Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter9 - Sorting and Searching Arrays
Încărcat de
Andrew Carts0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
293 vizualizări15 paginiStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter9_Sorting and Searching Arrays
Titlu original
Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter9_Sorting and Searching Arrays
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter9_Sorting and Searching Arrays
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
293 vizualizări15 paginiStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter9 - Sorting and Searching Arrays
Încărcat de
Andrew CartsStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter9_Sorting and Searching Arrays
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPTX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 15
Chapter 9:
Sorting and Searching Arrays
Starting Out with Programming Logic & Design
Second Edition
by Tony Gaddis
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
9.1 The Bubble Sort Algorithm
Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm for
rearranging the contents of an array
Useful for alphabetical lists and numerical sorting
Can be done in ascending or descending order
With the Bubble Sort, array elements are compared
and numbers bubble toward the end of the array
(assuming your sorting in ascending order)
Swapping elements must be done in order to
properly sort the array
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-2
9.1 The Bubble Sort Algorithm
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-3
9.1 The Bubble Sort Algorithm
Inside Program 9-1
maxElement variable holds the subscript of the last element
that is to be compared to its neighbor
index variable is an array subscript in one loop
The outer loop iterates for each element in the array
The inner loop iterates for each of the unsorted array
elements
The if statement does the comparison
Sorting an array of strings to put information in
alphabetical order can be done with a Bubble
Sort
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-4
9.2 The Selection Sort Algorithm
The selection sort works similar to the bubble
sort, but more efficient
Bubble sort moves one element at a time
Selection sort performs fewer swaps because it
moves items immediately to their final position
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-5
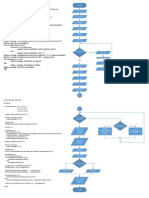
9.2 The Selection
Sort Algorithm
Figure 9-17 Flowchart for the
selectionSortmodule
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-6
9.2 The Selection Sort Algorithm
Inside Figure 9-17
minIndex holds the subscript of the element with
the smallest value
minValue holds the smallest value found
The outer loop iterates for each element in the
array, except the last
The inner loop performs the scan
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-7
9.3 The Insertion Sort Algorithm
The insertion sort algorithm sorts the first two
elements, which becomes the sorted part of the
array
Each remaining element is then inserted into the
sorted part of the array at the correct location
Also more efficient than the bubble sort
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-8
9.3 The Insertion Sort
Algorithm
Figure 9-24 Flowchart for the
insertionSort module
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-9
9.3 The Insertion Sort Algorithm
Inside Figure 9-24
scan is used to scan through the array
unsortedValue holds the first unsorted value
The outer loop steps the index variable through
each subscript, starting at 1
The inner loop moves the first element outside the
sorted subset and into its proper position
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-10
The Swap Module
A closer look at the swap module
In most of the sorts, a swap module can be called
It is the same in each sorting algorithm and only changes in
the parameter list to account for the type of data passed to it
//This swap module accepts two Integer arguments
Module swap(Integer Ref a, Integer Ref b)
Declare Integer temp
//swap the values
Set temp =a
Set a = b
Set b = temp
End Module
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-11
9.4 The Binary Search Algorithm
The binary search algorithm locates an item in an
array by repeatedly dividing the array in half
Each time it divides the array, it eliminates the half
of the array that does not contain the item
Its more sequential than the selection search
because each time it cuts the array in half and
makes a smaller number of comparisons to find a
match
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-12
9.4 The Binary Search Algorithm
How it works
Requires that the array is first sorted
The first comparison is done with the middle
element of the array to see if it is greater than or
less than the number that is being searched
If its greater than, then the number must be in the
first half of the array
If its less than, then the number must be in the
second half of the array
This process is continued until the match if found
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-13
9.4 The Binary
Search Algorithm
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-14
9.4 The Binary Search Algorithm
Inside Program 9-17
middle is used to store the calculated middle index
value stores the value being searched for
A loop hold the search and iterates as long as there
are elements or until a match is found
Nested if-then-else's perform the comparisons
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
1-15
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Assignment 10Document1 paginăAssignment 10Andrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 9Document1 paginăAssignment 9Andrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tools For Structured and Object Oriented Design - Making DecisionsDocument48 paginiTools For Structured and Object Oriented Design - Making DecisionsAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tools For Structured and Object Oriented Design - DO UNTIL StructuresDocument14 paginiTools For Structured and Object Oriented Design - DO UNTIL StructuresAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter13 - RecursionDocument19 paginiStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter13 - RecursionAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting Out With Python - Chapter3 - More About StringsDocument22 paginiStarting Out With Python - Chapter3 - More About StringsAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter15 - GUI ApplicationsDocument13 paginiStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter15 - GUI ApplicationsAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tools For Structured and Object Oriented Design - Simple Sequence Control StructuresDocument24 paginiTools For Structured and Object Oriented Design - Simple Sequence Control StructuresAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tools For Structured and Object Oriented Design - DOWHILE StructuresDocument22 paginiTools For Structured and Object Oriented Design - DOWHILE StructuresAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tools For Structured and Object Oriented Design - ArraysDocument48 paginiTools For Structured and Object Oriented Design - ArraysAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter8 - ArraysDocument20 paginiStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter8 - ArraysAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter7 - Input ValidationDocument9 paginiStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter7 - Input ValidationAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting Out With Python - Chapter9 - Dictionaries and SetsDocument29 paginiStarting Out With Python - Chapter9 - Dictionaries and SetsAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter10 - Menu Driven ProgrammingDocument15 paginiStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter10 - Menu Driven ProgrammingAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter14 - Object Oriented ProgrammingDocument19 paginiStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter14 - Object Oriented ProgrammingAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter5 - Repetition StructuresDocument14 paginiStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter5 - Repetition StructuresAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter4 - Descision Structures and Boolean LogicDocument16 paginiStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter4 - Descision Structures and Boolean LogicAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter6 - FunctionsDocument13 paginiStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter6 - FunctionsAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Computers and Programming: Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design Second EditionDocument39 paginiIntroduction To Computers and Programming: Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design Second EditiontimonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 7Document1 paginăAssignment 7Andrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 8Document1 paginăAssignment 8Andrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter2 - Input, Processing, and OutputDocument23 paginiStarting Out With Programming Logic & Design - Chapter2 - Input, Processing, and OutputAndrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 6Document1 paginăAssignment 6Andrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 5Document1 paginăAssignment 5Andrew Carts100% (1)
- Assignment 2Document1 paginăAssignment 2Andrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 4Document1 paginăAssignment 4Andrew Carts100% (1)
- Assignment 3Document1 paginăAssignment 3Andrew CartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5783)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- NRF51 Series Reference Manual v3.0Document174 paginiNRF51 Series Reference Manual v3.0johan straussÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unix-Linux Commands and Shell ProgrammingDocument22 paginiUnix-Linux Commands and Shell ProgrammingPranesh BrisingrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set up FreeRADIUS for Active Directory authenticationDocument20 paginiSet up FreeRADIUS for Active Directory authenticationcpasgraveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux-5-Logical Volume Manager Administration-En-USDocument132 paginiRed Hat Enterprise Linux-5-Logical Volume Manager Administration-En-USJagdish ModiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NewDocument22 paginiNewdodoman666Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1Document8 paginiLab 1Ihtisham UddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moving from RPG/400 to RPG IVDocument74 paginiMoving from RPG/400 to RPG IVsandra collaguazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Simulation & Modelling: Week 1Document61 paginiIntroduction To Simulation & Modelling: Week 1putri_dIYANiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluent TutrialDocument21 paginiFluent TutrialAbdullah Naseer HayReeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4K RAM Expansion for the DREAM 6800Document1 pagină4K RAM Expansion for the DREAM 6800Hernan BenitesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Installation Guide for Display Monkey Digital Signage SoftwareDocument1 paginăInstallation Guide for Display Monkey Digital Signage SoftwareArdan Dee'are OÎncă nu există evaluări
- L5 Table Driven Routing ProtocolsDocument7 paginiL5 Table Driven Routing ProtocolsSagar ChoudhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Failover With EIGRP Using VRF Configuration Example: Document ID: 113446Document7 paginiFailover With EIGRP Using VRF Configuration Example: Document ID: 113446Muhamad Syamsul FallahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz AnswerDocument3 paginiQuiz AnswerJaya Malathy100% (1)
- Scania: Software Development and TestingDocument33 paginiScania: Software Development and TestingMario Patty100% (2)
- ELO SamplesDocument7 paginiELO SamplesexasperatingcapitalizationÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Interaction Design?Document51 paginiWhat Is Interaction Design?Vairavel ChenniyappanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Easy Builder Pro WeintckDocument713 paginiManual Easy Builder Pro WeintckPacheco KarenÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATIDetectDocument17 paginiATIDetectアリエルÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAN-Cell 2 Release NotesDocument17 paginiLAN-Cell 2 Release NotesProxicastÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibm Db2 Mock Test1Document9 paginiIbm Db2 Mock Test1amansohalÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThesisDocument220 paginiThesisMac GarrÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMotions 7.0 Programming Guide (January 2018)Document47 paginiIMotions 7.0 Programming Guide (January 2018)potatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powerdown Octel 250 and Octel 350 SystemsDocument1 paginăPowerdown Octel 250 and Octel 350 SystemsTuiSlayer FotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teradata UtilitiesDocument139 paginiTeradata Utilitiessonu_palÎncă nu există evaluări
- PC-Based Microcontroller Programmer and Training KitDocument145 paginiPC-Based Microcontroller Programmer and Training KitElizabeth Oneford100% (1)
- ATAM Method of Architeture EvaluationDocument83 paginiATAM Method of Architeture EvaluationNadeera PathiranaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SoftLayer Network Guide Overview 20150501Document60 paginiSoftLayer Network Guide Overview 20150501Wilson Mosquera100% (1)
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 paginiMultiple Choice QuestionsJojo Cansino50% (6)
- Guide to Network Optimization ClustersDocument9 paginiGuide to Network Optimization ClustersPrasad KaleÎncă nu există evaluări