibilities for
the future
Change, rearrange life
Prefers adding new skills
Look at big picture
Identifies complex pattern
T-F DICHOTOMY
THINKING FEELING
Decision based on the
logic of the situation
Uses cause and effect
reasoning
Strive for an objective
standard of truth
Can be tough-minded
Fair- want everyone
treated equally
Decisions based on
impact on people
Guided by personal
values
Strive for harmony
and positive
interaction
May appear tender
hearted
Fair-want everyone
treated as an
individual
J-P DICHOTOMY
JUDGING PERCEIVING
Focuses on
completing task
Deciding and planning
Organizing and
scheduling
Controlling and
regulating
Goal oriented
Wanting closure even
when data are
incomplete
Wants only the
essentials of the job
Focuses on starting
task
Taking in information
Adapting and
changing
Curious and
interested
Open minded
Resisting closure in
order to obtain more
data
Wants to find out
about the job
TYPE TABLE
ADVANTAGES OF MBTI
Self awareness for better self-
management
Identification of behaviour trends that
have positive outcomes
Identification of behaviour trends that
have less desirable outcomes
Link trends with other data points to
clarify personal or professional
developmental opportunities
DISADVANTAGES OF MBTI
Trying to predict others behaviour
Trying to estimate another individual type
(eg. You must be an extravert because you
are so gregarious)
Assuming that how a preference plays for
you is exactly how it would play out for
someone else
Justifying behavior
THANK YOU
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Using the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator: How knowing your personality type can help youDe la EverandUsing the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator: How knowing your personality type can help youEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)Document15 paginiMyers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)TattsunÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Joosr Guide to... Do What You Are by Paul Tieger, Barbara Barron, and Kelly Tieger: Discover the Perfect Career for You through the Secrets of Personality TypeDe la EverandA Joosr Guide to... Do What You Are by Paul Tieger, Barbara Barron, and Kelly Tieger: Discover the Perfect Career for You through the Secrets of Personality TypeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)Document15 paginiMyers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)Anonymous sMqylHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discovering Your Path: A Step-by-Step Guide to Finding Your Best CareerDe la EverandDiscovering Your Path: A Step-by-Step Guide to Finding Your Best CareerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)Document15 paginiMyers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)Nihal MalviyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBTIDocument21 paginiMBTIRaj Gupta100% (1)
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)Document15 paginiMyers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)Nihal MalviyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers-Briggs Personality Type Indicator - MBTIDocument30 paginiMyers-Briggs Personality Type Indicator - MBTICheaque BhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBTIDocument53 paginiMBTIAndrew Williamson75% (8)
- Lecture Personality and Interest Inventories 8Document41 paginiLecture Personality and Interest Inventories 8Winny Shiru MachiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- PersonalityDocument21 paginiPersonalityDhairya GadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers-Briggs Type Indicator: Shelly Hoover-Plonk Assistant Director, Career ResourcesDocument25 paginiMyers-Briggs Type Indicator: Shelly Hoover-Plonk Assistant Director, Career ResourcesChandni Agrawal100% (2)
- MBTIDocument30 paginiMBTISeethalakshmi SivakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 3Document9 pagini5 3B1tt3rSw33tÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBTIDocument5 paginiMBTIAna Georgescu100% (2)
- Myers - Briggs Personality Type Indicator - MbtiDocument30 paginiMyers - Briggs Personality Type Indicator - MbtianikhanapurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding The Self Lesson 3 AnswerDocument6 paginiUnderstanding The Self Lesson 3 AnswerRichelle MasingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers Briggs Personality TraitsDocument30 paginiMyers Briggs Personality TraitsAntonius Elawitachya100% (4)
- M-Myers B - Briggs T - Type I - IndicatorDocument12 paginiM-Myers B - Briggs T - Type I - IndicatorNihal MalviyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- INSTITUTE UIE ..: Introductions To Management and Leadership UCT-242Document19 paginiINSTITUTE UIE ..: Introductions To Management and Leadership UCT-242KunwarNamanThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) : Orientation To World Take in Information Make Decisions Take in Info. or DecideDocument4 paginiMyers Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) : Orientation To World Take in Information Make Decisions Take in Info. or DecideArpit CooldudeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers-Briggs Personality Type - Mbti Indicator: Kathy Prem Engineering Career Services University of Wisconsin-MadisonDocument30 paginiMyers-Briggs Personality Type - Mbti Indicator: Kathy Prem Engineering Career Services University of Wisconsin-MadisonSidharth ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMP 261190Document9 paginiSMP 261190Allan Leon Casemiro100% (1)
- Chapter 8 LeadingDocument52 paginiChapter 8 LeadingaroojÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers Briggs Type Indicator PresentationDocument9 paginiMyers Briggs Type Indicator PresentationSatyam SachanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mbti AssessmentDocument2 paginiMbti Assessmentapi-270710360Încă nu există evaluări
- MBTIDocument53 paginiMBTIYuki Yusman RachmatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Azahra H C (19006069) Taks V Career CounselingDocument13 paginiAzahra H C (19006069) Taks V Career Counselingazahra hardi cusiniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers-Briggs Type IndicatorDocument11 paginiMyers-Briggs Type Indicatorvin1030% (1)
- MBTIin PersonalityDocument3 paginiMBTIin PersonalitySpandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator: A Leadership Workshop January 26, 2009Document37 paginiIntroduction To The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator: A Leadership Workshop January 26, 2009Emily KohÎncă nu există evaluări
- OB - Lect4 - ch5Document19 paginiOB - Lect4 - ch5Nahed AbduallahÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)Document38 paginiThe Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)George ChristianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synergistic Systems MBTI and LIFO MethodDocument23 paginiSynergistic Systems MBTI and LIFO MethodUmair DarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personality in Career DevelopmentDocument49 paginiPersonality in Career DevelopmentRamón JamónÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBTIDocument4 paginiMBTIElizabeth Nirmala JÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turtle ManDocument6 paginiTurtle ManSunnyMahajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBTI Test AnalysisDocument10 paginiMBTI Test AnalysisShweta InjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English GuideDocument24 paginiEnglish GuideYaisa GoudettÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mayers-Briggs Type Indicator MBTIDocument7 paginiMayers-Briggs Type Indicator MBTIResearchMonstersÎncă nu există evaluări
- MGMT 8760Document3 paginiMGMT 8760Joshua J KennedyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MyersbriggsDocument25 paginiMyersbriggsRonnel BrionesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod 57Document38 paginiMod 57reema_das_1Încă nu există evaluări
- Research Paper On MbtiDocument6 paginiResearch Paper On Mbtizgkuqhxgf100% (1)
- Case Study: Name Roll NoDocument47 paginiCase Study: Name Roll Noakshit sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Enjoyment of Employment MBTI WorkshopDocument33 paginiThe Enjoyment of Employment MBTI WorkshopElonic Airos100% (3)
- Personality and ValuesDocument18 paginiPersonality and Valueskeloo12345Încă nu există evaluări
- Doc1 - MBTI PACKETDocument25 paginiDoc1 - MBTI PACKETIcandrawÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBTI AssignmentDocument4 paginiMBTI AssignmentApoorv SarveshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do What You Are Handbook 2008Document23 paginiDo What You Are Handbook 2008q12345q6789Încă nu există evaluări
- Bridget Kendrick Interpretive Report For Organisations En-Gb 1923451 20150312 Best FitDocument10 paginiBridget Kendrick Interpretive Report For Organisations En-Gb 1923451 20150312 Best Fitapi-291337811Încă nu există evaluări
- 13 Domanais Jhon Kyle Donor A1Document5 pagini13 Domanais Jhon Kyle Donor A1Jhon Kyle DomanaisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers BriggsDocument1 paginăMyers BriggsJulian SobremonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBTIDocument2 paginiMBTIPratibha KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name Roll No Class Mba Session Morning Presentation Mayers Briggs Model Present ToDocument8 paginiName Roll No Class Mba Session Morning Presentation Mayers Briggs Model Present ToNicky BojeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers Briggs Personality TraitsDocument30 paginiMyers Briggs Personality Traitsnegreibs100% (2)
- Personality, Perception, and AttributionDocument23 paginiPersonality, Perception, and AttributionPreetam KamathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session 3 PersonalityDocument19 paginiSession 3 PersonalityVishal ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do Whart You AreDocument23 paginiDo Whart You Areharry2learnÎncă nu există evaluări
- FdhhdfhkfhgdffuucDocument1 paginăFdhhdfhkfhgdffuucarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuesday New Urs LNDocument1 paginăTuesday New Urs LNarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thursday Inventory 2015Document1 paginăThursday Inventory 2015arunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuesday New Urs LNDocument1 paginăTuesday New Urs LNarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- HfkbaslvbkvbolhDocument1 paginăHfkbaslvbkvbolharunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Net Neutrality - QuoraDocument9 paginiNet Neutrality - QuoraarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Business Level Strategies12Document20 pagini8 Business Level Strategies12arunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTERNational I and Inflation GDP FinalDocument1 paginăINTERNational I and Inflation GDP FinalarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Npi NI National Incom GDP NWDocument1 paginăNpi NI National Incom GDP NWarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- OB Rudani NewDocument21 paginiOB Rudani NewarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- National I and Inflation GDP FinalDocument1 paginăNational I and Inflation GDP FinalarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fera Fema12Document21 paginiFera Fema12arunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Income and GDP NWDocument1 paginăNational Income and GDP NWarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Case Study in Perfect CompetitionDocument6 paginiA Case Study in Perfect CompetitionephanendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Public GoodsDocument6 paginiPublic GoodsarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theories of MotivationDocument8 paginiTheories of Motivationankushsingh007100% (12)
- TCS Bonus Issue NewDocument5 paginiTCS Bonus Issue NewarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agreen Banking 12Document18 paginiAgreen Banking 12arunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Are Water Purifiers SafeDocument4 paginiAre Water Purifiers SafearunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibps So HR Notes NewDocument22 paginiIbps So HR Notes NewarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abbreviations For Competition ExamsDocument19 paginiAbbreviations For Competition ExamsarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- WearDocument13 paginiWeararunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Solve Case StudyDocument12 paginiHow To Solve Case Studyburhan_qureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cooperative Banks NewDocument2 paginiCooperative Banks NewarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Read A PaperDocument2 paginiHow To Read A Papersajidobry_847601844Încă nu există evaluări
- Big 5 Personality ScaleDocument4 paginiBig 5 Personality ScaleArif TrimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Capsule Ibps Po 2014Document22 paginiComputer Capsule Ibps Po 2014arunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On GH Stress Among Employees Working in BPOs With Special Reference To CoimbatoreDocument18 paginiA Study On GH Stress Among Employees Working in BPOs With Special Reference To CoimbatorearunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dusting Off The CompetitionDocument10 paginiDusting Off The CompetitionarunsanskritiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Campbell - Feeling The Pressure - 2015Document16 paginiCampbell - Feeling The Pressure - 2015MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluating Student Presentations: Presentation RubricDocument4 paginiEvaluating Student Presentations: Presentation RubrickiluÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Test Results - CocubesDocument42 paginiEnglish Test Results - CocubesJavaharReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spta Bod 1ST General Assembly Minutes 2022-2023Document5 paginiSpta Bod 1ST General Assembly Minutes 2022-2023Charlene P. BalderamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus Intro IctDocument10 paginiSyllabus Intro Ictmilyn maramagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument12 paginiReview of Related Literatureanne platonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reaction Paper 8-10-19Document5 paginiReaction Paper 8-10-19Christine Mycah AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Australian Scene 2018Document196 paginiAustralian Scene 2018Vicente TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions 1Document3 paginiQuestions 1krp_212003Încă nu există evaluări
- Horsemanship Merit Badge WorksheetDocument5 paginiHorsemanship Merit Badge WorksheetsrcouncilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incompetent People Too Ignorant To Know ItDocument3 paginiIncompetent People Too Ignorant To Know Itcarla_cbcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coed School Research PaperDocument6 paginiCoed School Research Paperapi-268666689Încă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 1 ThesisDocument10 paginiCHAPTER 1 ThesisCaesar Palma100% (1)
- B2 First Unit 11 Test: VocabularyDocument3 paginiB2 First Unit 11 Test: VocabularyNatalia KhaletskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Robert Frost Biography: Quick FactsDocument7 paginiRobert Frost Biography: Quick FactsCarla Jamina IbeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sonari Junior CollegeDocument7 paginiSonari Junior CollegeHimanshu BhuyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philo Long Test 1Document2 paginiPhilo Long Test 1Nastasia BesinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wayne Visser: Speaker Biography Idea-Monger, Story-Teller, Meme-WeaverDocument27 paginiWayne Visser: Speaker Biography Idea-Monger, Story-Teller, Meme-WeaverZola1348Încă nu există evaluări
- Project 1 Design 3Document4 paginiProject 1 Design 3Taimaa DarwishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Desain Tanpa JudulDocument14 paginiDesain Tanpa JudulRazmi Wulan DiastutiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCBTS Volume 1 Teachingprof Socdime FS 274 315Document85 paginiNCBTS Volume 1 Teachingprof Socdime FS 274 315justin may tuyorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample of Curriculum MapDocument12 paginiSample of Curriculum MapJardine CanoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nicola Jackson On Legal Problem Solving - How To Think and Reason Like A LawyerDocument6 paginiNicola Jackson On Legal Problem Solving - How To Think and Reason Like A LawyerJorace Tena LampaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pengembangan Model Warming Up Berbasis Permainan Tradisional Pada Peserta Didik SMPDocument11 paginiPengembangan Model Warming Up Berbasis Permainan Tradisional Pada Peserta Didik SMPbila inunÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRANSLATIONassessment CONFERENCEDocument21 paginiTRANSLATIONassessment CONFERENCEgrifonkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class Tardiness - Complete Research ProposalDocument5 paginiClass Tardiness - Complete Research ProposalJames Codeniera100% (1)
- Lac Mass Leadership Reflection EssayDocument3 paginiLac Mass Leadership Reflection Essayapi-270432871Încă nu există evaluări
- Clienteles of CommunicationDocument26 paginiClienteles of CommunicationKeat68% (41)
- Economics Internship Cover LetterDocument8 paginiEconomics Internship Cover Letterafdlxeqbk100% (1)
- BehaviourDocument4 paginiBehaviourapi-547203445Încă nu există evaluări