Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
03-03 Pptlect
Încărcat de
Beverly Carballo - MoguelDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
03-03 Pptlect
Încărcat de
Beverly Carballo - MoguelDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Vince Austin, University of Kentucky
Cells: The Living Units
Part C
Human Anatomy & Physiology, Sixth Edition
Elaine N. Marieb
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Golgi Apparatus
Stacked and flattened membranous sacs
Functions in modification, concentration, and
packaging of proteins
Transport vessels from the ER fuse with the cis face
of the Golgi apparatus
Proteins then pass through the Golgi apparatus to the
trans face
Secretory vesicles leave the trans face of the Golgi
stack and move to designated parts of the cell
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Golgi Apparatus
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.20a
Role of the Golgi Apparatus
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.21
Lysosomes
Spherical membranous bags containing digestive
enzymes
Digest ingested bacteria, viruses, and toxins
Degrade nonfunctional organelles
Breakdown glycogen and release thyroid hormone
Breakdown nonuseful tissue
Breakdown bone to release Ca2+
Secretory lysosomes are found in white blood cells,
immune cells, and melanocytes
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Endomembrane System
System of organelles that function to:
Produce, store, and export biological molecules
Degrade potentially harmful substances
System includes:
Nuclear envelope, smooth and rough ER,
lysosomes, vacuoles, transport vesicles, Golgi
apparatus, and the plasma membrane
PLAY
Endomembrane System
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Endomembrane System
Figure 3.23
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Peroxisomes
Membranous sacs containing oxidases and catalases
Detoxify harmful or toxic substances
Neutralize dangerous free radicals
Free radicals highly reactive chemicals with
unpaired electrons (i.e., O2)
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
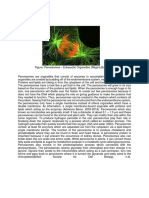
Cytoskeleton
The skeleton of the cell
Dynamic, elaborate series of rods running through
the cytosol
Consists of microtubules, microfilaments, and
intermediate filaments
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Cytoskeleton
Figure 3.24
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Microtubules
Dynamic, hollow tubes made of the spherical protein
tubulin
Determine the overall shape of the cell and
distribution of organelles
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Microfilaments
Dynamic strands of the protein actin
Attached to the cytoplasmic side of the plasma
membrane
Braces and strengthens the cell surface
Attach to CAMs and function in endocytosis and
exocytosis
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Intermediate Filaments
Tough, insoluble protein fibers with high tensile
strength
Resist pulling forces on the cell and help form
desmosomes
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Motor Molecules
Protein complexes that function in motility
Powered by ATP
Attach to receptors on organelles
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Motor Molecules
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.25a
Motor Molecules
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.25b
Centrioles
Small barrel-shaped organelles located in the
centrosome near the nucleus
Pinwheel array of nine triplets of microtubules
Organize mitotic spindle during mitosis
Form the bases of cilia and flagella
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Centrioles
Figure 3.26a, b
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Cilia
Whiplike, motile cellular extensions on exposed
surfaces of certain cells
Move substances in one direction across cell
surfaces
PLAY
Cilia and Flagella
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Cilia
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.27a
Cilia
Figure 3.27b
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Cilia
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.27c
Nucleus
Contains nuclear envelope, nucleoli, chromatin, and
distinct compartments rich in specific protein sets
Gene-containing control center of the cell
Contains the genetic library with blueprints for
nearly all cellular proteins
Dictates the kinds and amounts of proteins to be
synthesized
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Nucleus
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.28a
Nuclear Envelope
Selectively permeable double membrane barrier
containing pores
Encloses jellylike nucleoplasm, which contains
essential solutes
Outer membrane is continuous with the rough ER
and is studded with ribosomes
Inner membrane is lined with the nuclear lamina,
which maintains the shape of the nucleus
Pore complex regulates transport of large molecules
into and out of the nucleus
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Nucleoli
Dark-staining spherical bodies within the nucleus
Site of ribosome production
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Chromatin
Threadlike strands
of DNA and
histones
Arranged in
fundamental units
called nucleosomes
Form condensed,
barlike bodies of
chromosomes when
the nucleus starts to
divide
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.29
Cell Cycle
Interphase
Growth (G1),
synthesis (S),
growth (G2)
Mitotic phase
Mitosis and
cytokinesis
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Figure 3.30
Interphase
G1 (gap 1) metabolic activity and vigorous growth
G0 cells that permanently cease dividing
S (synthetic) DNA replication
G2 (gap 2) preparation for division
PLAY
Late Interphase
Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Legal Doc Guide LinesDocument5 paginiLegal Doc Guide LinesBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Five Kingdoms: Natural Science 2. Secondary EducationDocument10 paginiThe Five Kingdoms: Natural Science 2. Secondary Educationrizza cayabyabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scanned DocumentDocument2 paginiScanned DocumentBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSEC Principles of BusinessDocument48 paginiCSEC Principles of BusinessJuliet Hilaire100% (1)
- Momentum and CollisionsDocument27 paginiMomentum and CollisionsBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buoyancy and FloatationDocument21 paginiBuoyancy and FloatationManju AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buoyancyfloatation 150401095720 Conversion Gate01Document2 paginiBuoyancyfloatation 150401095720 Conversion Gate01Beverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Momentum Practice Problems SolvedDocument3 paginiMomentum Practice Problems SolvedBeverly Carballo - Moguel100% (2)
- Overview of The OSHA Standard: Topic: ElectricalDocument3 paginiOverview of The OSHA Standard: Topic: ElectricalBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malaria HowFibersForm StudentDocument7 paginiMalaria HowFibersForm StudentBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 204 Lab 7 Pork Lung DissectDocument5 pagini204 Lab 7 Pork Lung DissectBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Biology: Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles: The Water Cycle HumidityDocument2 paginiEnvironmental Biology: Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles: The Water Cycle HumidityBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedigree Analysis Answer KeyDocument1 paginăPedigree Analysis Answer KeySherlock Wesley ConanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2010 Csec Principles of BusinessDocument2 pagini2010 Csec Principles of BusinessBeverly Carballo - Moguel80% (20)
- The Making of The Fittest: Natural Selection in Humans: Quiz Student HandoutDocument4 paginiThe Making of The Fittest: Natural Selection in Humans: Quiz Student HandoutBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Battling Beetles - TEACHERDocument3 paginiBattling Beetles - TEACHERBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proofreading and EditingDocument20 paginiProofreading and EditingBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proofreading and EditingDocument71 paginiProofreading and EditinglucasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Battling Beetles - TEACHER PDFDocument11 paginiBattling Beetles - TEACHER PDFBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO Transpiration WRK SHTDocument2 paginiBIO Transpiration WRK SHTBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Agenda WorksheetDocument7 paginiAgenda WorksheetBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Making of The Fittest: Natural Selection in Humans: at A Glance Film GuideDocument1 paginăThe Making of The Fittest: Natural Selection in Humans: at A Glance Film GuideBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Living Processes: Cellular TransportDocument2 paginiLiving Processes: Cellular TransportBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active Transport WorksheetDocument2 paginiActive Transport WorksheetLola BeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO Factors Afftng Photosynthe WRK SHTDocument1 paginăBIO Factors Afftng Photosynthe WRK SHTBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Living Processes: Respiration: Breathing RateDocument2 paginiLiving Processes: Respiration: Breathing RateBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal Documents Guide LinesDocument4 paginiLegal Documents Guide LinesBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- EDPM Memo Block StyleDocument1 paginăEDPM Memo Block StyleBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of The OSHA Standard: Topic: ElectricalDocument3 paginiOverview of The OSHA Standard: Topic: ElectricalBeverly Carballo - MoguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- General Biology 1 Cell TheoryDocument12 paginiGeneral Biology 1 Cell TheoryPercival RiegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Quiz: Eukaryotic Organelles & StructuresDocument7 paginiCell Quiz: Eukaryotic Organelles & StructuresChris GayleÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISC 11th - Biology 2023-24 Council Syllabus-1-10Document10 paginiISC 11th - Biology 2023-24 Council Syllabus-1-10R HarryÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 4Document16 paginiBIOLS102-UOB-Chapter 4Noor JanahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structure and Function PDFDocument15 paginiCell Structure and Function PDFAbdul RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- You May Use The Back If You Need More Space To Answer The Following QuestionsDocument3 paginiYou May Use The Back If You Need More Space To Answer The Following Questionsmaggie mayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stem 12-Module 3Document25 paginiStem 12-Module 3Laarni ToleteÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.3 Components of The Cell II (Subcellular Organelles)Document20 pagini1.3 Components of The Cell II (Subcellular Organelles)Alexa Julienne RazÎncă nu există evaluări
- FullDocument1.497 paginiFullSyasa PembayunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 - Cell StructureDocument36 paginiChapter 5 - Cell StructureTosca MavourneenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science12 q1 Mod9 IntroductiontoLifeScience v3Document29 paginiScience12 q1 Mod9 IntroductiontoLifeScience v3Arnold PaombongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.mind Map - Cell - A Unit of LifeDocument100 pagini1.mind Map - Cell - A Unit of LifeAyush KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tatva CellDocument66 paginiTatva CellGuriya KumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 Foundations of ChemistryDocument114 paginiLecture 1 Foundations of ChemistryGaming JcÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 08Document72 paginiCH 08abdurÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 3 Cell Organelles PPT 1193949429900273 1Document19 pagini3 3 Cell Organelles PPT 1193949429900273 1kikkabuttigieg1466Încă nu există evaluări
- Classifying CellsDocument28 paginiClassifying CellskerbieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cytoplasm (Author V.Mazuru) PDFDocument46 paginiCytoplasm (Author V.Mazuru) PDFLexa KpvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 12Document86 paginiChap 12chemptnkÎncă nu există evaluări
- PeroxisomeDocument2 paginiPeroxisomeTian HanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument4 paginiCell Structure and Functionsvoice for islamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 26Document22 paginiChapter 26Vanessa Y. LouisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1st Quarter Module Generalbiology1 1-1-13Document13 pagini1st Quarter Module Generalbiology1 1-1-13Hubilla, Krisha Loveah M.Încă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 9 Biology Cell NotesDocument27 paginiCBSE Class 9 Biology Cell NotesT SunderamalolanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cells Structure & FunctionDocument80 paginiCells Structure & Functionderr barrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3 - Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic CellDocument34 paginiLesson 3 - Prokaryotic Cell and Eukaryotic CellVillanueva, Liv Harlet A.Încă nu există evaluări
- Session No 1.1. A Tour of The CellDocument40 paginiSession No 1.1. A Tour of The CellShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Medtechs EmeDocument3 paginiThe Medtechs EmeKathlene Anne MENDOZAÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Biology Semester 1 ReviewDocument44 paginiAP Biology Semester 1 ReviewGeelonSo100% (1)
- HSSRPTR - Botany Focus Area NotesDocument27 paginiHSSRPTR - Botany Focus Area Notesfiredrops122Încă nu există evaluări