Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Learning Theories
Încărcat de
riaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Learning Theories
Încărcat de
riaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Learning Theories:
Behaviorism
Learning permanent change of
behavior or capacity acquired
through experience.
Example
The
toddler sings, Old McDonald had a
farm
The kindergarten child screams when a
neighbors dog approaches.
Basic Premises of Learning Theories
We can learn things that are
beneficial and not beneficial to
us.
We are not always aware of
what weve learned.
The results of learning are not
always easy to see.
There are different types and
levels of learning.
Overview of Classic Theories
Cognitivism theory in which
learning is equated with changes in
the organization and use of internal
processes
Neobehaviorism theory which
believes that changes in behavior
are observable and influence by
internal processes
Behaviorism theory which
equates learning with changes in
observable behaviors.
CLASSICAL CONDITIONING
Classical Conditioning
Classical Conditioning type of
behaviorist learning in which
associations are established
between automatic emotional or
physiological responses and a new
stimuli
Unconditioned Stimulus
stimulus which automatically evokes
an emotional or physiological
response.
Unconditioned Response an
automatic emotional or
physiological response to an
unconditioned stimulus
Conditioned Stimulus a
stimulus which evoked a different
emotional or physiological response
to a conditioned stimulus after
conditioning.
Conditioned Response an
emotional or physiological response
to a conditioned stimulus after
learning
Making use of the horror movie
example,
The sudden appearance of monsters
or scary images (US)
Sense of fear (UR)
The sound effects. (NS Neutral
Stimulus prior to conditioning
evoked no physiological effect or
emotional effect.)
The sound effects. (CS)
Your feeling shivers down your spine
when the sounds are heard. (CR)
Stimulus Generalization
responding emotionally or
physiologically not only to the CS,
but also to stimuli that resemble the
conditioned stimulus.
Extinction strategies used to
undo classically conditioned
associations.
Habituation strategy used to
extinguish classical conditioning by
repeated presentations of the CS
until the CR is lessened.
Counterconditioning strategy
used to extinguish classical
conditioning by pairing the CS with
a new stimulus that will interfere
with the association between the CS
and CR.
OPERANT CONDITIONING
Operant Conditioning
Operant Conditioning type of
behaviorist learning in which
voluntary behaviors are controlled
by manipulation of follow-up
stimuli; also called r-s pattern
learning
Reinforcement the use of follow
up stimuli to strengthen a desired
behavior.
Positive
Reinforcers desired,
follow-up stimuli added to strengthen a
behavior
Negative Reinforcers inhibiting,
follow-up stimuli to withdrawn to
strengthen a behavior.
Schedule of Reinforcement
1.
2.
3.
4.
Variations in the frequency in the presentation
of reinforcers.
Fixed Ratio reinforcement is dispensed
following a constant number of desired
behaviors.
Fixed Intervals reinforcement is dispensed
following a constant amount of time.
Variable Ratio reinforcement is dispensed
following a varying a number of desired
behaviors.
Variable Intervals - reinforcement is
dispensed following a varying amount of time
Cueing strategy in which a
reinforceable behavior is set up by a
stimulus or a signal.
Shaping reinforcement strategy
in which remote approximations of
a target behavior are rewarded.
Premack Principle grandparents
rule reinforcement strategy in
which an if-then contingency is
established between a preferred
reinforcer and a less activity
Punishment follow-up stimuli used
in operant conditioning to decrease
the strength of the performance of
undesired behaviors.
Presentation Punishment followup stimuli added to decrease the
strength of an unwanted behavior.
Removal Punishment follow-up
stimuli withdrawn to decrease the
strength of an unwanted behavior.
Extinction strategy in which
voluntary, undesired behavior is
followed by no stimulus, or is ignored.
Response Costs strategy in which
units of reinforcement are removed for
each display of undesired behavior.
Extinction with reinforcement
strategy pairing extinction with
positive reinforcement of desired
behavior.
Satiation or negative practice
strategy emphasizing the
introduction of the overloading of
enjoyable (the student), yet
inappropriate behavior (to the
teacher) until the behavior losses its
attractiveness.
Observational Learning a social
learning strategy which emphasizes
learning by watching others.
modeling
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Mark L. Sundberg, PH.D., BCBA DDocument31 paginiMark L. Sundberg, PH.D., BCBA DGavroDjurickovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Introduction To Councelling&psychotherapy The Essential Guide Palmer S PDFDocument385 paginiIntroduction To Councelling&psychotherapy The Essential Guide Palmer S PDFayyappan.ashok6713100% (4)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Finals Lesson 3 Behavioral Learning Theories and Approaches To LearningDocument19 paginiFinals Lesson 3 Behavioral Learning Theories and Approaches To LearningVivian Paula PresadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- B. F. SkinnerDocument33 paginiB. F. SkinnerUmi Kalsum100% (1)
- Resilience Wheel: ToolkitDocument18 paginiResilience Wheel: ToolkitMar GallegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Support Positive Behaviour in A Learning Environment For Children and Young PeopleDocument33 paginiSupport Positive Behaviour in A Learning Environment For Children and Young Peoplepunkster4570% (1)
- EDUC 5240 Unit 2 Written AssignmentDocument6 paginiEDUC 5240 Unit 2 Written AssignmentSabrina Coppin-Kellman100% (1)
- Psychoanalytic TheoryDocument5 paginiPsychoanalytic TheoryKhalid Saeed50% (2)
- BEDS-M - ICanStudyDocument23 paginiBEDS-M - ICanStudySupreet Singh100% (1)
- Learning TheoriesDocument10 paginiLearning TheoriesJoanna Marie Villanueva DasallaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eng 2Document1 paginăEng 2riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes - CH 4 Integ System NewDocument54 paginiNotes - CH 4 Integ System NewriaÎncă nu există evaluări
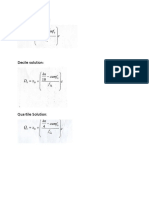
- Percentile, Decile, Quartile Solution Math 4Document1 paginăPercentile, Decile, Quartile Solution Math 4riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis Chapter 1Document9 paginiThesis Chapter 1riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- STOICHIOMETRYDocument8 paginiSTOICHIOMETRYriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lacambra, Ria T. BS PSYCH-1 Maestrado, Rica Marie BSBA-1: The Effects of Using Chinese Herbal MedicinesDocument1 paginăLacambra, Ria T. BS PSYCH-1 Maestrado, Rica Marie BSBA-1: The Effects of Using Chinese Herbal MedicinesriaÎncă nu există evaluări
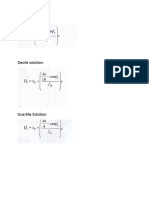
- Percentile, Decile, Quartile Solution Math 4Document1 paginăPercentile, Decile, Quartile Solution Math 4riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LearningDocument66 paginiLearningTejash TapadiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prof. Ajay Kumar AttriDocument9 paginiProf. Ajay Kumar AttriAnonymous CwJeBCAXpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Behaviorist PerspectiveDocument12 paginiBehaviorist PerspectiveBrian MaingiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data BaseDocument93 paginiData BasebraintreedesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- School of Thoughts in PsychologyDocument51 paginiSchool of Thoughts in PsychologyGel VelasquezcauzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus in Facilitating LearningDocument4 paginiSyllabus in Facilitating LearningMichael Figueroa100% (1)
- A Coaching Modality Meta-Analysis GuidebookDocument126 paginiA Coaching Modality Meta-Analysis GuidebookRodrigo BellottÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implikasi Teori Belajar Sosial Social Learning TheDocument8 paginiImplikasi Teori Belajar Sosial Social Learning TheZafarani HamkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Learning and Motivation True / FalseDocument10 paginiChapter 3 - Learning and Motivation True / FalseAnzilah DedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 - LearningDocument34 paginiChapter 5 - LearningKaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTB Mle 2 Maam AbadiesDocument6 paginiMTB Mle 2 Maam AbadiesMely DelacruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motivation: Prof - Dr.Anjum Bano Kazimi DateDocument13 paginiMotivation: Prof - Dr.Anjum Bano Kazimi DateSarah AndersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social Learning TheoryDocument16 paginiSocial Learning Theoryvampire88Încă nu există evaluări
- Learning: Adaptive Pathway Instructor Guide For Chapter 5Document42 paginiLearning: Adaptive Pathway Instructor Guide For Chapter 5Majesty Lidya KatiandaghoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Counseling: A Comprehensive Profession: Eighth EditionDocument71 paginiCounseling: A Comprehensive Profession: Eighth EditionSreednesh A/l MurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abraham Maslow BibliographyDocument4 paginiAbraham Maslow BibliographyHarry TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hovland 1937 IVDocument16 paginiHovland 1937 IVjsaccuzzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Albert Bandura: Social Learning TheoryDocument21 paginiAlbert Bandura: Social Learning TheoryMary Rose Guevarra JanabanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LearningDocument22 paginiLearningSumbal RafiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Oxford Handbook of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy Michael P Twohig Full ChapterDocument67 paginiThe Oxford Handbook of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy Michael P Twohig Full Chaptergeorge.wang839100% (7)